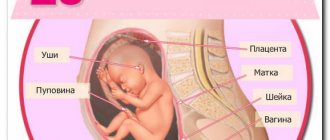
An ultrasound scan at 33 weeks of pregnancy is recommended for absolutely all pregnant women. This is the last mandatory study for the entire period of gestation. According to the established procedure, an ultrasound examination must be performed at 32–34 weeks. This diagnosis is carried out to accurately determine the development of the fetus. The results of an ultrasound scan performed at this time will provide an overall picture of the development of the fetus, whether the indicators correspond to the norm, and the presence of pathologies.
Ultrasound diagnostics is necessary to determine:
- Presentation of the baby;
- Localization of the placenta;
- Cervical length;
- Exclusion of anomalies in the development of the baby;
- Conditions of the cervical canal.
Mom's body, her condition at 33 weeks
At 33 weeks, maximum abdominal elevation is observed. Due to its large size, it puts pressure on the lungs, diaphragm, and digestive organs. As a result, the pregnant woman experiences shortness of breath, heartburn, and pain in the area under the ribs (where the baby’s tiny legs are now resting).
In the following weeks, the pregnant woman will experience some relief in her condition, as the stomach drops down and the pressure on the internal organs weakens.
From this period, the child rapidly gains weight, the daily gain is approximately 20 grams. There is a disappearance of heartburn and shortness of breath, but there is a shift in the center of gravity and a strong load on the spine.
At this time, the expectant mother needs to be extremely careful to avoid falling. It is also worth paying attention to the skin of the abdomen, which is stretched due to the rapid growth of the baby. Keep your skin moisturized to reduce the likelihood of stretch marks.
Ultrasound at 34 weeks
If an ultrasound is performed at the 34th week of pregnancy, then the position of the child, its main dimensions, the condition of the placental membrane, amnion and umbilical cord are examined in the same way. In parallel, the condition of the maternal organs is assessed, in particular, the cervical canal with pharynx and the uterus.
Fetal changes
The body length of the unborn child increases to 44-45 cm, and weight up to 2300 grams. The mechanisms of development of internal organs, especially the liver and lungs, continue. In preparation for a change in environment, they undergo slight changes.
This week, about 9% of the child’s body weight is represented by subcutaneous fat (including brown fat), which is why the color of the skin changes to lighter pink shades. The process of disappearance of lanugo, especially the cannon, which covered most of the body of the fetus, is progressing.
At the same time as the amount of fuzz decreases, the hair on the head becomes larger and thicker. At this stage, the pregnant woman feels less intense movements and tremors due to a decrease in the free uterine space.
Data decryption
Ultrasound indicators in a given gestational week, as a rule, do not differ from previous ones. The presentation is still cephalic, there is a moderate amount of amniotic fluid, and the degree of maturity of the placental membrane is within 1-2 degrees.
The length of the cervical canal should normally be more than 3 cm, and the internal and external pharynx should be closed. At the same time, the placenta itself is localized 7 cm above the cervical os.
Also this week, the size of the child’s bones is finally determined:
- the length of the femur reaches 70 mm;
- shoulder – up to 64 mm;
- shin bones are 55-65 mm;
- The length of the forearm is 49-55 mm.
What are the benefits of ultrasound examination?
Recently, there has been a conscious attitude towards the health of oneself and the unborn child. Expectant mothers are concerned about the likelihood of harm to the baby through ultrasonic waves. Experts say that this procedure does not pose any danger to the baby’s condition or development.
It is advisable to undergo an ultrasound to ensure that development is normal and that there are no pathologies. This diagnosis is especially important at 33 weeks. There is little time left before giving birth and the pregnant woman begins to worry about various fears, which a consultation with a gynecologist and the results of an ultrasound scan can dispel.
Sometimes there are cases where the sex of the child remains uncertain right up to the last ultrasound. Even the latest ultrasound may not always be able to visualize the baby's gender. An ultrasound still gives at least some chance, but a lot depends on the baby himself, his behavior, and position in the uterus.
The norm of child development indicators is also unable to indicate the sex of the fetus. If the child has taken a certain position before the third ultrasound examination, and there is already little amniotic fluid, then the gender cannot be determined.
Indicators of the child’s body
Using a small sensor from which ultrasonic waves emanate, you can examine at least 16 parameters characterizing the general condition of the baby.
Weight category
The average weight varies from 1850 g to 2300. However, deviations from the generally accepted value are not always a cause for concern. It is worth noting that the indicator under consideration directly depends on the BMI (body mass index) of both parents: if we are talking about a fairly large physique, the mark can exceed 2500–3000 g, and if it is fragile, then the parameter will be in the range of 1300–1600 g.
Height
Based on the ultrasound results, growth is also determined (not to be confused with the coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus). So, 40–43.5 cm is quite the optimal option. A slight error of 3–5 cm is allowed towards both the minimum and maximum.
Heart rate
Carrying out CTG (cardiotocography) in parallel with the ultrasound process allows you to calculate the exact digital index of heart rate or the number of heart muscle beats in 1 minute.
It is generally accepted that normal values equate to a period from 120 to 160 beats/min. ± 5 units. When the rate drops below 100, they speak of bradycardia; an increase from 170–175 is called tachycardia. Both cases require additional types of examination that will fully clarify the situation.
Head and abdominal circumference
In order to verify the proportional structure of a small body, a specialist uses ultrasound to identify a number of measurements, which include the circumference of the tummy and head. The first parameter should be 258–336 mm, the second – 285–335 mm. In the third trimester, the baby's head has already reached its normal harmonious size.
Results of measurements of coolant and exhaust gas during ultrasound
Chest diameter
Another classic indicator is DHA. The special comparative table shows a norm of 83–88 mm.
LZR and BPR
Two values related to each other determine the general structure of the child’s head. Thus, the LZR (fronto-occipital size) is a segment connecting the middle of the occipital bone with the frontal bone. BDP (bipariental size) is the distance between the parietal bones or, to put it simply, the width of the head.
| Indicator name | Norm (mm) | Allowable fluctuation (mm) |
| BPR | 80–85 | 75–91 |
| LZR | 102–109 | 95–115,5 |
Position in the womb
An extremely important factor influencing the tactics of childbirth is the location of the fetus in the mother's womb. If there is a so-called cephalic presentation detected on an ultrasound, then the birth is carried out in the classical way.
Indicators of fetal condition on CTG
Sometimes the baby takes less suitable positions:
- Transverse (perpendicular to the spine).
- Mixed (hips and knees bent at the same time).
- Gluteal (buttocks rest on the mother’s pelvic bones).
- Foot (legs pointing down).
There is an opinion that each of the listed cases requires only a cesarean section, but this is not entirely true. There are known medical facts that indicate the natural normalization of the child’s position even at such a late stage without any intervention.
Absence/presence of umbilical cord entanglement
The norm characteristic of 33-34 weeks of pregnancy practically does not allow the child to be entangled in the umbilical cord. The reason for this is the increased likelihood of fetal hypoxia, which is observed with numerous intrauterine loops. The presence of a single half-loop without tension is the only exception and is not a cause for concern.
Acceptable loop encircling the right leg
Nasal bone
This facial bone must be measured during an ultrasound scan, since in some cases it is an indicator of the presence or absence of Down syndrome. The average value is equivalent to 11.3–11.5 mm. If the detected figure reaches 9 mm or increases to 13.8 mm, then do not panic. Such variations are only a manifestation of individuality, not pathology.
Length of tubular bones
Elongated round bones include the hips, forearms, shoulders, and shins, consisting of the tibia and fibula. The combination of these 4 values reflects the condition of the musculoskeletal system:
| Name of bones | Allowable length (mm) |
| Shin | 83–85 |
| Hip | 63–65 |
| Forearm | 48–50 |
| Shoulder | 56–58 |
Anatomical features
In the form with ultrasound indicators, you can often find data reflecting the development of certain organs, facial structures, as well as bone elements. These include:
- nasolabial triangle;
- lungs;
- kidneys;
- spine;
- cerebellomedullary cistern;
- bladder;
- eye sockets;
- lateral ventricles of the brain;
- stomach;
- cerebellum;
- 4-chamber section of the heart.
The absence of violations is recorded using various entries in the corresponding columns - “no pathologies”, “b/p”, “examined”, “norm” or “+”. If the sonologist identified some abnormality during the ultrasound session, he will describe it in detail on the form.
Last ultrasound readings
An ultrasound at this stage is performed not only to determine development and its compliance with the norm, but also to clarify the date of birth. The day a child is born is determined by the degree of its maturity. The diagnosis determines the presence/absence of the child being entangled in the umbilical cord. If there are any problems with the location of the umbilical cord, experts recommend performing a caesarean section.
By the 33rd week of its development, the baby reaches a weight of 2 kilograms. The normal growth rate at this stage of pregnancy is considered to be 1,800–2,550 g.
Ultrasound diagnostic data is absolutely accurate, but it is very important to understand it. It is also worth considering the fact that each child develops taking into account the individual characteristics of the body. Inconsistency with the norm of development of the current period should not cause strong anxiety in the pregnant woman. The interpretation and analysis of ultrasound indicators is performed by a specialist who will explain everything.
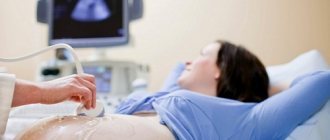
Preparation and performance of ultrasound
It is advisable to perform an ultrasound scan at the 33rd week of pregnancy before lunch. But you don’t need to starve for this. A light breakfast with a sweet drink will make the baby active, and the examination will provide more information. The study is carried out using transvaginal and transabdominal methods.
Before going to the procedure, you need to have breakfast
When going for a routine ultrasound, you must have a referral from your obstetrician-gynecologist, a sheet for the couch, a napkin for removing the gel and a pair of condoms for a vaginal ultrasound. Condoms will be required for transvaginal examination of the cervix.
If the cervix is slightly open, the woman will need to be admitted to the hospital for conservation or to prepare for premature birth.
Recommendations and advice for the expectant mother
- To avoid heartburn, watch your diet. Avoid spicy, fried, fatty, smoked foods. Eat small and frequent meals;
- To avoid swelling, it is sometimes recommended to drink no more than 1.5 liters of water per day;
- To avoid genital tract infections, strengthen your hygiene standards, wear cotton underwear;
- At this stage of pregnancy, you can already start looking for a maternity hospital. When choosing it, be sure to pay attention to the specialization, conditions and equipment, and qualifications of the medical staff;
- If you are expecting a second child, then it is time to prepare your eldest for the arrival of a new family member. Even before giving birth, try to “make friends” with them. Invite your child to stroke his tummy or talk to his brother or sister. And don’t let him feel out of place;
- Be grateful for everything that happens, and all future events will begin to please you;
- Don't worry too much about any of today's failures or problems. No matter how difficult it may be, remember that there is a reason for everything and nothing in the Universe remains without “payment.”
Previous: Week 32 Next: Week 34
Choose any other one in the pregnancy calendar.
Calculate the exact date of birth in our service.
How did you feel at the 33rd obstetric week? Share with us!
Basic information about the third screening during pregnancy
The third screening examination is prescribed to the expectant mother at 32–34 weeks of pregnancy and is mandatory for all pregnant women.
Even if the first two screening examinations did not show any abnormalities in the development of the fetus and the woman’s health status, the third screening should under no circumstances be neglected.
Mandatory diagnostic procedures during the third trimester of pregnancy include only ultrasound.
If any abnormalities are detected in a pregnant woman, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostic methods:
- cardiotocography (CTG);
- Dopplerometry;
- biochemical screening.
Indications for additional diagnostic methods:
- the age of the expectant mother is more than 35 years;
- father's age is over 40 years;
- identifying abnormalities on ultrasound;
- the presence of genetic diseases in close relatives;
- complications of previous pregnancy (premature birth, miscarriage, frozen pregnancy);
- infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy;
- taking medications that can affect the course of pregnancy;
- presence of occupational hazards or bad habits in a pregnant woman.
Mother's feelings in the last month of pregnancy
The state of health of the expectant mother at this time cannot be called ideal. Her spine is under serious stress, and her large belly often interferes with her ability to move. During this period, the woman gains about 12 kilograms in weight. It becomes especially difficult to fall asleep, since a rounded and raised belly slightly depresses the functioning of the lungs. Often women have the feeling that they just can’t breathe. Although this is rewarded with very beautiful and interesting dreams, since the nervous system is in an excited state. Doctors do not recommend resting on your back during late pregnancy, because in the final period of pregnancy in this position the uterus can put pressure on the abdominal aorta, leading to fainting.
The uterus also puts intense pressure on the bladder, so the expectant mother runs to the toilet even more often than at the very beginning of the term. At this time, the circulatory system of women works at full capacity, because more than 5 liters of blood circulate through it. Fortunately, at this time the normalization of red blood cells occurs, due to which anemia disappears. Hormones also work in an enhanced mode, provoking the production of colostrum.
It is especially worth noting the increased appetite, and this is the norm. But sometimes the expectant mother cannot control it, and uncontrolled consumption of lunch portions leads to weight gain. If you don’t want to painfully lose weight after childbirth, you don’t need to give up food under any circumstances. You just need to eat 7 times a day, but in small portions, and exclude flour and sweet foods rich in carbohydrates from your diet.
Some consequences of pregnancy can stay with a woman forever. For example, stretch marks. They appear when the skin on the abdomen is not elastic and dry. Therefore, especially in late gestation, it needs to be moisturized and softened with various cosmetics and oils. If your stomach starts to itch, this is a sure sign that it will soon be covered with stretch marks.
Biochemical screening
Biochemical screening is prescribed only if there are indications for a pregnant woman. The method is based on the fact that during pregnancy a woman’s body produces specific proteins, the content of which changes during pregnancy. Specific proteins are called:
- pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (Pregnancy-associated Plasma Protein-A; PAPP-A);
- human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG);
- alphafetoprotein (AFP).
If deviations in these indicators are detected, an additional blood test for placental lactogen and free estriol may be prescribed.
To determine the protein content of a pregnant woman, 10–20 ml of venous blood is collected and the concentration of substances is determined using reagents. A woman must prepare in advance for a blood test, following all the rules described above.
Evaluation of results
The norms for these indicators are calculated depending on the stage of pregnancy and the results should only be assessed by an experienced doctor. Screening can detect diseases such as Down syndrome, Shershevsky-Turner syndrome, and Edwards syndrome.
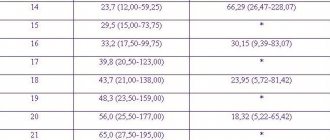
Table: norms of indicators depending on the stage of pregnancy
| Gestation period, in weeks | ||||||
| Index | 30–31 | 32–33 | 34–35 | 36–37 | 38–39 | 39–40 |
| PAPP-A, honey/ml | 1,47–8,54 | |||||
| HCG, honey/ml | 10000–60000 | |||||
| AFP, U/ml | 100–250 | |||||
| Placental lactogen, mg/l | 3,2–10,1 | 3,2–10,1 | 4,0–11,2 | 4,0–11,2 | 4,0–11,2 | 4,4–11,7 |
| Free estriol, ng/ml | 2,4–9,9 | 2,6–11,4 | > 3,0 | > 4,7 | > 6,6 | > 7,3 |
The importance of third screening during pregnancy
The third screening during pregnancy is mandatory for all expectant mothers and this procedure should not be neglected. The main objectives of the examination at this stage are to determine the woman’s ability to give birth to a child naturally, to assess the health of the fetus and its vital organs.
In practice, there are often situations when a pregnant woman neglects the advice of doctors, especially if she hears about delivery by cesarean section. It is important to remember that if a doctor gives indications for an operation, it means that he has objective reasons for this. Due to my profession, I quite often hear from women that they do not want surgery and prefer to give birth naturally. In some cases, it is possible to convince the woman and persuade her to choose the right decision, in other cases, the pregnant woman insists on her own. With this development of events, no doctor will guarantee the normal course of labor or the safety of the health of the mother and fetus. Often in such situations, complications develop during childbirth that can threaten the life of the mother and/or fetus. A pregnant woman is responsible not only for herself, but also for her unborn child, therefore, if a doctor, for medical reasons, makes recommendations for the birth of a baby by cesarean section, you should not object to him.
Cardiotocography
A diagnostic method that is based on measuring the fetal heart rate, changing the indicator depending on uterine contractions and exposure to external stimuli.
The position of the woman during the procedure is reclining or lying on her back. The doctor attaches sensors to the abdomen: an ultrasound sensor to record the fetal heart rate, a strain gauge to record uterine contractions. The duration of the procedure is no more than 40 minutes.
Attaching electrodes and the position of a pregnant woman during CTG
No special preparation is required before performing a CTG; if necessary, the expectant mother should visit the toilet, since the procedure takes a long time. It is important not to be nervous, forget about fears, and not be hungry. When performing CTG, it is necessary that the child is awake, the woman can eat something sweet, and the baby will be active.
Ilyina Natalia
https://dealinda.ru/magazine/3/457/
Evaluation of CTG results
During the procedure, five indicators are determined, each of them is scored from 0 to 2 points. The points received for each of the indicators are summed up and the final score of the results is calculated:
- 8–10 points corresponds to the normal development of the baby;
- 5–7 points — average score, indicating the initial degree of development of hypoxia in the child;
- less than 4 points - the presence of serious pathologies in fetal development.
Table: assessment of CTG indicators at the third pregnancy screening
| HR parameters (heart rate), beats per minute | 0 points | 1 point | 2 points |
| Basal heart rate | 180 | 100–120; 160–180 | 120–160 |
| Heart rate variability: oscillation frequency per minute | <3 | 3–6 | >6 |
| Oscillation amplitude per minute | 5 or sine wave | 5–9 or >25 | 10–25 |
| Heart rate changes: accelerations | None | Periodic | Sporadic |
| Decelerations | Late long or variable | Late short-term or variable | Absent or early |
When performing CTG, the following deviations may be expected:
- fetal hypoxia;
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- high and low water levels;
- premature maturation of the placenta;
- malformations of the cardiovascular system.
If low indicators are obtained, associated with dysfunction in the “mother-placenta-fetus” system, the issue of emergency delivery by cesarean section is decided.