Magnetic resonance imaging is based on exposure to a magnetic field of varying intensity. No negative consequences for the body were detected during native scanning; contraindications are individual in nature. To increase the information content, MRI with contrast is used, which allows you to visualize the slightest structural changes in tissues and organs. The number of contraindications to such an examination has been expanded, since during the scanning process a special solution is injected intravenously into the human body, which can cause a response. The procedure is considered a modern and safe technique, which helps to identify the disease at an early stage.
A series of MRI images of the brain for suspected Alzheimer's disease
General characteristics of MRI
MRI with contrast is a type of magnetic tomography. The method has its own characteristics, indications and contraindications, side effects. Magnetic resonance imaging is a method of studying the body using high-power magnetic radiation.
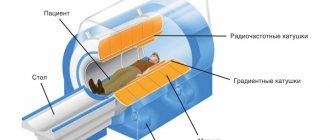
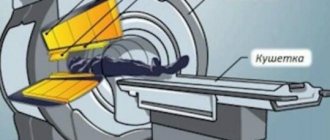
Its source is a special device - a tomograph. The rays distributed by it process the examined area of the body and act on the hydrogen particles of the cells, causing a certain reaction. It is fixed with a special device that creates a three-dimensional image. It shows the organ being examined clearly from the inside.
Magnetic resonance imaging differs from an x-ray in that it makes it possible to better examine soft tissues and obtain accurate information about the condition of blood vessels and nerve endings. The method is considered one of the safest, but is quite expensive.
Indications for magnetic resonance imaging with contrast
An MRI procedure with contrast is prescribed only with a doctor’s referral. Since the patient's response to a special substance may vary, supervision by an anesthesiologist is necessary. The study is indicated in the following situations:
- confirmation of pituitary adenoma;
- detection of metastases;
- severe stroke;
- clarification of the nature of neoplasms;
- immune diseases (for example, multiple sclerosis);
- head injury;
- infectious diseases (including meningitis);
- genetically determined diseases (neurofibromatosis);
- neurodegenerative diseases;
- vascular disorders;
- confirmation of detection of Alzheimer's disease.
An examination may also be prescribed for symptoms such as:
- frequent dizziness;
- regular nausea and vomiting;
- decreased hearing and vision;
- poor coordination;
- decreased mental abilities and memory impairment;
- confusion.
MRI with contrast: essence, mechanism of action
Sometimes a routine MRI examination does not provide the necessary results. A more accurate diagnostic method is required. Then an MRI with contrast is indicated.
The essence of the method is that a special dye is injected into the patient’s blood, spreading throughout all organs. Fluid accumulates in the affected tissues. The result is a clearer image. The tomograph provides a picture that allows you to see the volume of the affected areas, their size, boundaries and location.
Most often, a contrast examination is required for oncological examinations or when cancer is suspected. Thanks to this method, the benignity or malignancy of the identified tumor is easily determined. Contrast magnetic resonance imaging clearly depicts metastases. Their stage of development is easily determined.
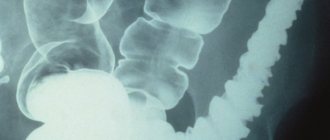
MRI of the brain with contrast can detect not only tumors of any degree, but also identify areas affected, for example, by a stroke. At the same time, the doctor can assess the size of dead cells and the complexity of the situation. There are no analogues to this diagnostic method yet.
A magnetic resonance imaging session with contrast can be used to examine any part of the body. The procedure is quite simple. It does not cause discomfort or pain. It costs more than conventional tomography and takes a little longer. However, the effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging is much higher in comparison with other examinations.
Indications for contrast-enhanced MRI of the brain
Suspected tumors of cerebral structures
Be it malignant neoplasia or benign neoplasms such as adenomas. This is one of the key indications for diagnosis. Gadolinium-based contrast for MRI of the brain accumulates in the changed tissues, due to good blood circulation, the picture becomes clear. And the more blood is supplied to the neoplasm, the more clearly the outlines of the structure are visible.
The doctor has the opportunity to assess the basic physical characteristics of the tumor: size, location, effect on neighboring tissues, growth pattern, including metabolism, estimated metabolic rate, structure (solid, cystic or mixed), and distinguish the tumor from the cyst. Unfortunately, the specialist does not receive complete information. Confirmation of guesses is carried out by biopsy, with histology in the laboratory, after collecting material using the stereotactic method or after surgery on cerebral tissues.
Gadolinium
Confirmed neoplasms to determine the dynamics of the pathological process
After confirming the pathological process, doctors have two options. The first is to schedule surgery, either planned or urgent, to remove the tumor. The second is to choose a wait-and-see approach. This is the more common option. The growth pattern of neoplasia needs to be monitored. For this purpose, systematic tomography is prescribed. Frequency - from once every 3 months to once every six months to a year. If there are no speakers at all, once every 2 years. After 3-5 years of observation, the tumor is considered not to develop, and observation is removed. The above does not apply to neoplasias, which are clearly malignant in nature and have a risk of further malignancy. Such as fibrillary astrocytomas, anaplastic gliomas and others.
Preoperative preparation
It makes sense to once again evaluate the future field of activity and the scope of surgical treatment. The doctor outlines the main access areas and the course of therapeutic measures. This cannot be done without sufficient visualization of the neoplasia.
Postoperative examination of the field where resection or total removal of neoplasia was performed
As part of dynamic observation and detection of continued growth and relapse of the tumor disease. Malignant structures almost always recur. The key to early stopping the recurrence of the pathological process is early detection of growth.
Demyelinating diseases
Among these, multiple sclerosis can be mentioned as the main one. Accompanied by the formation of areas of destruction of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers, which must transmit impulses. Due to the peculiarities of the biochemistry of cerebral structures during such changes, gadolinium-based contrast enhances areas of brain degeneration. At the same time, specialists must have sufficient qualifications to interpret. Large confluent lesions may be falsely mistaken for tumors.
Contrast is administered according to indications.
Contrast agent
Contrast MRI uses a substance with a high content of gadolinium salts. This element belongs to the class of soft metals (lanthanide group), is easily soluble, has low toxicity, and is practically non-allergenic. Among the drugs widely used for research are:
- "Gadovist";
- "Dotarem";
- "Magnevist";
- "Primovist";
- "Omniksan".
They enhance the magnetic beams of the tomograph. The amount of drug for examination is calculated based on the patient’s body weight. The drug is administered intravenously by injection. With the help of a dropper, the drug enters the blood in doses. The amount of the substance is adjusted as necessary.
How MRI contrasts work
Contrast enhancement increases the strength of the MR signal. Intravenous injection of paramagnetic compounds significantly increases the visibility of the area in which the substances are located.
Regardless of the type of contrast, they are made based on the rare earth metal gadolinium. In its pure form, the mineral is toxic, but in a strong complex with chelates it is absolutely harmless to the human body.
A slight difference in the composition of Gadovist, Omniscan, Dotarem, Magnevist allows the use of these MRI contrast drugs for different types of studies (brain, internal organs, pelvis). The degree of enhancement depends not so much on the type of substance, but on the correct dose and the intensity of blood supply to the area under study. Primovist and Gadovist are administered at a dose of 0.1 ml per kilogram.
Qualitative enhancement with Omniscan and Gadovist is achieved by calculating the injection in the ratio of 0.2 ml of the product per 1 kilogram of weight.
Who is the procedure indicated for?
The list of indications for MRI with contrast is quite wide. Magnetic resonance examination is done for:
- Detection of neoplasms of any kind. The contrast MRI procedure is indispensable in diagnosing tumors and distinguishing cancer from benign ones. Cancer cells have the greatest ability to accumulate dye, so the affected areas are easily identified during examination. Healthy tissues under the influence of magnetic rays are not illuminated with a contrast agent. This makes it possible to distinguish oncological formations from benign ones. A conventional MRI examination cannot always detect small metastases, but contrast can easily identify even minor lesions.
- In multiple sclerosis, testing can show whether the disease is progressing. Contrast dye accumulates best in fresh lesions. Old, inactive areas have poor contact with gadolinium.
- Dysfunction of cerebral vessels. Image analysis helps to assess the dynamics of capillaries, the size of their lumens, and other important parameters.
MRI with contrast may be prescribed for:
- dizziness;
- headaches accompanied by vomiting and nausea;
- absent-mindedness;
- decreased vision and hearing;
- violations of spatial orientation.
In these cases, magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed if a conventional study does not provide specific information about the causes of the disease.
Contrast MRI is used when examining patients after injuries (fractures, bruises) and operations to assess the condition of a specific organ. MRI is used to monitor the situation after cancer treatment. An examination is prescribed if there is a suspicion of intervertebral hernia, non-infectious jaundice, liver or kidney diseases. MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast is often used.
Magnetic resonance imaging is indicated when clarification of the diagnosis is required. The object of diagnosis can be any organ or system. The most commonly used method is contrast examination of the brain. This is a very complex system, in the event of violations of which conventional diagnostic methods are often powerless.
Indications and contraindications
MRI using a contrast agent is indicated for patients with vascular diseases or various tumors. The list of indications includes:
- spinal or brain tumor;
- prostate tumors (before and after operations);
- aneurysm;
- brain injuries;
- metastases;
- period after removal of a herniated disc.
This study is also used for overdiagnosis in cases of complaints of pain in the testicles, prostate gland or mammary glands. The substance is also necessary when examining the brain for diseases of the central nervous system, meningitis or Alzheimer's disease.
In some cases, testing with salts is not recommended or it is advisable to postpone it. Thus, contrast should not be administered to patients with liver or kidney failure. It is not recommended to undergo MRI during pregnancy, if you have electronic or metal implants, are overweight, or have severe somatic pathologies. If the patient is claustrophobic, only open tomography machines can be used.
Before administering a contrast agent, make sure that the patient is not allergic to it.
During lactation, contrast is relatively safe. The study can be carried out, but breastfeeding must be excluded for a day. Substances enter milk in small doses, but this may be enough to cause an allergic reaction in a child.
Adverse reactions following the administration of contrast agents are rare. These include:
- nausea,
- dizziness,
- vomit,
- headache.
All alarming symptoms disappear within 2-3 hours after the study. After the procedure, you can immediately return to your normal lifestyle.
Contraindications
Contraindications to MRI with contrast are divided into absolute and relative. They are not associated with irradiation, but with the introduction of a coloring agent. The absolute ones include:
- early pregnancy (up to 12 weeks);
- individual intolerance to a substance acting as a contrast agent.
Relative contraindications apply to people with:
- bronchial asthma;
- serious dysfunction of the liver and kidneys;
- complex cardiovascular diseases;
- myeloma;
- severe dehydration of the body;
- sickle cell anemia.
Contrast magnetic resonance imaging is not performed if the person has already been injected with a coloring agent over the past 24 hours, or if the patient is taking medications (interleukins, beta blockers).
MRI with contrast is not recommended for pregnant women from 12 weeks until the end of pregnancy. During all the years of using MRI, no abnormal changes in fetal development caused by the procedure were recorded. However, there is also no denial of the negative impact on the child.
In any doubtful situations, the decision on the advisability of the study is made by the doctor, who must be told about the state of his health and the circumstances that could become an obstacle to such a diagnosis.
Read also
Good blood supply to the brain is a prerequisite for its normal functioning. If a problem arises in any area, then not only the brain itself suffers, but also other organs. How to notice a violation in time, make a diagnosis and prevent serious complications?
We are all terrified of cancer because we consider it a ruthless killer. But if you compare the statistics of deaths from cancer and from cardiovascular pathologies, it becomes clear that the heart is a much more serious source of danger. What is it, who is at risk, and is it possible to somehow insure against this problem?
Both women and men are aware of the threat of diseases of the genitourinary system. But if representatives of the fairer sex undergo preventive examinations at the gynecologist, then you cannot force a man to see a urologist with a stick.
Approximately 20-30% of MRI examinations worldwide are performed with contrast. Most cases of contrast tomography are used for oncological diagnostics. The industry requires detection of the smallest neoplasms at an early stage, when pathological foci are not visually identified on tomograms. Only the identification of newly formed vessels allows one to suspect a tumor or metastasis.
Possible side effects
Despite the fact that gadolinium is considered a relatively safe element, substances containing it can still cause certain reactions in the body. However, it should be noted that this happens rarely (in about two cases out of a hundred). Sometimes after the examination the patient feels nausea, mild breathing problems, and dizziness. Itchy eyes may be present. Some people start sneezing.
The doctor always warns the patient about the possibility of side effects. If the discomfort is not severe or lasting, there is nothing to worry about. In cases where symptoms do not go away for a long time and are complemented by other negative sensations, you should seek medical help.
Contraindications to the use of MRI contrast agents
If you want to buy contrast for MRI at a pharmacy, you should pay attention not only to the gadolinium content, but also to the intended type of examination.
For example, gadobutrol, even in small doses, significantly improves T1 and T2 weighted imaging, which is used to scan the brain and spinal cord.
If Omniscan, an MRI contrast agent, is used for kidney disease, the likelihood of complications increases. For pyelonephritis, it is better to use a single-molar compound - Gadovist or Primovist at a dosage of 0.1 ml per kilogram.
- Decreased renal filtration (creatinine clearance below 30 ml per minute);
- Pregnancy (most of the substance passes through the placental barrier);
- Allergic sensitivity to gadolinium.
When choosing an MRI contrast whose name is unfamiliar, you need to study the manufacturer's instructions. Most drugs have no practical studies on their effects on children under 18 years of age. Gadovist is not used in cases of low seizure activity or a tendency to be allergic to gadolinium.
Features of preparation for examination using contrast
Features of preparation for MRI with a contrast agent depend on which organ will be the object of examination. People with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract should take the doctor's instructions seriously. Patients are advised to completely abstain from foods containing carbohydrates approximately three days before the procedure.
Food that can cause flatulence (cabbage, legumes, mushrooms) is prohibited. A day before the MRI, you can do an enema to cleanse your intestines. The last meal is allowed five hours before the procedure. Before the test, you should not drink for three hours. On the day of the procedure, you can take an antispasmodic.
If the pelvic organs are being examined, the patient needs to drink a large amount of water 60 minutes before the procedure. The average volume is liter. You cannot go to the toilet after this - the bladder must be full.
When examining other organs and systems, such preparation is not required. The recommendations are of a general nature only. The patient must remove all metal objects before the procedure. Otherwise, you may get burned. In the manipulation room, the patient must undress to his underwear and change into special clothing. Sometimes a contrast examination is carried out without it.
How to prepare for the examination
You should come to the procedure in loose clothing without metal inserts. You can leave your jewelry at home; you will still have to remove it during the procedure. Before the scan, it is better to cleanse your bowels and bladder naturally. Is it possible to eat: two hours before the procedure it is not recommended to eat food or drink a lot of water.
Before the procedure begins, the patient answers a series of questions, where he indicates the presence of metal and electronic devices in his body. Implants and artificial pacemakers are an absolute contraindication to scanning.
How to do the procedure:
- The patient gets ready: changes clothes, listens to the laboratory assistant’s instructions and lies down on the table.
- The nurse attaches a catheter to the vein through which gadolinium is administered. When the substance enters the bloodstream, patients often experience a tingling sensation in the body, especially the back of the head, warming of the arms, and a burning sensation. These are standard reactions that should not be alarmed.
- The table slides into the tomograph tunnel. The scan begins and lasts from 30 to 60 minutes. You cannot move during this time, otherwise the final picture will be distorted.
- After the examination, the table slides out. The catheter is removed, the patient changes clothes and is released. After a few days, the result is issued on a medium or sent by mail.
During scanning, the tomograph makes a knocking sound, so the patient is given earplugs or headphones.
Special instructions:
Due to the possibility of developing anaphylactic shock during drug administration, it is necessary to create all conditions for immediate, intensive therapy. Before each use of contrast media, obtain accurate patient information, including important laboratory data (eg, serum creatinine level, electrocardiogram, history of allergies, pregnancy).
Before the study, the patient should eliminate disturbances in the water-electrolyte balance and ensure a sufficient supply of fluids and electrolytes. This is especially true for patients with multiple myeloma, diabetes mellitus, polyuria or gout, as well as newborns, infants and young children, and elderly patients.
The absence of contrast enhancement is not unambiguous evidence of the absence of pathology, because Some types of neoplasms or non-contrast plaques in atherosclerosis are not contrasted. The presence or absence of contrast enhancement can be used for differential diagnosis.
Vials are intended for use on one patient only. When administering other drugs, you must use a separate syringe and needle.
Unused remains of the drug must be destroyed.
Each bottle or disposable syringe is designed to administer the drug to one patient.
It is not recommended to conduct preliminary testing of individual sensitivity using small doses of the drug, due to the risk of severe hypersensitivity reactions.
Patients who are afraid of waiting before the procedure require premedication with sedatives.
Omniscan distorts the results of measuring the concentration of calcium and serum iron in the blood when using some colorimetric (complexometric) methods commonly used in medical institutions. (It is not recommended to use these methods within 12-24 hours after Omniscan administration). If such studies are necessary, other methods of analysis should be used.
If the color of the solution changes or large particles are present, the drug cannot be used.
Effect on the ability to drive and use machinery:
Not described
Side effects
Classification of adverse reactions by frequency of development: very often (≥ 10%); often (from ≥ 1% to < 10%); uncommon (≥0.1% to <1%); rare (from ≥ 0.01% to < 0.1%); very rare (<0.01%, including isolated reports); frequency has not been established (it is impossible to estimate the incidence of side effects based on the available data).
When using Omniscan, the following side effects may occur on the systems and organs:
- mental disorders: rarely – anxiety; frequency not established – mental disorders;
- nervous system: often – headache; infrequently – transient perversion of taste, dizziness, paresthesia; rarely – short-term perversion of smell, drowsiness, tremor, convulsions, development of status epilepticus; frequency not established - tinnitus, ataxia, loss of consciousness, impaired coordination of movements, deep coma;
- immune system: uncommon – allergic reactions of mucous membranes and skin, hypersensitivity reactions; rarely – anaphylactoid reactions, anaphylactic shock; frequency not established - idiosyncrasy (may occur within a period of time from several hours to several days after administration of the solution);
- blood and lymphatic system: frequency not established - asymptomatic decrease in serum iron levels (within 8–48 hours after Omniscan administration);
- respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: rarely – cough, dyspnea; frequency not established - sore throat, sneezing, bronchospasm, shortness of breath;
- urinary system: rarely - the development of acute renal failure in patients with severe previous renal impairment; frequency not established - increase in serum creatinine levels;
- organ of vision: rarely – visual impairment;
- blood vessels: infrequently - redness of the skin;
- heart: frequency not established – tachycardia;
- gastrointestinal tract: often – nausea; uncommon – diarrhea, vomiting; frequency not established - belching, loss of appetite, abdominal pain;
- musculoskeletal and connective tissue: rarely – arthralgia; frequency not established – myalgia;
- dermatological reactions: infrequently – skin itching; rarely - rash, urticaria, swelling (including facial swelling, angioedema); frequency not established - development of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients with severe renal impairment;
- general disorders and disorders at the injection site: often - local pain, a feeling of coolness, warmth or distension at the injection site; rarely - chest pain, fever, chills; frequency has not been established - facial skin flushing, sensations of heat, increased sweating.