29162
Liver tests are a list of indicators in a biochemical blood test, which makes it possible to analyze the functioning of this internal organ. If there are any abnormalities, the patient is sent for an extensive diagnostic examination, which allows the exact cause of the pathology to be determined.
You should take a liver test at least once every six months. This allows you to identify any deviations from the norm at the initial stages. Treatment of diseases in the initial stages allows you to achieve more effective results.
Concept and meaning
Liver parameters of a biochemical blood test are a set of laboratory data by which one can judge the function of the liver and biliary system.
In order to know how the patient’s liver copes with its numerous functions, it is enough to determine the content in his blood:
- Enzymes:
- transaminases are enzymes that participate in the reactions of interconversion of lipids, carbohydrates and proteins, thereby establishing a connection between the main types of metabolism in the body (AST, ALT, GGT);
- hydrolases are enzymes that break down complex substances into simpler ones with the participation of water (AL).
- Belkov:
- globulins;
- albumins,
- their sum.
- Bilirubin is a pigment formed during the breakdown of substances containing heme (hemoglobin, myoglobin, cytochrome):
- toxic fraction;
- non-toxic fraction.
Often, together with liver parameters, the prothrombin index (PI), which characterizes the blood coagulation system, is determined.
Previously, the liver complex included thymol and sublimate tests, but now, due to their low specificity, they are rarely performed.
Physiological significance
- Transaminases (AST, ALT, GGT) are enzymes located inside cells. A sharp increase in their concentration in the blood is possible only with tissue death. Not only the indicators of each enzyme separately are important, but also their AST/ALT ratio (Ritis coefficient). The norm for this coefficient is 1-1.75 (regardless of gender and age).
- Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme that is part of a subgroup of hydrolases. Its main function is the removal of phosphorus from organic compounds. The enzyme is involved in the transfer of phosphorus across the cell membrane, so it is often present in the blood.
- Squirrels. Albumin is the main transport protein, synthesized only in the liver; other protein molecules are also synthesized here. When liver tissue dies, the amount of protein in the blood may change.
- Bilirubin, formed from heme during the death of red blood cells, is indirect bilirubin, toxic to the body; in the liver it is neutralized, turning into direct bilirubin, and enters the bile. As part of bile, bilirubin participates in the emulsification of dietary fats and is then excreted through the intestines.
- Prothrombin is a protein that is a precursor of thrombin. PI reflects not only the state of the blood coagulation system, but also the protein-forming function of the liver.
Indicators of “baked samples”
Diseases or damage to an organ by toxic substances invariably affect the state of its cells and the performance of its functions. The most informative indicators that allow you to assess the condition of the liver tissue, the norm of liver tests are listed in the table below.
| Sample indicators | What do they indicate? |
Blood chemistry | |
Bilirubin:
| Bilirubin is a breakdown product of blood cells that is normally taken up from the blood by the liver and excreted through the bile ducts. An increase in its quantity indicates a problem in this system:
|
Transaminase enzymes:
| In a healthy person, these enzymes are found only inside the cells of the internal organs. Elevated transaminases and the presence of other signs of liver damage are often a sign of liver cell destruction. |
Alkaline phosphatase (AP)
| These enzymes, as a rule, indicate the presence of bile stagnation, both intrahepatic and extrahepatic. |
| Gamma-glutamine transpeptidase (GGTP) Less than 60 U/l. | |
| Total cholesterol 3.1-5.0 mmol/l | One of the main indicators of fat metabolism in the body. The production of various types of cholesterol occurs in the liver. Therefore, a decrease in its quantity below normal values is an indirect sign of damage to this organ. An increase in the content of total cholesterol can occur with a large number of diseases, including the presence of stagnation of bile inside the liver ducts or in the gallbladder, and the presence of fatty degeneration of the liver. |
| Total protein 65-86 g/l | The amount of total protein reflects the liver's ability to create complex chemical compounds. Albumins are one of the types of proteins that have a small mass, but at the same time a large number of functions, in particular: transport of nutrients, retention of fluid in blood vessels. It should be remembered that a decrease in their number may also be associated with damage to the renal filter, therefore, to carry out a correct diagnosis, it is also necessary to perform OAM. |
Albumin
| |
Coagulogram | |
| Prothrombin index (PTI) 80-100% | These indicators reflect the ability of blood to clot, with the help of a number of special proteins - coagulation factors. Since the production of certain factors decreases against the background of diseases, the clotting time increases and the coagulogram parameters change. |
Fibrinogen
| |
| Partial activated thromboplastin time (aPTT) 25-37 seconds | |
General urinalysis (UCA) | |
| Protein | A decrease in protein levels and the development of edema can be observed not only against the background of diseases of the digestive system, but also when the renal filter is damaged. Therefore, to exclude this group of pathologies, it is always necessary to perform OAM |
After analyzing the above indicators, we can make an unambiguous conclusion about the presence or absence of pathology. Also, interpreting liver tests can help determine which organ functions are impaired and how severe these disorders are. However, the diagnosis and type of disease can only be clarified by additional examination methods.
Table of indicators is normal
| Biochemical substance | Therapy | Pediatrics | |
| M | AND | ||
| AST (units/l) | 0-40 | 0-35 | 1.5 months - up to 70 12 months – up to 60 15 years - 6-40 |
| ALT (units/l) | 0- 40 | 0-31 | First week - 59 12 months - 54 3 years - 35 6 years - 29 from 12 years old - 39 |
| GGT (units/l) | up to 45 | up to 32 | 1.5 months up to -200 1 year - up to -60 15 years - up to 25 |
| ALP (units/l) | 120-130 | 100-105 | 1.5 months - up to 350 12 months – up to 450 15 years - up to 360 |
| Total bilirubin (µmol/l) | 3,2-17,0 | 3,4-17,0 | newborns - 23.9-34.0 first 5 days - 90.14-205.0 14 days – 52.2- 69.1 30 days – 9.2-14.5 over 1 month – like adults |
| Direct bilirubin (µmol/l) | 0,7-7,9 | 0,9-4,3 | newborns – 8.72-14.4 first 5 days – 7.84 30 days – 2.57 over 1 month - like adults |
| Indirect bilirubin (µmol/l) | 6,4-16,8 | up to 16.2 | newborns – 8.72-14.37 first 5 days – 82.24 30 days – 8.55 Over a month old - like adults |
| Total protein (g/l) | 60,0-80,0 | 60,0-80,0 | in newborns - 42.0-62.0 12 months - 56-72 from 4 years 60-80.0 |
| Albumin (percentage) | 40-60 | 40-60 | Newborns – 32-40 12 months – 34- 43 from 11 years - 40.0-50.0 |
Liver enzymes during pregnancy
Most laboratory parameters during pregnancy remain within normal limits. If minor fluctuations in enzymes occur, they disappear soon after birth. In the third trimester, a significant increase in alkaline phosphatase is possible, but not more than 4 norms. This is due to the secretion of the enzyme by the placenta.
An increase in other liver enzymes, especially in the first half of gestation, should be associated with the development of liver pathology. This may be liver damage caused by pregnancy - intrahepatic cholestasis, fatty hepatosis. Also, changes in tests will appear in case of severe gestosis.
Symptoms of increase and decrease
The clinical picture that accompanies changes in blood biochemistry depends on the nosology that caused these changes.
When pathology occurs, the symptoms are scanty and nonspecific:
- weakness, decreased ability to work;
- unmotivated weight loss;
- stool instability and change in stool color;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- headache;
- insomnia.
It can be difficult to make a diagnosis at the first manifestation of the disease, based only on the clinic. As the pathology progresses, clear symptoms of damage to the hepatobiliary system appear
- Pain syndrome:
- Sharp pain in the right side is symptomatic of gallbladder damage (gallstone disease, purulent cholecystitis);
- discomfort in the upper abdomen that occurs after drinking alcohol is a characteristic sign of chronic liver pathology and occurs as a result of enlargement of the organ and stretching of its capsule;
- absence of pain syndrome is characteristic of most liver pathologies; pain appears only in the later stages of the disease, when the liver capsule is involved in the process.
- Skin. Depending on the disease that caused the liver pathology, the color of the skin may be grayish, pale, or icteric. The skin epithelium becomes thinner. Often, acne, petechial rash, and areas of dystrophically altered tissue are detected on the skin. The deposition of direct bilirubin in the skin is accompanied by severe itching.
- Hormonal changes. Hormones are protein molecules synthesized in the endocrine glands, but their deactivation occurs in the liver, with functional disorders of which, hormones accumulate in the blood, disrupting the functioning of the endocrine system.
- CNS. In case of disorders of the detoxification function of the liver, the neutralization of ammonia and metabolic products that have a detrimental effect on the central nervous system is disrupted. The result of this is hepatic encephalopathy, accompanied by severe neurological symptoms and often ending in coma.
Liver tests, interpretation of analysis, normal
A diseased liver rarely causes symptoms, and when they do, they are usually nonspecific. For example, with fatty liver disease, patients sometimes feel a slight pressure in the upper abdomen.
Inflammation does not cause pain, but only general symptoms - fatigue, loss of appetite or abdominal discomfort, diarrhea and nosebleeds, which also do not immediately indicate a diseased liver.
The typical yellowing of the skin and eyes is often not particularly noticeable and is barely recognizable to a wide range of people.
Liver tests and interpretation of this blood test are used to identify damage or disease in our filtration organ. Changes in liver cells and its function, which indicate disease, are recognized by various enzymes contained in the blood:
- Glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (GPT) is an enzyme that is released into the blood during the degradation of liver cells. It is found in liver cells and is also found in muscle tissue.
- Gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT) is found in the bile ducts, but can also be found in other organs.
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP). This enzyme can be found throughout the body, but especially in the liver, bones, intestines, kidneys and white blood cells.
- Bilirubin is a breakdown product of red blood cells that is excreted through the liver along with bile.
- Albumin is the most abundant blood protein produced by the liver and plays a role in the blood clotting process.
When are tests necessary, and how to prepare for them?
Liver tests are performed when there are possible signs of damage to the filtration organ. These include:
- yellow skin;
- dark urine;
- light stool;
- nausea, vomiting and diarrhea;
- loss of appetite;
- vomiting blood;
- bloody stool;
- stomach ache;
- weight loss;
- fatigue.
To obtain objective test results, the following recommendations should be followed before collecting a blood sample:
- Excessive physical activity should be avoided for at least 48 hours. You also need to exclude alcohol, spicy, fried, spicy and fatty foods from your diet.
- Blood sampling is best done in the morning on an empty stomach, in any case, not earlier than 8 hours after eating.
- You should first inform your doctor if you regularly take any medications. If possible, it is better to stop treatment 7-10 days before liver tests.
How to interpret the results? Normal indicators
The doctor will compare the liver test results with the normal range established for the patient's test results. When one or more scores are outside the normal range, it may indicate that there is a problem with the liver.
Reasons for promotion and demotion
Liver parameters of a biochemical blood test can change both as a result of liver diseases and various extrahepatic pathologies.
An increase in liver parameters is possible in the case of:
- long-term use of analgesics, statins, sulfonamides and other hepatotoxic drugs;
- herbal medicine (ephedra, skullcap);
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- metabolic disorders;
- burns and injuries;
- dehydration
Significant changes in the biochemical analysis of venous blood and indicators of liver function are observed in primary and secondary liver pathology :
- Diseases that occur with damage to the liver tissue (hepatitis, primary malignant neoplasia of the liver).
- Diseases that occur with a violation of the outflow of bile (cholecystitis, cholangitis).
- Diseases that occur with impaired blood circulation in the liver (vascular thrombosis, liver infarction).
- Metastases in neoplasia of other organs (stomach, bronchi, lungs).
- Pregnancy gestosis.
- Hereditary enzymopathies (hepatolenticular degeneration, hemochromatosis, steatosis).
Blood test for liver cancer and hepatitis
No disease passes in the body without a trace; markers will help determine the presence of antigens to certain diseases.
Hepatitis markers. Explanation:
- Marker for viral hepatitis A (HAV) - Anti-HAV-IgM, IgM class antibodies to virus A. Positive result: anti-HAV IgM, anti-HAV IgG, HAV Ag, HAV RNA.
- Marker for hepatitis B virus (HBV) - Anti-HBs antibodies to the HBs antigen of virus B. Positive result: Pre-S1, Pre-S2, anti Pre-S2, HBsAg, HBeAg, anti-HBs, anti-HBc IgM, anti -HBc IgG, anti-HBe, HBV DNA, DNA polymerase.
- Marker for hepatitis C virus (HCV) - Anti-HCV-total antibodies to virus C antigens. Positive result: HCV Ag, anti-HCV-IgM, anti-HCV-IgG, HCV RNA.
The tumor marker AFP (Alpha Fetoprotein) is a marker for cancer. AFP and albumin are similar in composition. A result exceeding 10 IU is considered pathological.
A high level of AFP indicates malignant oncology, metastases in the gland of other cancers, and a high value can also occur in embryonal cancer. A slight increase in AFP may indicate cirrhosis, hepatitis and renal failure.
Indications for the study
Blood biochemistry is included in the list of diagnostic examinations prescribed by the therapist during the patient’s initial visit.
Liver tests are added to the analysis if the patient is concerned about:
- discomfort in the right upper abdomen;
- bitter taste;
- stool instability;
- icterus skin;
- change in the color of urine and feces.
The analysis is required to be carried out:
- when a patient comes into contact with the blood of a patient with hepatitis (medical workers, rescue services);
- in case of long-term use of drugs with hepatotoxic effects;
- for chronic alcoholism;
- if examination reveals an increase in the size of the liver;
- for obesity.
If liver pathology is detected, the therapist refers the patient to a gastroenterologist (hepatologist).
Causes of decreased liver enzymes
A decrease in enzymes may occur with liver metastases
A drop in enzyme levels is observed less frequently than an increase. Deviation from the norm to the lower side may indicate the following pathologies:
- cirrhosis;
- metastasis of cancer tumors to the liver;
- stagnation of bile in the ducts.
A non-pathological reason for a decrease in enzyme levels is a woman taking a number of hormonal oral contraceptives for a long time. In this case, only a doctor can decide on the possibility of continuing to take a drug that has affected the functioning of the liver. Usually contraceptives are replaced.
How to determine
Liver parameters of a biochemical blood test are part of a detailed analysis of the biochemical ingredients of blood
The basis of the method is step-by-step chemical analysis . The results of chemical reactions are studied using special equipment. Only standardized chemical reagents and instruments are used.
What are liver enzymes
Based on their function, enzymes are located inside the cell, on the cell membrane, are part of various cellular structures and participate in reactions within it. The following groups are distinguished according to the function performed:
- hydrolases – break down molecules of substances;
- synthetases – participate in molecular synthesis;
- transferases – transport sections of molecules;
- oxyreductases – affect redox reactions in the cell;
- isomerases - change the configuration of molecules;
- lyases – form additional molecular bonds.
The functioning of many enzymes requires the presence of additional co-factors. Their role is played by all vitamins and microelements.
Preparing and conducting analysis
The reliability of the results of a biochemical blood test can be influenced by factors such as overeating, alcohol consumption, medications, and a stressful situation.
Therefore, conducting research requires preparation:
- two days before the test, you should exclude fatty and fried foods, alcohol, and, if possible, stop taking medications;
- the day before the analysis, refrain from drinking coffee, avoid stressful situations, limit physical activity;
- dinner on the eve of the study should not be heavy or late;
- on the day of the test before taking it, do not smoke;
- The test is taken in the morning, on an empty stomach.
If the patient is taking medications and it is impossible to stop taking them, then when taking the test, the form indicates the medications, their doses and how long the patient has been taking them.
Blood is drawn from the ulnar vein in the standard way:
- the procedure is carried out in a treatment room, in compliance with all rules of asepsis and antiseptics, using a disposable syringe;
- to avoid the occurrence of false indicators, the tourniquet is applied for a very short time (1-2 minutes);
- 5 ml of blood is taken for analysis;
- The collected blood is stored and transported in special darkened containers.
After drawing blood, you should remain seated for a while to prevent dizziness.
Diagnostic features
The condition and functioning of the largest gland in the human body is primarily assessed by the results of a biochemical blood test, during which the entire list of necessary enzymes is studied.
The LHC, based on data on the nature, speed and characteristics of the end products of metabolism, information on the metabolic processes of proteins, lipids and carbohydrates, allows you to determine all present disorders. In addition, the analysis makes it possible to identify the body’s needs for microelements and vitamins, and to determine the degree of their deficiency.
Pathological changes in the liver will certainly be reflected in blood biochemistry indicators, indicating the presence of deviations from the norm. The amount of information required to make, clarify, confirm or refute the diagnosis differs, which is determined by the clinical picture obtained on the basis of a general examination, anamnesis and ultrasound data.
Liver tests are mandatory during pregnancy.
A therapist or a doctor specializing in liver problems - a hepatologist, depending on the patient’s condition, can prescribe a standard blood biochemistry examination, studying 6 indicators, or a detailed one, including an assessment of up to 15 parameters.
In order for the LBC results to be reliable, the patient should fulfill several simple requirements, which must be reviewed in advance in the attending physician’s office. Preparation involves the following rules.
Blood testing must be done strictly on an empty stomach. The liver takes an active part in the digestion process, and the food itself, as well as its nature, have a significant influence on the results of the study, leading to their distortion. To avoid this, the time interval before collecting biomaterial and the last meal should be at least 8 hours.
The same applies to any drink. Some doctors recommend not only not drinking water before taking the test, but not even brushing your teeth, since getting water into your mouth causes a whole chain of digestive reactions that also extend to the liver. In addition, three days before the procedure, you should avoid fatty and spicy foods.
Consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited. Even a tiny dose of alcohol increases the load on the liver, can change the properties of the blood, and directly affect the quality of its clotting. Based on this, the minimum period for abstaining from alcohol-containing drinks before performing a LHC is three days.
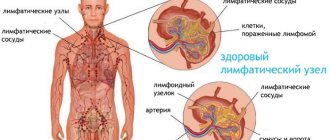
Reference! During the diagnosis of a certain list of diseases, liver tests are performed along with kidney and rheumatic tests.
Abstinence from smoking is mandatory. Since the influence of tobacco smoke can cause an increase in secretion of the organs of the digestive system and the liver itself, at least 12 hours must pass between the last cigarette smoked and blood sampling for biochemistry.
Refusal of intense physical activity. Three days before submitting the biomaterial, it is necessary to exclude heavy physical activity, and, in particular, sports. In addition, it is recommended to avoid, if possible, stressful situations and other psycho-emotional fluctuations, and you should also maintain a sleep schedule and get enough rest.
Cancellation of medications. Even vitamins can affect the level of liver enzymes in the blood, therefore, if the patient is taking any medications, it is necessary to stop taking them at least a week before the test.
This is due to the fact that some drugs can change the composition of the blood for a long time, which will directly distort the results of the study. If for some reason this cannot be done, then you must inform the doctor who ordered the test about the medications you are taking.
In addition to the above recommendations, women of childbearing age will need to take a pregnancy test before liver screening. Since this condition causes a fundamental restructuring in the body, caused by changes in hormonal levels, which also entails certain changes in the synthesis of enzymes, including those involved in digestion.
Preparation for analysis is an integral part of diagnosis
Decoding the research results
Liver parameters obtained as a result of biochemical studies are nonspecific.
When deciphering survey data, one should rely not only on the absolute numbers of changes in one or another indicator, but also correlate the change in one indicator with other changes, the clinical picture of the disease, laboratory and instrumental examinations. This is difficult analytical work, which only a doctor can carry out efficiently.
However, there is an algorithm for deciphering liver tests, which allows you to suspect some disorders in the hepatobiliary system and seek help in time.
All pathological processes in the body associated with changes in liver parameters in the blood can be divided into three groups:
- changes associated with the death of hepatocytes;
- changes associated with disruption of the basic functions of the liver (protein synthesis, detoxification function, disinfection and removal of bilirubin from the body);
- changes associated with stagnation of bile in the biliary system.
Signs of hepatocyte death
Cell death leads to an increase in the concentration of liver enzymes in the blood, coming from damaged cells. Normally, they are present in the blood in minimal quantities.
The death of hepatocytes leads to the release of a large amount of already formed bound bilirubin into the blood. Unbound toxic bilirubin newly entering the liver cannot be neutralized by the reduced number of functioning cells, therefore the unbound fraction increases, which means the total bilirubin level increases.
Signs of liver cell death are:
- Increase in AST and ALT levels;
- An increase in total bilirubin and its fractions.
Despite the fact that there is death of liver tissue, this usually does not manifest itself clinically. Only with high activity of the disease can icterus of the skin and sclera, changes in the color of urine and feces appear.
Signs of liver dysfunction
As the disease progresses and the liver stops performing its basic functions, many different symptoms appear and laboratory tests change dramatically:
- Impaired binding and excretion of bilirubin - unbound and total bilirubin increases (yellow coloration of the skin and sclera appears, darkening of the color of urine and feces).
- Violation of protein synthesis - a decrease in albumin and total protein in the blood (subcutaneous and intracavitary edema appears).
- Violation of the synthesis of proteins involved in the process of blood clotting - a decrease in the level of PTI, fibrinogen (bleeding of the gums, gastrointestinal mucosa, internal organs).
Disorders associated with stagnation of bile in the biliary tract
The cause of intrahepatic bile stasis can be diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts, but the most common cause is the proliferation of connective tissue replacing dead hepatocytes.
Rough connective tissue compresses intrahepatic structures, including the bile ducts. As a result of impaired outflow of bile, bile components enter the blood through the wall of the bile ducts.
As a result:
- the level of GGT and alkaline phosphatase increases;
- the level of total blood cholesterol increases;
- The amount of bound and total bilirubin increases significantly.
Interpretation of liver tests
Liver tests are a test through which you can determine any liver disease solely through a blood test.
Liver tests can detect the following conditions:
- Damage to liver cells - usually characterized by increased amounts of ALT and AST in the blood. Due to improper functioning of the liver, enzymes quickly penetrate into the blood. Often this condition indicates toxic liver damage, autoimmune diseases, and hepatitis.
- Congestion in the liver manifests itself as increased activity of alkaline phosphatase and LDH. This indicates that the liver cannot excrete a sufficient amount of bile; it remains in its cavity for a long time. This promotes the formation of stones.
- Impaired enzyme production and other pathological processes manifest themselves in the form of a decrease in total protein.
- Autoimmune diseases - there are more proteins than globulins.
- Damage to the liver tissue - manifests itself as a change in the level of bilirubin, an increase in ALT and AST.
Liver tests are an important diagnostic test that allows you to identify any abnormalities in the initial stages. If the doctor diagnoses any abnormality based on the results of such a study, he sends the patient for a more extensive study.
First of all, the patient undergoes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, which allows one to determine the structure of the liver tissue.
When to see a doctor
If, during a routine examination or examination for any pathology, changes are detected in the biochemical analysis of liver tests, you must immediately contact a physician. In this case, the absence of complaints does not play a significant role.
The therapist, after re-analysis and examination of the patient, will prescribe additional tests (blood test for viral hepatitis B, C, D, blood test for autoimmune pathology, abdominal sonography). If suspicions of liver pathology are confirmed, the patient is referred to an appointment with a gastroenterologist (hepatologist).
How to prepare for analysis
To obtain reliable liver test results, it is important to properly prepare for the tests. To do this, you need to follow some rules:
- Avoid eating spicy, fatty and fried foods 2–3 days before donating blood;
- give up alcohol and smoking;
- the day before the test, do not drink coffee or other strong or too sweet drinks;
- You can eat no later than 10 hours before going to the laboratory;
- the day before, exclude heavy physical labor or mental stress;
- If possible, 2 days before the test you should stop taking any medications.
To determine liver markers, venous blood is collected, which is taken from the vein of the elbow joint. After collection, the biomaterial is sent to the laboratory to study liver enzymes. Using modern equipment, indicators are studied, the norm and deviations to a lesser or greater extent are recorded.
Not only increased but also decreased levels of organic substances in the serum can indicate the development of pathology, so only a qualified doctor will be able to evaluate the results of the examination.
If the patient ignores recommendations for preparing for the analysis, there is a high risk of distorting the results. Therefore, if a person did not follow the preparation rules or took any medications the day before the procedure, the doctor should be informed about this.
The following factors may contribute to false liver test results:
- taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs or antidepressants;
- stress, physical activity;
- alcohol consumption;
- overweight;
- excessive compression of the vein with a tourniquet when drawing blood;
- eating spicy, fatty or fried foods.
You must take the test in the morning on an empty stomach; you can only drink small amounts of water. Reference values differ and directly depend on gender; also in children and pregnant women, the indicators differ significantly. With proper preparation, the results of the analysis will be as informative as possible, allowing the doctor to assess the condition of the liver, confirm or exclude possible diseases.
How to get it back to normal
Liver indicators of a biochemical blood test are only indicators of the functional state of the liver, so there is no single way to normalize these indicators. It is necessary to treat the disease that has caused changes in liver function.
In hepatology, agents with different mechanisms of action are used. They are capable of:
- normalize lipid metabolism in various ways;
- enhance hepatocyte regeneration;
- improve the flow of bile;
- dissolve small cholesterol stones.
Such drugs include:
- Essential phospholipids:
- Essentiale-forte 900 mg/day for 3 doses, course 3 months or more
- Essliver-forte 600 mg/day for 2 doses, course for at least 3 months.
- Medicines of animal origin
- Hepatosan 400 mg/day for 2 doses, the course is selected individually;
- Herbal medicines:
- Gepabene 3 capsules/day for 3 doses, the drug is taken for a long time;
- LIV-52 3 tablets/day for 3 doses, the course is prescribed individually;
- Karsil 35 mg/day for 1 dose;
- Medicines with amino acids:
- Heptral 500-800 mg/day for 1 dose;
- Heptor 400-800 mg/day for 2 doses, average course duration 2-4 weeks.
- Synthetic hepatoprotectors:
- Antral 0.4 g/day, course 3-4 weeks;
- Ursosan 250-500 mg/day, course of treatment 6-8 months.
Liver function indicators and possible abnormalities
Blood biochemistry is considered a universal analysis, which in its entirety is designed to determine the state of human health. Interpretation of results for the following enzymes:
- Total bilirubin. If the levels are elevated, it is suspected of liver cirrhosis. Accompanied by a yellow covering on the skin, as well as inflammatory processes.
- Direct bilirubin. When elevated values indicate a failure in the outflow of bile.
- Free bilirubin. Difference between general and direct. The numbers rise as red blood cells break down. Poor indicates cholestasis, anemia of liver tissue.
- Aspartate aminotransferase. Participates in protein metabolism. Increased levels may indicate the presence of an oncological tumor or viral hepatitis in the body.
- Alkaline phosphatase. Indicators above normal indicate disease of the bile ducts and malignant formations.
- Alanine aminotransferase. Regulates protein metabolism. Inflated values indicate gland dysfunction and the onset of hepatitis or cirrhosis.
- Cholinesterase. Indicates the destruction of organ tissue.
- Albumen. If there are deviations from the norm, it indicates that the absorption process is impaired. What is typical for hepatitis or cirrhosis.
- Amylase. Responsible for processing complex carbohydrates. Elevated amylase levels indicate liver failure.
- Prothrombin index. Responsible for blood clotting; if the numbers are too low, it indicates hepatocyte pathology.
Return to contents
Enzyme standards
Normal liver function indicators for a healthy person are presented in the table:
What additionally indicates problems with the organ?
Assessment of the functional state of the liver is prescribed for diseases of internal organs, as well as for preventive purposes. Noticeably expressed symptoms for analysis:
- Yellow skin color. Indicates the aspect that the disease has been in the body for a long time and greatly increased bilirubin.
- The belly has increased, but the weight has not changed. This indicates that the liver has increased in size.
- Nausea. Disturbances in the function of protein-nitrogen metabolism and digestion.
- With a constant regimen and quality of nutrition and lifestyle, weight loss is observed.
- Bitter taste in the mouth.
- Yellow-brown coating on the tongue.
- Feelings of tingling and heaviness in the side.
- During pregnancy.
Return to contents
Possible complications
Almost all liver diseases are initially asymptomatic. At this stage, the disease can only be suspected using laboratory methods, one of which is a biochemical blood test for liver tests.
If changes in liver parameters are ignored at this stage, the disease will progress, and by the time the first complaints appear, the process may be irreversible.
The most severe consequences include:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- liver neoplasia;
- massive, life-threatening bleeding;
- ascites, peritonitis;
- encephalopathy;
- coma.
Therefore, any changes in indicators of liver functional activity detected in the blood by a biochemical method require close attention and analysis.
Blood biochemistry in liver diseases: purpose
Biochemical blood test - effective laboratory diagnosis of liver condition
A biochemical blood test is prescribed for any disease, suspicion of it, or for prevention purposes. This is a quick and inexpensive test that can be used to diagnose problems with the liver, narrow the range of possible diseases, and determine the further direction of the examination.
The liver has many different functions, participating in the digestion process and detoxifying the body. In most cases, liver disease is detected in the later stages, when treatment is difficult. This is the largest gland in the body.
Disruption of its functioning leads to a number of complications and negatively affects the entire state of the body.
Liver biochemistry analysis can be prescribed for severe symptoms indicating disturbances in the liver or for other chronic diseases, before operations and taking medications.
Indications for analysis:
- Yellowness of the skin. One of the main signs of increased levels of bilirubin in the blood. Yellowness of the skin and sclera occurs when the disease has been present for a long time. If there are signs of jaundice, it is recommended to undergo examination.
- Enlargement of the liver. An enlarged liver can be seen not only on ultrasound. If the liver is greatly enlarged, the abdominal circumference begins to increase, but the overall weight does not change.
- Weight loss. With liver disease, nausea may occur, so a person refuses to eat, which leads to weight loss. Losing weight can be unmotivated with your usual diet and lifestyle. In this case, it is also recommended to check the liver.
- Bitterness in the mouth. With liver diseases, a constant bitter taste is felt in the mouth, the tongue becomes coated, a white or yellowish-brown coating appears, and cracks on the surface of the tongue are possible.
- Liver biochemistry is mandatory during pregnancy, as well as before taking serious medications that increase the load on the liver.
Enzyme groups
Based on the characteristics of synthesis and action, all liver enzymes are divided into several groups:
- Indicative. These enzymes indicate the presence of organ pathology in the form of destruction of its cells. These include AST (aspartate aminotransferase), ALT (alanine aminotransferase), GGT (gamma-glutamyltransferase), GDH (glumate dehydrogenase), LDH (lactate dehydrogenase). The first two enzymes are most often used for diagnostic processes.
- Secretory (cholinesterase, prothrombinase). Participate in supporting the functioning of the blood coagulation system.
- Excretory (representative - alkaline phosphatase). Found in bile components. During research, this enzyme shows the functioning of the biliary system.
Norms for men and women
Liver tests, interpretation of the analysis, the norm and its deviation differ in men, women and children. For males, liver blood test results may differ with the intake of a very fatty meal before it.
The norm for Alt and Ast liver tests in women is from 4 to 49 (4-46), in men from 4 to 34 (4-30).
Total bilirubin for both women and men is the same standard from 3.4 to 17. The same applies to direct bilirubin from 0 to 3.3 and indirect bilirubin from 2.4 to 13.4. Albumin is from 34 to 49. ALP is from 31 to 116. Total protein is from 64 to 84. GGT in women is from 2 to 54, in men from 4 to 37. Elevated liver parameters in the blood in people with kidney diseases are also considered normal. Elevated liver tests indicate the presence of pathologies.
When studying the norm of biochemical analysis of the liver, it is necessary to take into account the presence of various chronic diseases of the patient, the medications he takes, as well as his age and gender. For women who have not yet given birth, the norm of liver tests is different during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Of course, everything is individual, but the values of normal liver function test values are still worth knowing. After all, if the liver blood count is elevated, then you should immediately consult a specialist.