Bacterioscopy is the most common gynecological test. Women and girls of different ages are required to undergo this procedure when undergoing a medical examination. In 50-60% of them, cocci are detected in a smear for flora. In men they are much less common. This is due to the structural features of the female reproductive system. Cocci can also be detected in a child’s smear.
Under certain circumstances, bacteria can provoke serious diseases of the genitourinary and other organs, so it is advisable to find out what they are, when they threaten health and how to deal with them.
What is cocci
There are many different microbes present in the human body. Cocci are a family of single-celled organisms, named from the word coccus, which means “spherical” in Latin and “grain” in ancient Greek. Like other bacteria, cocci have the unique ability to reproduce intensively (about every half hour). Under favorable conditions, unicellular organisms divide in two, i.e. are crushed, which is why they are also called “fragmented”, and then either exist separately or are combined into groups. Cocci are nonmotile, do not form spores, and are anaerobic (can live in an airless environment).
What are Doderlein sticks
Doderlein bacilli, or, as they are also called, lactobacilli and lactobacilli, are microorganisms that protect the vagina from pathogenic infections by producing lactic acid, which helps maintain an acidic environment and destroy pathogenic flora.
A decrease in the number of lactobacilli indicates a disturbed acid-base balance of microflora in the vagina and a shift towards the alkaline side, which often occurs in women who are sexually active. The pH of the vagina is significantly influenced by both pathogenic microorganisms and opportunistic microorganisms (which are sometimes found in the vagina normally).
Normal microflora
The healthy microflora of the female genital organs consists of lactobacilli - Dederlein bacilli, bifidobacteria and a small (about 5%) amount of cocci. This ensures the normal course of processes such as:
- metabolism;
- regulation of acidity levels;
- destruction of pathogenic microbes.
The presence of cocci in a smear in women is not dangerous and natural. When the balance of microorganisms is maintained at the proper level, beneficial lactobacilli multiply in an acidic environment and create protection against fungi (thrush), E. coli and other harmful microbes. Accordingly, the genitourinary system functions stably and fully.
Symptoms of infection development
The onset of the disease is sometimes not characterized by any obvious signs, therefore, if an increase in the number of cocci is detected as a result of a smear analysis, it is imperative to undergo an extended, thorough examination.
The main frequently observed symptoms are expressed by the following phenomena:
- foul-smelling discharge;
- profuse and thick leucorrhoea;
- change in color of discharge;
- the appearance of purulent clots;
- burning sensation, itching;
- swelling of organ tissues,
- pain during sexual intercourse or urination.
Urgent local and general medical treatment is needed, since many diseases develop at lightning speed and lead to life-threatening consequences.
What do cocci say in a smear?
When the microclimate is disturbed, the picture changes: the content of cocci increases, and beneficial bacteria die, so if the number of cocci in a smear exceeds the norm, this indicates health problems.
Normal: pH (acidity level) – up to 5. Weakly acidic environment (beginning of the inflammatory process): pH – up to 7. Increased alkaline environment (infection or inflammation is actively developing): pH – more than 7.5.
To determine a specific disease, it is necessary to establish which type of spherical bacteria is present in excess, and also to determine the presence of gram-negative and gram-positive cocci in the smear. These terms originated with the Danish scientist Gram and his method for identifying drug-resistant cocci. The fact is that many bacteria have a very strong shell, impenetrable to most common antibiotics (Gram-negative). But those microorganisms whose cell wall is destroyed under the influence of antibacterial drugs (Gram-positive) are also capable of causing serious pathologies, since as a result of their breakdown products, intoxication of the body occurs. Only thanks to a strong immune system and compliance with all treatment rules, the bacterial norm is restored.
To the question: “What do cocci mean in a woman’s smear?” You can answer this: vaginal dysbiosis, decreased protective functions of lactobacilli and an increased likelihood of inflammatory processes. Cocci in a smear in men also indicate a malfunction of the genitourinary system.
Attention! This condition requires qualified medical care. Traditional methods, self-administration of antibiotics and other medications are extremely undesirable and can only aggravate the situation.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of pathology consists of conducting a comprehensive examination of the patient. Specialists listen to complaints, collect anamnesis, examine patients and take a vaginal smear for cytological examination.
- A gynecological examination using special mirrors is carried out by a doctor to examine the external and internal genital organs.
- Bacterioscopy is the simplest, but quite informative research method. A smear is taken from the woman's vaginal or cervical mucosa. The material is applied to a sterile glass slide and sent to the laboratory. There, the smears are Gram stained and examined under a microscope. Bacteria have a spherical shape and are located singly, in pairs, in chains, or in clusters. They stain red or blue and are gram-negative and gram-positive cocci. The color of individual microorganisms can change under the influence of the pH of the habitat, the presence of growth factors and other conditions. Cells that can perceive dyes differently throughout the development cycle are called gram-variable. The specialist counts the number of bacteria of each type and writes out the result.
- Bacteriological method : a smear from the vagina or cervical canal is taken with a sterile cotton swab and inoculated on selective nutrient media. The crops are incubated in a thermostat. Given favorable conditions, bacteria grow and multiply well, forming characteristic colonies on the dishes. The culture is accumulated, microscoped, and tested. Cocci are identified to genus and species.
- A general blood test can detect signs of bacterial inflammation in the body.
- PCR diagnostics is a fast and accurate way to determine bacterial DNA in a test sample.
- Additional methods are instrumental studies - ultrasound, colposcopy.
Types of cocci
There are several types of bacteria, many of which are opportunistic:
- Diplococci (more than 80 species are known). They exist in pairs and are gram-negative and gram-positive. The most pathogenic type is gonococcus, the causative agent of gonorrhea. The disease ranks first in terms of prevalence among STIs (sexually transmitted infections).
- Streptococci are microbes connected in a chain. Externally, cocci in a smear look like rods formed from several spherical cells. To date, more than 100 types of streptococci (all gram-positive) have been discovered. By multiplying in the genitals, they cause vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina), cystitis (inflammation of the bladder), cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix), endometritis (inflammation of the uterine lining) and other pathologies.
- Staphylococci (gram-positive). They are clusters similar to bunches of grapes. There are 27 types of pathogens, the most dangerous is Staphylococcus aureus. The presence of a large number of staphylococci in the vagina contributes to the active proliferation of other pathogens, such as candida fungi (thrush). Against this background, the mucous membrane and appendages of the uterus often become inflamed.
- Enterococci (oval-shaped cocci, arranged in chains or pairs) are opportunistic representatives of the intestinal microflora, which, in the absence of hygiene, can rapidly develop in the genitourinary system.
- Coccobacilli (an intermediate form between bacilli and cocci). Haemophilus influenzae, gardnerella, chlamydia are detected in the presence of sexually transmitted diseases and bacterial vaginosis.
- Gonococci. They have a gram-negative structure and an oval shape. When the genitourinary tract is damaged, they cause an inflammatory reaction with the subsequent development of cervicitis and salpingitis.
Degrees of vaginal cleanliness
The concept of degrees of purity was introduced in order to promptly identify women at risk for inflammatory diseases of the genital organs (vaginitis, cervicitis, endometritis, and so on). You can read more about this in our other article (follow the internal link). They are identified based on the results of a simple smear for flora and GN:
- 1First degree (second name - normocenosis): acidic environment. Normal number of lactobacilli, few epithelial cells, no cocci. It is rare, usually observed immediately after treatment or the use of antibiotics.
- 2Second degree: acidic environment. The number of lactobacilli is slightly reduced, leukocytes (up to 10) and small diplococci appear. The number of cocci is insignificant (one or two pluses).
- 3Third degree: the environment becomes slightly acidic or alkaline. The number of Doderlein rods is significantly lower than normal, there is a lot of epithelium, leukocytes 10-30, coccal or bacillary flora predominates, fungal mycelium can be detected. This condition is called dysbiosis (dysbacteriosis). Such women need to be monitored and receive timely treatment.
- 4Fourth degree: alkaline environment. Lactobacilli may be completely absent, a large number of epithelial cells, leukocytes (above normal), many cocci or other pathogenic bacteria. This degree corresponds to vaginitis, therefore, treatment of the woman is mandatory.
As the pH shifts toward the alkaline side, the quality and quantity of flora changes. The level of acidophilus bacilli gradually decreases, cocci multiply, then fungi and other bacteria join.
An alkaline environment is detrimental to Doderlein's bacilli, which leads to the development of vaginal dysbiosis.
It is worth noting that the following microorganisms can be found in normal smears: hemolytic streptococcus, aureus, epidermal and saprophytic staphylococcus, peptococci, micrococci, green streptococcus and others. All of them in small quantities do not pose a threat to health and are opportunistic representatives of the vaginal flora.
With 3-4 degrees of vaginal cleanliness, the following types of cocci can most often be detected:
- 1Streptococci. As mentioned above, these microorganisms are allowed in small quantities, but their increased proliferation leads to the occurrence of an inflammatory process - vaginitis.
- 2Enterococcus fecal. Often found in the intestines, if it enters the genitourinary tract it can cause cystitis or colpitis. Detection of it in large quantities in smears indicates a violation of the rules of intimate hygiene, including during sex.
- 3Staphylococcus is an opportunistic microorganism that normally lives on the skin. With increased reproduction, it can cause serious inflammation with damage to the external and internal genital organs.
- 4Diplococcus occurs in vaginal dysbiosis with disruption of the normal composition of the microflora of the mucous membrane.
There are other cocci, they usually cause nonspecific colpitis.
Important! If Staphylococcus aureus is detected in a gynecological smear, then there is a possibility of its detection on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract (oropharynx, nasal cavity).
Causes
There are a huge number of factors that provoke pathology. The main causes of cocci in a smear:
- Incompetent treatment. If a person takes antibacterial drugs without prescription or does not comply with the dosage, the likelihood of being affected by pathogenic microbes increases many times over.
- Neglect of personal hygiene. Ignoring basic rules and incorrectly performing procedures increase the risk of disruption of the vaginal microflora. It must be remembered that soap is an alkali, and washing too deeply has a negative effect on the acid-base balance. For women, girls and girls it is advisable to use special intimate hygiene products. It is also important to perform manipulations from the vagina to the anus, and not vice versa.
- Wearing underwear made of dense materials or synthetics has a bad effect on the microclimate of the genital organs.
- Disorderly sex life. Unprotected contact with a carrier of pathogenic microbes leads to infection in 99 cases out of 100. In addition, if you do not have a regular partner and regularly have sex, the microflora will inevitably be exposed to “foreign” bacteria.
- Douching. Due to frequent douching, beneficial flora is washed away.
- Hormonal imbalances. Hormonal imbalances cause bacterial imbalance.
- Weakened immunity. When the body's protective functions are reduced, it cannot resist dangerous pathogens.
Reasons for the appearance of coccal microflora in a smear
Coccal microflora begins to actively grow when the vaginal biocenosis is disrupted. The following factors contribute to this:
- insufficient personal hygiene;
- poor sexual hygiene;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics, vaginal suppositories;
- hormonal disorders;
- trauma to the vaginal mucosa;
- wearing synthetic underwear;
- chronic stress.
Abundant growth of coccal flora in smears of women is observed in chronic diseases, sexually transmitted infections, and dysbiosis. The reason for the identification of pathogenic gonococci is infection with gonorrhea.
Associated symptoms
Alarming signs associated with a violation of the microflora of the urogenital area are difficult to miss in 90% of cases. In women, vaginal discharge acquires a specific smell (fermented milk or fishy) and becomes abundant.
Common symptoms of cocci in a smear for men and women:
- discomfort during urination and intimacy;
- itching and burning of varying degrees of severity;
- swelling of the genitals;
- yellowish, white, purulent, bloody discharge from the genitals.
Women often complain of pain in the lower abdomen, weakness, and lack of appetite. This is due to the fact that during their life, pathogenic cells produce toxic substances. Foci of inflammation also form, causing noticeable discomfort.
If you have the above symptoms, you should immediately see a gynecologist, get tested and undergo a full course of therapy. Self-medication is prohibited!
What is a smear
The female internal genital organs are necessarily covered with a mucous membrane, and the condition of this mucous membrane and the state of the mucus can tell a lot about the female reproductive system.
The flora of the female vagina allows us to draw conclusions about the presence or absence of pathogenic fungi belonging to the genus Candida, which cause the well-known thrush, a variety of bacteria or protozoa, which cause a very large number of diseases; Also, based on the results of the smear, you can find out whether cancer cells have appeared, what condition the vaginal tissues are in, and even assess the state of hormonal levels.
Gynecological smears are different - there are four types: a smear for flora (the most common), a smear for sterility, a smear for cervical cytology (a test for so-called atypical cells) and a smear to detect hidden infections using the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method.
Complications
If you are not examined in time and treatment is not started, coccal infections will spread to neighboring organs, mucous membranes and skin. Complications largely depend on the type of cell. For example, streptococcus provokes meningitis, pneumonia, osteomyelitis (bone tissue damage). Staphylococcus causes endocardium (inflammation of the inner lining of the heart), pyoderma (purulent inflammatory processes under the skin), pneumonia, bronchitis, diseases of the upper respiratory tract (rhinitis, sinusitis) and the digestive tract. In addition, the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the vagina reduces the production of estrogen, which ultimately causes miscarriages and infertility.
Cocci in a smear during pregnancy complicate the process of bearing a child. The growth and development of the fetus are directly related to the health of the expectant mother, and the inflammatory process can affect not only the rectum and urinary canal, but also the uterus. To prevent danger, pregnancy should be planned in advance and, if necessary, therapy.
The most common consequences of coccal infections:
- cervical erosion;
- endometritis;
- pyelonephritis (kidney damage).
In men, in the absence of adequate treatment, cocci lead to prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate), damage to the testicles and seminiferous tubules. All this threatens impotence and infertility.
What is coccobacillary flora?
Coccobacilli - a mixed form of microbes, a symbiosis of cocci and bacilli - are gram-positive and gram-negative. Most often, such representatives of this pathogenic microflora are found as chlamydia, gardnerella and hemophilus influenzae. Parasites are transmitted sexually; a large number of them indicates the presence of a sexually transmitted disease.
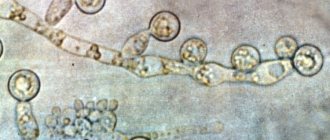
What do coccobacilli look like? Cocci look like rods, bacilli look like balls. Since coccobacilli combine the properties of cocci and bacilli, their shape is similar to an elongated ball.
Coccobacilli (mixed form of microbes) under magnification
Coccobacilli may be present in small quantities in the vaginal microflora; their active growth begins when the balance of bacteria is disturbed. Sometimes, during the treatment of sexually transmitted infections with antibiotics, the balance of the vaginal microflora is disturbed, which leads to the active growth of coccobacilli.
With sexually transmitted diseases, signs of infection with coccobacilli appear immediately; with bacterial vaginosis, determining the cause of the disease is much more difficult.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is a laboratory examination. In women, a smear is taken from the back wall of the vagina, urethra and cervical canal. For men, a special probe is inserted into the urethra (if inflammation has already begun, manipulation can be painful). Next, a sample of the biomaterial is sent to the laboratory, where it is stained (Gram method) and examined under a microscope. In some cases, additional diagnostics may be required: a swab from the throat and nasal cavity (if staphylococcus is suspected), general blood and urine tests.
Before carrying out the procedure, it is important to adhere to the following rules:
- do not urinate for 2 hours;
- do not consume spicy food and alcohol for 3-5 days;
- do not take medications for 3-5 days;
- abstain from intimacy for 2 days;
- do not use vaginal suppositories, do not douche for 2 days.
Attention! The analysis is taken before menstruation or 4-5 days after its end.
Treatment of infection
To eliminate coccobacillary infection, an integrated approach is required, which is aimed at getting rid of pathogenic microorganisms with the help of antibiotics, restoring the balance of vaginal microflora, and strengthening the immune system. Typically, several antibacterial drugs are used in therapy, since coccobacilli quickly develop protective immunity.
How to get rid of an infection - the main groups of drugs:
- When gardnerella is detected, Metronidazole is prescribed, an antibiotic with bactericidal, antifungal and antiprotozoal effects. Duration of treatment – 7 days.
- For chlamydia and gonococci - intramuscular injections of Ceftriaxone, an antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action. Duration of therapy is 7–10 days.
- For vaginal dysbiosis - Terzhinan, vaginal suppositories with a combined therapeutic effect, treatment is continued for 10 days.
- Amoxiclav tablets are a strong antibiotic, you need to take it for 7 days, it is effective against most undifferentiated coccobacilli.
- Vagilak, Acylact - suppositories, contain lactobacilli, restore the balance of microflora in the vagina. Duration of treatment – 2 weeks.
- Genferon, Interferon, Wobenzym are drugs to strengthen local and general immunity.
Ceftriaxone is an effective remedy for chlamydia and gonococcus.
If coccobacilli are detected during pregnancy, gentle forms of antibiotics are used for treatment - Klacid gel, Metronidazole suppositories. To restore the balance of microflora, you can use tampons with Lactobacterin for two weeks.
Treatment should be carried out by both partners at the same time, during therapy you should abstain from sexual intercourse or use barrier contraception.
Proper nutrition will help cure the infection faster - you need to exclude junk food, sweets, alcohol, the menu should be dominated by fermented milk products and plant foods. Probiotics should be taken during treatment with antibacterial drugs.
The presence of coccobacilli in the smear indicates an infectious disease or vaginosis; the pathology in women is more pronounced than in men. The disease requires immediate treatment with strong antibacterial drugs, otherwise infertility, adhesions and inflammation of the fallopian tubes may develop.
Treatment
If an abnormal number of cocci is detected in the smear, treatment should be carried out in accordance with all medical prescriptions. It is strongly recommended not to use general antibiotics. As already mentioned, many cocci are resistant to such medications, so therapy may be not only ineffective, but also dangerous. Under the influence of antibacterial agents, the growth of pathogenic cells will begin to increase, and the number of beneficial bacteria will begin to decrease.
In order for the fight against cocci to be as effective as possible, a sensitivity test is first carried out. Antibioticogram - bacterial culture of the vagina on a nutrient medium allows you to determine the level of susceptibility of pathogenic cells to certain drugs.
Metronidazole is considered one of the most effective drugs against coccal infections. Its main advantage is the absence of contraindications for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Together with antibiotics, medications containing lacto- and bifidobacteria are used. To restore normal microflora, vaginal suppositories, ointments and creams with antiseptic properties are used. At the same time, immunomodulatory agents can be prescribed. Douching with herbal decoctions should be performed strictly with the permission of the gynecologist.
Attention! At the same time, your regular sexual partner should also undergo treatment. At this time, it is better to refrain from sex, masturbation, and the use of tampons.
After completing the course of therapy, a smear on the flora is done again. If there is no positive result, another group of antibiotics is selected. In 70-80% of cases, hospitalization is not required; treatment is carried out at home or on an outpatient basis.
Treatment of cocci
When the first symptoms occur, a woman should consult a gynecologist and take a smear for flora. The smear is taken directly on the gynecological chair using a special sterile spatula. Before taking a smear, the woman does not douche, as this will affect the accuracy of the indicators. Mucus for the smear is taken from the urethra, cervical canal and vaginal vault. The material is applied to glass and subsequently dried and painted, after which it is studied in detail.
In a smear of a healthy woman, only single cocci located extracellularly can be detected. If a change in the vaginal microflora is caused by a sexually transmitted infection, then pathogens are usually found in the smear. With gonorrhea, for example, the normal microflora of the vagina is completely suppressed, and the smear is dominated by bean-shaped gonorrheal cocci.
With trichomoniasis, Trichomonas is detected in a smear. If microflora disturbances are not caused by sexually transmitted infections, but occurred as a result of other factors, an increased number of leukocytes, fungi (candida) and multiple cocci are observed in the smear.
As a rule, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. If cocci are present during pregnancy, the doctor prescribes medications that will not be potentially dangerous to the unborn child.
You should know that a woman can infect her sexual partner with cocci, so they should be treated for cocci together.
If the smear for cocci is outside the normal range, then the woman may be prescribed additional research to adequately treat the cocci. To detect a possible infectious pathology (mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, citalomegavirus, etc.), a woman is prescribed modern diagnostic methods: PIF, PCR, etc.
Symptoms of the disease
An increase in the amount of coccal infection in the body causes certain symptoms. Cocci can reveal themselves in that the discharge from the genital organs begins to smell unpleasant, itching appears, and urination becomes painful.
Normal vaginal discharge changes color. During sexual intercourse, unpleasant sensations appear.
It must be remembered that these symptoms are also observed in other diseases. Therefore, in order to make an accurate diagnosis, you need to go to the doctor and do laboratory diagnostics.
Any disease is accompanied by symptoms; cocci also have specific characteristics. Let's look at some of them:
- The most common symptom is the appearance of copious discharge, often quite thick, in the form of a clot on underwear and hygiene products. They are also noticeable when examined on the labia.
- The next symptom is an unpleasant odor, usually reminiscent of spoiled fish.
- Discharge of a yellow and sometimes green hue is a clear sign of the appearance of cocci.
- Another symptom is itching and burning in the groin area. The burning sensation when urinating is especially unpleasant.
- In extremely rare cases, there may be an increase in temperature and a deterioration in general condition.
These symptoms are quite obvious, so it is simply impossible not to notice them. Therefore, at the first symptoms, go to the doctor to get timely help.
If a woman belongs to the category of people who do not visit a gynecologist annually, you should know the most common symptoms of cocci infection.
- Vaginal discharge has an unpleasant odor (the smell is often said to resemble the smell of salted herring).
- The leucorrhoea becomes more profuse and thicker.
- Itching, burning, and discomfort are felt in the female genital area.
- The mucus takes on a yellowish tint, sometimes greenish.
- Pain when urinating.
- Pain during lovemaking.
These signs do not always indicate pest bacteria. They can be a consequence of other inflammatory processes in the body. To determine the cause, you need to consult a doctor. This way you will not harm your health, and will immediately eliminate the cause of your symptoms using the correct treatment method.
Diagnosis and treatment
Since cocci is a sexually transmitted disease, it requires simultaneous treatment of two partners. However, it is worth remembering that treatment is necessary only when symptoms appear that bother the girl.
In order to begin treatment, a laboratory test is carried out to determine the number of cocci, and a sensitivity test to certain drugs is also desirable.
First of all, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. The most common of them is Metrodinazole, which is quite effective and inexpensive, unlike others. Your doctor may also prescribe you an antifungal drug, most often Flucanazole.
Secondly, for greater effectiveness, vaginal and rectal suppositories are prescribed, which help cope with the problem from the inside (Hexicon, Polygynax, etc.).
Your doctor may also recommend douching with Miramistin or another remedy.
Coccal flora in a smear is prescribed by a doctor if it is difficult to determine the pathogen. Tests are taken at paid diagnostic centers and directly at an appointment with the attending physician.
It is advisable to take a smear test for flora in case of chronic infections of the throat and nose; complaints in the field of gynecology in women, prostate in men.
Types of bacteria
Bacteria vary in shape and structure, and can be solitary or located in groups. Some of them develop in aerobic conditions, others even without access to air.
To find out which microorganisms caused a specific disease, smears are taken from the mucous membrane in medical institutions. After staining the smear and examining the bacteria under a microscope, their further differentiation occurs.
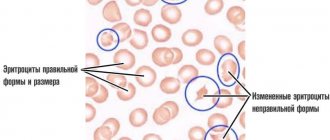
Cocci are spherical, round, sometimes slightly elongated bacteria.
Bacteria differ in shape, size, and growth pattern on nutrient media during incubation.
Thus, the gonorrheal bacillus has a characteristic bean-shaped shape. Candidiasis is accompanied by an increase in the number of fungi of the genus Candida and leukocytes, which are a sign of the inflammatory process.
Cocci in a smear in men are detected in the laboratory when examining the urethra. Bacteria are opportunistic and therefore do not normally cause discomfort or the development of diseases.
Against the background of a general weakening of the immune system, the prostate gland is affected with the subsequent development of bacterial prostatitis. The coccal flora is activated after injury to the genital organs, with slow healing.
Rarely, the cause can be a nosocomial infection - if the rules of asepsis and antisepsis are violated during operations on the reproductive organs.
Norm and deviations from indicators
When counting bacteria on nutrient media, there is a concept of the norm and its excess. Thus, in tests for pathogenic staphylococcus, attention is paid to exceeding the titer of 105. Normally, the vaginal microflora is acidic: therefore, bacteria do not develop.
With a slight increase in coccal flora in the smear, the reaction of the medium changes to neutral or slightly acidic (pH 5.0-7.0). A significant excess in the number of bacteria is indicated when the indicator is 7.5.
alkaline (pH at 7.5). The number of acidophilic lactobacilli, or Daderlein bacilli, is significantly reduced.
The microflora becomes gram-positive coccal. Single cocci that do not cause clinical symptoms are considered normal.
Why does infection develop - reasons?
Various reasons can provoke an increase in the number of cocci. Among the most common:
- long-term use of antibiotics
- genital infections
- chronic diseases
- early sexual life
- a large number of intimate partners
- failure to comply with hygiene measures
- abuse of oral contraceptives
- pregnancy
Do not put off visiting a doctor or self-medicate if you have one or more suspicious symptoms.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis is made on the basis of a comprehensive examination of the patient, which consists of collecting an anamnesis, studying the patient’s medical history, complaints, and cytological examination. Additionally, PCR diagnostics can be prescribed, which simplifies the differentiation of the causative agent of the disease.
Main symptoms of coccus infection
When visiting an ENT doctor, the patient may not even be aware of the presence of an imbalance in the microflora of the nasal mucosa and oropharynx. It is important to prevent the appearance of chronic foci of infection (dental caries, chronic tonsillitis), as they are an ideal environment for the proliferation of bacteria.
The infection can be threefold or chronic, in the latter case the symptoms are less pronounced. Upon visual examination, the doctor sees hyperemia of the mucous membrane and characteristic discharge.
A latent form of the disease will be confirmed by a smear for coccal flora. Mucus containing a small number of coccal cells is a sign of colpitis or dysbacteriosis.
What is the danger of cocci?
With a persistent increase in bacteria in the vaginal secretion, in addition to pronounced clinical symptoms, this negatively affects the state of the reproductive system of women as a whole. An excessive number of cocci in a smear leads to the following consequences:
- Estrogen production gradually decreases and completely stops.
- The balance of microflora is disturbed, the reaction of the environment becomes alkaline.
- Lack of estrogen leads to infertility and miscarriages.
The regularity of the menstrual cycle is disrupted.
- The presence of a chronic focus of infection causes a general weakening of the immune system.
Without treatment, serious diseases such as endometriosis and cervical erosion develop. In pregnant women, infection can cause miscarriage, bleeding, placental abruption, and premature birth.
A baby can also become infected in the womb. For the purpose of prevention, the gynecologist takes a smear on the flora twice during pregnancy in women.
How to treat cocci?
The human body is inhabited by a huge number of different bacteria involved in the course of basic processes. Moreover, the concentration of each strain has clear values and ensures the normal functioning of all human systems.
One of them is coca, which belongs to the opportunistic class of bacteria that can provoke the development of many diseases, including gynecological ones.
Normal vaginal microflora and possible types of coccal infection
In normal conditions, a woman’s vaginal microflora includes gram-positive bacilli or lactobacilli, the concentration of which can reach 90-95%.
Their purpose is to ensure the full functioning of the genital organs and prevent the development of pathogenic bacteria. Under the influence of lactobacilli inside the vagina, the level of acidity increases significantly, at which the formation of most pathogenic microorganisms becomes impossible.
The remaining 5-10% is occupied by other bacteria, among which there are various types of coca such as:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- tetracocci;
- diplococci;
- gonococci;
- meningococci;
- sarcins.
Most of these cocci can be present in the vagina, even with optimal acidity parameters. Single species of pathogenic bacteria may be present in the vaginal microflora.
- Treatment should begin as early as possible. Only a doctor can prescribe medications for this. Self-medication can lead to a worsening of a woman’s condition.
- During the course of recovery, it is worth giving up intimate relationships.
- If a coccal infection is caused by taking antibiotics, you need to exclude any types of them while the vaginal microflora is established. Or consult your doctor.
- A woman can infect her sexual partner with cocci, so they must undergo the course of treatment together.
A woman who visits a gynecologist on time avoids many health problems in the future, so don’t be lazy, but find time for your health.
Types of cocci, and what is their danger?
Coccus rods are microscopic organisms that live in the human body. They can be both useful and harmful.
It must be remembered that there are such concepts as opportunistic and pathogenic coccal microflora. That is, coccus bacteria are useful only when their population does not exceed a certain number.
How to treat cocci?
Treatment is prescribed by a doctor, it will differ depending on the cause of the disease. Timely contacting a medical center will prevent life-threatening complications.
Features of treatment of infection in women
Therapy consists of taking antibiotics orally, using antimicrobial drugs in the form of vaginal and rectal suppositories, and douching with antiseptic solutions. To restore normal microflora, probiotics are prescribed; in severe cases, the doctor additionally prescribes immunomodulators. The course of treatment ranges from 10-14 days.
After eliminating the pathogenic microflora, douching based on medicinal herbs with anti-inflammatory action is recommended: calendula, chamomile. Treatment of nonspecific colpitis in women consists of correcting hormonal levels. Often the disease occurs at the height of menopause due to a decrease in estrogen levels. Hormonal contraceptives are recommended for women of reproductive age.
If a coccal infection is detected in women, it is necessary to examine both partners.
How to treat pregnant women
Coccal flora during pregnancy is a dangerous condition that can lead not only to inflammation of the reproductive system, but also harm the fetus if left untreated. The doctor prescribes safe therapy for mother and baby, taking into account the side effects of medications. To make an accurate diagnosis, he uses modern methods of diagnosing diseases:
- PCR for detection of cytomegalovirus in the blood of a pregnant woman
- PIF to clarify the possible presence of an infectious disease (chlamydia, mycoplasmosis)
The cause of microflora imbalance in pregnant women is hormonal changes, decreased immunity, and stress factors.
Prevention measures
To ensure that cocci bacteria are not detected in a smear, you need to adhere to simple principles. Before taking antibiotics, you should always consult your doctor so that he can prescribe a safe dosage.
You need to wash every day. Linen is changed daily.
It is better to have one sexual partner than several at the same time. This will protect you from various diseases.
During sexual intercourse, the most reliable remedy against viruses and bacteria is a condom. Douching should only be used as prescribed by a doctor - as it disrupts the microflora.
The first sexual intercourse should only occur after full physical maturity. You need to carefully monitor your hormonal levels and regularly undergo laboratory diagnostics.
Support your immune system.
It is worth introducing a few simple habits into your daily life, thereby avoiding health problems.
- Minimize the “enemies” of the immune system: stress, strict diets, bad habits, etc.
- Avoid household chemicals as much as possible.
- Maintain daily intimate hygiene.
- Use personal items for hygiene.
- Use a special product for the intimate area.
- You need to wash from front to back using clean boiled water.
- Refuse synthetic and tight underwear, at least use them less.
- Decide on a sexual partner.
- During sex, give preference to barrier protection - a condom.
- Any antibiotic must be prescribed by a doctor. Some of them require the parallel use of special medications to maintain normal vaginal flora.
Source: ginekoloz.ru