Purpose of the study
The third screening study is carried out at 33-34 weeks. Ultrasound at 35 weeks is an additional method of examining a pregnant woman.
It pursues the following goals:
- determines the position of the fetus;
- excludes developmental anomalies;
- calculates the volume of amniotic fluid;
- assesses the child's maturity;
- determines the place of attachment of the placenta, its maturity;
- excludes or confirms umbilical cord entanglement.
Feel
34-35 weeks of pregnancy - not only the physical, but also the psychological sensations of a woman change. Hormonal changes occur in the body as the period of gestation enters the final stage. This can increase a woman’s touchiness and sensitivity to the actions and words of those around her.
Therefore, at this stage it is necessary to look for positive emotions. To do this, it is recommended to devote more time to your favorite activities that bring pleasure, avoid stress and communicate more often with pleasant people. Shopping for things for the future baby, as well as watching movies, also help to distract yourself.
During these weeks, women are increasingly worried about the upcoming birth, which contributes to anxiety and insomnia. Expectant mothers who had complications during a previous pregnancy or are giving birth for the first time are more susceptible to this.
In the absence of moral support from loved ones, this can lead to depression, increased panic attacks and complete immersion in the inner world. All this can negatively affect the health of mother and baby.
During this period, the support of relatives is very important, who will be able to take care of everyday problems, as well as listen and reassure. If necessary, you should additionally visit a psychologist and gynecologist, with whom you need to discuss issues that cause fears and worries.
Changes in the mother's body
For most women, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted during this period. The intestines are compressed by the enlarged uterus, which provokes the development of constipation. The displaced stomach acquires an almost horizontal position. Its contents begin to flow into the esophagus even if the woman has consumed a small amount of food. This leads to heartburn.
The increased load on the kidneys provokes swelling of the lower extremities, especially after overusing salty foods. Pain in the area of the pelvic bones and lower ribs becomes almost constant. Due to the enlarged uterus, the ribs move apart.
The pelvic floor muscles relax, which often leads to urinary incontinence, especially when sneezing or coughing. The uterus puts pressure on the lungs, making breathing difficult. Training contractions appear periodically, causing discomfort to the woman. Discharge from the genital tract often contains mucus. The cervix becomes softer, the cervical canal opens slightly, and the mucous plug that covers it is separated in a small amount.
Features of the fetus
The internal organs of the fetus have finally formed and are beginning to function fully. The formation of the genitourinary and nervous systems is completed. In the intestines, the amniotic fluid swallowed by the fetus is broken down into sugar and water. Meconium is also formed - original feces, which consists of exfoliated skin cells and bile that enter the digestive system along with amniotic fluid.
The immune system matures, and surfactant accumulates in the lungs, which allows them to open during the first breath. The adrenal glands are actively developing, in the cortex of which substances are produced that help the body in stressful situations. The bones of the skull are movable, which allows the baby to pass through the birth canal more easily.
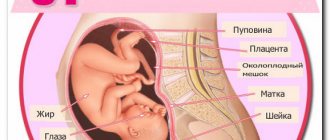
What does your baby look like at 35 weeks?
At the end of the third trimester, the baby has gained fat and muscle mass, so it already looks like a newborn. The skin gradually smoothes out and turns pale, vellus hair disappears, and the original lubricant remains in small areas.
On an ultrasound at 35 weeks of pregnancy, you can clearly see the folds around the neck, under the buttocks, in the area of the joints of the legs and arms. Nails have formed on the fingers of the upper and lower extremities. Cheeks become plumper, hair grows and accumulates pigment. The eyes are most often closed, the iris becomes the color that was genetically assigned.
In girls, the labia minora are hidden by the labia majora, and in boys, the testicles descend into the scrotum. The child is most often positioned head down in the pelvic area.
Physical activity at 35 weeks of pregnancy
Even though the thirty-fifth week of gestation has arrived, a woman should not stop leading an active lifestyle. A mother who wants to quickly get in shape after childbirth and give birth without any problems should perform a series of physical exercises right up to being sent to the maternity hospital. But when playing sports, the main thing is not to overwork and not overload the body.
By maintaining an active lifestyle and physical exercise, you can:
- Improve blood flow to internal organs and strengthen muscles;
- Learn to breathe correctly;
- Learn to relax and tense the muscles of the abdominal area, which will definitely help during childbirth;
- Minimize complications and ruptures when the baby is born;
- Get in shape quickly after giving birth.
When playing sports, a woman should not lift weights, jump or perform exercises that involve sudden movements. You should choose light loads that do not have a negative effect on the body.
Ultrasound technique of this period
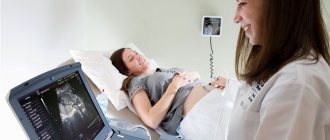
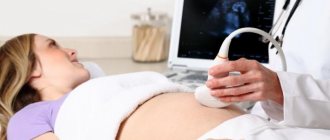
Ultrasound examination at this stage is carried out transabdominally. The woman lies down on the couch, the doctor applies a special gel to her stomach and conducts an examination using a sensor. Sometimes it may be necessary to perform the examination in the lateral position.
There is no need to prepare for such a procedure. It is advisable that the child behave calmly during the study, because its activity may interfere with accurate measurements.
When is an ultrasound necessary?
When the expectant mother comes to see her doctor, she is explained the need and timing of observations under an ultrasound machine. There are two types of ultrasound examinations: screenings and selective examinations. Screening is the mandatory examination of all pregnant women using ultrasound at a certain time. Typically, the expectant mother undergoes a routine ultrasound examination at 10 to 12 weeks, 22 to 24 weeks, 32 and 37-38 obstetric weeks of pregnancy. When conducting this type of examination, the size of the fetus and its compliance with standards, gestational age, condition of the uterus and placenta are measured. Selective studies are prescribed by the attending physician if there is a suspicion of a pregnancy complication. If pregnancy pathology is determined, such examinations can be carried out an unlimited number of times.
Research results
Ultrasound at 35 weeks of pregnancy is practically no different from the third screening study. The examination protocol includes:
- information about a pregnant woman;
- information on the state of provisional authorities;
- assessment of anatomical structures;
- fetal fetal data.
The section dedicated to a pregnant woman contains information about her age, stage of pregnancy, and date of her last menstruation. In addition, it includes information about the condition of the appendages, the walls of the uterus, and detected pathologies.
Fetal fetometry
The fetometric dimensions of the fetus according to ultrasound are important not only at this stage of pregnancy, but also at the rest. The doctor, by comparing the data obtained with normal indicators, can determine possible defects and intrauterine growth retardation.
Fetometric parameters of the fetus according to ultrasound at 35 weeks (normal):
- biparietal head size – 8.1-9.5 cm;
- abdominal circumference – 28.5-34.5 cm;
- head circumference – 29.9-34.5 cm;
- fronto-occipital size of the head is 10.3-12.1 cm.
Length of bones in different parts of the body:
- hips – 6.2-7.2 cm;
- shins – 5.5-6.3 cm;
- forearms – 4.8-5.6 cm;
- shoulder – 5.5-6.5 cm.
The length of the limbs is measured from both sides. This allows us to exclude developmental defects.
Brain Measurement Chart
At 35 weeks, deciphering the ultrasound of the anatomical structure of the fetus is important. At this time, developmental defects are identified or excluded that were impossible to identify during previous examinations. First, the doctor evaluates the structures of the central nervous system. When examining the brain, the specialist examines both hemispheres, the cerebellum, visual thalamus, interhemispheric fissures, and lateral ventricles.
Brain measurement chart at 35 weeks
| Index | 5th percentile (cm) | 50th percentile (cm) | 95th percentile (cm) |
| Rear horn width | 0,65 | 0,85 | 1,2 |
| Lateral ventricles | 0,2 | 0,49 | 0,77 |
| Large tank width | 0,56 | 0,75 | 0,85 |
| Transverse diameter of the cerebellum | 4,1 | 4,4 | 4,7 |
| Width of transparent partition | 0,42 | 0,67 | 0,93 |
| Corpus callosum thickness | 0,22 | 0,27 | 0,33 |
| Corpus callosum width | 0,54 | 0,71 | 0,88 |
| Corpus callosum length | 4,1 | 4,5 | 5 |
Provisional structures
Using an ultrasound at 35 weeks, the doctor evaluates the placenta according to the following criteria:
- thickness;
- attachment site;
- maturity;
- internal structure.
Placenta previa is detected exclusively in the third trimester. Thanks to such data, the doctor determines how the birth will proceed. At this stage, the thickness of the placenta should be 2.7-4.4 cm, and the degree of maturity should be the second.
The volume of amniotic fluid is determined using the amniotic fluid index. The normal value at this period is 2-8 cm. A deviation of the indicator to a lesser extent indicates oligohydramnios, and a greater deviation indicates polyhydramnios.
The umbilical cord connecting mother and child has 3 vessels: 1 vein and 2 arteries. If this organ contains only one artery and vein, then this indicates pathologies of fetal development. An ultrasound scan can reveal the umbilical cord entwined around the fetal neck.
Fetometry - what is it and why?
Fetal fetometry is considered one of the important procedures. During the procedure, the doctor analyzes the size of the fetus and whether it corresponds to the norm. The procedure is an ultrasound examination, the data of which is checked by a specialist against tables of norms. The test helps to detect defects and deviations in the baby’s development in a timely manner. When performing fetometry, the fetal head circumference is determined by week - the norm is an important indicator. Week by week, the doctor records the ultrasound readings and draws conclusions about the baby’s health. When the doctor notes that the fetus is smaller in size than established for a given period, they speak of a slowdown in fetal growth. If, as the pregnancy progresses, a delay of a couple of weeks appears, then doctors talk about intrauterine growth retardation. Such a delay can be caused by bad habits of the mother, internal infections, chromosomal abnormalities or placental insufficiency.
Risks at 35 weeks of pregnancy
At this stage, the doctor can detect low placentation. In this case, it is attached to the lower part of the uterus, partially blocking or completely closing the internal os. This leads to complications during childbirth or fetal death from insufficient blood supply. This pathology is also dangerous for a woman carrying a child. The resulting bleeding in 1-3% of cases leads to the death of the expectant mother. Sometimes the placenta rises under pressure from the enlarging uterus. Otherwise, a caesarean section is performed.
Sometimes labor may begin at 35 weeks. The baby is well developed physically, so his lungs are ready to breathe after birth. The physical and mental development of children born at this time is in no way inferior to the development of children born at the right time.
Recommendations
Nutrition
The best ways to prepare dishes are stewing, steaming, baking or boiling. It is recommended to consume food little by little and often.
Required on the menu:
- You should include foods rich in protein, iron, magnesium, calcium and folic acid.
- Limit your salt intake.
- Lean meat and fish, fresh vegetables, cereals, and low-fat broths should be present.
- It is recommended to replace sweets, sugar, buns and cakes with healthy dried fruits.
- It is important to maintain the correct drinking regime. Clean water without gas, homemade compotes, berry fruit drinks - you need to drink 1.5 liters of liquid daily. If edema occurs, fluid intake should be reduced to 1 liter per day.
Physical activity
The main rule is moderation and lack of fatigue when performing exercises:
- Leisurely walks in the fresh air away from polluted roads are an excellent option for daily activity. It is better not to plan long trips and always take an exchange card with you.
- It is recommended to perform a daily set of light exercises designed specifically for late pregnancy. You can exercise if there are no contraindications.
- It is useful to perform breathing exercises and Kegel exercises.
Intimate life
If the pregnancy proceeds without pathologies, sex at 35 weeks is allowed. Expectant parents should avoid rough movements and deep penetration. Poses that are comfortable for the mother and exclude pressure on the abdomen, such as penetration from behind, are suitable.
You should pay close attention to hygiene issues, especially if the mucous plug that protected the baby from infections has begun to come off.
At week 35, you need to eliminate from your life everything that upsets, causes fatigue or irritation.
Possible problems
At this stage, some complications may arise and the woman may encounter warning signs that should not be ignored.
These include:
- intestinal spasms;
- diarrhea;
- nausea with vomiting;
- gurgling sounds in the uterus and vagina;
- constant tormenting thirst;
- dizziness, ripples in the eyes.
If at least some of the symptoms listed above appear, you must call an ambulance. Only experienced specialists are able to assess the degree of danger to the life of the mother and baby, and also take measures to eliminate the cause.
By the end of pregnancy, edema occurs even in those women who have not experienced this before.
Most of the excess fluid accumulates in the lower extremities. In this case, you need to consult a doctor and reduce the amount of water consumed. There is also a nagging pain in the lumbar region, pubis and abdomen, which is associated with the active growth of the fetus and an increase in its weight.
At this time, many pregnant women face the problem of stretch marks. They appear in the abdomen, thighs and chest. At the same time, it is almost impossible to get rid of them, so prevention should be carried out in advance to prevent their occurrence.
34-35 weeks of pregnancy - this period is accompanied by false contractions. They are characterized by inconstancy, lack of growth and pass on their own. But if you feel strong pressure in the hips and it seems that the pelvic bones are moving apart in different directions, then you should immediately call an ambulance.
Spasms in the intestines and frequent bowel movements should also alert you, as these signs indicate that the body is preparing for childbirth and getting rid of everything unnecessary. At this stage, the baby is no longer moving as actively as before, since he has grown noticeably and the free space in the abdomen has decreased.
But the absence of tremors for 4 hours should be a cause for concern. In this case, the woman should sit down, calm down a little and listen to the sensations. If within 30 min. If not a single shock occurs, then you cannot hesitate and you should go to the hospital.