© Author: Z. Nelly Vladimirovna, laboratory diagnostics doctor at the Research Institute of Transfusiology and Medical Biotechnology, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
An important and reliable criterion for diagnosing anemia can be considered a morphological study of red blood cells, for which it is especially common throughout life (from “birth” to “death”) to retain all their inherent characteristics: shape - biconcave disks, diameter - from 7 to 8 microns, average volume – from 80 to 100 femtoliters (femto – 1/billiard), color – normochromic.
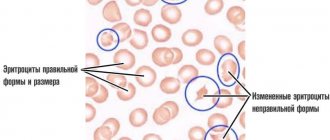
Pathological changes in erythrocytes: microcytosis, macrocytosis, and in other cases normocytosis, hypochromia and hyperchromia are characteristic of a number of anemic conditions.
The concept of “microcytosis” implies the presence in the community of erythrocytes of a large number of small midget cells, which is evidence of the development of microcytic anemia.
Development mechanisms
Microcytic anemia (another name for the process) is one of three types of anisocytosis and has multiple origins. That is, a whole group of factors, sometimes heterogeneous, takes part in its formation. There may be several influences at once, which only complicates the process of identifying the essence of the deviation.
The impact of certain toxic substances on the patient's body
Poisoning with poisons plays almost one of the key roles in the origin of the problem. In this case, we are talking about the effect on the body, bone marrow of heavy metal salts, vapors of other compounds that can potentially provoke hematopoietic disorders.
As a result of the influence of a negative factor, the maturation of red blood cells slows down, phenotypic changes begin and abnormally small cells, microcytes, are formed instead of normal cells.
Depending on the severity of intoxication, the duration of the disorder may vary. Sometimes, even after correcting the root cause, it is not possible to achieve high-quality recovery without specialized medical care. Requires the participation of a hematologist.
Taking certain medications has the same effect. Especially long-term or in large dosages. Features and side effects are usually indicated in the annotations; you can calculate this probability in advance.
Iron deficiency
A deficiency of the element quickly leads to insufficient hemoglobin concentration. This, in turn, starts a chain reaction.
Since there is no way to transfer the compound to tissues, the hematopoietic system ceases to synthesize normal red blood cells. Saves energy and produces small-sized cells.
Other variants of deviation from the norm are also possible, not only microcytosis. When the disorder passes, the anomaly regarding the volume of formed cells also resolves itself.
Various anemic processes
Not only iron deficiency, but also a lack of B vitamins, folic acid, and other compounds provokes problems with the synthesis of red blood cells and their structural characteristics.
The recovery technique is the same: treatment of the underlying condition, correction of the pathological process and, if necessary, artificial introduction of missing substances from the outside.
Effect of ionizing radiation
Radiation affects the condition of the entire body in an extremely negative way. The processes of cellular oxidation and the formation of free radicals begin. Ultimately, this effect is most dangerous for bone marrow tissue. It stops synthesizing cells and does not allow them to mature normally.
A similar problem is observed not only among people with acute radiation sickness, but also among those who live in areas with high background radiation on a long-term basis. For years. They are at increased risk of injury.
Infectious factors
It is relatively rare. The pyogenic flora has the most destructive potential. Also herpes viruses, human papillomaviruses. They are unpredictable in behavior, capable of provoking mutations and spontaneous deviations in the functioning of all organs and systems.
Especially without quality therapy, if their activity continues for a sufficient amount of time.
Genetic abnormalities
Disorders that are inherited. Mostly, disorders of hematopoietic processes pass through the mother, but not always. In addition to the actual transportation with the material, there are also spontaneous, sporadic mutations that are in no way related to family history. But the disorder is fixed in a person’s genotype and is passed on to his offspring.
Microcytosis of erythrocytes develops as a result of the influence of a group of mechanisms; they are heterogeneous and do not have a direct connection with each other. But cross-impact is possible, you need to understand the substance. This is the task of specialists; you should not hesitate to consult a doctor.
Effect on the body
Prolonged microcytosis leads to detrimental consequences. If such a condition is identified in a general analysis, the diagnosis should be immediately clarified and treatment should begin.
A decrease in volume characteristics leads to a deterioration in the functions of erythrocytes
A decrease in the volumetric size of some normocytes entails a reduction in the total surface area of the plasma membranes of all erythrocytes, both healthy and deformed. This change leads to a decrease in the proper level of performance of almost all functional duties assigned to red blood cells:
- gas transport, buffer, nutritional, protective functions;
- humoral regulation of adaptation processes;
- regulation of vascular tone;
- metabolism of catecholamines, acetylcholine and immune complexes.
A decrease in hemoglobin volumes further aggravates the picture in the gas transport and buffer erythrocyte functions. This is especially reflected in the respiratory function - the characteristics of the oxygen capacity of the blood begin to fall below the normal 18-20% vol.
Classification
It is not entirely correct to talk about the typification of microcytosis as such. A generally accepted method has not yet been developed, and it would not have sufficient information content.
The division is carried out on such a basis as the features of the provoked changes in general. Accordingly, we can talk about the following types of pathological process.
Iron-deficiency anemia
Classic disorder. It is typically caused by insufficient iron intake or weak, poor absorption as a result of disorders of the digestive system or other reasons.
The question is secondary in the context of the situation. The point is different. Due to an insufficient amount of iron, the concentration of hemoglobin drops, therefore, the normal synthesis and maturation of red blood cells is disrupted. As the previous sizes are no longer needed, they are reduced in volume in order to save money.
Only after eliminating the disorder does everything return to normal. Read more about IDA and its treatment methods in this article.
Thalessemia
A genetically determined type of pathological process. The result of the disorder is a dual symptomatic complex. Both manifestations are equally dangerous to health and life.
- The first characteristic sign is a natural (in the context of a clinical case) drop in hemoglobin production. The result is a problem with cellular respiration. There are several types of thalesemia, they are determined precisely by the degree of deviation and the severity of the disorder.
- The second typical symptom concerns the synthesis of red blood cells. They decrease in size (microcytes), and in addition, as a result of an abnormal reaction of the body, they begin to die in large volumes. Which also leads to a reduction in quantity.
The pathological process has many variations. Not everyone is so dangerous. Sometimes the patient does not even suspect that he has any health problem.
Attention:
There are also situations that lead to stillbirth or early death of children. In the very first days from birth. This is a hereditary or mutational abnormality.
Hypochromic anemia
Accompanied by a violation of the size of formed blood cells. On the other hand, there is an insufficient concentration of hemoglobin in their structure.
Cytological units are not able to transport oxygen, which leads to ischemia, hypoxia and unpredictable consequences in the long run. It is necessary to begin treatment as quickly as possible.
Read more about hypochromic anemia in this article.
There is also the opposite phenomenon. When red blood cells are smaller than normal in size but contain an abnormally large amount of hemoglobin. It carries no payload, typically. Because they still cannot tolerate it normally.
There are rarely exceptions. The origin of both this and that state is always secondary. That is, it is caused by other violations. To eliminate anemia, you need to deal with the source of the problem.
Hypochromia and microcytosis are the most common ligaments and are as widespread as the pathology associated with iron deficiency. Special diagnostics help to put an end to the issue of nature.
Microcytosis: Scientific Definition
Experts talk about microcytosis, what it is, what the deviation is when there are 30-50% of microcytes in the blood. If these bodies are of different sizes, then this phenomenon is called “anisocytosis.”
But what happens when microcytosis appears? What it is? It all starts with a mutation in the veins, which causes the encoding of membrane proteins. But they are the ones that are part of the cytoskeleton of erythrocytes. After this, water can easily penetrate into the microcyte. This leads to the fact that the double concavity disappears, the vessels are poorly supplied with glucose, and the erythrocyte membrane increases fragmentation. This can lead to phagocytosis or lysis.
Causes
The factors for the development of microcytosis in women and men are the same, the violations have been partially reviewed. It is worth saying more about them.
- Poor nutrition plays one of the key roles, if not the main one. It is accompanied by an insufficient supply of many useful compounds necessary for life. Be it iron or other substances.
The problem, despite the likelihood of negative phenomena and their severity, is solved relatively simply. It is enough to adjust the diet and enrich it with animal protein and fortified foods.
In case of serious disorders, temporary treatment with replacement drugs is carried out. The entire therapy takes on average 2 to 4 weeks. Plus or minus based on the severity of the clinic.
- Pathologies of the digestive tract. They occur frequently, but the severity of microcytosis is not always so great that it leads to the development of specific symptoms. We are talking about disorders at the level of the stomach, small and large intestines.
The absorption of nutrients slows down significantly, which becomes a source of deficiency phenomena. The result is anemia of one kind or another. Correction involves combating the underlying condition.
- Metabolic disorders. Microcytosis in a general blood test is possible as a consequence of a long abnormal chain of metabolic phenomena against the background of a number of pathologies: from diabetes mellitus to hypothyroidism, insufficient amounts of thyroid hormones.
Treatment is specific, determined by the main diagnosis. Such abnormalities are the responsibility of endocrinology specialists.
- Bone marrow diseases. Severe in most cases. It is here that the synthesis of precursor cells occurs, which, after differentiation, acquire the specific features of white blood cells, erythrocytes and others. Also the final maturation. It is necessary to identify the essence of the violation and eliminate it as quickly as possible. The longer the deviation exists, the more difficult it will be to eventually bring everything back to normal.
- Oncology. Mostly malignant tumors. Regardless of localization. The breakdown products of neoplasia, especially at advanced stages of the disease, inhibit the functioning of the bone marrow. If metastases form in this structure, the degree of danger increases many times, and restoration seems to be an impossible task. Oncology cannot be started.
- Poisoning. Vapors of non-metals, salts of other substances. Especially with systematic influence. Chronic intoxication creates conditions that are difficult to cure. Recovery is possible only by eliminating the negative factor and carrying out detoxification measures. It takes time and effort. Arsenic, lead, mercury, and radioactive isotopes of iodine are especially dangerous.
Attention:
In everyday life, people constantly encounter nitrogenous salts and nitrates. They are just as dangerous as other substances.
- Taking certain medications. The likelihood of microcytosis is indicated in the annotations for specific names. Therefore, minor deviations in cell shape do not come as a surprise to the patient and the doctor. However, if the number of changed structures reaches a certain point, the drug is discontinued. Replace with others, as needed.
- Exposure to radiation. It has already been said about it. Radiation sickness or chronic damage threatens the bone marrow. It is especially sensitive to the effects of such environmental factors.
- Insufficient intake or absorption of other substances. Vitamins B9, B12, etc. Specific forms of anemia develop.
The list is far from complete.
Macrocytosis of erythrocytes in a general blood test
The key point in the diagnostic search (in relation to macrocytic anemia) is a general blood test (hemogram), or rather, its individual parameters:
- Morphological characteristics of red blood cells (detection of macrocytes, poikilocytosis);
- MCV indicator (mean blood cell volume) - it shows values above 120 femtoliters with macrocytosis of erythrocytes;
- Hematocrit level (in severe vitamin deficiency anemia for a long time, the hematocrit drops to 30-25%, although in other forms of macrocytic anemia it may remain within normal values).
It should be noted that the nature of the process is significant, since it is the chronic course of the pathology that creates the preconditions for the disappearance of normal red cells and their replacement by macrocytes.
In patients suffering from anemic syndrome for a shorter period of time, the indicator may only slightly exceed the upper limit of normal values or even be within the normal range. Then you will have to take into account other circumstances that could create conditions for the development of macrocytic anemia. Macrocytosis, caused by the use of chemotherapy drugs or damage to the hepatic parenchyma, is usually mild or moderate. Reticulocytosis with a more or less uniform increase in red blood cells usually also does not raise doubts with the doctor. But with regard to vitamin deficiency conditions, questions always arise. However, the table below will help you compare and evaluate laboratory parameters for different conditions.
Table: options for increasing the size of red blood cells
| Pathological condition | MCV, fl | Morphological characteristics of cells |
| Megaloblastic anemia HCT (hematocrit) below 30% | 100 — 130 | Hyperchromia, macrocytes, poikilocytosis (ovalocytes, schizocytes) |
| Reticulocytosis (RET more than 10%) | 100 — 110 | Polychromatophilic elements - macrocytes (immature forms) |
| Lesions of the liver parenchyma | 90 — 110 | Macrocytes, uniform increase in cell diameter and volume (all red blood cells are approximately the same size) |
Macrocytosis caused by a lack of cyanocobalamin - vitamin B12, or folic acid - vitamin B9 (or both) has noticeable differences. When studying a smear morphologically:
blood for B12 deficiency anemia
- Poikilocytosis of erythrocytes;
- The presence of fragments of destroyed cells in the smear (schizocytosis);
- Hyperchromia;
- Changes in the “white” blood - a significant increase in the content of neutrophilic leukocytes, the nucleus of which has 5 or 6 segments, while normally the number of cells containing more than five segments in their nucleus is unlikely to reach 5% of the total number of segmented neutrophils .
The presence of a huge number of polysegmented neutrophil leukocytes is a kind of equivalent of poikilocytosis of red blood cells and is an important laboratory symptom of megaloblastic anemia.
Causes in children
The provocateurs of the violation in this case are approximately the same. However, according to statistical data, the following points prevail:
- Genetic abnormalities and deviations. The essence lies in hereditary chromosomal disorders. The classic case has already been named - these are thalesemias of various types. Spontaneous mutations are possible during intrauterine development. In the early stages of gestation. But this is a much rarer situation.
- Malnutrition. Since the body is growing rapidly, the need for nutrients is many times higher. With a poor diet, it is impossible to avoid disorders - this is the main cause of microcytosis in a child.
- Hormonal disorders. Mostly observed in adolescents who have entered early puberty. When changes in the body occur most actively and aggressively. During this time, support is needed through lifestyle changes or, in extreme cases, medication. Strictly under the supervision of endocrinologists.
The result of the influence of abnormal factors is microcytic anemia, which is typically characterized by a decrease in oxygen transport due to the physical inability of red blood cells to provide it. Restoring normalcy is possible.
Symptoms
Seizures in the corners of the mouth
A large number of altered red blood cells in the blood leads to certain changes in the human body, which can be recognized without laboratory tests.
The main symptoms characteristic of microcytosis:
- severe general weakness and rapid onset of fatigue;
- fainting and fatigue when performing simple physical exercises;
- rapid heartbeat (tachycardia), a feeling of interruptions in the functioning of the heart;
- pale skin;
- dry skin and mucous membranes;
- changes in the papillae of the tongue (their hypertrophy) and small erosions in the corners of the mouth (cheilitis);
- changes in taste preferences, periodic feelings of nausea;
- the appearance of a feeling of “lump in the throat” and difficulty swallowing, dryness of the nasopharyngeal mucosa;
- itching of the skin of the vaginal vestibule;
- brittleness and dryness of nails and hair.
Symptoms
The clinical picture is nonspecific. It is difficult to say exactly what caused it, since microcytosis gives approximately the same symptoms as other types of anemia.
In general, the following manifestations of the violation are present:
- Brain disorders. Pain, problems with spatial orientation and coordination of movements. The entire central nervous system suffers, since it is the most demanding in terms of nutrition and cellular respiration.
- Decreased memory, speed and quality of thinking. Cognitive and mnestic problems. Inability to quickly switch between tasks, learn new skills, etc. The phenomenon is reversible if treatment is started at the right time.
- Violations of gastronomic preferences. The need to eat something that is not suitable for food. Chalk, soil, raw or spoiled meat. There can be many options. This bizarre symptom is not always present, but in most cases.
- Skin and hair problems. Dryness, brittleness, change in natural appearance. The violation is not only cosmetic. It also causes a lot of discomfort to the patient. Because itching is present, a burning sensation is felt. Increased sensitivity is noted.
- Asthenic syndrome. Weakness, constant drowsiness, drop in performance to almost zero. The disorder will persist for a long time. Until cellular respiration is restored.
- Disturbances of hemostasis processes. Increased tendency to bleeding, hematoma formation, etc.
- Behavioral disorders. Aggressiveness, irritability, tearfulness, emotional instability.
- Heart problems. Rhythm disturbances. Pain. Angina pectoris as a result.
The clinical picture is nonspecific, but it immediately indicates anemia. What type needs to be identified under the supervision of doctors.
Additional examinations
Ancillary diagnostic methods are determined by the probable origin of the disorder. Mainly the following events are scheduled:
- Oral interview to determine the nature of the complaints. Symptomatic complex.
- Anamnesis collection. Including family to analyze heredity and possible genetic component. If necessary, a consultation with a specialized specialist is scheduled.
- Coagulogram.
- Biochemistry of venous blood.
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract.
As a rule, a general blood test is sufficient to establish the fact of microcytosis.
Further, all methods are aimed at identifying the origin. The list is approximate.
Diagnostics
Microcytosis is detected during a blood test. If the presence of anemia is determined, a smear of peripheral material is additionally prescribed.
Thanks to this measure, the initial symptoms of micro- and macrocytosis (the diameter of red blood cells exceeds the norm) or a mixed type of anisocytosis, combining signs of the first and second types, are revealed. Normo-, hyper- or hypochromia are detected in the same way.
A hematologist deals with the disease; it is he who prescribes further diagnostics, determines the cause, and the necessary treatment.
As additional diagnostic measures, tests are prescribed to determine celiac disease, blood and stool tests for the presence of the microorganism Helicobacter pylori.
The specialist clarifies in detail all the signs and symptoms present in the patient; it often becomes necessary to consult a gastroenterologist (if pain appears in the abdominal area). Sometimes the following diagnostic methods are needed:
- Transabdominal ultrasound examination.
- Endoscopy of the stomach and intestines.
- Computed tomography of the abdomen.
If adult women experience heavy periods with pain, it is necessary to exclude the presence of uterine fibrosis and other factors that cause heavy bleeding.
Treatment and prognosis
Therapy depends on the genesis of the disease.
- Iron deficiency anemia requires enrichment of the diet, as well as the prescription of ferrous-containing drugs for replacement. The concentration of the product decreases gradually. Depending on the dynamics of the condition, we can talk about several weeks or months of intensive work.
- Vitamin deficiency is eliminated in the same way.
- Poisoning requires detoxification therapy.
- With the development of pathologies of the digestive tract, it is necessary to use probiotics, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and others. Depends on a situation.
- Drug-induced disorders can be resolved by simply stopping the drugs.
- Oncology is corrected surgically. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be used.
The issue of correction is determined by doctors based on the profile of the root cause.
The prognosis is generally favorable. Critical disorders develop extremely rarely. Possible consequences include bleeding, decreased cognitive abilities up to dementia, angina pectoris, heart attack, stroke, and encephalopathy.
What is hypochromia?
There is a medical term "hypochromia microcytosis". What it is? This diagnosis can only be heard when a person undergoes research in a laboratory.
After this, the specialist can identify a lack of hemoglobin in red blood cells, which characterizes this disease. In addition, during the studies the color and shape of red blood cells are observed. When hypochromia appears, they become lighter in the center, and become noticeably darker closer to the edge.
There are such types of this disease:
- iron-saturated hypochromia;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- mixed type.
All of them lead to the development of microcytosis. What it is has already been mentioned.