Origin of cells
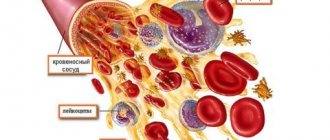
Where are T-lymphocyte cells formed? Although their main place of “residence” is the bloodstream (lymphocytes also live in other tissues), they are not formed there. The place of their “birth” is the red bone marrow. It is known as the hematopoietic tissue of the body. That is, in addition to lymphocytes, erythrocytes and white blood cells (neutrophils, leukocytes, monocytes) will also be formed here.
The “precursors” of our lymphocytes are stem cells. At the same time, some part of the lymphocytes will be “born” not only in the red bone marrow, but also in other immune organs - the thymus gland (thymus). Here they are based on lymphoid tissue.
Indicators are below normal
An insufficient number of lymphocytes in the body is called lymphocytopenia. At the same time, the proportion of these cells relative to all leukocytes will decrease. This process depends on the type of infection. Lymphopenia is considered absolute if the bone marrow is unable to produce immune cells.
Usually in adults it is caused by a cold. In this case, resistance from immune cells occurs, and new ones simply do not reproduce in the required quantity. According to this pattern, a lack of leukocytes develops in patients diagnosed with HIV.
A noticeable decrease in lymphocytes occurs in the following cases:
- Carrying a child.
- Anemia.
- When using corticosteroids.
- Endocrine diseases.
- When malignant tumors appear.
- After chemotherapy.
The level of active lymphocytes may vary. In this case, it is necessary to restore it and control this process. Timely research will help to detect complex diseases in time and begin effective treatment.
Only a doctor can determine the root cause. There is no need to try to correct the level of lymphocytes in the body on your own.
The structure of lymphocytes
T-lymphocytes, the functions of which we will consider further, are not visible to the naked eye - only under a special powerful microscope. Their size is relatively small compared to other blood cells (only 7-10 microns in diameter).
The “anatomical” features are as follows:
- Large kernel of round or oval shape.
- There will be no granularity in the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell itself).
- If there is little cytoplasm in a cell, it is called narrow-plasma, if there is a lot - wide-plasma.
In terms of their structure, the lymphocytes that inhabit the blood will be slightly different from their counterparts that live in other tissues. And that's okay. Moreover, cells “living” in one place will also have some external differences among themselves.
Types of lymphocytes
In addition to the types of T lymphocytes, there are various groupings of these cells in general. Let's look at them.
The first classification is by size:
- Small ones.
- Big ones.
The second classification is based on the functions performed:
- B lymphocytes. They can recognize foreign particles and produce deadly antibodies against them. In other words, they are responsible for humoral immunity.
- T lymphocytes. The main function is responsibility for cellular immunity. They come into contact with foreign bodies and destroy them.
- NK cells. Natural killers that can recognize cancerous, defective cells and destroy them. Responsible for maintaining the normal cellular composition of the entire body.
Types of T lymphocytes
This group of lymphocytes within itself will be divided into several more types:
- Killer T cells.
- T-helpers.
- T-suppressors.
- Memory T cells.
- Amplicators-lymphocytes.
Next, we analyze each of these groups in detail. Let's consider the functions of T-lymphocytes. Each type has its own purpose.
Killer T-cells: what type?
These are the most famous representatives of the group of T-lymphocytes. Their main task is the destruction of inferior, defective cells of the body. Another name for the group is cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. In other words, they are responsible for eliminating cells (“cyto”) that have a toxic effect on the entire body.
The main function of killer T cells is immune surveillance. Cells aggressively act on foreign protein. It is this useful function that can be harmful when organs are transplanted to a person. T-killers strive to quickly destroy the “stranger,” not realizing that it is he who is able to save the body. Therefore, the patient takes medications for some time after organ transplantation that suppress the immune system. The drugs reduce the percentage of T-killer cells in the blood and disrupt their interaction. Thanks to this, the transplanted organ takes root, and the patient does not face complications or death.
The mechanism of action of this type of lymphocyte on a foreign element is very interesting. Phagocytes, for example, aggressively “attack” the “stranger” for its subsequent devouring and digestion. Compared to them, T-killers are “noble killers.” They touch the object with their processes, then break contact and move away. Only after such a “kiss of death” does the foreign microorganism die. Why?
When touched, killer T cells leave a piece of their membrane on the surface of the body. It has properties that allow it to corrode the surface of the object of attack - up to the formation of through holes. Through these holes, potassium ions leave the microorganism, and water and sodium ions take their place. The cellular barrier is broken, there is no longer a boundary between the internal and external environment. The microorganism is inflated by the water entering it, the cytoplasmic proteins and organelles are destroyed. The remains of the “stranger” are then devoured by phagocytes.
Helpers
The main function of these T-lymphocyte cells is to help. Hence their name, which comes from an English word translated the same way.
But who or what do these T-lymphocytes come to the rescue of? They are designed to induce and stimulate an immune response. It is under the influence of T-helpers that the T-killers, with whom we have already become acquainted, will activate their work.
Helpers will begin to transmit data about the presence of a foreign protein in the body. And this is valuable information for B lymphocytes - they, in turn, begin to secrete certain protective antibodies against it.
T-helper cells also stimulate the work of another type of “guard” cells - phagocytes. In particular, they interact closely with monocytes.
Elevated lymphocytes
When the level of white blood cells increases, characteristic symptoms do not appear. This will be known after an analysis is carried out to diagnose a developing infection. Absolute lymphocytosis is a sharp increase in these cells. This is a response to the fight against the virus. In this case, lymphocytes will “squeeze out” other cells, and the indicators will increase significantly.
This situation is provoked by:
- any viruses;
- allergic reactions;
- chronic diseases;
- medications taken.
Test results during this period will show deviations from the norm.
But with proper and qualified treatment, the situation can be improved. In children, an increase in white blood cells is usually provoked by various viruses.
The body develops immunity to diseases:
- measles;
- rubella;
- chickenpox.
But exceeding the norm can be caused by an incipient cold.
Upon recovery, everything should return to normal. If this does not happen, you should not postpone your visit to the hematologist. It is necessary to undergo examination and find out whether mononucleosis is developing or not. In some situations, consultation with an oncologist is recommended.
Suppressors
The term itself means "suppression". From here the function of T-suppressors becomes clear to us. Helpers in our body will activate the protective, immune function, and these T-lymphocytes, on the contrary, will suppress it.
Don't think that this has any negative impact on the system. Suppressor T cells are responsible for regulating the immune response. After all, somewhere you need to react to a certain stimulus with restraint and moderation, and somewhere you need to accumulate all available forces against it.
Amplifiers
Let us now turn to the functions of T-lymphocytes of this group. After one or another aggressor penetrates the body, the content of lymphocytes immediately increases in the blood and tissues of a living creature. For example, in just a few hours their volume can double!
What is the reason for such a rapid growth of the army of protective cells? Maybe the fact is that somewhere in the body they are “hidden” in reserve for the time being?
This is true. Some mass of mature, full-fledged lymphocytes lives in the thymus and spleen. Only up to a certain point these cells are not “defined” with their purpose and function. They will be called amplifiers. If necessary, these cells turn into one or another type of T-lymphocyte.
Definition of indicators
The number of immune cells in the blood can only be determined through laboratory tests - a blood test is performed for lymphocytes, but other indicators of blood components are also taken into account.
For the results of the study to be reliable, the following recommendations should be followed:
- You need to donate blood for research in the morning on an empty stomach - if this is not possible, at least two hours after the last meal;
- the day before the procedure, exclude heavy foods, alcoholic drinks, and taking medications (only in consultation with the doctor);
- the blood test should not be taken during the active phase of the menstrual cycle;
- You need to undergo the procedure while being in a calm physical and psychological state.
If the tests show a significant deviation from the norm, a repeat procedure for collecting biological material is carried out in order to eliminate the error.
Memory cells
Experience, as you know, is the main weapon. Therefore, having coped with any threat, our T-lymphocytes remember it. In turn, the body produces special cells that will store this information until a new “battle” with this foreign element. These elements will be memory T cells.
A secondary aggressor (of the type that the immune system has already resisted) enters the body. The memory T cell recognizes it. Then this particle begins to actively multiply in order to give the foreign organism a secondary worthy immune response.
What are lymphocytes needed in the body?
There are two types of white blood cells, one of them is lymphocytes. They are produced by the human immune system. Their main task is to promptly identify a virus or infectious process in the body. Such bodies are responsible for identifying harmful substances and actively combating them. They can be of two types:
- T cells;
- B cells.
B cells lead to the production of antibodies, and T cells destroy foreign bodies in the body. There are also atypical lymphocytes, which are also called zero.
To activate the work of the corpuscles, the cell receives special information. The bone marrow is responsible for the number of lymphocytes produced in the body. Many people think that lymphocytes move throughout the human body and fight infection, destroying it. But in reality everything is completely different. The blood inside the vessels includes only 2 percent of the lymphocytes of all those in the human body. The rest is in the lymph nodes.
Normal indicators of T-lymphocytes in human blood
In this category it is impossible to provide any specific figure - normal values will vary depending on the age of the person. This is due to the peculiarities of the development of his immune system. With age, the volume of the thymus gland will decrease. Therefore, if in childhood lymphocytes predominate in the blood, then with adulthood they transfer the leading position to neutrophils.
The level of T-lymphocytes in the blood helps determine a general clinical blood test. The normal indicators here are:
- (50.4±3.14)*0.6-2.5 thousand.
- 50-70%.
- The “helper/suppressor” ratio is 1.5-2.
Kinds
Reliable protection of the body from parasites is ensured by the coordinated work of three components. All of them are formed in the thymus, but differ in their functionality. Some are responsible for recognizing antibodies, others for destroying them.
A lack of even one type can completely undermine a person’s immune system. Each type of T cell has a different role. For example, if the affected areas of the body are not detected, then the immune system will not be able to heal them.
T helper cells
This type of white blood cell is needed to trigger the work of other components of the adaptive immune response. Without them the following will not be activated:
- Killer T cells;
- B lymphocytes;
- monocytes;
- NK cells.
T-helper cells send particles of the affected areas to all these elements to inform the body about a new disease. They also release cytokines in response to antigens. Helper cells include CD4 molecules, which. They do not occur in other types of thymocytes.
There are several types of T-helpers:
- Th0 are the simplest representatives that have not yet been differentiated;
- Th1 - helps the immune system develop successfully and secretes interferon-gamma;
- Th2 - starts the work of B-lymphocytes, creates 4, 5 and 13 interleukins;
- T-reg - creates CD25 molecules on its surface and transmits information about the Foxp3 factor to genes;
- Th17 is the main type of thymocyte that triggers the production of IL-17, a pro-inflammatory cytokine;
- Th22 - activated during skin lesions, isolated in biology relatively recently.
Attention! Newborns have more T2 helper cells in their blood. Over time, their concentration changes.
Killer T cells
Elimination of the disease would be impossible without lysis of infected cells. It is the killer T cells, sometimes called cytotoxic thymocytes, or CTLs, that destroy antibodies. These cells attack parasites, viruses, bacteria, tumors and other types of pathogens. Killer T cells are a major component of the acquired immune system. They are the ones who directly work with pathogenic areas of the body and destroy them.
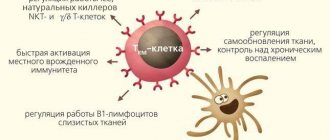
γδ T lymphocytes
This population is the least studied. The largest number of them is found in the mucosa. γδ thymocytes simultaneously possess the properties of acquired and innate immunity. These cells can recognize many different antigens that science has not yet been able to accurately characterize. Also, scientists have not yet been able to establish the exact mechanism of operation of γδ T lymphocytes.
T-suppressors
These cells produce class 1 MHC genes. They can also function as killers. There are several types of suppressors:
- effector - block the antigen and release a secretion that triggers the work of T-helper cells;
- Ts3 is a suppressor that binds antigens and triggers a hypersensitivity reaction;
- T-suppressors are able to recognize MHC molecules of the second class and prevent the proliferation of thymocytes;
- T-suppressors, which can recognize the idiotype and activate the work of B-cells.
Normal lymphocyte counts
Immediately after birth, the baby's blood contains the most lymphocytes. Over time, the situation changes and neutrophils begin to predominate in the body. People who are not familiar with medicine often do not understand what this means. To understand how any changes in the level of thymocytes affect a person, it is necessary to understand their permissible content in the blood. Normal lymphocyte counts are:
- from 19 to 37% for adults;
- from 22 to 55% for adolescents from 13 to 15 years old;
- from 24 to 54% for children under 12 years of age;
- from 26 to 60% in children under 6 years of age;
- from 42 to 74% in children under 1 month;
- from 12 to 36% in newly born children.
To determine the level of thymocytes, a blood test is performed. It separately determines the number of T and B cells. The first should be no less than 50% and no more than 70%. Any difference from these numbers may indicate the development of a pathogen in the body. It is important that the number of helpers and suppressors is also normal. Their ratio should be within 1.5-2.0%. If lymphocytes are elevated in an adult, this is no less or more dangerous than the same concentration in children. Any deviation from the norm indicates a disease that causes disruption of the immune system.
Attention! The concentration of thymocytes can change due to most viral diseases: from common acute respiratory viral infections to herpes, mononucleosis and measles.
What do increased and decreased indicators indicate?
An increased level of T-lymphocytes in the blood may indicate the following:
- Chronic or acute lymphocytic leukemia.
- Hyperactive immunity.
- Sézary's syndrome.
On the contrary, a reduced content of T-elements indicates the following pathologies and diseases:
- Chronic infections - purulent processes, HIV, tuberculosis.
- Reduced production of lymphocytes.
- Genetic diseases causing immunodeficiency.
- Tumors of lymphoid tissue.
- Renal and heart failure observed at the last stage.
- T-cell lymphoma.
- The patient is taking medications that destroy lymphocytes.
- Consequence of radiation therapy.
We got acquainted with T-lymphocytes - the protector cells of our body. Each type performs its own special function.
Causes of lack of lymphocytes
An insufficient amount of them in the human body is diagnosed in the following cases:
- pregnancy;
- anemia;
- when taking corticosteroids;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- during the formation of benign and malignant processes in the body;
- after a long course of chemotherapy.
The number of activated lymphocytes in a blood test can vary greatly. It is important to restore it and monitor any changes in condition. Modern examination methods help to timely identify human health problems and begin comprehensive treatment aimed at restoring the level of lymphocytes.
The primary cause of the disease can only be determined by the treating specialist. You should not try to restore the number of white cells in the body on your own, since in this way you can only worsen the general condition and provoke complications.