Today, each of us can go to the laboratory and donate blood to see if there are any serious health problems, and if there are any, begin treatment on time. If, after receiving the test results, it is discovered that all indicators are more or less normal, but AST in the blood is increased, then questions immediately arise: how dangerous is this, what do the three mysterious capital letters mean and many other related questions. Our article will help you get answers to them.
What is AST
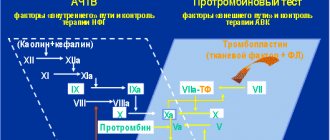
Aspartate aminotransferase, or AST for short, is the name of an enzyme that is part of absolutely all cellular structures of our body. But the largest amount of aspartate aminotransferase is found in the myocardium and skeletal muscles, then in liver cells, in nervous tissue, and in the kidneys. If the body is normal, then the levels of AST activity in the blood are quite low.
But when various organs or systems of the body are damaged, the enzyme begins to be released and enter the bloodstream. Thus, with a biochemical analysis, it becomes clear that AST in the blood is increased - this gives the doctor reason to suspect the beginning of destructive processes in the cells. The enzyme aspartate aminotransferase is necessary for proper cell function. It performs transport functions, delivering groups of atoms to various amino acids.
Age norms of ALT and AST in men: table
Using the table of indicators, you can track the norm of enzymes in accordance with age. Normal results look like this:
| Age | ALT (units/l) | AST (units/l) |
| 1 year or less | 56 | up to 58 |
| from 1 to 60 years | 10-40 | up to 40 |
| 60-90 years | 13-40 | up to 40 |
The numbers remain at their highest value only for the first year of life, gradually decreasing. In men over 90 years of age, ALT values begin to decline even more.
Normal AST values
Normal indicators for the optical determination method (in ME) look like this:
- for women - up to 35 IU;
- in men - up to 41 IU;
- in children - up to 50 IU.
Reitman-Frenkel reaction (mcomol/h/ml):
- for women - up to 0.35;
- for men - up to 0.45;
- in children - up to 0.5.
If blood biochemistry showed AST not exceeding the specified values, this indicates that the enzyme systems of the heart, liver, and kidneys are functioning normally, and the cellular composition of the organs is not damaged. If there are deviations in the tests and it is discovered that AST in the blood is increased, other specific markers (troponins, creatine phosphokinase, ALT, etc.) should be checked.
It must be said that different laboratories can use different reagents and research methods. Therefore, results obtained in different locations may vary slightly.
Standards for adults
If ALT and AST levels become higher than generally accepted, then this often indicates the presence of a disease. This indicator can be seen after biochemistry. It is important for a person to take it on an empty stomach and early in the morning in order to obtain reliable information.
For men, the maximum is as follows:
- AST – 47 U/l.
- ALT – 45 U/l.
Please understand that this is an average. That is why each laboratory can interpret studies differently. A person will not be able to understand on his own whether he has a disease. You will definitely have to visit a doctor so that you can understand exactly what is happening with your health.
Increased AST in the blood: causes
If the level of the enzyme in the blood is elevated, this may indicate the presence of any disease from the following list:
- myocardial infarction is one of the most common causes of too high AST levels, and the larger the area of myocardial damage, the higher the concentration of the enzyme aspartate aminotransferase in the blood;
- open or closed heart injury;
- rheumatic heart disease;
- angina pectoris;
- autoimmune or infectious myocarditis;
- bile duct cancer;
- liver cancer;
- liver damage by metastases;
- cholestasis;
- alcoholic hepatosis;
- fatty hepatosis;
- viral hepatitis;
- toxic liver damage;
- heart failure;
- extensive destruction of muscle tissue (crash syndrome, generalized myositis, muscular dystrophy);
- acute pancreatitis.
Also, if AST is elevated in the blood, this can be observed in case of injury to skeletal muscles, severe alcohol intoxication, burns, heat stroke, emboli in blood vessels and poisoning with poisonous mushrooms.
A slight increase in AST levels occurs during intense physical exertion and while taking certain pharmacological drugs (sedatives, antibiotics, etc.).
AST analysis: elevated values
An AST test may show an increased value in the following diseases:
- myocardial infarction (the occurrence of a focus of necrosis of the heart muscle caused by a violation of the coronary circulation). With the development of necrosis in the myocardium, an analysis for AST may show an excess of the norm several times (from 2 to 20). Moreover, changes in the results of the analysis on AST may precede the appearance of typical signs of a heart attack on the ECG;
- some other diseases of the cardiovascular system (acute rheumatic carditis, pulmonary thrombosis, severe attack of angina);
- hepatitis of various etiologies (infectious, toxic, alcoholic). In order to determine whether the increase in AST is caused by liver or heart problems, the AST/ALT ratio is used (ALT is another enzyme - alanine aminotransferase, present in significant amounts in the liver). Normally, the AST/AlAT ratio is 1.33±0.43. In case of liver diseases, this indicator is less than normal, in case of heart disease, on the contrary, it is more;
- other liver diseases: cholestasis (impaired bile secretion), liver cancer;
- skeletal muscle injuries;
- acute pancreatitis;
- myopathies (muscular dystrophies).
What can you find out when determining the level of aspartate aminotransferase in the blood?
If AST in the blood is slightly increased (about 5 times), then this may be due to fatty hepatosis, taking certain medications (barbiturates, statins, antibiotics, drugs, chemotherapy drugs, etc.).
A moderate, average increase in the enzyme (up to ten times higher than normal) can be caused by chronic liver diseases, cirrhosis, myocardial infarction, myocardiostrophy, processes occurring with damage to kidney and lung cells, mononucleosis, cancer.
If AST in the blood is greatly increased (10 times or more), this tells the doctor that the patient may have viral hepatitis in the acute stage, toxic damage to the liver structures, drug-induced hepatitis (acute), and this may also indicate a disease in the body processes accompanied by tissue necrosis (for example, with tumors).
At the beginning of the disease, in its acute stage, when the process of tissue destruction is fastest, the highest level of aspartate aminotransferase is observed. A decrease in AST in the blood serum means the beginning of restoration processes in organ cells and the patient’s recovery. Slight excesses of the norm are not a sign of tissue destruction.
Norm AsAt and AlAt in a biochemical blood test
The concentrations of these enzymes change over time, which is normal in childhood. For example, infants have higher levels than adults due to the nature of the birth period. Due to the massive release of red blood cells into the blood and their subsequent transformation into bilirubin, jaundice, characteristic of newborns, develops and, accordingly, an increase in the amount of ALT.
For AsAt and AlAt, the norms for children of different ages and adults can be found in the table:
Age
Maximum permissible values of AlAt, U/l
As can be seen from the table, normal indicators constantly fluctuate in childhood and adolescence, and from the age of 12 they also differ according to the gender of the subject. In addition, a slight increase in ALT levels is normal in women in the blood during early pregnancy. However, in the last trimester, an increase in enzyme concentration indicates gestosis, which threatens the health of the mother and fetus.
Aspartate aminotransferase is also determined in different quantities according to gender and age. In adult men, the upper limit of normal is 37 units per liter, in women - 31. The highest level is observed in children in the first days of life (up to 97 units / l), by one year it decreases to 82, and by six - to 36. For adolescents 12 -17 years old are considered normal values not exceeding 29 and 25 U/l for boys and girls, respectively.
What can distort the analysis results
Sometimes a doctor, seeing that AST in the blood is elevated, but not finding any visible signs of illness in the patient, recommends that he donate blood again, and this additional test shows normal levels of the enzyme. Upon detailed questioning, it turns out that the patient was taking medications on the eve of the first blood donation, which affected the correctness of the indicators. To avoid such situations, you need to know what can distort the result:
- Taking certain pharmaceuticals. It is important to inform your doctor about all medications you are taking. The doctor may prohibit taking certain medications a few days before donating blood.
- Use of herbal remedies: echinacea or valerian.
- Intake of large doses of vitamin A into the body.
- Pregnancy.
- Severe allergy.
- Catheterization or recent heart surgery.
If AST in the blood is elevated, the reasons may be different, sometimes even unexpected. In order not to worry unnecessarily because of incorrect results, it is not recommended to donate blood for testing for several hours after undergoing the following procedures:
- fluorography;
- rectal examination;
- Ultrasound;
- physiotherapy;
- radiography.
How to test for AST blood levels
A blood test to determine whether the enzyme level is elevated or not is done in the following sequence: to determine the content of aspartate aminotransferase in the blood, a biochemical study is necessary. The material is taken from a vein only in the morning and only on an empty stomach.
First, the nurse applies a tourniquet to the arm above the elbow, then a needle is inserted into the vein and approximately 15-20 ml of blood is withdrawn. The tourniquet is then removed and a cotton swab is applied to the injection site. The patient is instructed to bend the elbow and firmly grasp the injection site to stop the bleeding. You can sit for a few minutes and then go home.
And in the collected blood, the plasma is separated using a centrifuge, and the necessary chemicals are produced. reactions and AST activity is determined. Results are usually ready the next day. It is better not to independently decipher the results given to you; this should be done by a doctor.
Elevated aspartate aminotransferase: what treatment is needed?
It is important to understand that if an analysis was performed and it was confirmed that AST in the blood was greatly increased, then this could not just happen on its own. This is due to the presence of some pathology in the body, with the destruction of the structures of the liver, heart muscle or other tissues. This means that it is impossible to lower AST without treating the disease that caused the jump in enzyme concentration.
Therefore, the main task of the attending physician will be to find the reasons for this when AST in the blood is elevated. That is, the priority is to carry out an early diagnosis, and then prescribe treatment. After eliminating the disease, the level of aspartate aminotransferase will also decrease.
How to properly prepare for an AST test
To make the test results more reliable, you need to donate blood on an empty stomach. Moreover, at least 8 hours must pass after the last meal. It is very important the day before going to the laboratory to give up alcohol, fatty and fried foods, and also to avoid both physical, emotional or mental overload. In the morning before the test, you can only drink clean water, but under no circumstances drink coffee, juices or teas - this can negatively affect the blood test.
Whether AST is elevated or not is determined no earlier than seven days after being sent for analysis, so that there is time for preparation. One, or better yet, two weeks before the test, experts strictly recommend stopping taking medications. If it is not possible to fulfill this requirement, you must notify your doctor about this so that he can make the necessary corrections when deciphering the analysis data or schedule the procedure for another day. If you have an allergy or pregnancy, you should also inform your doctor about this.
Indications for the purpose of analysis
The described analysis is prescribed for certain diseases:
- Acute or chronic heart disease.
- All liver diseases.
- Diseases of the circulatory system.
- Infections.
- Kidney failure.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Encephalopathy of unknown etiology.
- Bilirubin metabolism disorders and different types of jaundice.
- Pathologies are purulent-septic.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Gallstone disease and impaired bile outflow.
- Malignant tumors.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Skin diseases caused by allergies.
- Preparation for major surgery.
- Injuries to the chest or abdomen.
In addition, it is prescribed to assess the dynamics in the treatment of cardiac and liver pathologies and during the use of antibiotics (long-term), various toxic drugs, as well as chemotherapy drugs.
About the ALT indicator
What is increased AST in the blood, we have found out the reasons for this phenomenon. Now let's talk about an equally important indicator. Usually, when prescribing a biochemical blood test, the doctor wants to look not only at the AST level, but also at the content of another enzyme - ALT.
This is alanine aminotransferase, which, like AST, is present in the cells of all organs, but the largest amount is found in the liver and kidneys. When problems occur in the liver, ALT enters the bloodstream. Its increase makes it possible to diagnose serious liver diseases even before the appearance of jaundice, a characteristic symptom of various hepatitis. Therefore, an increased level of ALT in the blood is interpreted by doctors as an indication of damage to this organ.
If a person has undergone a biochemical blood test, AST and ALT are elevated, this may mean that serious destructive processes are occurring in the body. Let us recall that both enzymes enter the blood in increased quantities only if there is destruction of cellular structures. This does not necessarily indicate the presence of the disease. Only a doctor can draw the correct conclusions after additional diagnostic procedures. There is no need to panic, but you also shouldn’t delay your visit to the doctor.
Decoding the results
Only the attending physician is responsible for deciphering the indicator. At the same time, it takes into account the gender, age, and health status of the patient. Excess weight, stress, and significant physical activity the day before affect the results. For example, during pregnancy and chronic pathologies, aspartate aminotransferase is increased. In healthy people, if the rules for taking the test are followed, it should be within normal limits.
Medical institutions use different equipment and reagents, so test results in each laboratory may vary. The column with the normative figures of a particular diagnostic laboratory is called “reference values”.
Enzyme activity is measured in units per liter (U/L). It is very rare to find another indicator - mkat/l (microcatal per liter). Its conversion into units is carried out in accordance with the fact that 1 unit/l = 0.0167 mkat/l. Therefore, 40 units/l = 0.668 mkat/l.
Normal values
In adults, an AST level of up to 40 U/L is considered normal. There are also boundaries below which he should not fall. Aspartate aminotransferase norm for people of different ages (in units/l):
- newborns: 22−70;
- infants up to one year: 15−60;
- children under 15 years old: 6−40;
- adults (women/men): <32/<40;
- people over 60 years old: 3−40.
Exceeding the norm
Aspartate aminotransferase is always present in small quantities in the blood. However, a significant excess of the norm indicates the destruction of cellular structures in which the enzyme is in high concentration. These are cells of the liver, heart, brain, kidneys, and skeletal muscles.
AST levels increase within 6-10 hours after organ destruction, usually before the appearance of clinical signs and symptoms of the disease. They remain very high for a long time, which depends on the course of the disease. It happens that in the early stages of liver pathology and hepatitis C they do not go beyond normal limits, and this can complicate diagnosis.
If aspartate aminotransferase is increased 5 times or more, the reasons may be:
- hepatitis in acute or chronic form;
- myocardial infarction or necrosis;
- pancreatitis;
- heart failure;
- muscular dystrophy, internal organ injuries;
- hemochromatosis (genetic pathology caused by the accumulation of iron in the liver);
- fatty liver (in people who abuse alcohol);
- cirrhosis, liver cancer.
Other equally serious reasons for exceeding the indicator include poisoning, hypoxia, ulcerative colitis, and myocarditis. Aspartate aminotransferase is abnormally elevated after an alcoholic party, taking antibiotics and valerian. A comparison of the AST level with another indicator - ALT (alanine aminotransferase) - will allow us to suggest the cause of the increase.
The AST/ALT ratio is called the Ritis coefficient. Its value below one indicates pathologies such as viral and autoimmune hepatitis, hemochromatosis, toxic or drug effects on the liver. When the Ritis coefficient is above one, liver damage due to alcohol and drug abuse, cirrhosis, destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis), pathologies of the thyroid gland and muscle tissue can be detected.
Reasons for the downgrade
Along with an increase in the indicator, situations can be observed when aspartate aminotransferase is reduced. There is no lower limit for adults, however, very low values indicate the transition of the disease to the terminal stage and extensive damage to the problem organ.
The level of the enzyme is reduced when the body is exhausted, in the last stages of cancer and cirrhosis, and when the liver ruptures. A similar phenomenon is observed in acute pancreatitis, cerebral infarction, and lack of vitamin B6 in the body.