Urine test interpretation
Physical properties of urine:
Quantity
morning urine is usually 150 - 250 ml and does not give an idea of daily diuresis. Measuring the quantity is necessary to determine the density of urine.
Color
depends on the volume of urine excreted and the amount of coloring pigments. Normal urine color is straw-yellow, due to the presence of the urinary pigment urochrome.
Transparency
urine reflects the properties of the substances it contains. Normally, all substances are in solution, so fresh urine is absolutely transparent.
Density (specific gravity)
depends on the concentration of substances dissolved in the urine (protein, glucose, urea, salts).
Chemical examination of urine:
The acidity of urine
Ph
is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions H+, which are formed during the dissociation of organic acids and acid salts of inorganic acids contained in the urine.
Protein in the urine of a healthy woman is practically undetectable. This is due to tubular reabsorption of protein filtered in the glomeruli. The detection of protein in the urine is called proteinuria. It can be physiological and pathological. In uncomplicated pregnancy, orthostatic proteinuria (protein concentration in urine up to 0.033 g/l) can sometimes be detected. The cause may be compression of the inferior vena cava by the liver and the uterus of the renal veins. Physiological proteinuria also includes the appearance of protein in the urine after eating a large amount of protein food, after intense physical activity, or emotional stress.
Glucose,
that gets into the primary urine is also completely reabsorbed in the renal tubules, and cannot be detected by standard methods. Glucose is detected in the urine when its concentration in the blood increases above the renal threshold - 8.8 - 9.9 mmol/l or when the renal threshold decreases (diabetes mellitus).
important Physiological short-term glucosuria can also occur in healthy people with a large amount of carbohydrates in the daily diet, or under stress. Glucosuria during normal pregnancy is associated with an increase in glomerular filtration of glucose.
Bilirubin
It is not detected in the urine of healthy people, because only direct bilirubin, the content of which in the blood is insignificant, can pass through the glomerular filter. And there is a very small amount of it in the urine, which is not detected by qualitative samples.
Urobilinogen
is formed from bilirubin in the intestine, which comes with bile from the liver. Normally, traces of urobilinogen are found in the urine. Their complete absence indicates a violation of the flow of bile into the intestines.
Ketone bodies
are absent normally and appear with an increase in their concentration in the blood.
Microscopic examination of urine sediment:
There are organized (erythrocytes, leukocytes, epithelium and cylinders) and unorganized sediment (various salts).
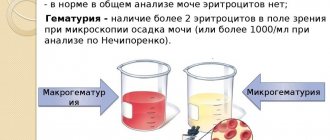
Red blood cells
in the urine of healthy people are absent or rare. They do not pass through the glomerular filter and appear in the urine during pathological processes in the kidneys and/or urinary tract.
Leukocytes
absent or single in the field of view. Leukocyturia (more than 5 leukocytes in the field of view) can be aseptic and infectious.
Epithelial cells
There may be single ones in the field of view, heard from different parts of the urinary tract: flat (urethra), transitional (pelvis, ureter, bladder). Renal (tubular) epithelium is normally absent. By increasing a certain type of cell, the localization of the pathological process is determined.
Cylinders –
These are casts of the renal tubules with cellular or protein composition. Hyaline casts, composed of protein, may be present normally after exercise. Cell casts always indicate the presence of pathology.
Bacteria
normally absent, but bacteriuria does not always indicate an inflammatory process; the number of bacteria is of primary importance.
Salt.
The appearance of crystals of various salts in the urine indicates a change in the urine reaction. Normally, only oxalates and amorphous urates may be present in small quantities.
Grainy cylinders
If the sediment elements are granular, pathologically altered renal epithelium is present in the urine. His cells are degenerate, decayed and deformed. They are formed from a yellow mass, characterized by opacity and a clear outline. They can be detected during analysis using osmic acid.
Cylindruria of a granular appearance always indicates the presence of a disease or pathological condition. These particles cannot be detected in the urine of a healthy person.
Grain means an uneven surface. It occurs due to the settling of fat particles, which refract light and give the cylinders a lumpy appearance.
This type of sediment warns of the possible presence of pathologies such as:
- glomerulonephritis;
- viral diseases characterized by kidney damage;
- amyloidosis;
- pyelonephritis;
- fever;
- diabetic nephropathy.
Cylindruria granular in appearance may be a consequence of lead poisoning.
Grainy casts in urine
Normal indicators of general clinical urine analysis in pregnant women:
Table:
| Index | Characteristic or meaning |
| Quantity | 150 – 200 ml |
| Color | Straw to amber yellow |
| Transparency | Full |
| Density | 1.010 – 1.030 |
| PH | 5.0 – 7.0 |
| Protein | Up to 0.033 g/l |
| Glucose | Absent |
| Bilirubin | Absent |
| Urobilinogen | Footprints |
| Ketone bodies | None |
| Red blood cells | 1 – 2 in field of view |
| Leukocytes | Up to 5 in sight |
| Epithelium | Single cells of transitional and squamous epithelium in the field of view |
| Cylinders | Single hyaline casts in the field of view |
| Salts | Single amorphous urates and oxalates |
Additionally If there are changes in the urine test, a repeat test is first prescribed for confirmation, and then additional examination methods are prescribed.
Waxy cylinders
When the renal tubules thin or necrosis, pathological cylinders are found in the urine, resembling a wax ball in appearance. These elements are formed from granular and hyaline microparticles. They are opaque, yellow in color and appear as a shapeless mass. Waxy casts are shorter than hyaline casts.
If urine tests are taken regularly, including by children, the cylindrical shape of the sediment can be detected in time. The resemblance of microparticles to wax balls is a sign of dangerous violations. This type of sedimentary fluid occurs due to pathologies such as:
- CRF (chronic renal failure);
- amyloidosis;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- glomerulonephritis of malignant type;
- late stages of chronic kidney disease;
- acute form of glomerulonephritis.
Waxy cylindruria is a consequence of poor outflow or stagnation of urine. At the same time, urine is concentrated and has a pungent odor.
Waxy casts in urine
Additional tests (if indicated)
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
allows you to study the cellular composition of urine in more detail. This study is prescribed:
- with changes in the general urine analysis (appearance of a large number of red blood cells, leukocytes, casts),
- If you have symptoms of kidney disease,
- As a treatment control.
Table: normal indicators:
| Indicators | Number of units/l |
| Red blood cells | Until 2000 |
| Leukocytes | Up to 1000 |
| Cylinders:Hyaline | Up to 20 |
| Grainy | Up to 20 |
| Waxy | Up to 20 |
| Other | Up to 20 |
The most common reasons for increased performance:
Red blood cells:
- Urolithiasis disease;
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Polycystic kidney disease;
- Complicated pyelonephritis;
- Urinary tract infection;
- Malignant hypertension;
- Systemic diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, collagenosis).
Leukocytes:
- Pyelonephritis;
- Cystitis;
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Fever of any origin.
Cylinders:
- Preeclampsia, Eclampsia;
- Acute renal failure;
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Pyelonephritis;
- Nephropathy of pregnancy;
- Toxicosis of pregnant women;
- Intense physical activity.
Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky
allows you to assess the concentration ability of the kidneys. The study is prescribed for kidney diseases, systemic diseases, complications of pregnancy (severe toxicosis, gestosis, nephropathy).
To do this, you need to collect urine every three hours in different containers. Three hours before the start of collection, you must completely empty your bladder. You also need to record the amount of all liquid consumed. The study evaluates:
- The amount of urine and its density in each portion. Normally, the change in volume can range from 40 to 350 ml. The difference between the maximum and minimum density indicators must be at least 0.012 – 0.015 (for example, 0.015 – 0.028);
- The total amount of urine excreted per day is normally 70–80% of the fluid consumed;
- The ratio of daytime and nighttime diuresis. The amount of daily urine averages 60–70% of the daily volume.
Determination of daily diuresis
gives an idea of the fluid consumed and excreted from the body. A simpler and more economical method compared to the Zimnitsky analysis, when you simply need to determine whether fluid is accumulating in the body. You just need to measure the amount of all urine per day and write it down along with the amount of liquid you drink and the vegetables, fruits and liquid portion of soups consumed. The normal water balance is 70-80%. Analysis is prescribed when edema occurs in pregnant women and in the treatment of gestosis.
Urine analysis for glucosuric profile
carried out when glucose is detected in a general urine test and in the presence of diabetes mellitus. For the study, daily urine is collected in three jars: from 800 to 1400 you need to urinate in the first jar, from 1400 to 2200 in the second and from 2200 to 800 in the third. The total amount of glucose excreted per day is determined.
Bacteriological culture of urine (bacteriological culture)
carried out to identify and identify pathogens of diseases of the urinary system, as well as determine their sensitivity to antibiotics. To do this, urine is placed on a nutrient medium (agar, sugar broth) and the growth of microorganisms is observed. Indications:
- Urinary tract infections;
- Monitoring the treatment;
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women;
- Diabetes;
- Immunodeficiency;
- Suspicion of antibiotic-resistant flora.
For the study, an average portion of morning urine (3–5 ml) is taken, collected in a sterile container.
Physiological changes in the urinary system during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman’s kidneys work in an intensive mode, removing from the body not only the products of their metabolism, but also the products of the fetus’s metabolism. That is why frequent and careful monitoring of changes in the quality, quantity of urine and its cellular composition is necessary.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, renal blood flow increases and gradually decreases thereafter, which allows other organs to receive additional blood volume. Glomerular filtration increases, and tubular reabsorption does not change throughout pregnancy, this contributes to fluid retention in the body, which manifests itself as pastyness on the legs at the end of pregnancy.
As the uterus grows, the location of adjacent organs changes. Towards the end of pregnancy, the bladder moves upward beyond the boundaries of the small pelvis, its walls hypertrophy to resist compression by the uterus. Sometimes the development of hydroureter can be observed (impaired patency of the ureter and, as a result, accumulation of urine in it), which occurs more often on the right. The reason is that the pregnant uterus turns slightly to the right, pressing the ureter against the innominate line of the pelvic bone.
Under the influence of hormones (mostly progesterone), the urinary tract expands and decreases tone, which contributes to the development of infection during pregnancy (pyelonephritis).
Why is OAM prescribed?
The task of the urinary system in the body is to remove waste products in the form of urine. When a woman becomes pregnant, many processes in the body change due to hormonal changes.
A general urine test during pregnancy shows the condition of a woman’s internal organs: liver, intestines, pancreas, heart and kidneys. With normal readings there is nothing to worry about.
If the study reveals an abnormal amount of any element in the urine, additional examinations of the pregnant woman and appropriate treatment are prescribed.
Comments (5)
- Leia July 05, 2013 00:11
I remember that these constant urine tests really bothered me. And so you often go to the doctor, and also test your urine constantly. but it is very useful and necessary for monitoring the development of the child and the health of the mother. So don't neglect it. And it’s good that expectant mothers have the opportunity to read such an article to be aware of why this analysis is being carried out. - Tatiana 06 July 2013 00:50
When I was 37 weeks pregnant, I began to swell terribly, to such an extent that my most worn boots (this was in December) would not fasten, despite the fact that I had only oversized tights on my legs. My blood pressure was 160/100, but I was fluttering like a butterfly. Naturally, I was sent to the maternity hospital for safekeeping. So there, after protein was detected in my urine test, I had to take several types of it every morning: general, and for sterility (according to Nechiporenko), and daily... After reading the article, I clarified a lot for myself, it’s a pity, I didn’t know the normal indicators then, but now it’s easy to fix.
- Olga 07 July 2013 00:15
Doctor's instructions must always be strictly followed. And constant urine supply is no exception. It was these tedious tests that saved the child for my sister, who simply did not feel the gestosis that was developing in the body. It was precisely because of a poor urine test that the doctor referred her for examination and preservation accordingly. So tedious tests are the surest way to the birth of a healthy baby.
- Olya 08 July 2013 00:34
Yes, of course, a very useful article. Tatyana, I’m wondering if you were able to identify the cause of your swelling. The fact is that I am now also 38 weeks pregnant and I noticed that my legs began to swell a little. This usually happens in the evening, maybe it’s just from fatigue, it’s summer and very hot, because my urine test is quite normal.
- zaya July 16, 2013 09:29
I don’t even remember how many times during my entire pregnancy I had to take a urine test. But definitely a lot. True, when I took the test for the first time, the doctor called it a “cocktail” - it turns out I did everything wrong. After toileting the genitals, it was also necessary to use a cotton-gauze swab so that the analysis was clean. When I did everything correctly, the analysis turned out to be good - nothing suspicious was detected in the urine.