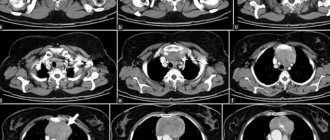
Introduction
Soft
tissues
are structures of the human body that vary in structure; soft tissues usually include muscles, tendons, synovial membranes, adipose tissue, fibrous connective tissue, blood vessels and nerves.
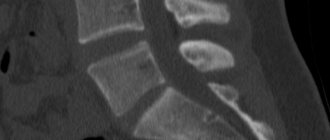
MRI of soft tissues can be performed in conjunction with examination of other structures (upper or lower extremities, joints, spine, internal organ systems), or prescribed individually based on identified symptoms.
| Types of soft tissues in the human body | MRI of soft muscle tissue |
Classification of tomographs
MRI of soft tissue structures is performed on a special installation - a tomograph. The devices differ in appearance (open and closed) and generate different levels of magnetic field voltage.
According to external design features, tomographs are divided into:
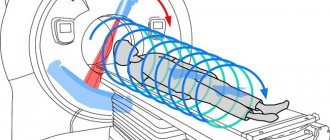
Closed or tunnel tomograph
– a device consisting of a cylindrical scanning capsule and a retractable couch for placing the patient. The magnetic field voltage of such an installation is 1.5 -3 Tesla, high scanning speed and image resolution.
Advantages of closed-type tomographs in diagnosing the condition of soft tissues:
- Creates targeted projections with the smallest slices. Capable of visualizing in detail the brain and spinal cord, blood vessels, lymph nodes, and internal organs.
- Detects pathologies at the formation stage.
- Explores neurophysical processes within soft tissues.
Negative sides:
- Examination in such a device can provoke a panic attack in a patient with a pathological fear of closed spaces.
- The diameter of the capsule limits diagnosis in obese patients.
- The load capacity of a pull-out couch is less than that of open-type equipment.
Open tomograph
– a device consisting of a movable table, upper and lower magnets. It has weaker technical indicators, generates a weak magnetic field voltage of up to 1 Tesla, due to this the scanning duration increases.
Positive aspects of the equipment:
- Low cost of research.
- Low energy consumption.
- Convenient accommodation for children, disabled people, patients with anxiety disorders.
Disadvantages of the devices:
- The low quality of images makes it difficult to diagnose pathologies at the formation stage.
- It takes twice as long to conduct the study.
| Open MR tomograph | Closed-type MR tomograph |
According to magnetic field voltage indicators, tomographs are divided into:
- A device with an ultra-low magnetic field up to 0.1 Tesla.
- Low-field installation that generates an operating magnetic field voltage of up to 0.5 Tesla. It has a highly specialized area of application, for example MRI of soft tissues of the hand. The non-aggressive environment allows for examination of patients with metal implants.
- A mid-field tomograph generates voltages up to 1 Tesla. Creates low-quality projections and is not effective for determining the disease at the initial stage of formation.
- The high-field unit with a magnetic field of 1.5 Tesla is a tunnel tomograph. Creates projections in high resolution and with sufficient detail to detect incipient foci of pathology.
- The ultra-high-field device generates a magnetic field with a voltage of 3 Tesla and higher. To conduct clinical studies, equipment with a voltage of 3 Tesla is used. A field exceeding this limit is considered potentially dangerous to the body. Such installations are found only in research laboratories.
For a high-quality diagnosis of the condition of soft tissues, a tomograph with a voltage of 1.5 Tesla is sufficient.
| Image quality depending on equipment power |
Progress of the procedure
The tomograph is a capsule camera with a retractable table. There are open and closed type devices. To scan the desired area, the patient lies down on a retractable couch. Limbs are fixed if necessary. The table slides into the camera of the device, the doctor begins scanning the desired area.
During the entire procedure, it is important to remain in a supine position and not make any movements. A stationary posture will ensure an accurate examination result. You cannot move your head, body, arms or legs. The device has an intercom, which is used to negotiate between the patient and the diagnostician.
After the scan is completed, the patient returns home to his normal life. The results should be communicated to the attending physician.
Indications
The attending physician may refer the patient for examination of soft tissue structures using magnetic resonance imaging if there is a history of one or more factors:
- Old and recent injuries. Presence of hematomas, abscesses, fractures.
- Pain in the muscles for no apparent reason.
- Swelling.
- Chronic inflammatory processes.
- Increased size of lymph nodes.
- Vascular pathologies.
- Suspicion of tumor neoplasms.
MRI of soft tissue structures of the neck is prescribed if the following symptoms are present:
- Impaired functioning of the salivary glands.
- Partial or complete loss of voice without obvious reasons.
- Cerebrovascular accident.
- Problems with the thyroid gland.
- Changes in the structure of soft tissues in the larynx area.
- High blood pressure.
Examination of the soft tissues of the upper and lower extremities is carried out in cases of manifestation:
- Pain in the absence of excessive physical exertion and injury.
- Swelling.
- Formation of internal scars at the site of old injuries.
- Hematomas.
- Numbness and weakness in the muscles, tremors.
- Bone calluses.
- Inflammatory processes in the joints.
- Impaired motor activity.
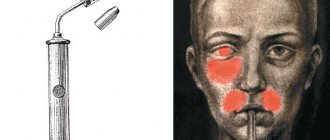
An MRI scan of the soft tissue structures of the face is performed in the presence of the following symptoms:
- Neuritis of the facial nerve.
- Unpleasant and painful sensations during operation of the jaw joint.
- Non-stop headaches.
Indications for MRI of soft tissues of the gluteal region are the following factors:
- Severe pain in the area of the sacrum, coccyx, buttocks.
- Poor circulation in the pelvic organs and gluteal region.
- Pinched nerve endings, numbness of muscle tissue.
MRI of soft tissues is also performed to determine the need for surgical intervention, carry out postoperative monitoring, and evaluate the effectiveness of conservative therapy in the treatment of tumor formations.
Types and features of the procedure
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of soft tissues does not have a radioactive effect on the body and is completely safe for humans. Unlike CT, the study clearly depicts the bone structure and any necrotic process. Using a tomograph you can identify:
- tumors;
- malignant neoplasms;
- fibrosis;
- scar complications;
- nodes;
- abscess;
- neuropathy;
- pathologies of glands and lymph nodes;
- nerve inflammation;
- post-traumatic change;
- hematoma;
- tendon damage.
In the human body, soft biomaterial accounts for a significant proportion. A unique diagnostic method is based on the effect of an electromagnetic field on organic structures. Magnetic resonance imaging produces an accurate scan that provides all the information the doctor needs. The examination is carried out using modern equipment, which reveals even the smallest changes in structural tissues. The waves pass through the biomaterial and do not have any destructive effect on the cells.
The method helps to diagnose a number of soft tissue diseases and inflammatory processes. Possible scanning of the spine, MRI of joints, brain (MRI and CT). Frequent MRI studies are performed in cases of oncological processes.
The procedure visualizes tissue sections from different angles. The diagnostician detects pathology at the earliest stage. In addition to conventional scanning, if necessary, an MRI of soft areas with contrast is performed. The procedure involves the introduction of a tissue-staining drug into the body. The contrast agent helps to visualize even the deepest layers. The biomaterial is stained with the injected drug, resulting in accurate images. After the procedure, the contrast is excreted from the body through urine and feces.
The advantage of the MRI method of soft zones is the detection of pathology in the most inaccessible tissues. This is a tomography that allows you to scan the ligamentous apparatus, spinal cord, intervertebral space and columnar discs, and the inner ear.
MRI of soft tissues of the face
Using the MRI procedure, inflammation of the facial nerve, pathologies of the salivary glands, internal hematomas, and fibrosis of adipose tissue can be easily determined. Scanning is prescribed to detect cancer and inflammatory processes. The procedure reveals circulatory disorders, atrophy and necrosis, and determines cell metabolism.
A tomograph allows one to distinguish the benign nature of a neoplasm from a malignant process. This is especially important for a positive prognosis of cancer. The procedure helps to determine how much the biomaterial has changed. MRI when examining the soft tissues of the face shows the presence of compactions, tumors, inflammation, the size and characteristics of the lesion.
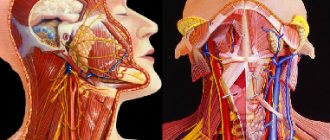
MRI of soft tissues and organs of the neck
The neck is a part of the human body in which the thyroid gland, larynx, lymph nodes, vertebral arteries, and muscle structures are located. Using the procedure, cysts, neoplasms, proliferation of cellular structures, fistulas, and inflammations are differentiated. The advantages of the MRI technique of the neck - it helps to identify pathologies of the parathyroid glands and lymph nodes, vascular pathologies. All this biomaterial requires careful diagnosis for various diseases.
During the procedure, the specialist identifies pathologies of the vascular bed and the direction of blood flow, changes in the thyroid gland and throat, and enlarged cervical lymph nodes. The tomograph also helps to visualize the condition of the cervical intervertebral space. Typically, a neck scan is performed with a contrast agent injected.
MRI of soft tissues of the gluteal region
The development of pathologies in the gluteal region is sometimes closely related to diseases of the spine. The soft biomaterial of the buttocks is subject to various inflammatory processes. Magnetic resonance imaging can show all the internal structures of the buttock. The procedure does not cause discomfort and allows for thorough examination of biological material. MRI of the buttocks is prescribed for:
- soft tissue injury;
- infiltration;
- pathology of the great vessels;
- abscess;
- muscle strains;
- impaired blood circulation;
- nerve damage in the coccygeal-sacral region;
- malignant process;
- phlegmon.
The scan shows the gluteal region in a section in various projections. The diagnostician evaluates the condition of muscles, blood vessels, and nerve trunks. The received data is displayed on the monitor and processed by a computer. Examination of soft tissues is carried out both with and without the introduction of contrast.
MRI of soft tissues of the extremities
The area of interest is displayed on the monitor in a layer-by-layer image. Human limbs are permeated with various structures. Legs and arms may be subject to injury, stretching, damage to blood vessels and nerve endings. Sometimes there is a need to diagnose connective tissue, tendons, and muscles. All this soft material of the human body is successfully scanned using a tomograph.
For pain, general weakness, swelling, numbness and swelling in the limbs, it is necessary to undergo a limb examination (MRI). A joint scan (MRI of the knee joint) is performed if space-occupying lesions are suspected, after tendon damage, before and after various surgical interventions. A detailed analysis of the limbs helps the doctor establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct therapy.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging examination of soft tissues does not harm the body. But even he has a number of contraindications.
All contraindications to MRI are divided into two categories: relative and absolute.
Relative contraindications
– these are rather restrictions on conditions, rather than a complete ban on conducting research.
Absolute contraindications
– risk factors for the health and functioning of the body. If at least one of them is present, MRI is impossible.
Relative contraindications include:
- Mental disorders and fear of confined spaces.
- Body weight exceeding the maximum load capacity of the pull-out couch.
- Body dimensions exceeding the diameter of the tomograph tunnel.
- First trimester of pregnancy.
- Epilepsy or EPI syndrome in the acute stage.
- Having colored tattoos or permanent makeup on the body using metallic ink.
- Alcohol intoxication or the presence of drugs in the body.
- Severe physical exhaustion and dehydration.
The list of absolute contraindications consists of the following items:
- The presence of electronic life support devices in the body: artificial pacemaker, pacemaker, defibrillator.
- Presence of devices dosing medications: insulin pump.
- Cochlear apparatus.
- Ilizarov apparatus and other metal implants that fix the bone structure.
- Ferromagnetic hemostatic clips.
- Stuck metal fragments or bullets near vital organs.
Contraindications for the administration of a gadolinium-based contrast solution are discussed separately.
Before starting a magnetic resonance examination of soft tissues, consult with a specialist in order to promptly identify possible contraindications to the procedure.
Indications and contraindications
The main indications for the procedure are:
- limited body mobility;
- pain in muscles, joints, tendons;
- change in shade of soft fabric;
- swelling;
- impaired lymphatic drainage;
- redness;
- suppuration;
- increase in body temperature with pathological changes;
- disturbances in the functioning of the organ that covers the soft material.
Pain, poor circulation, inflammation and purulent abscess should be the reason for immediate scanning of the soft structures of the body. This diagnostic method is prescribed to search for metastasis in cancer. For dizziness and headaches, a scan of the soft tissue of the brain and an MRI of the pituitary gland are performed. The study allows you to evaluate pathological changes in tissues and the condition of soft areas. Scanning of a tumor of soft structures can be performed to determine its size and effect.
Contraindications for MRI are the presence in the body of metal prostheses, staples and implants, a pacemaker, or a hearing aid. Scanning is not performed in the first trimester of pregnancy, in case of claustrophobia and mental disorders. During pregnancy, MRI is performed only as prescribed by the attending physician.
How does the procedure work?
Carrying out magnetic resonance imaging examination of soft tissues consists of several stages: organizational arrangements, preparation for MR scanning, procedure, issuance of results.
Organizational aspects of MRI include:
- Preparation of documents.
- Checking the necessary documentation for undergoing a study under the compulsory medical insurance or voluntary health insurance program.
- Concluding an agreement for paid services during examination on a paid basis. Making payment.
Preparing the patient for magnetic resonance scanning:
- Determination of possible contraindications: filling out a questionnaire or conversation.
- Conducting an MRI with contrast requires an additional test for the body's sensitivity to gadolinium.
- Weighing.
- Selection of a suitable drug and calculation of the maximum permissible dose.
- Changing clothes: comfortable home clothes without metal elements or a disposable hospital gown.
- Instructing the patient: the nurse explains the rules of behavior during the procedure and the sequence of the study.
Stages of soft tissue MRI:
- The patient is placed on a retractable couch, the body is secured with special fixations, and additional sensors are installed if necessary.
- The table moves into the area where the scanner is located and the study starts.
- MRI with contrast takes place in two stages: a basic scan without the drug, injection of a contrast solution and repeating the procedure.
- After completing the study, the patient must wait for the conclusion. The specialist will notify you in advance about the time the results will be received. It is also necessary to spend some time under the supervision of medical staff if the reaction to the contrast solution was too strong.
Output of results:
- The conclusion can be obtained within an hour from the completion of the study or the next day. The time depends on the workload of the radiologist performing the description of the images.
- The patient receives a printed report, a completed image and/or a recording of MRI images on an electronic disk.
- Some medical institutions send MRI results to the client and/or referring physician by email.
In some clinics, it is possible to ask a question to the radiologist based on the results of the study. A specialist can tell you what steps to take next.
How to prepare for the procedure
On the eve of the study, you must not drink alcoholic beverages and eat light food. Before the study, a woman should not apply makeup, as decorative cosmetics may include microdoses of metal. This may cause distorted scan results.
The administration of a contrast agent is required if a tumor is suspected. Before using contrast, it is tested for allergic reactions.
Preparing for the study:
- The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach, it is necessary to empty the bladder of fluid.
- Wear comfortable underwear and do not wear makeup.
- Remove any metal jewelry, glasses, or watches from your body.
- When conducting an examination of the abdominal organs, the intestines are cleansed using an enema.
- If it is necessary to examine the organic structures of the pelvis, then the scan is performed on a full bladder. For this purpose, the patient drinks about two liters of water 2 hours before the diagnosis and does not visit the toilet, refraining from urinating.
Duration of the procedure
MRI diagnostics of soft muscle tissue is performed in approximately 45 minutes using a closed-type device with a working magnetic field strength of 1.5 Tesla.
A similar study on a tomograph with a lower magnetic field voltage will increase the procedure time from 45 to 90 minutes.
Examination of soft tissues using an installation with a magnetic field voltage of 3 Tesla will require no more than 15 minutes.
Dual-phase MRI with contrast doubles the examination time, regardless of the technical characteristics of the tomograph. The specialist performs a basic scan without gadolinium, after which a solution is injected to form a contrast medium and the study continues.
What does it show
In the absence of pathological processes in soft tissue structures, the decoding protocol will contain the following indicators:
- The structure is homogeneous, without compactions.
- There are no signs of traumatic injuries.
- Lymph nodes have no signs of deformation, their sizes are normal.
- The blood flow is not impaired.
- Calcifications and other signs of neoplasms have not been established.
MR imaging of soft tissues allows us to identify a number of the following pathologies:
- Developmental defects and genetic abnormalities of the structure of soft tissue structures.
- Traumatic injuries of various types: rupture and stretching of muscles, violation of the integrity of ligaments, damage to tendons, compression of blood vessels, rupture of the outer membrane of the lymph node.
- Post-traumatic manifestations: fibrosis, scar, hematoma.
- Inflammatory process: fluid accumulation, infiltration, abscess.
- Vascular pathologies: thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, aneurysm, pinching.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms, their size, location, degree of development.
Indications for research
Damage to soft tissue occurs due to the inflammatory process, traumatic effects and due to the growth of tumors. The choice of diagnostic method in favor of MRI is indicated in the following cases:
- developmental anomalies leading to dysfunction of the organ;
- injuries with suspected complete or partial ruptures of tendons, muscles, hematomas;
- benign and malignant formations, cysts;
- foreign bodies;
- autoimmune connective tissue diseases;
- inflammatory changes in tendons, ligaments, muscles;
- inflammatory processes with purulent complications: abscess, phlegmon;
- muscle pain of unknown origin, limitation of movement;
- scar tissue changes that disrupt normal blood flow;
- vascular pathology (aneurysm, thrombosis, malformation);
- damage to peripheral nerves;
- damage to lymphatic vessels, nodes;
- dysfunction of the thyroid and salivary glands.
What's the difference with and without contrast?
Contrast agent
is a special component to increase diagnostic accuracy.
To create a contrast medium, preparations based on gadolinium chelates containing metal ions are used. They are classified into two groups: organ-specific and extracellular. Pharmacology has provided several types of such contrasts:
- Magnevist
- Gadovist
- Prohens
- Optimark
- Omniscan
- Let's do it.
The ability of a contrast agent to illuminate tissue makes it possible to determine as accurately as possible the location of the pathological focus, the size and shape of the defect, and the direction of spread of pathological disorders.
| On the left is an MRI performed with contrast; on the right without contrast solution | ||
The circulatory system is responsible for transporting the drug, and the ability to accumulate in the damaged area is influenced by the speed of chemical processes and blood circulation.
Contrast enhancement is indicated for patients with a preliminary diagnosis of an oncological neoplasm in soft tissues, when assessing the response of the pathology to therapy.
Methods for administering contrast solution:
- A one-time intravenous injection before the start of the study.
- Dynamic enhancement of the contrast medium through gradual administration of the drug through a dropper.
The method of drug administration is determined by the doctor, based on the purpose of the examination.
Rules for conducting and preparing for MRI with contrast:
- Prescribing contrast-enhanced MRI diagnostics is possible only if there are appropriate clinical indications. It is necessary to evaluate the possible risks and benefits of such a study.
- Before referring you for an MRI with contrast, the doctor must order laboratory tests of blood composition to determine the level of functioning of the kidneys and liver.
- A test for the body's sensitivity to a contrast agent is a mandatory condition for patients with allergic reactions to food, pharmacological drugs, and household chemicals. It is necessary to use a drug that has shown minimal adverse reactions. The doctor may also prescribe a prednisolone injection to minimize the manifestation of allergies.
- There is no need to fast before an MRI with contrast; it is enough to refuse food 3 hours before the procedure. Active digestion at the time of scanning can provoke vomiting.
Undesirable adverse reactions to contrast:
- Acute reactions that appear instantly.
- Late reactions may occur some time after the examination.
- Interactions with medications that the patient is taking at the time of the study.
Contraindications for administration of contrast solution:
- Pregnancy. If the grounds for such a diagnosis are compelling, the specialist must select a drug that guarantees a stable effect when administered at a minimum dose.
- Breast-feeding. In emergency cases, when the use of contrast cannot be avoided, you should refrain from feeding the baby for 2-3 days. During this time, the body will be completely cleared of gadolinium. The baby can be fed formula or pre-expressed milk.
- Gadolinium has a certain degree of nephrotoxicity. With normal kidney function, the drug will not cause harm to the body, but with renal failure the patient runs the risk of developing contrast-induced nephropathy or nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.
- Some gadolinium compounds in contrast agents place excessive stress on the liver and are contraindicated in patients with liver failure.
- Allergy.
There are little-studied specific side effects, so MRI with self-referral contrast should not be used. Before the study, you should consult a specialist.
Soft tissue MRI
What is soft tissue MRI
Soft tissues make up about 50% of the human body weight. These include nerves, blood vessels, lymph nodes, subcutaneous fat, tendons, and striated muscles.
MRI of soft tissues is a unique diagnostic method that allows you to see abnormalities caused by tissue diseases of a traumatic, chemical, biological or other nature. It is noteworthy that this method gives almost 100% results.
Cost of soft tissue MRI
Below you can see the prices for MRI:
Disabled people, pensioners, combatants, members of large families, Chernobyl victims, children under 18 years old - 1st category Health workers - 2nd category; Veterans and participants of the Great Patriotic War – 50% discount
| Type of service | Price | 1 cat. | 2 cat. | -25% |
| MRI examination of soft tissues | ||||
| MRI of SOFT TISSUE of any area | 4700 | 4450 | 4250 | 3530 |
| MRI OF SOFT TISSUE OF THE NECK (muscles of the floor of the oral cavity, parotid salivary glands, submandibular salivary glands, pharynx and larynx, neck spaces, thyroid gland, neck vessels, neck muscles, neck lymph nodes) | 4700 | 4450 | 4250 | 3530 |
| MRI OF THE MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITIES IN NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES (assessment of muscle structure and atrophic changes) | 4200 | 4000 | 3800 | 3150 |
Indications
This diagnosis is prescribed in the following cases:
- in the presence of inflammation or sharp pain in the tissues;
- in the presence of tumors or voluminous neoplasms in tissues;
- if there is a feeling of excessive pressure on tissues, blood vessels, nerve fibers;
- in the presence of various diseases in blood vessels and degenerative changes;
- in case of infringement of nerve fibers and the development of abnormalities in tissues;
- in case of muscle injuries.
What does soft tissue MRI show?
This diagnosis examines the following tissues and organs:
-loose intermuscular and synovial tissue;
-lymph nodes;
- skin-fat layer;
- nerves and blood vessels;
-striated muscles and connective tissue layer.
MRI of soft tissues shows the anatomy, relative position and pathological changes in soft tissues, and allows visualization of the initial stages of diseases.
This method allows you to carefully examine the found transformations.
MRI of soft tissues with contrast
A distinctive feature of this diagnosis is that before the study is carried out, a special substance is administered to the patient. It should be noted that before this, a special test will be carried out, which indicates that a person is allergic to the substance or to the elements that make up its composition.
It is usually administered through a medical injection. Spreading throughout the vessels and organs, a special substance paints the problem areas of the area under study in the appropriate color. This makes them more distinct in the image and helps identify various formations in them.
The contrast agent is absolutely harmless to health. This has been confirmed by clinical trials and many years of experience in using the substance in medical practice.
Contraindications to MRI of soft tissues
Absolute contraindications to MRI are:
- installed pacemaker,
-metallic ferromagnetic foreign bodies in the orbital cavity,
-large metal ferromagnetic implants,
-ferromagnetic hemostatic clips on brain vessels.
Relative contraindications to MRI are:
-insulin pumps,
-nerve stimulators, non-ferromagnetic inner ear implants,
- prosthetic heart valves (in high fields, if dysfunction is suspected),
-hemostatic clips (except for ferromagnetic clips on cerebral vessels),
- decompensated heart failure,
-I trimester of pregnancy,
-claustrophobia (panic attacks while in the apparatus tunnel may not allow for research),
-need for physiological monitoring,
-the presence of tattoos made using dyes containing metallic compounds (or the examination time should be significantly reduced); exception is the presence of tattoos made using dyes based on titanium compounds,
- the presence of a cochlear implant (contains metal parts) - inner ear prostheses.
This list of contraindications is not final. Do not forget that the absoluteness of indications and contraindications in any case is determined by the doctor conducting the study and the doctor referring for the study.
Contraindications to MRI with contrast:
-renal failure,
-severe form of bronchial asthma,
-liver failure,
- polyvalent drug allergy,
-previous adverse reactions to the contrast agent.
Preparation for MRI of soft tissues
No special preparation is required for soft tissue MRI. Including when using contrast.
Soft tissue MRI results
MRI results, in most cases, are prepared within an hour and are issued in the form of a study protocol, X-ray film and a recorded study on electronic media.
In our center you can undergo MRI of soft tissues and be confident in the results and quality of the study!
* consultation with a specialist is required regarding contraindications and areas of examination.
CT or MRI, which is better?
CT and MRI studies are based on different technological processes, so it is not entirely correct to compare them with each other. To understand which diagnostic method has more advantages in specific circumstances, it is necessary to analyze a number of indicators:
- Operating principle of the devices.
MRI studies are based on the magnetic resonance effect. Vibrations of hydrogen atoms in cells create waves of different frequencies; in pathological cells, the rhythm changes, allowing the structure to be visualized. CT uses a diagnostic imaging technique and the ability of X-rays to leave different traces depending on the density of tissue. - Hardware capabilities.
CT has advantages in studying bone structures, while MRI's strength is studying soft tissue. - Restrictions and safety.
MRI is not safe for patients with pacemakers and metal implants, but for other categories of patients it has no restrictions on the number of studies. Diagnostics can be repeated as many times as the state of the body requires. CT can be used to examine patients with ferromagnetic implants and electronic life support devices, but it can be performed no more than 2 times a year. - Duration of the study.
A comprehensive soft tissue MRI will require 45 minutes or more if the examination is performed with contrast. For a CT scan, it only takes 2-3 minutes.
| CT | Soft tissue MRI |
- CT allows you to build 3D models:
3D model
Price and location of the procedure
MRI of soft tissues can be performed in any district of the capital in various diagnostic and treatment centers and clinics. There is an MRI center in Tushino on Volokolamsk Highway. Tomography services are available at the European Diagnostic Center on Nagatinskaya Street, 1. Tomography can be performed at the LCD on Vernadsky Avenue, at the Kuntsevsky Treatment and Rehabilitation Center at Partizanskaya Street, 41. In Moscow, on the street. Nizhny Novgorod also has an MRI center.
The average cost for the procedure is 3500-6000 rubles, depending on the zone. It is better to call the center in advance and sign up for the procedure in advance.
X-ray or MRI, which is better?
X-ray examination and magnetic resonance imaging are fundamentally different techniques. Comparing them with each other is not entirely appropriate. To give an objective assessment of these diagnostic methods, the following factors should be analyzed:
- Operating principle of the equipment.
MRI imaging is made possible by analyzing the vibrational frequency of hydrogen atoms in cells. Each type of tissue has its own rhythm of impulses. X-ray radiation passes through soft tissue and leaves a trace in denser areas. - Device capabilities.
MRI visualizes all types of tissues, but achieves the greatest results in the study of soft tissues. X-rays pass through soft tissue unless contrast enhancement is performed. This method is suitable for diagnosing pathologies of bone structures. - Image quality.
MRI projections have high resolution, show many details, and allow you to identify the disease at an early stage of formation. An X-ray image has low resolution, and pathology in soft tissues can only be recognized in an advanced stage.
| X-ray | Soft tissue MRI |
- Security and restrictions.
MRI negatively affects the operation of implanted electronic life support devices and causes discomfort in the area where metal implants and fragments are located. During a routine MRI scan, your doctor may order a preliminary x-ray to make sure there are no ferromagnetic hemostatic clips in the body. The number of MRI studies is unlimited. Excessive radiation exposure during x-rays has an adverse effect on the body; it can be performed no more than 2 times a year. - Cost and availability.
X-rays are available as an outpatient examination at your local clinic. It is included in the list of services under the compulsory medical insurance policy and is provided free of charge. An MRI can be done at a regional diagnostic center or commercial clinic. The procedure is carried out on a paid basis; patients in inpatient departments can undergo it under the compulsory medical insurance policy. At the same time, prices for x-rays are 3-4 times lower than for MRI examinations.
Advantages of the technique
The study of soft tissue structures using magnetic resonance imaging is widely practiced due to the following advantages:
Quick diagnosis, without prior preparation or hospitalization of the patient.
- The ability to examine soft tissue structures in different planes.
- High image quality, clear visualization of even the smallest elements.
- The ability to identify tumors and other pathological processes at the initial stages of development.
- There is no need for radiation exposure to the patient or surgical interventions.
- Possibility of safe diagnostics in pregnant women, young children and the elderly.
MRI of soft tissues is a very informative procedure that gives the most accurate results. This method is used to make a diagnosis, monitor the patient’s condition after injuries and surgical interventions, as well as evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. MRI of soft tissue structures allows you to identify the slightest pathological changes and urgently take appropriate measures!
Sovinskaya Elena, doctor, medical columnist
9, total, today
( 42 votes, average: 4.67 out of 5)
Electroencephalogram of the brain: what it shows, interpretation of the results
Electroneurography: what is it?
Related Posts
Ultrasound or MRI, which is better?
Ultrasound and MRI are based on different technological processes for visualizing the internal structures of the body; in order to make an objective assessment of these methods, it is worth considering the following factors:
- Operating principle of the devices.
The image of tissues during ultrasound diagnostics is formed by analyzing the ultrasonic waves reflected from the organ. MRI uses the magnetic resonance effect. The processor processes pulses caused by vibrations of hydrogen atoms. - Hardware capabilities.
The interpretation of data from an ultrasound examination is performed by a diagnostician. The human factor significantly influences the quality of the examination, so there is no guarantee of a 100% result. In MRI, information is processed by a processor, so the level of errors is minimized. - Image quality.
An ultrasound image has multiple noises and low resolution, which greatly complicates the early diagnosis of diseases. MRI projection is performed in high resolution and with maximum detail, providing ample opportunities for detecting pathologies at the stage of formation.
| Ultrasound | Soft tissue MRI |
- Availability and cost.
Ultrasound is included in the basic list of medical services provided under the compulsory medical insurance program. It can be taken at a regular clinic for free. Patients of inpatient departments can count on a free MRI examination. In an outpatient setting, the procedure is carried out on a paid basis; it can be performed in a commercial MRI center or a medical institution of regional/regional significance. If we compare prices, the cost of MRI is 2-4 times higher than ultrasound.
Features of the diagnostic method
MRI of soft tissues is a unique research method. Thanks to him, you can see the tiniest elements. Using MRI, you can examine tendons, muscle bundles, and even the thin walls between them. There is no longer a radiation method that will allow such an accurate study.
MRI creates the necessary level of contrast, so everything can be seen in great detail. Tomography is based on the magnetic resonance method. To get a clear picture, a magnetic field and radio waves are used.
To kid
Magnetic resonance imaging of soft tissues is safe and has no age restrictions.
MRI is prescribed to children from the first days of life. However, some commercial medical institutions set an age limit of 7 years. This is due to the internal regulations of the clinic and the lack of a license to conduct diagnostics under anesthesia.
For the examination to be effective, you must remain still during an MRI. It is difficult for kids to spend half an hour in the device without moving. The doctor may perform a scan with premedication - superficial anesthesia. The main thing is that the child’s body can withstand the effects of the drug without complications.
At 7 years old, the child is able to follow the doctor’s instructions. They can conduct research without anesthesia. Therefore, commercial medical centers work with young patients, starting from this age.
Sensitive children are frightened by unidentified noises and the confined space of a closed tomograph. They can carry out diagnostics using an open tomograph. The parent can be nearby to support the child and ensure that he follows the doctor's instructions.
Indications and contraindications for MRI in young children are the same as for adult patients.
Benefits of MRI
The advantages of this type of examination include:
- Safety. It does not cause radiation exposure to organs and tissues, so the study can be carried out repeatedly. MRI is allowed for women in the second half of pregnancy and children, provided that they can remain still during the examination.
- High information content. Tomography allows you to obtain an image in any plane, with any degree of magnification, and the image will be as clear and detailed as possible.
- Accuracy. Allows you to get a clear picture of even minor pathologies that cannot be determined by other diagnostic methods.
- Non-invasive. The examination does not cause any discomfort to the subject, and the integrity of the skin membranes is not compromised. The procedure is absolutely painless and allows you to avoid other, less informative and more invasive techniques, such as arthroscopy.
Photo
| Soft tissue hemangioma |
| Cavernous hemangioma of the soft tissues of the face |
| Soft tissue fibroma |
| Chondrosarcoma of soft tissues |
| Cervical myositis |
Price
On our website, many clinics list prices for MRI, including soft tissue MRI.
To see prices, you need to go to the list of clinics in your city. To do this, select your city on the “Addresses” page.
On the page for the list of city clinics, in the form for selecting a clinic based on parameters, in the “Research area” field, select “MRI of soft tissues”.
The list will be filtered and the clinics will be sorted by ascending price, which will allow you to find out where to get an MRI of soft tissues cheaper.
| List of clinics filtered by MRI of the brain using the example of the city of Moscow |
If prices are not indicated on the website, then you need to call all the clinics and find the best price for you yourself.
When talking with the operator, be sure to ask if there are any promotions or discounts. For example, some 24-hour clinics offer discounts on MRIs at night.
You can get an MRI with compulsory medical insurance or VHI insurance. To do this, you need to find out which clinic does MRI under insurance, using the information on the website or calling the clinics yourself if there is no information on the website. In the form for selecting a clinic by parameters, there is a field “MRI under insurance”. Next, you need to find out the list of documents that the clinic operator will tell you, collect them and you will be able to undergo an MRI with insurance, which will allow you to save a lot.
Reviews
On our website, people leave reviews for clinics about their MRI experience.
To read patient reviews, you need to go to the list of clinics in your city. To do this, select your city on the “Addresses” page.
The list in the block of each clinic will show a button to go to the list of reviews, if there are reviews, or a button to go to write a review, if there are no reviews yet.
| This is what review buttons look like, using the example of the city of Moscow |
You can also leave a review about your MRI experience so that other people can choose the most suitable clinic.
To leave a review, you need to click the “Your review” button and you will be taken to the review writing form. Or if there are already reviews, then you need to go to the end of the list of reviews and there will be a form for writing a review.
To open the review writing form, click the “Leave a review” button.
Fill out the form and send it for moderation.