Introduction
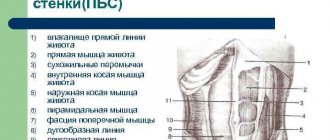
The soft tissues of the neck
are the skin, muscle structure, blood vessels, lymph nodes, and nerve roots located in this part of the human body.
MRI of the soft tissues of the neck can be part of a comprehensive examination of all soft tissue structures, or can be carried out as a targeted examination, if there are characteristic signs of pathology in this region.
| Anatomical structure and location of the soft tissues of the neck | MRI images of soft tissues of the neck |
Indications for MRI and CT of lymph nodes
These examinations are prescribed in the following cases:
- in the presence of injury;
- with inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- when lymph nodes change in size;
- to confirm or refute the presence of various tumors, as well as accurately determine their number and location;
- to clarify the location of a foreign body;
- for the purpose of diagnosing cysts;
- for a more detailed study of a specific area of the body;
- to assess the current condition of the lymph nodes.
Classification of tomographs
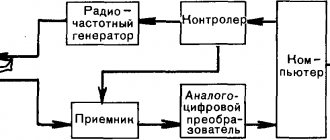
Magnetic resonance imaging is performed in special equipment called a tomograph
.
By type, tomographs are divided into open and closed
.
| Open MR tomograph | Closed-type MR tomograph |
The advantages of an open type tomograph are:
- It is suitable for patients suffering from claustrophobia and for children who may be scared in the confined space of a closed CT scanner;
- It has an air gap in which the patient is placed, usually larger than that of closed-type tomographs. This makes it possible to conduct examinations for overweight patients.
The advantages of a closed-type tomograph are:
- The examination time is shorter than that of the open one. The timing of the examination is important for those patients who, for one reason or another, cannot remain motionless for a long time.
- The quality of images from a closed tomograph is higher, because the quality of images depends on the magnitude of the created magnetic field strength, measured in Tesla units. Due to their design features, open-type tomographs cannot create tension comparable to closed-type tomographs.
According to the strength of the created magnetic field, tomographs are divided into
:
- Low-floor - up to 0.5 Tesla.
- Mid-field - from 0.5 to 0.9 Tesla.
- High-field - from 1.0 to 1.5 Tesla.
- Super high-field - 3 Tesla.
As a rule, a voltage of 1.5 Tesla is enough to obtain images of acceptable quality.
| Image quality depending on equipment power |
How to prepare for the examination
MRI of hard and soft tissues of the neck does not require special preparation. The day before, the patient is allowed to continue his usual lifestyle: he can eat regular food and take prescribed medications. But before the MRI procedure, he must remove all metal objects and inform the doctor about some nuances that may interfere with the progress of the study. These include:
- Hyperkinesis. This is a condition when a person cannot control his movements. You must remain motionless inside the tomograph tunnel. And with hyperkinesis, it is difficult to keep the neck and head at rest.
- Medical devices, metal or metal-ceramic crowns, dental implants. If they contain steel, they will interfere with MRI scanning of tissues, and treatment based on the data obtained may be ineffective.
- Tattoos with metallic inclusions. They distort the real picture if they are located on the part of the human body being examined (if they are on the arms and legs, they will not affect the reliability of the research results).
Be sure to notify the MRI specialist if you are pregnant. Pregnancy is a relative contraindication for magnetic resonance imaging. It is not necessary to abandon this diagnostic method. But it is better to inform about the situation so that the doctor can exclude the abdominal area from the area of influence of the device. This precaution is necessary, since it has not yet been determined how a high-intensity magnetic field can affect the fetus.
Indications
MRI studies are prescribed in cases where other methods of laboratory and radiation diagnostics could not provide a complete picture of the pathology.
Indications for conducting research are the following factors:
- The presence of anomalies in the structure of the neck.
- Cervical injuries.
- Pain in the neck area.
- Impaired mobility of the cervical vertebrae.
- Inflammatory and infectious lesions of muscles and organs.
- Problems with the vocal cords.
- A history of chronic ENT diseases, vascular and thyroid pathologies.
- Changes in the size of lymph nodes.
- Suspicion of a hernia of the cervical vertebrae.
- Headaches, tinnitus, numbness of the upper extremities.
- Suspicions of the development of neoplasms of an unknown nature.
- Search for metastases.
- Monitoring disease progression.
- Checking the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Preoperative preparation, including determining the need for surgical intervention.
- Postoperative control.
- Complications after surgery.
When is an MRI examination necessary?
Typically, magnetic resonance imaging of the neck is used when it is necessary to assess the condition of the cervical spine and determine the contents of the canal. As a magnetic resonance angiography, the procedure is indicated for diagnosing the vascular network that supplies blood to the brain.
Indications for an MRI examination of the neck include:
- soreness in the arms and neck;
- migraine;
- damage to the anatomical area (bruises, fractures);
- visual impairment, speech impairment;
- insomnia;
- deterioration of memory and attention;
- loss of consciousness;
- disruptions in the blood circulation of the brain;
- stiffness in the neck;
- signs of cancer, metastases;
- suspicion of an intervertebral hernia or a decrease in the lumen of the canal in the thoracic spine.
More often, an MRI is performed to determine the cause of a disruption in the blood flow to the brain. Upon completion of the MRI of the neck vessels, the specialist forms a conclusion in which he can make one of the following diagnoses:
- arterial stenosis;
- vascular abnormality;
- aneurysm;
- atherosclerosis, vascular thrombosis.
The study allows you to diagnose protrusions and hernias, demonstrate the condition of the thyroid gland, lymph nodes, larynx, and spinal cord in this area.
Contraindications
Contraindications to MRI of the soft tissues of the neck are divided into absolute, when it is impossible to do an MRI, and relative, when it is possible to do it under certain conditions.
Absolute contraindications
:
- Installed pacemaker. Magnetic fields can interfere with the operation of electronic equipment, causing it to malfunction.
- The presence in the body of metal implants or other metal objects (for example, fragments) that react to the influence of a magnetic field. If the patient has implants in the body that do not respond to the magnetic field, then documents confirming this should be provided.
Relative contraindications
:
- Claustrophobia. This contraindication is relevant for closed-type tomographs and can be avoided by conducting examinations on open-type tomographs.
- First trimester of pregnancy.
- The patient cannot remain still during the entire examination. The images will be blurry and therefore not suitable for diagnosis if the patient moves during the examination. The solution may be a sedative or anesthesia.
- The patient's weight exceeds the permissible weight for which the tomograph table is designed. In this case, you need to look for tomographs with a large permissible weight. As a rule, open-type tomographs have an advantage in this regard over closed-type tomographs.
- The diameter of the circumference of the widest part of the body exceeds the length of the air gap of the tomograph. In this situation, you also need to look for a tomograph with the necessary parameters. As a rule, open-type tomographs have a larger air gap than closed-type tomographs.
- The patient has decompensated heart failure.
- The patient is in serious condition.
- Inappropriate behavior, including alcohol intoxication.
Decoding the results
The doctor deciphering the data obtained does not make a diagnosis. This is the task of the attending physician. The patient receives a conclusion within an hour after the procedure. After a detailed analysis of the images in various projections, the specialist makes a diagnosis and prescribes a therapeutic course.
In photographs of the soft tissues of the neck, the doctor is able to examine the following pathological phenomena:
- cystic formation, abscess;
- neoplasm of a benign or malignant nature;
- metastasis;
- hematomas;
- foreign bodies;
- pathologies of the neck organs (thyroid, salivary glands, larynx, etc.).
Tumors
The procedure is effective in diagnosing muscle tissue in a local area. When interpreting MRI images, the doctor may indicate stretching, atrophy or inflammation in the muscles.
What does MRI diagnostics of neck lymph nodes show? If the size of the lymph nodes is increased, the specialist draws conclusions about the active resistance of the immune system to infections, cancer or autoimmune diseases. When analyzing the resulting images, the doctor will probably identify signs of the following pathologies:
- tumors;
- infectious processes (acute respiratory infections, HIV, STDs, tuberculosis);
- autoimmune pathologies (rheumatoid arthritis, hepatitis).
After an MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck, one of the following diagnoses is likely to be formulated:
- thrombophlebitis;
- vascular aneurysm;
- vein fusion;
- vasculitis (in the process of angiography of the vascular system, not only inflammatory processes affecting the vascular walls are visualized, but also necrosis);
- benign and malignant tumors;
- tortuosity of the carotid artery;
- damage to the vascular wall;
- compression of a vessel by scar tissue after an injury.
MR angiography
If a patient has a disturbance in the process of blood circulation in the brain, using MRI images of the arteries, the doctor has the opportunity to determine not only the type of pathology, but also the reasons for its occurrence. The results of magnetic resonance imaging of the veins will help to see blood clots in anatomical structures.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the neck organs is one of the most informative methods for diagnosing pathological conditions. The reason for prescribing the procedure is regular migraines, pain in the arms and neck, sleep disturbances, hearing, vision and other alarming symptoms, most often caused by problems with the cervical spine.
For a detailed examination of anatomical structures during diagnosis, a contrast agent, gadolinium, is used. This method is justified in the case of detection of tumor formations in the local area.
The list of contraindications in the case of magnetic tomography is standard: the procedure is not performed for pregnant women in the 1st trimester, or for carriers of metal elements and devices in the body. Contrast cannot be used in diagnosing persons with liver failure or substance intolerance.
There is no preliminary preparation before scanning. The procedure takes an average of half an hour, and when using contrast it can be extended to an hour. The results of the study and the conclusion are transferred to the attending physician, who makes a diagnosis.
How does the procedure work?
Carrying out an MRI of the soft tissues of the neck consists of three stages: preparatory, the procedure itself, and issuance of results.
Preparatory stage.
The patient needs to arrive some time before the appointment in order to:
- Complete the documents. If the procedure is paid, then a contract for the provision of paid medical services must be drawn up. If the procedure is for compulsory medical insurance or voluntary medical insurance, then the necessary package of documents is checked.
- Find out contraindications. Contraindications are described in the section of the same name in the article.
- If an MRI with contrast is required, contraindications for administering contrast are clarified. The doctor also needs to select the type and dose of contrast agent, which will take a certain amount of time.
- Next, before the examination, you should change into loose clothing without metal elements and remove all metal objects.
Procedure
:
- The patient is escorted to the tomograph.
- Placed on the table.
- The body is secured with soft straps to avoid micro-movement. Movements during MRI lead to blurring of the image and the examination needs to be redone.
- If necessary, fix the area being examined with a special coil.
- The examination is accompanied by specific noises produced by the tomograph mechanisms. To reduce the negative effect of noise, the patient is given headphones in which music is played, and the instructions of the doctor conducting the examination can be transmitted to the headphones.
- If the procedure is performed on a closed type tomograph, the patient is in a confined space.
Delivery of results
:
- Immediately after the examination, the patient is given an image on film and/or disk.
- For some time after the examination, the patient is given an examination report from a radiologist. Usually this time is about 30 minutes, but it can be longer depending on the doctor’s workload. It may be that the conclusion will be issued the next day. Some MRI centers send the report by email.
In some MRI centers, you can ask the radiologist any questions you have after the procedure.
Duration of the procedure
MRI of the soft tissues of the neck in a closed high-field tomograph with a magnetic field strength of 1.5 Tesla takes up to 20 minutes.
A similar examination using open-type equipment takes up to 40 minutes. If tomography using a contrast agent is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis, the duration of the procedure increases approximately 2 times. An initial scan is performed without contrast, then the solution is injected, and the manipulations are repeated.
Examination using a contrast agent
In certain situations, when there is a suspicion of oncological processes in the neck or vascular pathologies, a study with contrast is performed. To do this, the patient is injected intravenously with a contrast agent made from gadolinium salts. Due to minimal toxicity and the absence of allergic reactions, the use of the substance does not pose any threat to the subjects.
But still, each patient must undergo a drug tolerance test in advance.
After the procedure, the contrast is removed from the body naturally, and this process takes no more than a few hours. Such an examination is carried out only as prescribed by the attending physician or radiologist. This procedure takes twice as long - up to an hour and a half and, accordingly, costs more, but the result ensures a reliable diagnosis. An absolute contraindication for MRI with contrast is pregnancy.
What does it show
In the absence of pathologies, all structures of the soft tissues of the neck will be displayed unchanged and have the correct size and contours.
MRI of the soft tissue structures of the neck allows you to timely detect all possible deviations from the norm and pathology.
Magnetic resonance imaging detects the following diseases with an accuracy of 95%:
- Improper development of tissues and organs associated with a genetic code disorder.
- Traumatic injuries to ligaments, muscle tissue, blood vessels: cracks and fractures of the spine, violation of the integrity of cartilage, joint capsule, pinched blood vessels, sprained ligaments, hematomas.
- Pathologies of the vascular bed: aneurysms, stenosis, thrombosis.
- Increased size and distortion of the shape of lymph nodes.
- Accumulations of liquids. Abscesses, necrotic lesions.
- Various disorders in the structure and functioning of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism, cyst, cancer).
- Pathologies of the salivary glands.
- Benign and malignant processes in soft tissues.
- Formation or penetration of metastases.
What is assessed and what does tomography of the soft tissues of the neck include?
Rate:
- neck muscle symmetry
- condition and clarity of the image of fatty tissue
- blood flow in the vessels, the presence of blood clots or stenosis due to atherosclerosis
- localization and symmetry of the salivary glands
- MRI of the neck organs: condition of the thyroid gland (uniform structure or with the presence of nodes). On MRI images, the gland tissue must have a homogeneous structure, have a clear boundary with the surrounding tissues, and have a certain size that does not exceed the permissible limits. The volume of the gland can vary from 20 to 25 ml. If the volume of the gland is exceeded, the trachea is examined for compression and suspected narrowing. A benign goiter can spread retrosternally and displace vascular bundles located above the aorta in the lateral direction. The structure of a thyroid nodule in cancer is almost always heterogeneous; the nodule does not have a clear border with the unaffected part of the gland.
- tracheal lumen (is there any narrowing)
- condition of the pyriform sinuses, vocal cords, laryngeal cartilages
- spread of the inflammatory process within the fascial spaces of the neck (limited by the fascia)
- assessment of lymph nodes (number, size)
MRI of neck lymph nodes - what shows
The MRI result for an inflamed lymph node in the neck will include its/their enlargement in the form of delimited nodular formations within one section and are rarely detected in adjacent sections. In large lymphomas and in conglomerates of lymph nodes, areas of necrosis in the center are often found. In such cases, an MRI of the neck with contrast should always be performed, as in these cases it is difficult to distinguish them from an abscess with central disintegration.
What's the difference with and without contrast?
The contrast consists of saline solution and a special substance, is injected into the body intravenously, and transported through the circulatory system to the object of study.
Thanks to the reaction of the components to the influence of the magnetic field, the area of localization of the pathology is “highlighted”, the size and shape of the defect is clearly indicated. Secondly, due to its properties, contrast affects pathological areas in such a way that they are shown on images more clearly (in contrast) relative to areas without pathologies.
This is what the doctor will see in the image taken with and without a contrast solution:
| On the left is an MRI performed with contrast; on the right without contrast solution | ||
There are contraindications for the use of contrast agents
:
- Hypersensitivity to components
- Allergic reactions
- Kidney failure
- Pregnancy
- Lactation.
Types and methods of carrying out
The lymph node through which lymph flows is examined using computed tomography or resonance imaging. X-ray and magnetic radiation help assess the condition of a person with affected nodes. Each diagnostic procedure has its positive and negative sides, which are taken into account when choosing the appropriate research option.
When a CT or magnetic resonance imaging scan is performed, an open or closed type of scanner may be used. The open option is considered more acceptable for people who are afraid of being in a confined space for a long time.
A contrast agent may be used during the examination. It becomes necessary if there is a need to identify the presence of a tumor formation. The contrast is administered intravenously by the doctor to the patient. With its help, pathological areas are stained.
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging examination does not require special preparation. The patient only needs to discuss the presence of allergic reactions in advance if the use of a contrast agent is necessary. The patient can begin the procedure 4 hours after the last meal.
Metal prostheses and implants can negatively affect the reliability of diagnostic results. This issue needs to be discussed with a specialist before starting an MRI.
The procedure consists of several stages:
- The patient is prepared for the procedure in the tomography room. He must lie down on a special couch and try not to move during the diagnostic process.
- The couch and the patient are moved inside the tomograph.
- If the diagnosis requires the use of contrast, then before starting the procedure the patient is given a dropper with the required solution. A certain area of the human body accumulates this substance. The accumulating effect lasts until reliable information about the condition of the lymph node is received and longer. Once the contrast has accumulated, you can begin diagnostics.
On average, an MRI procedure lasts 40-80 minutes. The duration of diagnosis directly depends on the size of the area being examined and the presence of contrast agent.
CT
Using computed tomography, you can determine the presence of pathological changes in the lymph nodes
As with MRI, CT scans do not require special preparation. The patient only needs to do the following:
- provision of documents that confirm the need for diagnostics;
- presenting results of previous research;
- providing an opinion on the patient’s condition from specialists;
- notification of possible contraindications.
If a patient needs to receive contrast, he will first need to undergo tests confirming the safety of this procedure for his body.
The examination of the axillary lymph node (located directly in the armpit) and any other formation is carried out in a special room. An X-ray scanner should be located here, which is designed to identify lymph nodes in the armpits and other areas.
The patient is put on a sterile gown and then sent to a room with an installed scanner. Next, the lymph node is scanned and the results of the study are obtained.
CT or MRI, which is better?
It is not entirely correct to compare these methods with each other, since they are based on different principles of image acquisition. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses. The doctor decides whether to send the patient for a CT or MRI based on the purpose of the examination.
If we consider the difference between CT and MRI, then for comparison it is necessary to take the following factors:
Device capabilities
. MRI scans best soft tissue, ideal for assessing the condition of the muscles, ligaments, and tendons around the shoulder joint. CT most accurately demonstrates bone tissue. If a fracture, arthritis or bone tumor is suspected, it is better to entrust the diagnosis to a computed tomography scan. The device is capable of constructing a 3D projection of the joint based on the data obtained during scanning.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, you may need to use both methods.
Duration of the procedure
. For a computed tomography scan, it only takes 1-2 minutes. Scanning using magnetic waves will require the patient to remain motionless for 15 to 30 minutes.
Harmfulness
. A magnetic resonance imaging scanner has no restrictions on the number of examinations, since it emits impulses that are less harmful to the body than X-rays. A CT scan, on the other hand, is based on X-rays and cannot be performed on a single patient more than twice a year.
A visual demonstration of the capabilities of CT and MRI devices:
| CT | MRI of soft tissues of the neck |
CT allows you to build 3D models:
| 3D model |
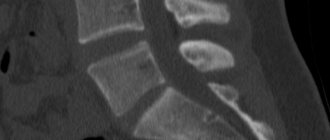
What does MRI of the spinal canal and cervical spine show?
Scanning the spinal cord can detect small foci of demyelination in multiple sclerosis, which is one of the criteria for diagnosing this disease. In addition, space-occupying processes in the spinal cord can be detected. These include tumors growing directly from brain tissue, as well as metastatic lesions, granulomas, cysts, and parasitic infestations. The level of compression of the spinal cord and roots, as well as the degree of ingrowth into the spinal canal, is also assessed. The ability to detect these diseases elevates MRI several steps above diagnostic methods such as x-rays.
MRI is widely used for cervical spine injuries. These are mainly so-called craniovertebral injuries (the junction of the spine and the skull). These include: cervico-occipital injury, fracture and/or rupture of the transverse atlas ligament (first cervical vertebra), allantoaxial instability and subluxation (junction of the first and second vertebrae).
Particular attention is paid to so-called “whiplash” injuries. They occur in accidents when one car rear-ends another. As a result, due to sudden excessive extension and flexion of the neck, the soft tissues of the neck are significantly injured, this often leads to severe neck pain, chronic headaches, decreased memory and concentration, paresthesia, pain in the arm, and stiffness of the cervical spine. .
When diagnosing osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, MR scanning allows one to assess the presence of protrusion of the intervertebral discs, the degree of protrusion of the accompanying hernia, straightening of the cervical lordosis, degenerative changes in the joints (marginal bone growths, etc.)
Magnetic resonance allows us to detect instability of the cervical spine (pathological mobility of its individual elements). Occurs when the anterior and/or posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine, vertebral body, vertebral processes and their ligaments are damaged. It manifests itself as pain in the neck and upper limbs due to irritation of the spinal roots. Sometimes it is to determine instability that an MRI of the child’s neck is performed, since this pathology occurs quite often in children.
MRI also allows for a unique 3D reconstruction in Klippel-Feil syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by a decrease in the number and fusion of cervical vertebrae with the formation of a shortened neck. A three-dimensional image allows you to study the degree of reduction of the vertebrae, the features of their innervation and blood supply, and estimate the size of the spinal canal.
X-ray or MRI, which is better?
X-ray and MRI are fundamentally different examination technologies. If we compare them with each other, then according to the following criteria:
Image quality
. A tomograph scans the human body and builds an image in layers. The image has high resolution, detail, data on soft and bone tissues. An X-ray machine can highlight only one layer and demonstrate the condition of the tissues; the quality of the image will be worse.
| X-ray | MRI of soft tissues of the neck |
Harmfulness
. X-ray radiation in large quantities is dangerous to health, while MRI can be done at least every day.
Availability of procedures
. An X-ray machine can be found in every ordinary clinic. Equipment for MRI requires large financial costs and the availability of specialists who know how to operate it, so large city and regional medical centers and commercial hospitals can afford a tomograph. You can get an X-ray quickly, but the appointment for an MRI is distributed over weeks in advance.
Price
. An X-ray examination can be done free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy in a regular clinic. Only patients from surgery and inpatient departments can get an MRI free of charge.
Ultrasound or MRI, which is better?
Both methods are safe, effective and informative. However, it is necessary to know their capabilities, advantages and disadvantages in order to determine what is more appropriate to apply in a particular case. To do this, let's compare the following aspects:
- Operating principle of the devices
. MRI uses magnetic pulses to visualize internal organs, and ultrasound diagnostics is based on the conversion of ultrasonic waves. People with metal implants, dentures, pins, cochlear devices, and pacemakers are not safe from exposure to electromagnetic fields. The ultrasound technique is suitable for them. - Research speed
. For MRI you need to spend 20-30-40 minutes and at least an hour for description. The ultrasound procedure takes 5-10 minutes, and the result is immediately available. - Device capabilities
. Ultrasound examination does not provide 100% accurate results. The processing of the received data is carried out by a person. The information content and reliability of the examination depends on the experience and skills of the specialist. An MRI machine processes signals, generates images, and interprets data using a computer processor. And only then does the radiologist begin decoding. The likelihood of errors and errors in this case is reduced. - Availability and cost of the procedure
. An ultrasound machine can be found in rural clinics, while an MRI scanner is the prerogative of large regional centers. It is easier to undergo ultrasound diagnostics through compulsory medical insurance. In the case of paid services, the cost of ultrasound is 2-3-4 times lower than MRI.
| Ultrasound | MRI of soft tissues of the neck |
To kid
There are no age restrictions for MRI of the soft tissues of the neck.
To perform an MRI, a prerequisite is immobility throughout the entire examination. Children may find it difficult to lie still, so anesthesia may be considered.
Children may be afraid to be in the confined space of a closed-type CT scanner. In this case, an examination can be performed using an open-type tomograph. The parent will be able to stay next to the child and hold his hand.
Treatment of cervical lymphadenitis
Acute lymphadenitis:
- Parenteral antibacterial therapy (penicillin, II and III generation cephalosporins)
- Opening and draining abscesses
- Treatment of the underlying disease.
Chronic lymphadenitis:
- Treatment of the underlying disease (eg, anti-tuberculosis drugs, pyrimethamine for toxoplasmosis)
- Combined antibacterial therapy in the presence of atypical mycobacteria
- Local lymphadenectomy, in some cases with removal of the affected salivary glands
- Strengthening the immune system.
Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: Usually spontaneous recovery.
Photo
| Neck infiltration |
| Lipoma of the neck |
| Meningocele |
| Laryngeal cancer |
| Chemodectoma of the neck |
Price
On our website, many clinics list prices for MRI, including MRI of soft tissues of the neck.
To see prices, you need to go to the list of clinics in your city. To do this, select your city on the “Addresses” page.
On the page for the list of city clinics, in the form for selecting a clinic based on parameters, in the “Research area” field, select “MRI of soft tissues of the neck.”
The list will be filtered and the clinics will be sorted by ascending price, which will allow you to find out where to get an MRI of the soft tissues of the neck cheaper.
| List of clinics filtered by MRI of the brain using the example of the city of Moscow |
If prices are not indicated on the website, then you need to call all the clinics and find the best price for you yourself.
When talking with the operator, be sure to ask if there are any promotions or discounts. For example, some 24-hour clinics offer discounts on MRIs at night.
You can get an MRI with compulsory medical insurance or VHI insurance. To do this, you need to find out which clinic does MRI under insurance, using the information on the website or calling the clinics yourself if there is no information on the website. In the form for selecting a clinic by parameters, there is a field “MRI under insurance”. Next, you need to find out the list of documents that the clinic operator will tell you, collect them and you will be able to undergo an MRI with insurance, which will allow you to save a lot.
What diseases have symptoms similar to cervical lymphadenitis
Reactive lymphadenitis
— Most often develops with viral infections of the upper respiratory tract
- Usually painless enlargement of the lymph nodes without the formation of cavities in them
Infectious mononucleosis
— Generalized enlargement of lymph nodes with fever and sore throat
— Hepatosplenomegaly
Lymphoma, metastases
– Painless enlargement of lymph nodes
— Possible formation of cavities in the lymph nodes
— Systemic manifestations (fever, night sweats, weight loss)
Reviews
On our website, people leave reviews for clinics about their MRI experience.
To read patient reviews, you need to go to the list of clinics in your city. To do this, select your city on the “Addresses” page.
The list in the block of each clinic will show a button to go to the list of reviews, if there are reviews, or a button to go to write a review, if there are no reviews yet.
| This is what review buttons look like, using the example of the city of Moscow |
You can also leave a review about your MRI experience so that other people can choose the most suitable clinic.
To leave a review, you need to click the “Your review” button and you will be taken to the review writing form. Or if there are already reviews, then you need to go to the end of the list of reviews and there will be a form for writing a review.
To open the review writing form, click the “Leave a review” button.
Fill out the form and send it for moderation.