What is staphylococcus in adults
The staphylococcal family includes 27 species of bacteria, 14 of which can parasitize the skin and mucous membranes of humans, but only three species can cause serious diseases, therefore staphylococci in medicine are classified as opportunistic flora. This type of bacteria is immobile and has a spherical shape. When favorable conditions occur (lowered immunity, stress, exacerbation of chronic diseases), staphylococcus begins to actively multiply, leading to purulent-inflammatory processes in the human body.
Infections caused by staphylococci can affect any part of the body, internal organs and mucous membranes of an adult. The list of such diseases includes more than 100 medical names, with the most common being those that provoke the appearance of ulcers, boils, carbuncles, and barley. The type of disease depends on where staphylococcus began to multiply:
- respiratory tract - sore throat, sinusitis, rhinitis, pneumonia, bronchitis, etc.;
- intestines – constipation, diarrhea, indigestion, poisoning;
- blood - sepsis;
- brain – meningitis, abscess;
- bone tissue – arthritis, osteomyelitis;
- heart – endocarditis, heart failure;
- mammary glands – cyst, purulent mastitis.
Possible complications of infection with Staphylococcus epidermidis
Such a disease does not always pass without a trace for the body. People with weakened immune systems have a high risk of developing complications and long-term consequences of the infection. On average, the duration of therapy takes from 2 to 8 months (depending on the extent of the lesion). A huge role in successful recovery is played by the patient’s age, the presence of acute or chronic illnesses, and recent surgical interventions.
An unfavorable prognosis for patients suffering from HIV infection, since in them Staphylococcus epidermidis can lead to death in 70% of cases.
The patient's attitude towards his health plays a huge role. While working in a hospital, I had to deal with the fact that one of the patients was constantly drinking alcohol. Ethyl alcohol in combination with antibacterial drugs caused nausea and vomiting, as a result of which the man refused to take the pills. His condition steadily worsened, and one day the victim was urgently hospitalized with an attack. A long-term infection provoked the appearance of acute heart failure. Despite all the efforts of the doctors, the patient could not be saved, since most of his liver was destroyed due to prolonged alcohol consumption.
Possible complications of the disease:
- Development of bacterial endocarditis. One of the most severe consequences of epidermal staphylococcus is the settling of pathogenic microorganisms on the valve apparatus of the heart. They form vegetations that disrupt the normal contractility and conductivity of the organ. Even after long-term treatment, the patient may still have problems in the form of ari class=”aligncenter” width=”1000″ height=”1000″[/img] Endocarditis is accompanied by damage to the heart valves
- Disturbances of normal motility of the gastrointestinal tract. If a pathogenic microorganism reaches the intestinal mucosa through the blood or lymph fluid, colitis develops. In this case, the patient experiences severe discomfort during digestion, he is bothered by constant bloating and loose stools. One of the consequences of poor absorption of nutrients is anemia - anemia.
Colitis - inflammatory changes in the intestinal mucosa - Formation of purulent-inflammatory pathologies. During their life, bacteria release toxins that damage cells and tissues. This leads to the formation of purulent formations - abscesses, boils or phlegmons, which are removed only with surgery.
How is staphylococcus transmitted to humans?
This type of bacteria is resistant to all environmental factors: it easily tolerates heat, long drying, cold, severe frosts. Staphylococcus can remain on the surface of household items, in soil, and water for up to six months, so infection often occurs through the skin if there are scratches or open wounds. Due to its amazing viability, this type of bacteria often parasitizes in hospitals: on the floor, walls, and medical devices.
Scientists have identified several main routes of transmission:
- Contact and household. The bacterium enters the body through common objects - door handles, bed linen, shoes, towels.
- Airborne. Infection occurs through the air during contact with a carrier by sneezing, kissing, coughing.
- Generic. This type of infection is typical for newborn children, when staphylococcus is transmitted to the child from the mother during childbirth.
- Fecal-oral. This type of infection is associated with non-compliance with rules and hygiene standards. Staphylococcus aureus in the stool of an adult and some other types of bacteria can be detected if a person ate unwashed vegetables, berries, fruits, or came into contact with vomit or feces.
- Dusty. Bactria are very difficult to remove from fleecy surfaces (carpets, towels, rugs) and can exist in dust for a long time, entering the body with small particles when breathing.
- Artificial. Infection occurs through medical instruments that have undergone insufficient processing or during surgical operations.
Some types of staphylococci are part of the body's microflora and do not manifest themselves in any way until the onset of favorable conditions. The reasons for the activation of infection in the processes of active reproduction are: exacerbation of chronic diseases, nervous overstrain, decreased immunity. Risk groups for the development of purulent-inflammatory diseases include:
- pregnant women;
- patients with various forms of immunodeficiency, including AIDS or HIV;
- people with endocrine disorders - diabetes, hypo- or hyperthyroidism;
- elderly patients;
- people with a history of allergic reactions.
- How to lose 3 kg in a week - effective ways
- What to do if your ear is blocked
- Radish with honey for cough
Signs of the disease
Immediately after birth, most babies become infected with staph, but within a few days or weeks a healthy immune system controls or expels the invaders. Infections develop only in weakened organisms - with prematurity, injuries, concomitant infections.
It is not surprising to find Staphylococcus aureus in the stool of an adult - the bacterium is a full-fledged participant in the intestinal flora. The peculiarity of intestinal staphylococcal infections is that the bacterium itself does nothing against the human body; the main danger comes from poisons that get inside.
Many foods serve as an excellent breeding ground for staphylococci. Ready-made meals, meat products, butter creams are not a complete list of sources of staphylococcal food poisoning. In a suitable environment, the bacteria multiply rapidly, releasing about six enterotoxins. The more time the bacteria have, the greater the dose of poison that people who eat contaminated food will receive.
The body's natural reaction is to try to expel the poison that has gotten inside. By the nature of these reactions, it is possible to determine which part of the gastrointestinal tract is affected. If the symptoms are dominated by vomiting, the stomach is infected; diarrhea means the bacterium and its toxins are in the intestines.
There are two types of diarrhea :
- with a predominance of liquid - the infection has affected the small intestine;
- with impurities - blood, mucus, greenish inclusions - the poisons entered the large intestine.
Other symptoms are associated with the general condition of the body, which is affected by enterotoxins - fever, chills, headache, weakness, and so on.
Causes
The infection can enter the body of a healthy person through wounds or scratches on the skin, during medical procedures or due to contact with a patient. The development of staphylococcal inflammation can be triggered by frequent colds and acute respiratory viral infections. ARI, ARVI and influenza are considered especially dangerous. These diseases greatly weaken the body and require a long time to fully restore its protective functions.
A number of predisposing factors can weaken the immune system:
- frequent stress, nervous, emotional stress, fatigue;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- unhealthy diet - eating fast food, canned foods, too fatty foods;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- living in an environmentally unfavorable area;
- long-term use of certain potent medications, especially immunosuppressants and vasoconstrictors.
Staphylococcus epidermidis normal
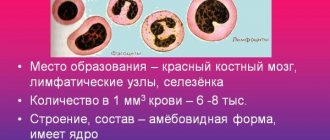
Pathogenic bacteria cause diseases in humans and animals. They can have different shapes, appearances, virulence, and drug resistance. The most common forms of bacteria are rods and cocci. The first group includes intestinal, pseudomonas, and tuberculosis pathogens.
Cocci are round in shape and may consist of varying numbers of spherical clusters. For example, the causative agent of gonorrhea includes 2 parts. Staphylococci consist of many clusters of round cells and resemble a bunch of grapes in shape. They have been known to science since the 19th century as one of the most common bacteria.
If staphylococcus is stained using the Gram method, it will be visible in the smear, that is, positive.
Diseases caused by staphylococci
The main symptom of a staphylococcal infection in the body is purulent inflammation. In this case, damage can occur in any organ and tissue. The clinical manifestations of the disease, which can be very diverse, depend on the location of the inflammation.
The pathogen enters the body through wound surfaces on the skin, with weakened immunity (viral infections). Often, staphylococci accumulate on the primary source of the disease, thereby worsening the person’s condition.
When pathogens enter the bloodstream and the immune system is weakened, bacteria are very difficult to treat (especially in children).
Normal and pathological amounts of a microorganism
Almost all people have Staphylococcus epidermidis in cultures taken from the skin or mucous membranes. However, not everyone has more than normal levels. This is due to the presence or absence of an infectious process caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis.
The number found in the bacterial culture determines whether the disease is caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis. The norm of the pathogen in the culture is up to 10 to the 5th power.
If its amount exceeds this figure, then etiological treatment should be used aimed at combating Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Kinds
Scientists separately identify some types of staphylococci, which are more common and are considered the most dangerous for both adults and children:
- Epidermal - a bacterium that affects the surface layer of the skin (epidermis). Provokes the appearance of acne, boils, carbuncles.
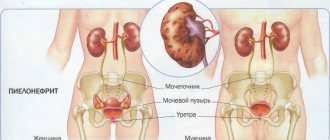
- Saprophytic is a type of infection that affects the walls of the bladder, mucous membrane and skin around the genitals. It provokes the development of cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, and is more often found in women than in men.
- Hemolytic is a bacterium that causes infectious and inflammatory reactions in the body of an adult. It often causes complications of influenza, sore throat, and inflammation of the tonsils.
- Golden is one of the most dangerous types of gram-positive bacteria. Can cause a wide range of illnesses, from mild skin infections to brain damage.
- Otic is a type of staphylococcus that affects the inner ear. Capable of spreading to adjacent tissue. It is characterized by purulent discharge from the ears, severe pain, and increased body temperature.
Symptomatic picture of the disease
The incubation period of infection ranges from 12 hours to 7 days. In this case, patients note a gradual deterioration in general well-being, increasing weakness and lethargy. In adults, the following local manifestations predominate:
- Inflammatory rashes. They resemble regular pimples and can be localized on the stomach, back, face and neck. They are distinguished by pain when palpated and the formation of dense lumps filled with pus, as well as peeling. Squeezing may leave scars and pits.
- Formation of ulcers. Poor blood circulation occurs on the skin of the lower extremities (mainly in the area of the feet and legs). An ulcer forms in this place, from which serous or purulent contents flow.
- Changes in mucous membranes. When the tissues of the nasal cavity, mouth or pharynx are damaged, swelling and redness develop, breathing and the passage of food bolus are impaired.
Photo gallery: local manifestations of the disease
Swelling causes pain and difficulty swallowing
Rashes with epidermal staphylococcus are differentiated from demodicosis
Peeling of the skin indicates the beginning of healing
Common symptoms of Staphylococcus epidermidis include:
- increase in body temperature to 37.5–38 degrees;
- decreased performance and resistance to physical activity;
- pain and rumbling in the stomach;
- stool breakdowns;
- dizziness and migraine.
The main clinical signs of the disease in children
In the first years of life, the immune system of babies is extremely poorly developed. This explains the high incidence of infection with Staphylococcus epidermidis. In children, general symptoms predominate with an increase in body temperature to 38–39 degrees, intoxication phenomena in the form of headaches, vomiting and refusal to eat, lethargy and weakness. For newborns, this can result in the development of dehydration and convulsions, which is an indication for immediate hospitalization in the intensive care unit. It is also typical to increase gastrointestinal motility and the formation of gases that do not pass away on their own. A special tube has to be inserted to alleviate the baby’s suffering.
In children with immune deficiency (congenital or acquired), the clinical symptoms of the disease are expressed almost the same as in adults.
Local changes in the skin manifest themselves in the form of pemphigus - the formation of large detachments of the epidermis with bloody or transparent contents. After opening them, reddened areas remain on the surface of the soft tissues. Another type of rash can be represented by small transparent formations, slightly painful when pressed.
Photo gallery: what babies infected with Staphylococcus epidermidis look like
Damage to the skin of the face is accompanied by increased intoxication
Rash on the palms of the hands occurs in older children
Scars may remain at the site of wounds if not properly cared for.
Features of the course of the disease in pregnant women
During the period of bearing a child, the body of the expectant mother becomes extremely sensitive and vulnerable to external influences. Even minor hypothermia or a cold can cause the development of clinical symptoms. Pregnant women are more likely to experience skin manifestations of Staphylococcus epidermidis: acne forms. The forehead, cheeks and back are predominantly affected. Staphylococcus epidermidis extremely rarely passes through the placenta (baby place), so the risk of infecting the child is almost minimal. Other signs of the disease in pregnant women do not differ significantly from other patients, but asymptomatic bacteriuria occurs - the appearance of microbes in the urine in the absence of any other reactions.
Inflamed rashes indicate an increase in the number of bacteriaStaphylococcus faceInflamed rashes indicate an increase in the number of bacteria
There is a possibility of bacteria being transmitted through breast milk during feeding. During my internship in the department of obstetrics and gynecology, I had to deal with a patient whose child became infected with Staphylococcus epidermidis in the first few days of life. The baby had to be urgently transferred to another department for further therapy and observation.
Symptoms
When you have a staph infection, symptoms appear almost instantly. They largely depend on the location of the inflammatory process. All types of infections give the following signs of staphylococcus in adults:
- local increase in body temperature (at the site of inflammation) or general fever;
- symptoms of intoxication - loss of appetite, weakness, drowsiness, joint pain;
- the presence of pustules on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes - boils, pyoderma, abscesses;
- runny nose or cough with yellow, green, or purulent discharge;
- the presence of mucus in the stool, stool upset;
- nausea, vomiting.
One of the common habitats of Staphylococcus aureus is the nasal cavity. Settling on the mucous membrane, the infectious agent provokes the development of sinusitis, purulent rhinitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis with characteristic symptoms:
- intoxication of the body - chills, weakness;
- swelling and nasal congestion;
- skin redness;
- formations of pustules on the nasolabial folds and mucous membranes;
- difficulty breathing;
- yellow or green discharge.
Staphylococcus is often found in the throat, and the infection in adults can spread throughout the respiratory tract, causing diseases such as bronchitis or pneumonia. Infectious infection is accompanied by the presence of the following symptoms:
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- swelling of the lymph nodes;
- purulent plaque on the palate, tongue;
- inflammation and redness of the tonsils, which makes swallowing difficult;
- dizziness, weakness;
- hoarseness;
- separation of purulent or greenish sputum;
- loss of appetite.
If the causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus, a throat infection can worsen the condition of adults with chronic diseases of other organs. Patients who have a history of lung and heart problems are at risk. Without timely treatment, this type of pathogen can provoke the development of complications such as purulent pneumonia, endocarditis, and lung abscess.
The epidermal type of infection most often affects the upper layers of the skin, provoking inflammatory and purulent processes of varying severity, scalded skin syndrome. This type becomes a common cause of complications after prosthetic limbs, installation of shunts or heart valves. You should suspect something is wrong and consult a doctor promptly if small blisters with cloudy liquid, eczema, dermatitis, or inflamed hair follicles appear on the skin.
When eating unwashed vegetables, fruits, berries, or not observing personal hygiene rules, harmful microorganisms can enter the stomach and intestines. The first symptoms may appear several hours after eating or within 24 hours. Intestinal staphylococcus in adults is manifested by the following symptoms:
- nausea with frequent bouts of vomiting;
- bowel disorder - diarrhea or, on the contrary, constipation;
- abdominal pain;
- bloating;
- the presence of blood or pus in the stool;
- skin rashes.
Treatment
In half of the cases, intestinal infections are caused by viruses, for which there is no effective treatment, and only in half of the cases - by bacteria, for which there is still no effective treatment. The paradox is that the danger in bacterial intestinal infections does not come from bacteria at all.
Important: the human body has various mechanisms to overcome intestinal infections, so it is able to cope with them. The person is required not to interfere and to assist a little.
In the first hours after poisoning, gastric lavage is effective . To do this, you need to drink a large amount of water and induce vomiting. When the infection has entered the intestines, the best thing to do is to refuse food . This is a natural reaction, which is why most people lose their appetite when they suffer from food poisoning.
Important: Dehydration is the main problem with intestinal infections, so you should drink plenty of fluids, and if you are vomiting uncontrollably, take small portions and tiny sips to avoid further dehydration. Any unsweetened (environment for the development of bacteria) drinks are suitable; for children, a solution of rehydration salts is best to maintain electrolyte balance in the body; an alternative can be a decoction of dried fruits.
A fasting diet, drinking plenty of fluids and rest are the three pillars of help (self-help) for intestinal poisoning . Considering the impact of strong poisons on the body, it is important that the patient is not left alone, and that there is someone to monitor his condition and, if necessary, seek qualified help.
Video from Dr. Komarovsky about the basic rules of behavior for any intestinal infections, including those caused by Staphylococcus aureus:
Staphylococcus aureus in feces without signs of an infectious disease (fever, pain, chills, vomiting, serious stool abnormalities that cannot be explained by other reasons) does not require treatment, no matter what the results of any studies say. A competent doctor always treats a patient, at least his illness, but not tests.
Complications
With massive damage to internal organs, mucous membranes or skin, the pathogenic microbe can cause a generalized infection. An increase in the number of colonies often develops into pyoderma or an extensive purulent process. Treatment in this case is carried out exclusively in a hospital, under the strict supervision of a doctor, since without proper therapy, death is possible. Frequent complications of streptococcal infection are:
- extensive phlegmon affecting adipose tissue;
- toxic shock;
- damage to the heart, lungs, brain;
- soft tissue sepsis;
- development of septicemia (blood poisoning);
- exacerbation of diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis and other chronic diseases;
- the addition of other bacteria - streptococci, pneumococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and others.
- Lumbodynia of the lumbar spine
- How to cook pasties at home. Step-by-step recipes for dough and filling for chebureks with photos
- Knitted blouse for a newborn
Staphylococcus aureus symptoms. Etiology
The cause of the disease is staphylococci, which are gram-positive cocci belonging to the Micrococcaceae family. These bacteria have a regular spherical shape and are immobile. Staphylococcus in the smear is located in the form of clusters or bunches of grapes.
Staphylococci that cause pathology in humans include only three types:
- S. aureus is the most harmful,
- S. epidermidis – less dangerous, but also pathogenic,
- S. saprophyticus is practically harmless, but can cause disease.
These are opportunistic bacteria that are permanent inhabitants of the human body, without causing any illnesses.
When exposed to unfavorable external or internal factors, the number of microbes increases sharply, they begin to produce pathogenicity factors that lead to the development of staphylococcal infection.
Staphylococcus aureus is the main representative of this group, causing severe illness in humans. It coagulates blood plasma, has pronounced lecitovetylase activity, ferments anaerobic mannitol, and synthesizes a cream or yellow pigment.
Properties of bacteria:
- Staphylococci are facultative anaerobes that can live and reproduce both in the presence of oxygen and without it. They obtain energy through oxidative and fermentative pathways.
- The bacteria are resistant to freezing, heat, sunlight and certain chemicals. Staphylococcal enterotoxin is destroyed by prolonged boiling or exposure to hydrogen peroxide.
- Microbial resistance to antibacterial drugs is a problem in modern medicine. New multidrug-resistant strains are constantly being formed in medical institutions. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci are very important epidemiologically.
Pathogenicity factors:
- Enzymes – hyaluronidase, fibrinolysin, lecitovitellase;
- Toxins – hemolysins, leukocidin, enterotoxins, exfoliatins.
Enzymes break down fats and proteins, destroy body tissue, supply staphylococci with nutrients and ensure their movement deep into the body. Enzymes protect bacteria from the effects of immune mechanisms and contribute to their preservation.
- Fibrinolysin promotes the penetration of microbes into the blood and the development of sepsis - blood poisoning.
- Hemolysins suppress the activity of immunocompetent cells and help staphylococci survive in areas of inflammation for a long time. In children and the elderly, due to these factors, the infection acquires a generalized form.
- Exfoliatin damages skin cells.
- Leukocidin destroys leukocytes - white blood cells.
- Enterotoxin is a strong poison produced by staphylococci and causes foodborne illness in humans.
Diagnostics
Considering that staphylococci are constantly present in the body of an adult and appear only when factors favorable to them occur, tests are prescribed after the appearance of symptoms or complaints from the patient. During laboratory tests, in addition to the type of bacterium, its sensitivity to the effects of antibiotics is determined in order to prescribe competent treatment. Among the diagnostic procedures, preference is given to:
- blood test if extensive infection is suspected;
- skin scraping in the presence of dermatological symptoms;
- stool analysis for digestive disorders;
- a swab from the nose or throat if there are problems with the respiratory tract;
- urine analysis.
Diagnosis of the disease
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes blood, urine, and feces for clinical testing, as well as bacterial culture from the following materials:
- scrapings from the skin;
- sputum;
- smears from mucous membranes;
- pus and discharge from the wound.
Before submitting biological material for research, it is prohibited to smoke, drink alcohol, or eat fried or fatty foods. There is no need to wash or use external antibacterial agents on the skin, since the latter may affect the results of the study.
The norm of staphylococcus in a smear culture is up to 103. If this indicator is exceeded, the doctor prescribes treatment to combat the infection.
Treatment of staphylococcus in adults
Local forms of pathology respond well to treatment outside the hospital. Those patients who have massive damage to the skin, internal organs, or complications are present are subject to hospitalization. The choice of the optimal treatment regimen depends on the location of the inflammatory process:
- If adults have an epidermal type of pathogen, surgical treatment without the use of antibacterial drugs is possible. The external abscess is opened and the doctor removes the pus. To treat wounds, any liquid antiseptic is used - brilliant green, iodine.
- Staphylococcus in the throat in adults must be treated with the use of local remedies in the form of ointments or liquid rinses. The affected areas are treated with chlorophyllipt, eucalyptus tincture, vinylin (Shostakovsky balm).
- Staphylococcal dermatitis in adults involves taking antibiotics and using local antibacterial drugs - ointments, gels, sprays. The affected areas are regularly treated with hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green, and ethyl alcohol. Vitamins are prescribed to restore immunity.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in adults can be complicated by the fact that the pathogen is resistant to most types of antibiotics. In addition to measures to strengthen the immune system, the doctor prescribes drugs with bacteriophages - special viruses that can kill this type of microorganisms. Bactriophages are available in the form of tablets, ointments, mouth rinses or injections.
Antibiotic therapy
The first antibacterial drugs from the penicillin group were active against a large number of staphylococci, helped to successfully stop purulent processes, and prevent the occurrence of sepsis. Over the years, pathogenic microorganisms have managed to develop resistance to this type of drug, so penicillins are rarely prescribed today. Antibiotics belonging to the tetracycline, lincosamide, cephalosporin groups and macrolides are considered first-line drugs. Often prescribed:
- Ceftriaxone is a 3rd generation antibiotic belonging to the celofasporin series. Available in the form of a white or yellow powder for injection. The drug acts to inhibit the cell walls of microorganisms. Prescribed for joint damage, sepsis, meningitis, infected wounds or burns. The antibiotic has minimal contraindications, but can cause multiple side effects, the most common of which are headache, dizziness, allergies, anemia, and indigestion.
- Amoxiclav is a combined antibacterial drug. Available in powder and tablet form. The medicine is prescribed for diseases of the urinary tract, skin, joints, and ENT organs. Amoxiclav is strictly contraindicated in case of liver dysfunction, hypersensitivity to penicillin or amoxicillin. When taken, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, jaundice, and urticaria are possible. Analogues of Amoxiclav in composition - Augmentin, Oxacillin.
- Ofloxacin is a 2nd generation fluoroquinol. Available in the form of tablets and eye drops. The drug inhibits the enzyme DNA gyrase, causing the death of microorganisms. Prescribed for bronchitis, pneumonia, sinusitis, pharyngitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, meningitis. Use with caution for atherosclerosis and cerebrovascular accidents. Ofloxacin often provokes headache, dizziness, gastralgia, and allergic reactions.
- Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic. Available in the form of a white powder for the preparation of a solution for injections. The antibacterial agent blocks the synthesis of the cell membrane of viruses and is able to change the permeability of the walls. Vancomycin is prescribed for sepsis, meningitis, bone and joint diseases. Due to the increased number of microorganisms that have developed resistance to its active components, it has been used very rarely in recent years.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes are used only as an aid aimed at strengthening the immune system. Some types of medicinal plants additionally have analgesic properties and are able to quickly remove waste products from the body. Preference is given to medicinal mixtures based on string, thyme, licorice root, plantain, and rose hips. Alcohol tincture with propolis has proven itself well:
- Take 3-4 tbsp. l. soft finely chopped propolis.
- Place it on the bottom of a liter jar, fill it to the neck with any strong alcohol - alcohol, vodka, cognac.
- Cover the container with a lid and leave to infuse in a dark place for 10-14 days.
- For intestinal disorders, take 20-30 ml before or during meals. Course – 15–20 days.
- For sore throat, sinusitis or sinusitis, use the tincture as a rinse.
Staphylococcus epidermidis is normal in men
We are surrounded by countless pathogenic microorganisms. Some of them are quite harmless, but there are those that cause a lot of inconvenience, thereby causing various diseases. When conducting research, you can detect staphylococcus epidermis in a smear in men. In the article we will talk about what symptoms this microbe gives and how to deal with it.
Bacteria are so diverse that each of them requires an “individual approach.” The most common are cocci and rods.
The latter are often represented by intestinal, tuberculous and pseudomonas pathogens. Cocci are round in shape and have several spherical elements. Known to many, staphylococci look like a bunch of grapes.
They occur very often. People started talking about these bacteria back in the 19th century.
Staphylococcus epidermis in a smear in men can be detected by staining staphylococci using the Gram method.
Influence
The pathogenicity of the bacterium is that, while living in the human body, it secretes a special substance - an exotoxin. Two powerful destructive actions of these bacteria have been identified:
- Blood cell disorder. Staphylococci destroy red blood cells (erythrocytes). As a result, the correct structure of the blood is disrupted.
- Tissue necrosis. The bacterium has a detrimental effect on the tissues of the body, so they begin to die.
The negative impact caused depends not only on how many microbes are in the body, but also on the response of the immune system. Drug therapy aimed at inhibiting the growth and development of staphylococci also has an effect.
Types of bacteria
Staphylococci are different. Not all of them affect the human body. Usually, the pathogen can be recognized by the symptoms it causes. The main pathogenic microorganisms of this genus are presented below:
- staphylococcus epidermis;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- Staphylococcus saprochityx;
- Staphylococcus chaemolytix.
There are types that require mandatory treatment. Some of them are not dangerous at all and do not require the use of medications.
Infection
Staphylococcus epidermis in a smear in men may indicate the presence of a purulent process, but not always. In this case we are talking about the genitourinary system. But in general, infection can occur anywhere in the body.
Bacteria can enter the body through wounds on the skin or in case of weakened immunity. It happens that a person is already sick with something and then a staphylococcal infection occurs, complicating recovery.
If the pathogen has entered the bloodstream and the immune response is weak, then it is very difficult to treat the disease.
Men always have Staphylococcus epidermidis in their bodies. This species is classified as opportunistic microbes. It lives in the upper layer of the skin, as well as on the mucous membrane of the nose, mouth, outer ear, and urethra.
As long as the body works stably, no changes occur - staphylococcus does not cause disease.
If a man has experienced severe stress, suffered from hypothermia, contracted a serious infection, or been injured, then the bacteria begin to attack, causing discomfort.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of infection may be:
- pain in the genital organ;
- disruption of urine outflow;
- hyperemia and swelling of the penis;
- purulent discharge from the urethra.
The bacteria are detected when the material is taken for analysis. With such symptoms, it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Microorganisms live in all people without exception. It all depends on their norm, which is determined by sowing. If the number of microbes exceeds 10 to the fifth power, then this is a staphylococcal infection. Usually the doctor prescribes treatment to combat the bacteria.
Staphylococcus often enters the urethra during examinations that involve the use of a catheter. Thus, it causes urethritis, pyelonephritis. Therefore, they try to conduct studies for men, avoiding the introduction of a contrast agent through a catheter into the bladder. Prostatitis can also occur due to the fault of staphylococcus.
Antibiotics are always prescribed as treatment. If the penicillin group does not produce a positive effect, stronger drugs are used. For example, vancomycin, fluoroquinolones and others. Additionally, the doctor prescribes immunomodulators and anti-inflammatory drugs.
So if staphylococcus epidermis is found in a smear in men, this does not mean the presence of an inflammatory process. Often the infection must manifest itself in some way. Therefore, it is very important to look exactly at the numbers as a result of the analyzes. You should not allow injuries to the urethra and, if possible, avoid manipulations that lead to them.
Editor
Source: https://zhivizdravo.ru/info/staphylococcus-epidermidis-norma-u-muzhchin/
Staphylococcus and pregnancy
Among various pathogenic microorganisms, staphylococcus is identified as particularly dangerous for pregnant women. Due to a natural decrease in immunity, this type of bacteria easily penetrates the body, causing inflammation of the bladder, kidney disease, and exacerbation of infectious viral infections. The golden subtype is especially dangerous because it is able to penetrate the placental barrier, leading to abnormalities in the development of the fetus, in some cases causing miscarriage.
Pregnant women should be tested regularly for infection, even if there are no outward signs of the disease. If a bacterium is detected and mass infection develops, the following treatment regimens are possible:
- taking antibiotics;
- prescription of local anti-inflammatory drugs;
- the use of drugs aimed at increasing immunity;
- quartz treatment.
Staphylococcus epidermis is normal in women
Staphylococcus epidermidis (epidermal staphylococcus) is an opportunistic microorganism that lives primarily on human skin and is part of its microflora.
It has a relatively low pathogenic potential, but under certain conditions it causes various pathological processes. Children, the elderly and those with immune dysfunction are at greatest risk of infection.
For people with strong immunity, the bacterium is absolutely not dangerous.
Staphylococcus epidermidis produces a number of strong toxins and enzymes, under the influence of which the normal functioning of the macroorganism is disrupted.
In addition to the skin, subcutaneous fatty tissue and connective tissue fibers are affected. The pathogenic effect of these microbes is due to their basic properties.
It consists in the development of inflammation, cell destruction, the appearance of foci of necrosis, and dysfunction of internal organs.
In addition to the skin, staphylococcus colonizes the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, oral cavity and auditory analyzer. The microbe is present in all people in quantities not exceeding the permissible level. The rapid proliferation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and activation of its pathogenic properties leads to the development of inflammation of vital organs and tissues.
Staphylococcus epidermidis is the causative agent of various diseases, the course and outcome of which are determined by the localization and extent of the lesion, concomitant pathology and protective properties of the body, the timeliness and effectiveness of the therapy. These bacteria are resistant to most antiseptics, disinfectants and antibiotics.
Etiology
Staphylococcus epidermidis is a member of the genus Staphylococcus of the Micrococcaceae family.
Staphylococcus epidermidis under a microscope
Morphological properties. Staphylococcus epidermidis is a spherical or spherical bacterium that lacks flagella and forms microcapsules that protect against negative factors. These asporogenous microbes are capable of transformation into L-forms.
- Tintorial properties. Bacteria are Gram stained blue and are located in clusters or randomly in the smear.
- Physiological properties. Staphylococci use chemical compounds as energy and organic substances as carbon. Bacteria grow well in aerobic conditions, but can also exist in the absence of oxygen. Temperature optimum is 30-37 degrees.
- Cultural properties. On plate media, microbes grow in the form of round, convex, white or cream colonies. In the saline broth, growth is observed in the form of a diffuse turbidity. Bacteria are able to multiply in concentrated salt solutions and grow on media containing sodium chloride.
- Pathogenicity . The virulence factors of Staphylococcus epidermidis are adhesins, enzymes and toxins.
- Resistance. Bacteria remain viable when exposed to direct sunlight, low and high temperatures. They are sensitive to aniline dyes.
The virulence of Staphylococcus epidermidis is due to its film-forming ability. Multilayer biofilms slow down cell metabolism and protect it from the effects of antimicrobial agents.
Epidemiological significance
Staphylococcus epidermidis is widespread. It lives in the external environment: in the air, soil, on household items and medical instruments, as well as in various loci of the human body.
The source of infection caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis is the patient or the bacteria carrier. It is asymptomatic carriers that pose the greatest danger in epidemiological terms. The entry point for infection is damaged skin and mucous membrane.
Ways of spread of infection:
- Airborne - during coughing, sneezing, talking;
- Airborne dust - through air and dust that has been in contact with the vector of infection;
- Contact and household - through household items, dirty hands, kisses and hugs;
- Artificial - through medical equipment, contaminated instruments and hospital equipment;
- Nutritional – through contaminated or thermally unprocessed food products.
Factors contributing to the development of infection:
Staphylococcus epidermidis is the causative agent of nosocomial infections. Persons in surgical wards are at greatest risk of becoming infected.
Poorly processed instruments, infected implants and catheters, and the hands of medical staff are the causes of serious diseases that threaten the patient’s life. The microbe is easily airborne and can infect open wounds. Sometimes it reaches the patient during surgery.
During venous puncture or catheterization of the bladder, Staphylococcus epidermidis penetrates the internal organs and leads to the development of endocarditis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, vulvovaginitis, and urethritis.
The infection spreads upward to neighboring organs, which is manifested by the development of endometritis in women and prostatitis in men. Patients are prescribed antibiotics, the prosthesis is removed, and the infected catheter is replaced.
Pathogenesis
Staphylococci are tropic to various organs and tissues of the human body.
This property is due to the ability of bacteria to fix on epithelial cells, multiply, penetrate inside the cell and exhibit their pathogenic properties, causing purulent lesions.
Stress and hypothermia accelerate the growth of bacteria. Under the influence of endogenous and exogenous negative factors, their pathogenic properties are enhanced.
The risk group for staphylococcal infection includes:
- Pregnant women,
- Patients after operations and invasive procedures,
- Intensive care patients,
- People with dysbiosis
- Aged people,
- Newborn children,
- Patients with autoimmune pathology,
- Patients with chronic diseases in the stage of decompensation.
Staphylococcus epidermidis causes various diseases: dermatological, bronchopulmonary, osteoarticular, endovascular, as well as wound and nosocomial infections, purulent-focal processes. Most often, inflammation develops under the influence of bacteria:
- Skin, subcutaneous tissue, lymph nodes, occurring in the form of furunculosis, lymphadenitis, pyoderma, eczema, soft tissue abscessation,
- Respiratory organs - bronchi, lungs, pleura,
- ENT organs - middle ear, throat, paranasal sinuses, tonsils,
- Various sections of the visual analyzer,
- Biliary tract and gallbladder,
- Genitourinary organs - kidneys, urethra, prostate,
- Musculoskeletal system - bones, muscles and joints,
- Digestive organs - various parts of the intestine.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of diseases caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis is varied. It depends on the localization of the source of infection, the characteristics of a particular strain, the state of the immune system of the macroorganism and consists of the following characteristic signs: general symptoms, local focal skin lesions, dysfunction of internal organs.
- Common symptoms of staphylococcal infection include: weakness, cephalalgia, disorientation in space, hyperthermia, chills, exacerbation of chronic diseases, loss of appetite, nausea, drop in blood pressure, sleep disturbance.
skin manifestations of infection
When the skin is damaged, acne, rashes, peeling, redness, abscesses, felons, paronychia, phlegmon, ulcers and ulcers appear. Local forms have local symptoms of inflammation, and pathologies such as furunculosis or abscess are often accompanied by severe intoxication.
Source: https://gemoglobin.top/stafilokokk-jepidermis-norma-u-zhenshhin/
Prevention
It may be impossible to completely get rid of staphylococcus, so the key goal for doctors is not to destroy the bacteria, but to prevent the development of serious diseases. One of the main tasks of prevention is maintaining personal hygiene standards. Since the microorganism is easily transmitted by air, droplets, or household contact, it is important to follow the following rules:
- eat only high-quality food - washed vegetables, fruits, berries, fresh food;
- wash your hands every time after visiting public places and before eating;
- treat wounds with brilliant green, peroxide, iodine;
- draw water only from clean, proven sources, do not drink tap water;
- expose hospital clothing to prolonged boiling and then thoroughly steam after drying;
- Regularly ventilate the room and do wet cleaning of the house.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of diseases caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis is varied. It depends on the localization of the source of infection, the characteristics of a particular strain, the state of the immune system of the macroorganism and consists of the following characteristic signs: general symptoms, local focal skin lesions, dysfunction of internal organs.
- Common symptoms of staphylococcal infection include: weakness, cephalalgia, disorientation in space, hyperthermia, chills, exacerbation of chronic diseases, loss of appetite, nausea, drop in blood pressure, sleep disturbance.
skin manifestations of infection
When the skin is damaged, acne, rashes, peeling, redness, abscesses, felons, paronychia, phlegmon, ulcers and ulcers appear. Local forms have local symptoms of inflammation, and pathologies such as furunculosis or abscess are often accompanied by severe intoxication.
- When a microbe penetrates the body from the surface layers of the skin, signs of intoxication, asthenia, and dyspepsia appear. Patients' general condition worsens, lethargy, pallor, fatigue occur, and body temperature rises.
- Staphylococcus epidermidis, penetrating the body by airborne droplets and settling on the epithelium of the respiratory tract, causes acute inflammation of the tonsils or pharynx. In patients, the mucous membrane of the pharynx becomes hyperemic, the tonsils swell and become covered with purulent plaque, and the regional lymph nodes enlarge. They complain of pain and sore throat, a rise in body temperature, difficulty swallowing food, and coughing.
- If bacterial growth is observed in the nose, rhinitis occurs with copious mucopurulent discharge, which is often complicated by sinusitis or frontal sinusitis. Patients constantly develop crusts in the nose, they are tormented by stuffiness and runny nose.
- When the infection goes lower, the armor and lungs become inflamed, a cough with purulent sputum occurs, and pain under the ribs occurs. Pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis manifests itself as intoxication and pain, respiratory failure, and severe shortness of breath.
- When the outbreak is localized in the intestine, stool is disrupted, and pathological impurities appear in the stool - mucus and pus. Patients complain of cramping abdominal pain, dyspeptic symptoms - nausea, vomiting, flatulence, diarrhea.
- Inflammation of the genitourinary organs in men is characterized by signs of dysuria: pain and burning during urination, hematuria, frequent urge to go to the toilet. In women, the pathology is manifested by discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen, copious discharge with an unpleasant odor, and painful sensations during coitus.
- Purulent meningitis is a serious complication in which microbes penetrate the meninges through hematogenous routes and cause inflammation. Clinical signs of the pathology are: intoxication, focal neurological symptoms, meningeal signs, epileptic seizures, confusion, disorientation in time and space, hemorrhagic skin rash.
Staphylococcus aureus in feces: causes, symptoms, treatment methods
Staphylococcus aureus detected in the stool means that a harmful, dangerous infection has entered the body.
A pathogenic microorganism can affect almost all organs and tissues. Strains of different types of staphylococcus can exist in the oral cavity, pharynx, nasal mucosa, intestines and many other organs. Treatment is often lengthy, since staphylococcus is resistant to most antibacterial agents.
In addition, re-infection may occur because the body does not develop protection against infection.
Infection options
Staphylococcus aureus found in feces can be due to various reasons. The infection is transmitted by contact with a carrier through airborne droplets.
Infection may occur in the womb, as well as ingestion of the microorganism through food or its introduction during examination in a medical facility.
There are many options for infection, and the risk increases with weakened defenses, general malaise, and taking antibiotics.
Specifics of microorganisms
Some staphylococci and enterococcus fecalis (previously this type of bacteria was also classified as staphylococci) are present in the microflora of the intestines and oral cavity. Staphylococci have a round shape and do not form capsules or spores. In a normal state of health, these bacteria do not manifest themselves in any way, and enterococcus fecalis in small quantities is even useful, since it is involved in digestion.
The danger of inflammation caused by staphylococci lies in the characteristics of these microorganisms. They are extremely resistant to environmental changes and various factors: they can exist even with a lack of oxygen and are actively divided due to the energy of fermentation (oxygen-free type of respiration).
Streptococci are immune to the effects of many antibacterial drugs, which is why there is often an increase in their number even after taking antibiotics. At the same time, such drugs disrupt the intestinal microflora, and streptococci and enterococci fecalis remain viable and replace the destroyed bacteria.
Streptococcal infection and pregnancy
Staphylococcus aureus is very dangerous during pregnancy, since this type of bacterium is difficult to treat. At the same time, it is the one that is detected most often and becomes the cause of many health problems.
With the active spread of staphylococcus, the disease has a characteristic course, according to which it can be judged that a staphylococcal infection has occurred. The pathology is mainly indicated by the existing purulent process. If there is no infectious rash and no characteristic discharge, then the cause of poor health is not hidden in a staphylococcal infection.
How to pass the test correctly
Before taking a stool test for staphylococcus, you need to stop taking any medications, in particular laxatives, a week before. The biomaterial is given in a special container and delivered to the laboratory no later than 3 hours after defecation.
Before transportation, feces must be stored in the refrigerator!
If staphylococcus is detected in the feces, a sensitivity test to antibacterial drugs is carried out. The maximum amount that feces can contain should not exceed 10 to the 4th power. If the concentration of these microorganisms is higher, this is already a sign of an infectious process.
Signs of infection
A stool test is ordered if there are signs of infection. These include a skin rash or inflammation in a separate area of the skin with clear boundaries.
Purulent formations can be deep under the skin, which threatens further spread of infection through the tissues when the capsule with pus is opened.
Often, patients begin to detect damage to the hair follicles - an abscess forms under the skin around the hair.
Aggressive microbial toxins, when released into the blood, cause decreased blood pressure, fever, headaches, abdominal pain, vomiting, and clouding of consciousness. The stool will be frequent, liquid with greenish streaks. When analyzed, fecal enterococcus and staphylococci are detected in high concentrations.
Staphylococcal enterocolitis can be “earned” after treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Due to infection, after about 5 days a sharp increase in temperature and other symptoms of acute poisoning are observed.
The spread of Staphylococcus aureus throughout organs and tissues is difficult to miss, since it includes a rash on the skin, a fever, and intestinal disorders.
Such symptoms require urgent intervention from a specialist; you need to submit your stool for a culture test. After this, the sensitivity of staphylococcus to an antibiotic or bacteriophage is established, and then effective therapy is selected in combination with measures to strengthen general health.
Features of therapy
If the analysis reveals the presence of a staphylococcal infection or fecal enterococcus, then treatment is prescribed based on eliminating the causes of the pathology. Taking into account the high resistance of strains to the action of many antibacterial agents, when conducting research, laboratory assistants determine which drugs a particular bacterium is sensitive to.
Treatment agents are selected according to the results obtained. The most commonly prescribed drugs are cephalospirins and penicillins. To eliminate pathogenic cells, taking special bacteriophages can be effective. Their use is advisable when a strain with high resistance to antibiotics is discovered.
A severe excess of Staphylococcus aureus or “increased” fecal enterococcus in the stool requires additional measures, namely taking probiotics. Therapy aimed at eliminating the pathogen usually lasts 5-7 days.
But to restore the intestines and prevent the development of dysbiosis, additional treatment is required. The doctor prescribes the use of food supplements, vitamin complexes, mineral and immunomodulatory drugs to maintain general health and normalize metabolic processes.
Self-medication for infection with staphylococcus is excluded; observation in a hospital setting is required.
Preventive action
To reduce the risk of contracting an infection, you should keep in mind simple preventive measures. First of all, it is worth noting keeping the house clean and fulfilling basic personal hygiene requirements. A proper diet and balanced diet can also be considered preventive measures.
Any actions aimed at strengthening the body’s defenses are also important: physical exercise, adequate sleep and rest, and a positive attitude.
Conclusion
Staphylococcal bacteria can be found in any organ. Staphylococcus aureus is a dangerous infectious agent. Infection with the bacterium can lead to the development of serious pathological conditions. Chronic and congenital diseases worsen, other opportunistic microorganisms rapidly spread throughout the body, blood poisoning and even death are possible.
Unfortunately, the consequences of infection with Staphylococcus aureus are difficult to predict. People with weak immune systems are at risk, so it is very important to stimulate the body's protective functions.
Source: https://nashainfekciya.ru/bakteriya/kokki/zolotistyj-stafilokokk-v-kale.html
Specifics of treatment of the disease
Staphylococcal type of intestinal dysbiosis in adults develops quickly. Qualified doctors recommend using vitamins B and C after taking antibiotics. It will not hurt to use an enema or desensitizing therapy. For moderate forms of the disease, antibiotics are used, discussed with the doctor.
In practice, Penicillin and Streptomycin are used, which effectively eliminate pathogenic microflora. The first compound has a dosage of 300 thousand units (5 times every 24 hours), and the second – 500 thousand units. The duration of treatment is 1 week. If the therapeutic effect is insufficient, the treatment regimen is revised. The child has his own recovery plan.
"Sigmamycin" is an alternative option. The drug allows you to effectively fight staphylococci in tandem with pathogenic microbes. It is rational to take the medicine every 6 hours, 250 mg for 10 days. After therapy, the patient experienced a noticeable improvement in general condition and normalization of temperature. Gastric juice is optimized.
Along with the above antibiotics, a staphylococcal type toxoid is used. The medication is administered subcutaneously in gradually increasing doses: (from 0.1-0.3 to 1.7-2.0 g). The duration of injections is 10 days. Pharmacists claim that the drug provokes the development of immunity to bacteria in humans.
When staphylococcus (other pathogenic microorganisms) is reliably associated with other harmful microorganisms, the treatment process is adjusted. When yeast fungi are active, Nystatin is prescribed, and for Proteus infections, Furazolidone is prescribed. In order to normalize the intestinal microflora, “Coli-bacterin” is prescribed. The medicine is used for 30-60 days, 2 times a day. Antihistamines are represented by Diphenhydramine and Pipolfen. It will not hurt the patient to normalize the level of electrolytes.
For acute pathologies, repeated courses of treatment are prescribed. Erythromycin and Monomycin are excellent for such purposes. In the process of therapeutic intervention, clinical studies on the composition of the microflora will not interfere. Complications are possible with nonspecific ulcerative colitis and other purulent-septic pathologies.