Tomography of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is a reliable and accurate research method that allows specialists to obtain visual data on the functioning of internal organs. Thanks to this study, it is possible to timely detect pathologies of various types: cysts, tumors, metastases, bleeding, etc. In order for the procedure to be successful and reliable diagnostic results to be obtained, it is necessary to clearly know how to prepare for a CT scan of the abdominal organs.
When can the procedure be scheduled?
Computed tomography of the abdominal organs (hereinafter referred to as CT) can be performed in the following cases:
- If you suspect the presence of various types of tumors.
- With damage to the lymph nodes.
- For urolithiasis, kidney prolapse, cirrhosis, hepatitis.
- For problems with the gallbladder and pancreas.
- If abscesses, phlegmons, cysts are suspected.
- For injuries to internal organs.
Also, a CT scan of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is performed if neither radiography nor ultrasound helped to create a clear picture of the disease; these research methods turned out to be ambiguous and dubious.
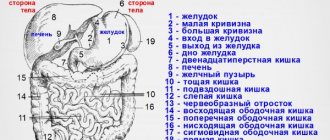
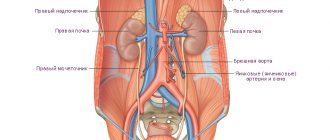
For accurate diagnosis of the abdominal cavity, computed tomography is the optimal way to scan the body. Thanks to CT scans, specialists have a clear picture of the health of the liver, pancreas, intestines, gallbladder, kidneys, and lymph nodes.
Is there a diet to be followed before a CT scan?
If a person requires a CT scan of the abdominal cavity, it means that he has serious problems with the digestive or other system of the retroperitoneal space. Computed tomography diagnoses problems in the intestines, stomach, spleen, kidneys, and pancreas.
You need to take this problem seriously and find out what is happening to your health. The study will determine the nature and severity of the disease and identify the presence of a tumor or inflammation.
In order for the diagnosis to be successful, it is necessary to adequately prepare for the study.
Is it possible to eat before a CT scan? What exactly? Your doctor will answer these questions. Adhering to a special diet is essential. The goal is to avoid gas and constipation.
On the day of the examination, intestinal motility should be reduced in order to obtain high-quality images. 3-4 days before tomography, you should follow the principles of a healthy diet, exclude gas-forming foods that enhance intestinal hypermotility: legumes, white bread, sauerkraut and fresh cabbage, nuts, raw vegetables, dried fruits.
Products that cause constipation: strong brewed tea, chocolate, pasta, milk, coffee, sweet confectionery.
Preparatory measures
Preparation for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity is carried out in order to achieve truthful, informative results of the study. The doctor must tell you how to prepare for the procedure. In order for the study to be successful, it is necessary to start preparing for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity 2 days in advance. To do this you need to do the following:
- Go on a diet, giving up foods that cause flatulence. Eliminate cabbage, legumes, whole milk, fruits, bread and pastries from your diet. You should also not drink carbonated drinks or alcohol.
- Many people are interested in: “Can I eat before a CT scan? " . Immediately before the procedure, eating any food is prohibited, as this may complicate the procedure. If the study is scheduled for the first half of the day, then you can sit down at the dinner table for the last time the evening before. If the study is carried out in the afternoon, a light breakfast is allowed.
- When preparing for a computed tomography scan of the abdominal cavity, it is imperative to take enterosorbent medications that prevent the occurrence of flatulence. You can drink activated carbon, Smecta tablets.
- Drink a laxative (for example, Fortrans) to cleanse the intestines. The drug should be taken on the eve of a CT scan of the retroperitoneum (in the evening or in the morning, depending on the time of the tomography).
- If the patient complains of pain in the abdomen, then he needs to drink any antispasmodic drug before starting the scan.
- Preparation for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity without contrast is slightly different from the same diagnosis, only with contrast. In the latter case, the patient needs to be injected with an iodine-based radiopaque agent. If intravenous infusion is planned, it is carried out only on an empty stomach.
- If the contrast agent will be administered rectally, then the evening before you need to give an enema.
- Often, patients are prescribed an abdominal CT scan with contrast , where the contrast agent is used orally. That is, a person takes the drug orally. Often doctors prescribe substances such as Urografin or Omnipaque.
You need to prepare for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity with contrast in the same way as without contrast, adhere to a diet, take laxatives, and enterosorbents. If a person has an allergic reaction to iodine, then a medical scan with contrast of the abdomen will be contraindicated for them.
How to prepare for an organ examination?
Preparation begins a few days before the study . It is quite simple and directed:
- to exclude possible contraindications ;
- cleansing the intestines and reducing the amount of gases in it ;
- contrasting of the gastrointestinal tract;
- solution to the issue of introducing medicated sleep in children.
What is it for? The main goal of the preparatory stage is to improve the quality of the resulting image.
Indeed, in the presence of food masses or gases in the digestive tract, the visualization of nearby organs deteriorates. Yes, and intestinal loops can be mistaken for a tumor or enlarged lymph nodes. The patient’s physical activity also distorts the results.
Pronounced artifacts that complicate the interpretation of results are caused by residual barium suspension in the intestine. In this regard, persons who have undergone X-ray contrast examination of the intestines should refrain from performing computed tomography until the contrast is completely evacuated from the body. This may take several days. Monitoring the process is possible using plain radiography of the abdominal cavity.
Important Preparation is neglected if the study is performed for health reasons.
Diet before the procedure
The amount of preparation of the gastrointestinal tract during MSCT of the abdominal cavity may differ depending on which part of it needs to be visualized.
Table 1. Preparation of the gastrointestinal tract.
| Digestive system department | Recommendations |
| Stomach, duodenum, pancreas | · do not eat solid food for 12 hours; · do not eat or drink for 6 hours. |
| Small intestine | · do not eat solid food during the day; · follow a low-slag diet (2-3 days); · ensure plenty of fluid intake (up to 3 l); · cleanse the intestines on the eve of the study using mild laxatives. |
| Colon | · drink a lot and not eat solid food for 2-3 days; · follow a diet; · use laxatives; · in the morning on the day of the study - microenema. |
The diet before the study consists of eating easily digestible foods and limiting foods that increase the formation of gases in the intestines and complicate digestion. These include:
carbonated drinks;
- legumes;
- baked goods;
- sweets;
- fresh vegetables;
- smoked meats;
- fatty meat or fish;
- fast food;
- coffee, strong tea;
- nuts;
- fresh milk;
- some porridges (millet, pearl barley);
- dried fruits.
What you can eat before the test:
- vegetable soups;
- broths;
- porridge;
- lean fish or boiled meat;
- jelly, compotes, juices;
- dairy products.
Table 2. Sample menu before the study.
| 1st day | |
| Breakfast | Mashed potatoes, boiled fish, weak tea |
| Dinner | Vegetable soup, oatmeal, steam cutlet, apple juice |
| Afternoon snack | A glass of kefir |
| Dinner | Steam omelette, compote |
| 2nd day | |
| Breakfast | Cottage cheese casserole, juice |
| Dinner | Meat broth soup, meatballs, buckwheat porridge, weak tea |
| Afternoon snack | Baked apple |
| Dinner | Cream soup, jelly |
Medicines
Recommendations regarding taking medications are given by the doctor. For each patient they may have their own characteristics. Most often prescribed:
- sorbents (activated carbon) and espumisan - to reduce gas formation;
- laxatives - to cleanse the intestines;
- antispasmodics - to eliminate abdominal pain as a result of cramps, if any;
- enzymes – for digestive problems.
Enzymes to improve digestion
The time of administration of contrast and its volume is determined by the doctor. It depends on which part of the abdominal cavity is being examined.
- If it is necessary to visualize only its upper part , then contrast is administered in a volume of 500 ml 30-60 minutes before the start of the procedure.
- To contrast all parts of the intestine, the amount of contrast is increased to 1-1.5 liters. Preparation starts earlier. To do this, the patient drinks water with a dye dissolved in it at the specified time (12 hours, 2 hours and 30 minutes before the start of the study).
Barium sulfate, iodine-containing agents, and methylcellulose preparations can be used as a contrast.
If it is planned to study parenchymal organs (for example, the liver) or blood vessels (the abdominal aorta), contrast agents are additionally administered intravenously. In these cases, a tolerance test should be performed. For allergy sufferers, preparation is supplemented by the administration of antihistamines and, if necessary, corticosteroids.
Please note: If the patient has concomitant diseases and regularly takes any medications, he should inform the doctor about this, as this may affect the course of the procedure.
General recommendations for preparing for a body scan
For the procedure to be successful, you need to take into account every detail, know how to prepare for a CT scan so that the results of the study are complete and reliable:
- Take care of comfort. Wear comfortable clothes without zippers, fasteners, or buttons. Do not wear jewelry.
- Take the necessary documents - passport, results of previous examinations, medical card, etc.
- Breath control. During the procedure, the specialist instructs the patient to hold his breath for a few seconds at a certain time (before each new cut).
- Before CT scanning of the abdominal cavity, it is necessary to remove existing dentures.
- Be sure to inform your doctor about the presence of any diseases or pathologies. And also inform him about the presence of a pacemaker, an allergy to iodine and other factors due to which the diagnostic process may be disrupted.
Proper preparation for computed tomography allows you to obtain the highest quality images, from which the doctor assesses the patient’s condition and makes an accurate diagnosis.
Safety of the procedure
Since diagnosing internal organs using computed tomography involves irradiating the body, it is logical that many people ask the question: “How safe is the procedure and how often can an abdominal CT scan be done?”
The safety of the procedure depends on the equipment used and the area of exposure. In modern installations, the radiation dose is small compared to a conventional X-ray machine, so there is no need to worry about side effects. If the diagnosis is carried out once, it will not be hazardous to health. In cases of repeated or frequent CT scanning, it should be understood that radioactive substances accumulate in the body, so it is advisable to perform tomography once a year. If it is necessary to carry out the procedure more than once, an interval of 1–2 months should be maintained.
Only a doctor can determine how often a CT scan of the abdominal organs should be done.
Additional preparation measures
Preparation for MSCT takes place directly at the medical center where the study is carried out. An agreement is drawn up and the necessary signatures are placed.
If the patient has pictures taken from previous tomographs, they must be given to the doctor. This will help him create an idea of the dynamics of the disease.
Before the diagnostic room, the patient must remove metal items (earrings, chains), lay out his cell phone, bank cards.
If the subject’s body contains metal prostheses, implants, a pacemaker or other electrical devices, tattoos, the paint of which contains metal-containing particles, the procedure cannot be performed.
These factors will prevent you from obtaining correct results during the examination.
Limitations in scanning internal organs
Despite the safety of the procedure and the high degree of information content, in some cases CT scanning of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is prohibited.
Absolute contraindications:
- Pregnancy - there is a risk of pathologies in the unborn child.
- Nursing women – after the procedure, the level of radioactive substances in breast milk increases.
- Severe pain syndrome. First, you need to relieve the pain using painkillers, and only then begin the study.
- Hyperkinesis is a pathology associated with the appearance of involuntary movements. After all, for a computed tomography scan of the abdominal cavity, it is important that the patient lies still. Only under this condition can high-quality photographs be obtained.
Relative contraindications to CT:
- Age up to 18 years. A child's body is 5 times more susceptible to radiation than an adult. If it is possible to replace tomography with another research method, for example, MRI, then it is still better to resort to the latter.
- Overweight people. In this case, the limitations are related to the characteristics of the equipment. Closed-type tomographs are not designed for obese or overweight patients. To perform a tomography, you need to go to those hospitals that have open-type devices. Excess fat can also interfere with abdominal CT examinations in obese people.
- Panic attack. If the patient cannot control himself, he panics, he is in a state of passion, then the scanning process will be difficult. In this case, the person is given a sedative or sleeping pill to drink. In some cases, they resort to general anesthesia (often it is used in relation to children, because it is very difficult for them to lie still during the entire procedure and not move).
- Presence of metal objects, plaster. These items affect the quality of the research being carried out - glare and darkening will appear in the pictures.
A more extensive list of contraindications will be provided if tomography is performed with a contrast agent. Then it is prohibited to carry out the procedure for the following problems:
- Liver or kidney failure. After all, it is the kidneys and liver that are responsible for removing the contrast agent from the body. And if these organs are not functioning well in a patient, then performing a CT scan of the abdominal cavity with contrast can greatly harm them. The patient may experience poisoning, and it will take a long time for him to recover after the procedure.
- Problems in the functioning of the endocrine system. If the functioning of the thyroid gland is impaired, tomography with contrast will be unsafe, since iodine can enhance the development of the disease and aggravate its course.
- Allergic reaction to iodine. It is prohibited to perform a CT scan of the retroperitoneum and abdominal cavity on people sensitive to iodine, since this substance can cause poisoning in them, even leading to anaphylactic shock.
- Severe general condition. If on the day of the procedure the patient is in a very serious condition, then it will be more important to provide first aid to him than to perform a CT scan.
Purgation
To obtain the best quality images, it is necessary to thoroughly cleanse the intestines of feces. This problem is especially relevant for people who have intestinal conditions such as constipation or increased gas production.
In these cases, bowel movements are performed using cleansing enemas and laxatives. The medications are taken for three days before the CT scan.
List of products used to cleanse the intestines, eliminate gas formation and constipation: Enterosorbents of the old and new generation: Espumisan, activated carbon, White coal - reduce gas formation. Drink plenty of water to avoid constipation.
Fortrans is a powerful, cleansing laxative. Apply the day before the scan.
Antispasmodics - for intestinal hypermotility: Spasmolgon, No-shpa.
Dysfunction of the digestive tract - enzyme preparations: Mezim, Festal.
CT technique
It's time to find out how the tomography procedure works:
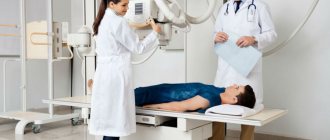
- After presenting all the necessary documents, previous test results, consultation, the patient is asked to take a horizontal position, lie down on the tomograph table and lie still.
- If a patient undergoes a CT scan with contrast, then he is first given an injection with a contrast agent (provided that he did not take the contrast agent orally).
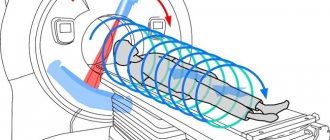
- After the patient lies down on the couch of the device, he is automatically moved inside the ring of the device. This is where the CT scan procedure is performed.
- During a CT scan of the retroperitoneal space and abdominal cavity, the specialist can ask questions to the patient via two-way communication, give commands to hold his breath, ask how he feels, etc. When CT scanning the abdominal organs, and indeed any organ in general, it is forbidden to move .
The duration of a medical scan of the abdominal organs depends on the type of study and the quantitative indicators of checking the internal organs. Typically, a CT scan with contrast lasts no longer than 30 minutes, without it – 15 minutes.
Computed tomography does not cause pain or discomfort. All that is required of the patient is to lie still and listen to the doctor.
Specialized training
When examining retroperitoneal lymph nodes, drink two glasses of boiled water with a contrast agent dissolved in it (25 ml per liter). The first portion is drunk 45 minutes before the procedure, the second glass - 10 minutes before the examination.
CT scan of the bladder: contrast concentration - as in the previous description. A glass of solution is drunk 4-7 hours before the scan. Next, before the procedure, the urologist performs manipulations.
A pelvic examination in men should be performed with a full bladder. 3 hours before the examination, a contrast solution is taken orally or, at the discretion of the radiologist, intravenous contrast is used.
During tomography of the female pelvic organs, the patient drinks a similar solution 6 hours before the procedure. Before starting the examination, the doctor injects a mixture of water (distilled) and contrast through a catheter into the patient’s bladder.
Results of the analysis
A CT scan of the abdominal cavity is interpreted immediately after the diagnosis is completed. The specialist receives the finished images and begins to decipher them. This process usually takes 1 hour. After deciphering the results, the patient is given the photographs, as well as a doctor’s report with his signature and seal.
What does an abdominal CT scan show? Based on the results of the procedure, specialists are able to obtain the following data:
- The exact location, size and shape of the organs being examined.
- The presence of benign or malignant tumors, metastases, infections, bleeding, excess fluid.
- Detection of stones in the kidneys and gall bladder.
- Presence of inflammation in internal organs, etc.
Abdominal CT is a modern, accurate method for diagnosing diseases of internal organs. This research method is performed only according to doctor's indications. A CT scan is prescribed if the specialist is unable to obtain accurate information about the condition of the organs during an ultrasound scan.
Features of preparation for contrast administration
Intravenous administration of contrast agent is carried out strictly on an empty stomach. If you plan to administer rectal contrast, you should drink a laxative or do a cleansing enema the day before.
It is necessary to consult with your doctor about the need and method of taking a contrast agent if oral contrast is planned. The generally accepted design may vary depending on the purpose of the study.
If the oral route of administration of contrast is recommended, the patient must, on the eve of the study, purchase a contrast agent from a pharmacy according to a doctor’s prescription and prepare the solution in accordance with his recommendations. The typical regimen for taking the drug, which may be indicated in the instructions, can be changed depending on the purpose of the study and the characteristics of the patient’s body. Typically, the pharmaceutical solution is diluted in 1 - 1.5 liters of boiled water and taken in 3 or 4 doses during the day before the test.
Indications, restrictions
Considering the potential risk of radiation damage to organs and tissues, MSCT of the OBP is prescribed over the low information content of ultrasound methods and endoscopic examinations.
The method is indicated for diagnosis:
- volumetric formations of the abdominal cavity;
- focal lesions of parenchymal organs;
- prevalence of malignant neoplasms;
- purulent destructive diseases;
- acute mesenteric ischemia;
- traumatic injuries;
- perforations;
- acute pathology of the gallbladder;
- intra-abdominal bleeding;
- obstructive jaundice;
- intestinal obstruction;
- dissection, rupture of the abdominal aorta.
The procedure is limited during periods of active growth and development in children and adolescents under 18 years of age and in pregnant women.
In patients with pathology of the kidneys, thyroid gland, or a history of allergic reactions, scanning is performed only after assessing the functional state of the organs and carrying out specific preparation.
How does the scan work?
Patients, having received information about the study, change into loose clothes and go to the diagnostic room.
If diagnostics with contrast are planned, a peripheral venous catheter is installed. In the hardware room, a laboratory assistant helps you take the correct position on the mobile tomograph device.
Starting position: lying on your back, arms above your head. The limbs are secured with straps.
The table with the patient moves inside the tomograph frame and stops at the level of the study area.
When scanning is started, the table moves continuously and covers the area from the dome of the diaphragm to the pubic symphysis. During the diagnosis, you will need to hold your breath while inhaling once upon the doctor’s command.
After data collection, the couch moves out of the frame, the patient is released from the restraints and escorted to the waiting room.
MSCT with contrast agents
For the study, iodine contrast agents are used in a volume of 100 ml. The drugs are injected into the bloodstream through an automatic syringe injector attached to the venous catheter. The delivery rate of iodine-containing contrast is 4 ml/sec.
Contrast enhancement makes it possible to diagnose oncological processes, acute surgical pathology - acute pancreatitis, perforations, bleeding, etc.
Scan duration
Diagnostics of the abdominal cavity using MSCT machines takes 9-14 seconds. With bolus contrast enhancement, the examination may take up to 15-20 minutes due to repeated scans that are taken at each contrast phase.
Cost of the study
The price for 1 tomography session depends on the examination area, the use of contrast agents, narcotics, sedatives and antispasmodics.
Average prices per procedure:
- native examination of the abdominal cavity - 5-6 thousand rubles;
- scanning of the abdominal cavity with bolus contrast - 9-10 thousand rubles, excluding contrast agent;
- MSCT angiography of the abdominal aorta and its branches - 8-10 thousand rubles;
- iodine-containing contrast agent - 7-10 thousand rubles.
Description of the MSCT technique
Diagnostics is based on the effect of X-rays on the object under study, followed by analysis of the degree of absorption of radioactive radiation by tissues.
During scanning, an X-ray tube rotates around the patient and generates beams that pass through the body and are picked up by sensors.
The obtained data is converted into a planar image of the slice under study. In 0.5 sec. the doctor receives up to 64 sections, and in 15 seconds more than 2000 images.
From the images of the sections, three-dimensional models of organs are created with the possibility of subsequent reconstructions.