Causes
Hypochromic anemia can occur for the following reasons:
- blood loss, which may be chronic or long-term, associated with uterine or gastric bleeding. This phenomenon becomes the beginning of the development of hypochromia;
- chronic inflammatory processes associated with changes in iron absorption into the gastrointestinal tract;
- malignant neoplasms in the stomach area;
- strong need for micro and macroelements, especially iron, which occurs during pregnancy, breastfeeding, as well as in younger and puberty;
- lack of iron, as well as vitamins that facilitate its absorption in food when entering the body, for example, with vegetarianism or other diets.
Degrees of hypochromia
Gradation of hypochromic anemia:
- 1st degree - the rim of the cells is colored, the clearing area is larger than usual;
- 2nd degree - the central clearing is wider than usual, approaching the membrane, the colored area is clear;
- 3rd degree - only the area near the membrane is colored, the red blood cell visually looks like a pale ring. It manifests itself in severe anemia, in very advanced stages.
Very often, hypochromia is accompanied by microcytosis; these symptoms are signs of hypochromic anemia. They become even more important if it is necessary to distinguish microcytic anemias from each other or differentiate them from other blood pathologies.
Classification of hypochromia (hypochromic anemia)
This disease can be classified into 4 types:
- iron deficiency;
- sideroachrestic;
- iron redistribution;
- mixed.
Hypochromia in a general blood test
In iron deficiency anemia, there is a lack of the required amount of hemoglobin.
This may happen for the following reasons:
- bleeding that continues for a long time, or when even a small amount of blood has been lost;
- a case when iron is poorly accepted by the body, for example, this can happen after surgery in the stomach area.
For treatment, medications with iron are prescribed. Along with drug treatment, it is recommended to maintain a special diet, which must contain meat, beets, liver and other products. With sideroachrestic anemia, which is otherwise called iron-saturated anemia, there is an excess of hemoglobin.
In this condition, the body is not able to process and produce hemoglobin.
The cause of this disease may be the following:
- chemical poisoning. This applies to those who work in enterprises with chemicals;
- long-term medication treatment.
Chemical poisoning is one of the causes of hypochomia
For treatment, it is prescribed to take the necessary vitamins, for example, vitamin B6, together with a diet that excludes meat and other products. With iron redistribution anemia, hemoglobin is not able to enter the blood system.
The reason may be the following:
- inflammatory diseases with a purulent nature;
- tuberculosis;
- invasion.
Before treating this pathology, you first need to eliminate the cause. After which a course of vitamin therapy is prescribed.
With the mixed type, there is a lack of vitamin B12, as well as iron. A person gets tired very quickly, his immune system decreases, and his upper limbs swell. This type of pathology does not require taking medications containing iron, otherwise the situation will only get worse.
Causes
In many cases, microcytosis indicates serious health problems. The main reason for the appearance of such modified cells is that the synthesis of the protein responsible for the formation of red blood cells is disrupted. This happens for various reasons. For example, frequent consumption of low-quality or chlorinated water can cause such disorders. In addition, some infectious diseases, such as acute respiratory viral infections or influenza, can lead to complications affecting the composition of the blood.
The following pathologies become more serious causes of microcytosis:
- iron deficiency or microcytic anemia;
- hereditary anomaly of genes responsible for the formation of the erythrocyte membrane;
- thalassemia is a genetic disease, inherited, in which the formation of hemoglobin is reduced;
- malignant tumors or their metastases in the thyroid or other glands, spinal cord, lungs, and also in the bone marrow;
- some infectious diseases, such as hepatitis;
- chronic inflammatory pathologies of the kidneys, liver, stomach - peptic ulcer, cirrhosis;
- chronic alcoholism;
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- congenital blood abnormalities.
Symptoms of pathology
The disease may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dizziness, which occurs quite often, there may also be manifestations of black spots or fainting;
- shortness of breath after mild physical activity;
- feeling depressed;
- rapid heartbeat;
- pale epidermis;
- change in well-being, most often an irritable state;
- fast fatiguability.
Dizziness is one of the signs of hypochomia
All of the above symptoms are characteristic of all categories of hypochromia. If suddenly they appear, then you need to do a general examination of the blood system. After the procedure, the specialist will diagnose the disease and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Symptoms of hypochromia
Brittle and peeling nails are a possible sign of hypochromia
Depending on the underlying causes of hypochromia, its manifestations may be different. If the following symptoms are persistently present, a blood test should be performed:
- sudden general weakness of the body or muscle weakness;
- fragility and weakness of hair and nails;
- stomatitis and regular appearance of ulcers in the oral area and corners of the mouth;
- aggravation of taste buds;
- urinary incontinence, especially when coughing or laughing;
- increased heart rate;
- instant shortness of breath after minor physical exertion;
- the appearance of small black dots in the field of vision.
Typically, the most obvious sign of iron deficiency is a general feeling of fatigue, often called “chronic fatigue,” and accompanying weakness, drowsiness, and lethargy. If a combination of any of these signs is detected, you should consult a doctor.
Why is hypochromia dangerous?
Lack of hemoglobin is not a threat to human life. However, if this deficiency is not corrected with appropriate medications, complications may occur. This pathology is more often observed in the elderly generation, which leads to various diseases.
Why is hypochromia dangerous?
During pregnancy, having a lack of hemoglobin is very dangerous, since the fetus will then begin to suffer from oxygen starvation, and it may not survive in the womb. Also, a pregnant woman may experience premature labor, or the child may be born underweight and become weak-minded.
When a danger occurs, the following symptoms may appear:
- the spleen and liver will increase in size;
- an edema condition will occur;
- all limbs will become numb;
- the work of the heart will be disrupted.
What possible threats does hypochromia pose?
Low iron during pregnancy is a threat to the fetus
Hypochromia of unadvanced forms (first and second degrees) in itself is not life-threatening, but it is dangerous in the presence of serious concomitant diseases that provoked it. A long course of a hypochromic state can aggravate existing diseases. Elderly people, who may develop severe complications without timely treatment, should pay special attention to hypochromia.
If there is a lack of oxygen in the cells, which is typical for hypochromia, the following dangerous situations may arise:
- oxygen starvation, which is especially dangerous for pregnant women and the development of their fetus;
- premature birth;
- deficiency of body weight and muscle mass in relation to fat;
- enlarged liver, spleen;
- water retention in the body, swelling in the body;
- loss of sensation and numbness of the limbs;
- disruption of cardiovascular system processes.
Iron supplements during treatment can provoke individual intolerance: depending on the state of the patient’s body, fainting, increased heart rate and other consequences may occur. This makes it important to carry out treatment exclusively under medical supervision.
With timely consultation with a doctor and treatment, hypochromia may not cause any complications.
Qualitative and quantitative analysis
Hypochromia in a general blood test is the most important indicator of a blood test; thanks to it, the level of hemoglobin is assessed. However, if anemia is present, then other indicators are also taken into account, for example, qualitative and quantitative changes in the circulatory system.
Qualitative and quantitative analysis
In order to determine the morphological analysis you will need:
- investigate the smear;
- find out the size of red blood cells;
- see with your eye how much the red blood cell is saturated with hemoglobin.
What does iron deficiency lead to?
The long course of iron deficiency anemia leads not only to a decrease in the hemoglobin content of red blood cells, but also to a decrease in the size of blood cells. This pathology is called “hypochromic microcytic anemia.” Standards for average erythrocyte volumes throughout life range from 110–128 μm3 in the neonatal period to 80–100 in an adult.
The microcytic reaction causes a significant decrease in the indicator. At the same time, other blood cells do not change either in quantity or in shape.
When is hypochromia not associated with pathologies?
Hypochromia cannot be associated with pathologies only when a person eats the wrong way. For example, he consumes too many sweet and useless foods, which in turn leads to a decrease in the level of iron in the blood, which is confirmed by a general blood test. In this case, only adjusting the diet will help.
By maintaining proper nutrition over a long period, you can bring your hemoglobin level back to normal.
Otherwise, if you start to develop incipient anemia, organs such as:
- heart;
- spleen;
- vessels;
- kidneys;
- Gastrointestinal tract;
- liver;
- brain.
Symptoms
All of these types of hypochromic anemia have certain symptoms:
- General weakness.
- Increased fatigue.
- Headache.
- Dizziness.
- Decreased ability to work.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Tachycardia.
- Nervousness, irritability.
- Dyspnea.
- Flashing "flies" before the eyes.
Attention! The most important thing is that during long-term processes, due to hypoxia of organs and tissues, damage to internal organs develops. This phenomenon occurs because hemoglobin is an oxygen carrier, and a decrease in hemoglobin, accordingly, leads to oxygen starvation.
A specific symptom is its absence in the early stages. Patients do not feel any initial changes in their condition. Even when the first general signs begin to appear, this is identified with a high rhythm of life, fatigue, and stress. In fact, according to hematologists, in most cases these are already the first signs of the disease.
First of all, such triggers depend on the stage of the disease:
- First degree – there are practically no symptoms. Periodically there are complaints of weakness and general fatigue. The hemoglobin level is 90 g/l and above.
- Second degree - dizziness, headaches, pallor, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, visual disturbances, and increased photosensitivity already appear. Hemoglobin levels are from 70 to 90 g/l.
- Third degree - accompanied by numbness of the arms and legs, fragility of the legs, baldness, perversion of smell and taste. Hemoglobin is low – falls below 70 g/l. In such cases, the development of decompensated conditions leading to death is possible.
In such situations, careful diagnosis comes first. Only the consciousness of the patient and the literacy of the doctor will allow timely determination of the reasons for the deterioration of the condition.
Treatment of pathology with drugs and folk remedies
Hypochromia in a general blood test, when the pathology is confirmed by a laboratory assistant, is amenable to the following drug therapy:
- "Ferrum - Lek";
- "Totem";
- "Maltofer";
- "Sorbifer";
- "Tradiferon".
Ferrum – Lek
Vitamins are also prescribed together with medications , since anemia mainly develops due to a lack of elements that are so necessary for the body:
- iron;
- copper;
- zinc;
- vitamins from group B;
- ascorbic acid;
- vitamins A, E, D.
Anemia can also be treated with folk remedies. It was in this way that ancient ancestors were treated in order to heal even a severe form of pathology.
Medicines do not always help cure anemia, as they have side effects that make it simply impossible to fully cure the disease. Therefore, thanks to traditional medicine, you can increase your hemoglobin level without any consequences. The following proven recipes can be used for traditional medicine.
Recipe No. 1. Ingredients:
- dry strawberries;
- boiling water.
Dried strawberries
Directions for use:
- Berries must be filled with 1 tbsp. hot water.
- Leave to steep under the lid closed for 4 hours.
- The tincture must be filtered before use.
- Drink the prepared decoction all at once.
Recipe No. 2. Ingredients:
- chokeberry;
- dog-rose fruit;
- boiling water.
Method of use:
- Berries must be taken in equal quantities.
- Fill them with hot water.
- The decoction should be infused in an enamel or glass container for 30 minutes.
- Filter the broth and consume several times a day.
Development mechanisms
Microcytic anemia (another name for the process) is one of three types of anisocytosis and has multiple origins. That is, a whole group of factors, sometimes heterogeneous, takes part in its formation. There may be several influences at once, which only complicates the process of identifying the essence of the deviation.
The impact of certain toxic substances on the patient's body
Poisoning with poisons plays almost one of the key roles in the origin of the problem. In this case, we are talking about the effect on the body, bone marrow of heavy metal salts, vapors of other compounds that can potentially provoke hematopoietic disorders.
As a result of the influence of a negative factor, the maturation of red blood cells slows down, phenotypic changes begin and abnormally small cells, microcytes, are formed instead of normal cells.
Depending on the severity of intoxication, the duration of the disorder may vary. Sometimes, even after correcting the root cause, it is not possible to achieve high-quality recovery without specialized medical care. Requires the participation of a hematologist.
Taking certain medications has the same effect. Especially long-term or in large dosages. Features and side effects are usually indicated in the annotations; you can calculate this probability in advance.
Iron deficiency
A deficiency of the element quickly leads to insufficient hemoglobin concentration. This, in turn, starts a chain reaction.
Since there is no way to transfer the compound to tissues, the hematopoietic system ceases to synthesize normal red blood cells. Saves energy and produces small-sized cells.
Other variants of deviation from the norm are also possible, not only microcytosis. When the disorder passes, the anomaly regarding the volume of formed cells also resolves itself.
Various anemic processes
Not only iron deficiency, but also a lack of B vitamins, folic acid, and other compounds provokes problems with the synthesis of red blood cells and their structural characteristics.
The recovery technique is the same: treatment of the underlying condition, correction of the pathological process and, if necessary, artificial introduction of missing substances from the outside.
Effect of ionizing radiation
Radiation affects the condition of the entire body in an extremely negative way. The processes of cellular oxidation and the formation of free radicals begin. Ultimately, this effect is most dangerous for bone marrow tissue. It stops synthesizing cells and does not allow them to mature normally.
A similar problem is observed not only among people with acute radiation sickness, but also among those who live in areas with high background radiation on a long-term basis. For years. They are at increased risk of injury.
Infectious factors
It is relatively rare. The pyogenic flora has the most destructive potential. Also herpes viruses, human papillomaviruses. They are unpredictable in behavior, capable of provoking mutations and spontaneous deviations in the functioning of all organs and systems.
Especially without quality therapy, if their activity continues for a sufficient amount of time.
Genetic abnormalities
Disorders that are inherited. Mostly, disorders of hematopoietic processes pass through the mother, but not always. In addition to the actual transportation with the material, there are also spontaneous, sporadic mutations that are in no way related to family history. But the disorder is fixed in a person’s genotype and is passed on to his offspring.
Microcytosis of erythrocytes develops as a result of the influence of a group of mechanisms; they are heterogeneous and do not have a direct connection with each other. But cross-impact is possible, you need to understand the substance. This is the task of specialists; you should not hesitate to consult a doctor.
Iron-deficiency anemia
For this pathology, it is recommended to take medications containing iron, as well as eat foods that are rich in this element. The course of therapy can be 6 months or more.
Drugs for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia include:
- "Maltofer" is given for treatment to adolescents and older adults - up to 300 mg per day (3 tablets) for 5 months, to pregnant women - up to 300 mg per day. Next, after replenishing the iron deficiency, the drug is taken for some more time, when anemia is no longer present. Teenagers and older adults are given up to 100 mg per day for 2 months;
- "Sorbifer", given to adolescents and older up to 1 tablet. 1 or 2 r. per day, if necessary, increase the dose to 4 tablets. per day. The course of therapy is 4 months. Pregnant and lactating women are given - 1 tablet. per day (for prevention), up to 1 tablet. 2 r. per day (for treatment). The drug should be taken immediately with water and should not be chewed;
- "Hemofer", given to premature babies up to 2 drops. every day up to 5 months, infants up to 1 year are given up to 19 drops. every day, children under 12 years of age are given up to 28 drops. 1 or 2 r. during the day, for adolescents - up to 28 drops. 2 r. during the day, for older people - up to 55 caps. 2 r. in a day. The drug is taken between meals, added to water or juice.
Maltofer
Traditional medicine recipes that help increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood system.
Recipe No. 1:
- dandelion (leaves, roots) 3 tbsp. l.;
- boiling water.
Mode of application:
- Medicinal raw materials must be filled with boiling water.
- Leave to infuse for 30 minutes.
- Filter.
- You need to take no more than 1 tbsp of the decoction. l. 3 r. per day.
- The course of therapy is 14 days.
Dandelion
Recipe No. 2:
- rosehip, 25 g;
- rowan, 25 g;
- boiling water.
Mode of application:
- The berries are poured with boiling water.
- Let it brew.
- Use no more than 1 tbsp. during the day.
Recipe No. 3:
- dried apricots;
- prunes;
- raisin;
- walnuts;
- lemon;
- honey, 200 g;
- fresh cranberries.
Cooking method:
- Dried fruits and nuts should be taken in equal quantities, chopped and mixed.
- Add honey and, if possible, cranberries.
- All ingredients must be in a glass container.
- Use 1 tbsp. l. 3 r. during the day on an empty stomach, before meals. Children are given - 1 tsp. no more than 3 r. per day, on an empty stomach.
What is hypochromia?
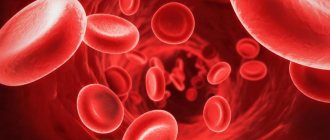
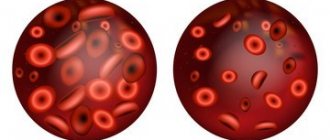
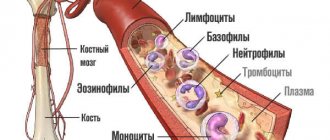
Red blood cells are round blood cells with a biconcave surface (that is, there are depressions on both sides). Their main function is to transport oxygen molecules and carbon dioxide through the bloodstream throughout the body. It is thanks to this process that life is maintained in every person. So, if tissues and organs do not receive enough oxygen, they will begin to starve and then die.
As long as the red blood cells contain a sufficient number of hemoglobin globules, the formed elements of the blood will be able to retain on their surface and transport to their destinations the amount of oxygen particles necessary for normal metabolism. During hypochromia, red blood cells undergo dangerous changes: their hemoglobin level drops sharply, causing the red blood cells to fade and weaken.
Comparative analysis of healthy and damaged blood cells involved in supplying the body with oxygen
One blood test for hypochromia is not enough to make a specific diagnosis, so the attending doctor simultaneously prescribes other types of diagnostics to his patient, such as a gynecological examination, rectoscopy, ultrasound, MRI, CT, etc.
Iron-rich anemia
For this pathology, it is necessary to use the following drugs:
- "Pyridoxine", for internal use no more than 200 mg per day, for intravenous infusion up to 100 mg 2 times. per week for 2 months;
- sodium salt, prescribed for lead intoxication;
- "Desferal", for intravenous infusion no more than 1000 mg with a break.
Mumiyo
The following traditional medicine methods will help reduce high hemoglobin levels:
- hirudotherapy, thanks to leeches that suck blood, red blood cells decrease. A few sessions will be enough to achieve the desired result;
- mummy, you need to take up to 1 pill, which is first dissolved in 1 tbsp. warm water overnight. The course of therapy is 10 days with a break of 5 days, repeat again;
- medicinal herbs (willowherb, chickweed and chickweed) will also help reduce high hemoglobin.
Important characteristics of a red blood cell
Regarding the state of red blood cells, which carry out numerous and very important functions in the body, deviations in their sizes from normal values (80 – 100 fl or µm3) can tell a lot:
- Towards a decrease (MCV in the hematology analyzer <80 fL) – microcytosis;
- In the direction of increase (MCV>100 fL) – macrocytosis;
- The size of red blood cells remains unchanged – normocytosis.
In addition, usually, for the diagnosis of certain types of anemia, they not only do not neglect, but also assign a significant role to such laboratory indicators as coloring, taking into account which they distinguish between: normo-, hyper- and hypochromia. Since, due to a lack of iron, the synthesis of the red pigment (hemoglobin), which determines the color of the blood, is impaired, hypochromia, as a rule, is combined with microcytosis, and the pathology that develops due to these disorders is called microcytic hypochromic anemia.
Thus, if you have a suspicion of anemia, you can safely rely on the size of red blood cells and their color, since, as practice has shown, these signs are distinguished by the greatest degree of constancy. One of them (size deviation downwards - microcytosis) will be discussed in this material.
Diet therapy for hypochromia: general principles and rules
Maintaining a diet for hypochromia is not difficult, the main thing is to adhere to certain rules that will help you absorb the necessary element:
- rejection of bad habits;
- limit the consumption of coffee and tea;
- You cannot immediately consume protein dishes after fermented milk products;
- It is better to drink kefir and milk before bedtime;
- Iron-boosting drugs should not be taken with tea or coffee, only with water;
- prefer a healthy diet, avoid overly fried foods.
Recommended Products
For anemia, in order to maintain normal iron levels, it is recommended to include the following foods in the diet:
- rich in amino acids and proteins: meat products (rabbit, beef, pork, pigeon, chicken, lamb), butter and cream;
- microelements necessary for hematopoiesis are found in: beets, carrots, peas, lentils, beans, tomatoes, corn, liver, fish products, oatmeal, apricots, baker's or brewer's yeast;
- the required amount of folic acid is found in: green vegetables, salads, herbs, and breakfast cereals;
- for better absorption of iron, it is useful to drink mineral water from healing waters;
- products that are fortified with iron: bread products, baby products, confectionery products);
- Honey is well capable of absorbing iron;
- no more than 3 mg of the iron element is found in 1 tbsp. plum nectar.
Meat products
In addition to the above list, there are other products that are recommended for use in case of pathology:
- bananas;
- nuts;
- garlic;
- onion;
- apricot;
- cherry;
- viburnum;
- tomatoes;
- potato.
Prohibited Products
It is necessary to limit or completely forget about such products as:
- fat;
- milk;
- baking;
- coffee;
- Coca Cola;
- dishes with brine and vinegar;
- alcoholic drinks.
Menu for the week
Hypochromia in a general blood test indicates developing anemia, in which it is necessary to adhere to the correct diet.
Monday:
| Breakfast | Snack | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner | Before bedtime |
| Milk tea, 1 slice of fillet sausage, cottage cheese + sour cream, radish and grinder salad, bread and butter. | Fruit nectar + baking. | Meat and noodle soup, fried steak + onions, fried potatoes, cauliflower, freshly cut tomatoes, strawberry cream, bread. | Fresh cream + cookies. | Omelet + green peas, bread with mala and tea. | Fruits |
Tuesday:
| Breakfast | Snack | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner | Before bedtime |
| Coffee with cream, scrambled eggs, fresh cut grinder, bread and butter. | Chopped herring, bread + butter + tea. | Beetroot soup, puff pastry pies, fried veal liver, buckwheat porridge, radish and sour cream salad, pears drenched in sweet sauce, bread. | Coffee + cookies. | Vegetable salad seasoned with mayonnaise, lean ham, bread + tea. | Just kvass |
Wednesday:
| Breakfast | Snack | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner | Before bedtime |
| Semolina milk porridge + little bread with Dutch cheese. | Herring, fresh cucumbers, bread, tea + cookies. | Borscht in meat broth, boiled lean meat + fried potatoes, freshly cut cauliflower, whipped cream + cherry jam, bread product. | Coffee + baked goods. | Pancakes filled with cottage cheese and fruit cream, nectar from fruits or vegetables. | Any fruit |
Thursday:
| Breakfast | Snack | Dinner | Dinner | Before bedtime |
| Boiled eggs, low-fat ham, coffee + milk, butter, bread, hematogen-based biscuit. | Buckwheat milk porridge, grated carrots or sauerkraut. | Potato soup - mashed potatoes with green peas, tenderloin or semi-fried steak, any vegetable salad, fresh fruit, bread. | Cutlets + mushrooms or vegetables, nectar from fruits or vegetables, bread product. | Rosehip berry decoction |
Friday:
| Breakfast | Snack | Dinner | Dinner | Before bedtime |
| Cottage cheese + sour cream, hematogen-based noodle maker, butter, bread, tea. | Fish pudding + egg butter sauce, fruit nectar or fresh fruit, bread product. | Liver-based brine soup, piece of beef + sauce, zucchini, berry jelly, fresh fruit, bread product. | Pike perch fried in oil in dough, fruit-based jelly, bread product. | Decoction of rose-neck berries |
Saturday:
| Breakfast | Snack | Dinner | Dinner | Before bedtime |
| Schnitzel coated in breadcrumbs, fresh vegetable salad, bread product, fruit nectar or fresh fruit. | Fried egg + fried potatoes, fresh vegetable salad, hematogen-based biscuit, fresh fruit, bread product. | Borscht with meat broth + sour cream, fried meat, boiled potatoes, cake, nectar, fresh fruit. | Pancakes based on semolina + honey and jam, milk. | Just kvass |
Sunday:
| Breakfast | Snack | Dinner | Dinner | Before bedtime |
| Pate based on herring and potatoes, or based on liver, a sandwich of butter and cheese, fresh vegetable salad, coffee, fresh fruit. | Boiled eggs, sour milk drink, bread product. | Soup based on vegetables + sour cream, pilaf based on lamb and fruits, tomatoes, nectar from fruits or vegetables, bread. | Boiled chicken meat, cheesecakes + raspberry jelly, milk. | Infusion of thorn berries |
It is important to donate blood for a general analysis once a year. Thereby protecting yourself from serious consequences if hypochromia develops.
Stages of erythrocyte hypochromia
As a result of studying the stained smear, three degrees, or stages, of hypochromia can be distinguished:
- In the first degree, the zone of central clearing in red blood cells is only slightly, 10-15% wider than usual, the rim around the edges is intensely colored;
- The second, or intermediate, degree of hypochromia indicates that the colored zone of cells is always clear, and the central blanching is always wide, but the blood cells do not yet resemble anulocytes;
- If the blood cells resemble a pale pink ring, with staining only on the periphery, and the entire mass of red blood cells consists of such anulocytes - ring cells, then this indicates severe hypochromic anemia, third degree. Usually this condition has characteristic symptoms. Such a severe morphological defect does not occur when found accidentally in a well-feeling person.
Hypochromic anemia: causes and symptoms, treatment and prevention of the disease
A clinical blood test is the simplest test that helps identify serious diseases. A low hemoglobin level is a sign of hypochromic anemia, or hypochromia.
What is hypochromic anemia
Hypochromic anemia is a collective term for several types of anemia. Characterized by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin (iron-containing protein present in blood cells). This leads to oxygen starvation of the organs and tissues of the body. As a result of lack of oxygen, they cease to perform their functions, which is fraught with serious complications.
Anemia is translated from Greek as anemia. It can occur with any disease that is in any way associated with blood damage.
Hypochromia is characterized by a decrease in hemoglobin levels and the number of red blood cells (erythrocytes)
Important! People with low hemoglobin levels suffer from intestinal infections and acute respiratory infections 2 times more often.
With anemia, not only the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells decreases, but also the color indicator changes. Blood cells also change size and shape; they take on the appearance of a ring with a clear area in the middle and a dark rim around the edges.
With hypochromic anemia, the color index of red blood cells changes. They become discolored and have a dark edging around the edges.
The problem of anemia is often encountered in pediatric practice. At birth, the baby produces a certain amount of iron. Subsequently it must be replenished. If this does not happen, the likelihood of developing the disease increases.
How to increase a child’s hemoglobin at home: https://krasnayakrov.ru/analizy-krovi/povyshaem-gemoglobin-rebenku-v-domashnix-usloviyax.html
Causes
The causes depend on the type of anemia. However, the most common causes of the disease are:
- heavy bleeding (menstruation, post-operative or severe injuries);
- unbalanced diet with insufficient amounts of vitamins and proteins. Typical for people who adhere to a strict diet, as well as for vegetarians;
- internal hemorrhages. Blood loss may be minor, but constant (frequent). These include bleeding gums, hemorrhoids, and gastrointestinal diseases. With fibroids (benign tumors) of the uterus and ovarian cysts, their cavities are filled with blood, hemoglobin is converted into other compounds and gradually dissolves. In medicine, this phenomenon is called “pseudo-blood loss”;
- chronic infectious diseases - with tuberculosis, enterocolitis, hepatitis, redistribution of iron occurs or its poor absorption. In older people, anemia is often caused by liver and kidney diseases;
- intoxication, poisoning with chemical elements - occurs in iron-saturated anemia;
- pregnancy - during this period the body requires an increased amount of iron;
- worms;
- blood diseases;
- autoimmune diseases provoke the death of red blood cells, which leads to a decrease in hemoglobin.
Anemia in newborns and premature babies appears when:
- Rhesus conflict;
- infection of the fetus during gestation with herpes and rubella viruses;
- improper nutrition of the expectant mother;
- birth trauma.
In infants, the disease can develop due to poor nutrition. This mainly happens with artificial feeding.
Hypochromic anemia often occurs in adolescence, when hormonal changes occur.
Doctors distinguish several types of hypochromic anemia:
- iron deficiency (microcytic) – occurs most often. The cause may be frequent bleeding, lack of iron and its poor absorption, physiological processes (lactation, pregnancy). Seen more in children and young women;
- iron-saturated (sideroachrestic) - characterized by a normal level of iron in the blood, but this element is not absorbed, as a result of which hemoglobin is not produced. More common in older people. Pathology is observed with alcohol intoxication, poisoning with poisons or chemicals, long-term use of medications;
- iron redistribution - occurs when there is a high concentration of iron in the blood after the breakdown of erythrocytes (red blood cells). The disease often occurs in tuberculosis and purulent infectious processes;
- mixed - develops due to deficiency of vitamin B12 and iron. The main symptoms include fatigue, decreased immunity, and swelling of the upper extremities.
The disease can be hereditary or acquired.
- The acquired form occurs after operations, infectious diseases, and poisoning.
- Congenital anemia occurs with blood diseases.
According to WHO, every third woman and every sixth man suffers from a chronic form of the disease. The fact is that chronic diseases, unbalanced nutrition, and diets lead to a lack of iron in the body and a decrease in hemoglobin levels. Patients get used to weakness and poor health, attributing this to overwork and stress.
Symptoms of hypochromia
For a long time, patients do not pay attention to the deterioration of their condition, attributing their poor health to stress and fatigue.
Symptoms depend entirely on the severity of the anemia. First, all patients complain of:
- general malaise;
- rapid fatigue;
- violation of attention;
- decreased physical endurance;
- drowsiness.
Features of manifestation in children
In children, especially infants, symptoms are mild. The disease can often be diagnosed only after a blood test. Parents need to pay attention to the following signs:
- pale skin;
- poor sleep and appetite;
- lethargy;
- frequent colds;
- cracks in the corners of the mouth;
- retardation in physical and psychomotor development.
Prolonged neglect of the disease can lead to death, so the pathology requires mandatory treatment.
First of all, the doctor conducts an external examination, studies clinical manifestations and hereditary pathologies. The diagnosis is confirmed by a complete blood count, which shows the level of hemoglobin and the number of erythrocytes (red blood cells), which determine the type of anemia and the color index.
Interpretation of the results of a general blood test - table
Normally, the hemoglobin content in red blood cells ranges from 0.85 to 1.15. With hypochromic anemia, the color index becomes below 0.85.
Additionally, differential diagnosis is carried out:
- stool occult blood test;
- gastroscopy - examination of the gastrointestinal tract using a flexible hose that is inserted through the mouth;
- colonoscopy - examination of the large intestine with a special probe;
- Analysis of urine;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- chest x-ray;
- gynecological examination (women);
- study of blood serum for iron content and bone marrow samples.
To confirm anemia, patients undergo a clinical blood test
Treatment
Therapy depends entirely on the clinical manifestations and severity of hypochromia. First of all, treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease.
Drug therapy
The main emphasis is on taking medications that compensate for the deficiency of iron and vitamin B12.
It is necessary to take into account that vitamins are quickly excreted in the urine, so it is impossible to achieve quick results only from taking vitamin-containing preparations.
- Iron supplements are taken for 4 to 8 weeks until hemoglobin levels normalize. These can be: Ferrum Lek, Fenyuls, Hemofer. Drugs that need to be administered by drip or injection are recommended to be used only in a hospital setting to exclude allergic manifestations.
- If insufficient intake of vitamin B12 is detected, subcutaneous injections of Cyanocobalamin are prescribed. The course of treatment is 1–2 months until the condition normalizes.
- Vitamin B deficiency is often accompanied by folic acid deficiency. In this case, additional medications are prescribed. The course of treatment is up to 30 days.
It is recommended to take medications in the form of syrup, capsules or tablets. Injections are prescribed if the patient has gastrointestinal diseases or acute blood loss.
It should be borne in mind that therapy for moderate and severe forms of anemia is carried out only in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor.
Increasing hemoglobin with drugs and folk remedies: https://krasnayakrov.ru/analizy-krovi/sposoby-povysheniya-gemoglobina-preparaty-narodnye-sredstva.html
Drugs for the treatment of the disease - gallery
Ferrum Lek Fenyuls Hemofer
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is taken only as maintenance therapy and in combination with medications.
- In the morning, it is recommended to eat 100–150 g of grated carrots with sour cream.
- Eat several pieces of boiled pumpkin throughout the day.
- Nettle improves blood composition, increases the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells. To prepare the infusion, you need to grind 10 g of leaves, steam with a glass of boiling water and leave for 10 minutes. Liquid take 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day.
- Dried fruit mixture. Grind dried apricots, prunes, raisins, figs, rose hips in equal proportions, add honey. Take 3-4 times a day, 1 tbsp. l.
- Rose hip decoction.
Diet therapy
Diet therapy is recommended for patients in combination with drug treatment.
Basic principles:
- Every day the diet should contain at least 130–150 g of animal proteins (beef, veal).
Proteins contribute to the production of hemoglobin and red blood cells. - It is recommended to limit fat intake, since anemia causes obesity of the bone marrow and liver, which inhibits hematopoiesis.
- In patients with anemia, there is a decrease in appetite, which is explained by a deterioration in secretory function. To improve your condition, you should include fish, meat, and mushroom decoctions in your diet.
- The menu must include foods rich in vitamin B - eggs, fish, cottage cheese, brewer's yeast. Take 100 g of liver daily or every other day.
Recommended Products:
- fish, meat, liver (low-fat);
- cottage cheese;
- mushrooms;
- eggs;
- black and white bread;
- yeast;
- pomegranate juice;
- legumes (peas, beans, lentils);
- berries and fruits with a high content of vitamin C - rose hips, black currants, pomegranate juice.
It is not recommended to consume pomegranate juice in its pure form; it is better to dilute it with beet juice in a 1:1 ratio.
Featured Products - Gallery
Beef is good for blood formation.
High content of vitamins B, C and minerals have a beneficial effect on blood quality. With one apple, about 480 mg of iron enters the body, which helps maintain normal hemoglobin levels. Fish is a source of vitamin B12. Pomegranate juice contains a large amount of ascorbic acid, which promotes the absorption of iron.
Foods that interfere with iron absorption:
- oatmeal, millet;
- tea;
- leafy greens;
- dairy products;
- coffee;
- dishes high in fat.
Foods that should be excluded from the diet - gallery
Alcohol contributes to pathological processes in anemia Dairy products should be consumed in limited quantities, as they delay the absorption of iron Coffee and tea wash out iron, so you should not abuse these drinks
Sample menu - table
What foods increase hemoglobin levels: https://krasnayakrov.ru/analizy-krovi/produkty-povyshayushhie-uroven-gemoglobina.html
Recipes
- Millet porridge. Soak 250g of flakes in 500ml of apple juice overnight. In the morning, boil the mixture in a thick-bottomed saucepan for 10 minutes. Millet contains microelements that are necessary to strengthen the immune system.
- Baked beets.
Wash the vegetable, cut the shoots to a height of 1.5 cm from the root crop. Brush generously with olive oil and season with sea salt. Bake in the oven at 175°C for about 45 minutes. - Drink made from yeast. Grind 10 g of live culture in 100 ml of water, leave for 50 minutes. Drink in small sips.
- Berry salad. To prepare, you will need to take 50 g of raspberries, blackberries, and strawberries. Add 1 banana and apple. Mix the fruits, sprinkle with lemon juice and pour over liquid honey (1 tbsp.).
- Rowan fruit juice.
Grind 100 g of dried berries, add 300 g of rowan flowers and 10 g of mint. Pour boiling water in the proportion of 2 tbsp. l. for 200 ml of water. Cool.
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable in most cases. If left untreated, hypochromic anemia can lead to:
- decreased immunity;
- growth retardation, mental and psychomotor development (in children);
- development of cardiomyopathy - with insufficient oxygen supply, the heart begins to work with redoubled force. This leads to heart failure;
- liver enlargement;
- chronic anemia.
Low hemoglobin levels negatively affect the nervous system.
Prevention
The main preventive measure is a proper and balanced diet. The diet should contain foods rich in iron.
- Beef liver, kidneys.
- Quail and chicken eggs.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits - Brussels sprouts, persimmons, pomegranates, beets, dried apricots.
Women should pay special attention to the prevention of anemia, since they lose twice as much blood as men due to menstruation.
When the first signs of illness appear, you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination. Otherwise, hypochromic anemia can lead to serious health problems.
- Irene Saratova
Source: https://krasnayakrov.ru/organizm-cheloveka/gipohromiya-ili-gipohromnaya-anemiya-osobennosti-protekaniya.html
Treatment
Drug correction of low iron levels
Treatment of hypochromia must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor and depends entirely on its type and degree. First of all, it is necessary to identify the root cause of the hypochromic state and begin to eliminate it.
Treatment of the underlying disease is most often accompanied by long-term use of iron-containing drugs. They are prescribed by a doctor for iron deficiency. Iron intake from medications usually lasts more than six months (with breaks if required by the optimal course of a particular medication) to achieve positive results.
For iron-saturated anemia, vitamin B6 is prescribed. In the case of iron redistribution anemia, they normalize the absorption processes in combination with vitamin preparations for a better effect. With these two types of hypochromia, additional intake of iron from medications is contraindicated so as not to cause excessive oversaturation.
In particularly severe cases of iron deficiency, intravenous administration of iron-containing medications may be required.
Self-treatment of hypochromia is prohibited - there is a high risk of worsening the situation. Only prevention can be done independently if the indicators are within standard limits.
Hypochromia – microcytosis
Our service will select the best hematologist for you free of charge when you call our Unified Appointment Center by phone. We will find an experienced doctor near you, and the price will be lower than if you contact the clinic directly.
Iron deficiency anemia or microcytosis is a separate type of hypochromia. What is this and why can this disease occur?
- First of all, due to the fact that a person has significantly reduced the intake of iron in his daily diet.
- It also develops due to periodic loss of blood in small volumes.
According to statistics from the International Health Organization, 30 percent of females and 15 percent of males, which is more than 200 million people from all over the world, suffer from this disease.
Symptoms and signs
A rapid pulse is a sure companion of anemia
The clinical manifestations of microcytic anemia are varied. An asymptomatic course may occur, or severe hemolytic conditions may develop that require urgent medical care in a hospital setting.
The appearance of symptoms and signs of pathology can occur at any age and appear spontaneously.
Common manifestations of all microcytoses are:
- hypoxia;
- increased activity of the cardiovascular system due to oxygen deficiency. At the same time, the heart rate increases, blood pressure in the initial stages is normal or reduced. As the condition progresses, arterial hypertension develops;
- weakness, loss of consciousness;
- decreased performance, increased fatigue, drowsiness, feeling “broken”;
- decreased physical and mental activity;
- difficulty concentrating;
- dyspnea;
- blurred vision;
- headaches, dizziness;
- cheilitis (seizures);
- brittle nails and hair.
With sideropenia, patients experience taste perversions, impaired sense of smell, and frequent stomatitis.
In hemolytic anemia, one of the clearest signs of the disease is jaundice.
Delays in physical development may occur due to anemia
Microcytosis in children is accompanied by weight loss or excess weight, the need to taste inedible objects, and retardation in physical and psycho-emotional development.
In addition to clinical symptoms, all microcytic anemias are characterized by special biochemical changes due to iron deficiency:
- decrease in ferritin - a protein that is responsible for maintaining iron in the depot;
- reducing the concentration of substances in the liver and bone marrow, the task of which is the formation of heme;
- an increase in the total iron-binding capacity of blood serum due to a decrease in iron concentration;
- growth of free erythrocyte protoporphyrins. At the same time, these substances have nothing to form complexes with for heme synthesis;
- a decrease in the functionality of enzymes that are responsible for the iron content in cells.
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable in most cases. If left untreated, hypochromic anemia can lead to:
- decreased immunity;
- growth retardation, mental and psychomotor development (in children);
- development of cardiomyopathy - with insufficient oxygen supply, the heart begins to work with redoubled force. This leads to heart failure;
- liver enlargement;
- chronic anemia.
Low hemoglobin levels negatively affect the nervous system.
Hypochromia in a general blood test: causes, symptoms, treatment
Hypochromia in a general blood test indicates problems with hemoglobin. This pathology has other names - hypochromia of erythrocytes or hypochromic anemia. All these names refer to several types of anemia, each of which requires special diagnosis and treatment.
Let us remember that anemia in any form, especially with prolonged exposure to the body, leads to oxygen starvation of cells, which cannot but affect their condition. This is especially true for brain cells. In advanced cases, it is possible to develop a stroke with a transition to the “vegetable” state followed by the terminal stage. Most often, this scenario concerns the female body.
What is hypochromia
This definition characterizes a group of anemias that are caused by a low concentration of hemoglobin, an iron-containing protein, in red blood cells. In the medical literature there is a synonym for this manifestation, which is interpreted as hypochromic anemia.
This condition is called so because it is only due to the normal content of hemoglobin, and therefore iron, that healthy red blood cells have a red color.
And with a syndrome such as hypochromia of erythrocytes, their color is lost.
In addition to the fact that hypochromic anemia is characterized by a deficiency of hemoglobin in red blood cells, the following symptoms are also inherent:
- Change in the shape of red blood cells.
- Loss of color in red blood cells - the red blood cell becomes two-colored, with a dark red outer ring and a discolored middle.
- The acquisition of an abnormal shape by red blood cells.
When examining a general blood test for the level of hypochromia, it is always necessary to pay attention to the color indicator, which directly characterizes the level of hemoglobin in red blood cells. These two indicators should always be tested together for an accurate diagnosis. An important diagnostic sign is a decrease in color index below 0.8.
For reference. Hypochromic anemia is not one disease, but a whole group of pathological changes in the blood system. Each such condition requires different diagnostics and treatment. Therefore, for this it is necessary to know the cause of hypochromia.
A common symptom for all hypochromic anemias is a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in red blood cells.
The leading causes of this pathology are considered to be:
- Low iron levels in the body.
- Chronic lead intoxication.
- Vitamin B6 deficiency.
- Inflammatory processes in the body (more typical for chronic diseases, for example, hepatitis, intestinal lesions).
- Heredity.
- Menses.
- Extensive blood loss after trauma and surgery.
- Chronic internal bleeding.
- Unbalanced diet, low in protein.
- Pregnancy.
- Blood diseases.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Long-term donation.
There is such a thing as “pseudo-blood loss”. This phenomenon occurs with cystic transformation of the ovaries and benign neoplasms in the uterus. In this case, the resulting cavities are filled with blood, which stagnates. In it, hemoglobin breaks down into various compounds and disappears over time.
Classification of hypochromia (hypochromic anemia)
As mentioned above, hypochromia is a collective concept that includes several subtypes of lesions, which are characterized by certain signs:
- Iron deficiency is also known as microcytic.
Is the most common. Typical for children and young women. Occurs during pregnancy, breastfeeding, bleeding, poor absorption and lack of iron, prolonged diarrhea, high need for iron, limited nutrition (absence or low content of meat products). - Iron-saturated – sideroachrestic (sideroblastic).
In this condition, there is no lack of iron in the body. The condition develops because iron is not recycled. Such changes occur when there is a large deposition of iron due to the massive death of red blood cells. The most common causes of this process are chemical intoxications and long-term use of certain groups of medications. - Iron distribution - in this situation, there is insufficient supply of iron in the blood.
The reason for this is its retention by cells. Factors leading to this pathology are tuberculosis, infectious diseases of various etiologies and other inflammatory reactions - Mixed - includes any combinations.
A feature of this condition is the difficulty in diagnosis, since when one cause is identified, treatment is often immediately prescribed, which, unfortunately, turns out to be not completely effective, since the therapy affects only one link in the development of the disease. Most often, this condition is observed with a lack of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) and iron.
According to the etiological factor of occurrence, all hypochromic anemias are divided into the following:
- Congenital pathology – associated with diseases of the hematopoietic system.
- Acquired - manifests itself due to a variety of reasons affecting the composition and parameters of the blood.
According to severity, the disease is divided into:
- First degree - microscopic examination reveals a characteristic zone of lighter color, which is not inherent in a healthy red blood cell.
- Second degree - red blood cells are colored in the peripheral part.
- Third degree - the color of red blood cells is determined only in the membrane.
Despite the commonality of the final main cause - low hemoglobin content, each type has its own specific symptoms.
Symptoms
All of these types of hypochromic anemia have certain symptoms:
- General weakness.
- Increased fatigue.
- Headache.
- Dizziness.
- Decreased ability to work.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Tachycardia.
- Nervousness, irritability.
- Dyspnea.
- Flashing "flies" before the eyes.
Attention! The most important thing is that during long-term processes, due to hypoxia of organs and tissues, damage to internal organs develops. This phenomenon occurs because hemoglobin is an oxygen carrier, and a decrease in hemoglobin, accordingly, leads to oxygen starvation.
A specific symptom is its absence in the early stages. Patients do not feel any initial changes in their condition. Even when the first general signs begin to appear, this is identified with a high rhythm of life, fatigue, and stress. In fact, according to hematologists, in most cases these are already the first signs of the disease.
First of all, such triggers depend on the stage of the disease:
- First degree – there are practically no symptoms. Periodically there are complaints of weakness and general fatigue. The hemoglobin level is 90 g/l and above.
- Second degree - dizziness, headaches, pallor, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, visual disturbances, and increased photosensitivity already appear. Hemoglobin levels are from 70 to 90 g/l.
- Third degree - accompanied by numbness of the arms and legs, fragility of the legs, baldness, perversion of smell and taste. Hemoglobin is low – falls below 70 g/l. In such cases, the development of decompensated conditions leading to death is possible.
In such situations, careful diagnosis comes first. Only the consciousness of the patient and the literacy of the doctor will allow timely determination of the reasons for the deterioration of the condition.
Diagnostics
Anemia is a disease whose causes can be so diverse that only an experienced diagnostician can make a timely correct diagnosis.
The problem remains that this condition is “masked” for a long time by general symptoms, which can be attributed to simple fatigue, high pace of work activity, and stress.
If hypochromic anemia is suspected, the doctor is obliged to conduct a thorough diagnosis of the patient. The main criteria that must be checked immediately are:
- Carrying out a general blood test.
- The number of red blood cells in peripheral blood.
- Erythrocyte indices.
- Hemoglobin concentration.
- Color index.
- Careful history taking.
- Inspection of the skin, especially in the joint area.
It is necessary to focus on the fact that each type of hypochromic anemia has its own specific diagnostic signs:
- Iron deficiency - hypochromia of erythrocytes is determined, the color index is below 0.8, erythrocytes take on the shape of rings, the concentration of iron is reduced.
- Iron-saturated - red blood cells are discolored, the color index is also low - less than 0.8, the level of iron in the blood serum is normal.
- Iron distribution - hemoglobin concentration is reduced, red blood cells do not have a normal color, iron is within normal limits.
- Mixed - indicators depend entirely on the predominant cause.
In order to exclude many dangerous diseases, additional research is carried out, which includes:
- Endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Fecal occult blood test.
- Colonoscopy (examination of the mucous membrane of the large intestine).
- General urine analysis.
- Urine analysis for specific markers depending on indications.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and urinary system.
- Bone marrow puncture.
In addition to all these hypochromic anemias, there is a certain pathological condition that occurs in children, which differs from the pathological condition of adults and requires the administration of iron supplements.
Hypochromia in a child
This condition can develop already in the prenatal period, as well as after birth.
Hypochromic anemia in children is of several types:
- Latent form - the main symptom is iron deficiency, but without anemia. Occurs rarely.
- Iron deficiency anemia is the most common form, which is caused by insufficient intake of iron from food. Also, such conditions are typical for premature babies and twins, especially females. If treatment is not timely, one of the first signs is rickets.
- Thalassemia is a hereditary disease that affects at the genetic level the structures that determine the parameters of healthy hemoglobin.
Often attention is drawn to symptoms that develop already in the final stages of anemia. Therefore, parents of young children need to pay attention to the following signs:
- Disturbed sleep.
- Poor appetite.
- Pallor.
- High susceptibility to respiratory infections.
- Angular stomatitis (jams).
- Delayed physical, mental, mental development.
Important! For both children and adults, in order to avoid the development of complications, sometimes fatal, it is necessary to carry out effective therapy.
Such conditions require care and painstaking care, since the treatment of hypochromic anemia is a long process.
The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the underlying cause of the disease. The choice of therapeutic tactics depends on the type of anemia:
- Iron deficiency anemia - first of all, requires replenishment of the lack of glands and the intake of vitamin B12 into the body. In addition to this, it is necessary to add foods rich in iron to the diet - liver, pistachios, beets, apples, pomegranate. Treatment and diet are long-term.
- Iron-saturated anemia - one of the main methods of treatment is the use of vitamin B6. Iron supplements have no effect.
- Iron distribution form - also do not use preparations that contain iron. It is recommended to take B vitamins, treat the underlying condition and utilize excess iron.
- Mixed forms - treatment depends on the nature of the combination of several types of anemia.
In case of severe lesions, it is advisable to administer red blood cells and treat only in a hospital setting.
Attention. Hypochromia, or hypochromic anemia, is a sign of a serious disorder in the body. It is necessary to pay attention to changes in your condition in order to carry out timely diagnosis, determine the causes, and most importantly, begin effective, efficient treatment using the best drugs, aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease.
Source: https://serdcet.ru/chto-takoe-gipoxromiya.html