Urine (urine) is an important indicator of the functional functioning of the body. Through a general analysis, the presence of mucus in it can be detected. By the amount of mucous discharge, its color, transparency, acidity, protein in urine in women, one can judge the functioning of the body and the presence of any pathologies. In a healthy body, urine contains a small amount of mucus, and often it cannot even be detected. Many people wonder why mucus forms in the urine of women, the reasons that provoke its appearance?
Reasons for appearance
Mucous formations in the renal secretion can be both normal and pathological. If the organs of the excretory system are in good condition, the amount of the mucous component remains up to 1+. If the inflammation is severe, the mucus concentration may increase to 2+-4+.
Physiological
Mucus in urine is formed from epithelial cells of the inner lining of the organs of the excretory system. The walls of the bladder are highly susceptible to inflammation and increased bacterial counts. Cellular structures are constantly renewed, dying, they are excreted along with urine. This mechanism is necessary for protection. Epithelial cells, tearing away from the wall of the bladder, take bacteria with them and remove them with kidney secretions.
Pathological
Mucus in a urine test may increase if there are infections of the urinary or genital organs. When mucous inclusions are detected at 2+, this indicates damage to the urethral canal. If the indicator increases to 3+ or 4+, the patient can be assumed to have an inflammatory focus in the kidneys or ureters. An increase in mucus is also possible with sexual diseases: prostatitis, vaginitis, endometritis, STDs.
This may include:
- urolithiasis;
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- nephritis;
- oncopathology of the excretory system;
- cystitis;
- urethritis.
If the material contains mucous formations, then to facilitate diagnosis, the number of epithelial cells is also examined. The epithelium is divided into transitional, squamous, and renal. If transitional epithelium is detected in the TAM, it can be assumed that the patient has pathologies of the renal pelvis and ureters, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, and tumor formations.
The presence of flat epithelial cell structures makes it possible to identify pathologies of the urethral canal, as well as the bladder. These include prostatitis, cystitis, urethritis. These diseases are often accompanied by the following symptoms: increased urination, hyperthermia, pain when emptying the bladder, burning sensation and pelvic pain.
If renal epithelial cells are found in the TAM, this indicates damage to the kidney, namely the glomeruli. They are damaged by glomerulonephritis, nephritis. Such pathologies necessarily have accompanying symptoms: swelling of the legs, face, lack of urine or a small amount of urine, increased blood pressure. Kidney cell structures are also present in urolithiasis (passage of stones), since solid formations severely damage the tissue of the kidney and pelvis as they move.
Treatment of mucus in urine
Drug therapy is prescribed after identifying the cause that provoked the increase in pathogenic sediment in the urine.
In urology and gynecology, doctors use:
- Non-steroidal drugs – Nurofen, Faspik.
- Antispasmodic and analgesic drugs - No-shpa, Diclofenac, Drotaverine, Ketorolac, Baralgin.
- Antibacterial and antiviral drugs - Augmentin, Furagin, Zovirax, Levomycetin, Monural, Nolitsin, Vilprafen, Amoxiclav.
- Means for strengthening the immune system - Genferon, Cycloferon.
- Medicines for stones in the kidneys and urinary tract - Cyston, Purinol, Blemaren, Canephron, Uralit, Avisan.
Faspik tablets are prescribed for drug treatment of abnormalities
Auxiliary products include herbal medicines - Kaneon, Cyston, Monurel, Peponem.
The influence of gender and age on the number of mucous formations
Mucus discharge can be detected at any age. In women and men, mucus is determined normally to 1+. Representatives of the fairer sex are more likely to detect such cases, and this depends on the structural features of the reproductive system.
It is also possible that mucus may appear in the urine of women due to violation of hygiene standards or improper preparation for the OAM. The presence of mucous inclusions can also determine inflammatory diseases of the genital organs and urinary tract, depending on the analysis parameters. Often, a large amount of mucus in the urine of women appears with cystitis, vaginitis, urethritis, urolithiasis, and genital infections.
In a healthy man, mucus is not detected at all or is determined to be 1+. The appearance of mucous inclusions greater than 1+ indicates improper preparation for OAM or violation of hygiene standards. The amount of mucus in the urine of men may increase with prostatitis and urolithiasis.
In newborn children, due to the physiological characteristics of adaptation after birth, there is an increase in the amount of mucous component of urine to 1+-2+. This is an acceptable value, since the kidneys begin to actively function. In newly born girls, white vaginal mucus may be released immediately after birth, persisting for up to 1 month, which provokes an increase in the concentration of the mucous component of the urine.
Mucus in the urine of a child under 1 year of age (up to 1+) is normal, since it is not always possible to wash the perineum well before taking the test. Collecting urine from young children is quite difficult under sterile conditions, so a combination of bacteria (in small quantities) and mucus is also acceptable. Parents should follow the rules for collecting OAM in order to get as close as possible to the reliability of the result. If the urine test shows minor abnormalities, it is taken a second time.
Norm of mucus and its excess
A healthy adult should have no mucus in their urine at all. Only a little clear mucus is allowed if other indicators are normal. But when it is detected in large quantities for the first time, a repeat study is usually prescribed. Only when the results are confirmed can the doctor conclude about the presence of pathology.
How to submit a urine culture for flora
When interpreting test results, the laboratory technician uses certain criteria. There are four levels of mucus presence, which are indicated by a “+” sign:
- normal state of mucus in urine – 1+;
- mucus in urine 2+ means a moderate amount;
- an increased level is indicated by three pluses;
- if there are 4 pluses next to the word mucus on the analysis form, this means that there is a lot of it and special treatment is required.
If there is a high level of mucus, it can even be detected visually. The urine becomes cloudy and contains sediment. Sometimes clearly visible flakes of mucus may appear. This condition most often indicates a serious inflammatory process, in which the body intensively produces mucus to protect the organs from the penetration of bacteria.
And a moderate increase in the level of mucus almost does not manifest itself externally. The patient can only feel the symptoms caused by the pathologies that cause this condition. If such sensations appear, it is advisable to undergo an examination in order to take timely measures to eliminate the disease. Most often, this is a violation of urination: retention, too frequent, strong urges that do not lead to the release of urine, urinary incontinence. When urinating, a burning sensation, stinging or pain may occur. Sometimes itching of the external genitalia, rash, redness, discomfort during sexual intercourse and pain in the lower abdomen also occur.
Diagnostics
A general urine test cannot always make a definitive diagnosis. If necessary, the doctor conducts additional diagnostics using other examination methods (radiography, ultrasound, and others).
Techniques
To identify various urological diseases, it is necessary to look not only at the presence of mucus, but also other indicators. They help determine a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe additional examination.
Possible combinations of the appearance of mucus with other indicators of OAM:
| Possible combinations | Causes |
| Bacteria | infectious diseases of the urinary and genital tract, incorrect sampling of material, poor hygiene. |
| Protein | diabetic nephropathy, nephrotic syndrome, glomerulonephritis, multiple myeloma, urethritis, cystitis, neoplasms of the genitourinary system. |
| Leukocytes | inflammatory diseases of the urinary system. |
| Salts | neurogenic disorders, poor nutrition, infectious diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems, changes in metabolism. |
| Oxalates | diabetes mellitus, urolithiasis, abnormal metabolism. |
| Blood | glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, oncopathologies, damage to the renal pelvis, ureter, bladder. |
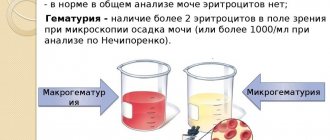
| Red blood cells | urolithiasis, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, oncopathology of the urinary and reproductive system, kidney injury, hemorrhagic diathesis, SLE, large dosages of hemostatic agents. |
| Crystals | diseases of the urinary system (urolithiasis and others), unhealthy diet, altered metabolism. |
Collection rules
For OAM results to be reliable, it must be collected correctly. A poorly collected analysis can lead to distorted data, namely the appearance of a large amount of mucus, fungi, bacterial agents and other indicators. To collect TAM, the patient needs to prepare a sterile container. This will prevent the proliferation of microbes. Previously, glass jars were used, which were processed together with the lid. Today, doctors and laboratory technicians recommend using special sterile plastic jars. You can buy them at pharmacies.
For OAM, urine is taken in the morning immediately after waking up. Before collecting urine, a woman needs to wash her perineum with soap, and a man needs to wash the head of the penis. For a reliable result, you should pass the first third of a portion of urine past the jar in order to wash away possible bacteria from the urethra. The middle part is collected in a jar. The third one is skipped past the can. After collecting the analysis, the container is tightly closed. It can be placed in a bag before transporting to the laboratory.
In the laboratory, the test is taken along with a form issued by the doctor. In it, the doctor writes the patient’s last name, first name, patronymic, age, and area where the patient is being observed. After a few days, you can find out the results from your doctor.
To collect urine from a newborn or infant, you can use special urine bags. They can stick to the skin, thereby facilitating the process.
Before taking the test, the girl’s perineum should be washed with soap. It is better to wash from front to back to prevent bacteria from entering the urethra from the rectum. The boy needs to wash his penis before collecting urine. After the procedure, the skin should be dried with a diaper and a urinal should be glued to the skin of the perineum. At the end of collecting a urine test, you need to peel it off and pour the contents into a sterile jar.
Treatment methods
Once the cause of mucus is determined, appropriate treatment is prescribed. For urethritis, cystitis, and kidney inflammation of infectious origin, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. This is done exclusively by the attending physician, who also determines the dosage, dosage regimen and required course duration.
Inflammation of the bladder and urethra requires drinking large amounts of fluid, at least 2.5 liters per day. You can drink clean water, rosehip decoction, herbal teas, unsweetened fruit drinks. Salty, spicy foods and dishes, marinades, spices, and smoked foods should be excluded from the diet.
In case of inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system, in addition to antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen).
Nephrolithiasis may require surgical treatment. Modern medicine has a wide range of minimally invasive and non-invasive methods for crushing and removing stones. For attacks of pain during an exacerbation of urolithiasis, doctors recommend taking painkillers and antispasmodics. Such products are used as needed; constant use is not necessary and can cause harm.
Detection of mucus in the urine is a deviation from the norm, so you need to consult a doctor and undergo an examination. Most often, impurities visible to the eye in urine that is transparent under normal conditions indicate the occurrence of a pathological process.
Analysis transcript
In the laboratory, the quality of the analysis is checked based on specific characteristics. Each of them has its own normal indicators. Deviations from them indicate the presence of a disease.
| Sign | Normal values |
| Color | yellow |
| Volume | 10 ml or more |
| transparency | transparent |
| pH | 5.5-7.0, sour |
| specific gravity | 1010 – 1022 g/l. |
| leukocytes | 0-3 per visual field (f/o) for men, 0-5 for women. |
| red blood cells | No more than 2 per p/z |
| epithelial cells | flat – women – single on p/z, men – single on all material. |
| cylinders | hyaline – single, no other species |
| salt | |
| protein | — |
| glucose | — |
| bilirubin | — |
| urobilinogen | — |
| Ketone bodies | — |
| nitrites | — |
| hemoglobin | — |
| slime | A little |
| Salts, crystals | — |
How is the color of mucus determined?
The color of the mucus may have distinctive features caused by impurities. Brown tint - formed when red blood cells enter the urine due to damage to the parenchymal tissue of the kidneys:
- toxic substances in case of poisoning;
- for infectious diseases with high fever;
- in conditions of impaired blood circulation.
White mucus is observed with leukocyturia caused by:
- inflammatory diseases of the urinary system;
- prolonged stagnation of urine.
Why mucus appears in children can be found in this article.
Let's consider the clinical significance of identifying combinations of mucus with other elements in urine analysis.