Pelvic structure
We can distinguish certain components in the named part of the skeleton: the sacrum, the coccyx and two pelvic bones. The latter are among the largest in the body. They are endowed with an atypical structure and are responsible, first of all, for the supporting function of the skeleton. The pelvic bones are held together by joints into a ring and form a cavity of the same name.
The pelvis of children and adolescents under sixteen years of age is formed by three separate bones, over time they grow together and begin to function as a single bone.
Differences in the structure of the pelvis change throughout a person's life. This factor can be influenced by biological processes occurring in the body, professional reasons and unexpected turns of fate, which include injuries or pathological processes in the pelvic bones or spine.
By looking at the pelvic bones of the skeleton, you can easily find out what gender people belong to. This fact is taken into account during archaeological excavations or during medical examinations.
The difference between the male and female pelvis
A woman's pelvis has distinct distinctive features. He performs an important function - he takes part in childbirth. This part of the skeleton is the channel along which the baby moves, trying to leave the mother’s womb. The dimensions of the female pelvis are wider and shorter than that of the male. The joints are located at a greater distance, the bones are thinner than in men. The structure of the female pelvis also differs in the shape of the sacrum; in the fair sex it is wider and less protruding than in men.
The shape of the angle of the pubis of the weaker sex is straighter than that of men, the wings of the pelvis are deployed, the protrusions of the ischial bones are located at a distance. In front and on the sides, the pelvis is limited by the innominate bones, and behind it by the coccyx, which continues the spinal column. A woman's hole looks like a transverse oval, while a man's looks like a longitudinal one.
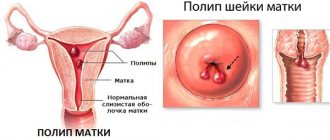
Uterus: structure, changes during pregnancy and childbirth
Diagrams of the location of human internal organs with inscriptions by zone. Knowledge of the structure of the body is the key to understanding the processes occurring in it and malfunctions.
The set of required knowledge for a person is constantly expanding. However, without a clear understanding of the functioning of the body, its needs and the interconnection of organs, all other achievements of science and progress are useless.
Students of medical universities study anatomy in detail. It is enough for the average adult to have an idea of the location of organs inside himself at the school curriculum level. We suggest brushing up your knowledge in this area.
diagram of the distribution of organs within the human body
MORE ABOUT: Nurofen: instructions, composition, indications, action, reviews and prices
The internal organs of the human body are compactly placed in the torso in conventional zones:
- chest
- abdominal
- large and small pelvis
The first zone is separated from the second by a diaphragm. The second and third zones do not have such a clear boundary.
The thoracic region in turn consists of:
- 2 lung spaces
- cardiac zone
The abdominal cavity is also divided into 2 components:
- directly abdominal
- retroperitoneal
Their functional tasks are radically different from each other and at the same time closely related.
So the organs of the chest are responsible for:
- breath
- absorption of oxygen and disposal of waste air
- pumping blood
The abdominal organs provide:
- digestive processes
- absorption of nutrients
- immunity strength
- filtering toxins, poisons
- participation in the hematopoiesis of one’s body, and in the female version, of the fetus
- formation of acids for digestion
- hormonal regulation of the correct functioning of all abdominal organs
In the large and small pelvis, their tasks are carried out:
- release of waste substances
- reproduction
- hormonal control of the functioning of the organs of the zone in question
Based on their structure and appearance, internal organs are divided into:
- tubular, or hollow - for example, the stomach
- solid, without a cavity - for example, liver
The first category of organs consists of a number of layers, each of which has its own purpose. For example:
- muscles contribute to contractions of the organ,
- mucous membranes - moisturizing and absorbing substances,
- slippery outer layer - lack of friction between organs.
The second category consists of “working” cells of the same type and a supporting layer. Each of them implements the tasks of the organ as a whole, and the support layer is responsible for nutrition and maintaining the location of the organ.
In our body, some organs are paired, for example, the lungs, and some are unpaired, for example, the heart.
See the internal structure of the human body in the photo below.
variant of the diagram of the internal structure of the human torso
structure of the human chest, inside view
The chest is the location of the respiratory organs, in particular the lungs.
- They occupy almost all of her space, especially at the moment of inhalation. From below, the lungs rest against the diaphragm. Around them there is protection from the ribs.
- The bronchial tree branches inside the lungs and connects them to the trachea.
- Moreover, its left branch is thinner and longer than the right.
The heart is the engine of your body, pumping blood through a network of blood vessels. It is located between the lungs above the diaphragm and has a slight backward slope. 2/3 of the heart is on the left side of the center of the chest, and 1/3 is on the right.
The thymus gland is a mysterious organ of the chest. Located in the upper part of the latter above the bronchial branch into the lungs. Participates in the functioning of the human immune system.
On the diagram of the chest organs, consider their location.
enlarged diagram of the location of organs inside the human chest
Diagram of the abdominal cavity: location of organs
The abdominal cavity is filled with more organs than the previous one. Let's consider their placement according to 3 parameters:
- in the center
- to his right
- left
The first category is the intestines.
- The small intestine appears to be a thin, tangled tube. It is formed at the site of narrowing of the stomach and can reach 6 m in length. It gradually expands into the large intestine at the bottom right. The latter forms a semicircle clockwise throughout the entire abdominal cavity and ends at the anus.
The intestine is the most important organ of the immune system. Thanks to its ability to pulsate compression, poisons, toxins, and harmful substances are removed from the body.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jU1cxgmCpAM
The second category is the stomach, pancreas, spleen.
The stomach is an extension of the esophagus that resembles a bag. It is located immediately below the diaphragm.
- As it fills, it is able to change its size. People who are addicted to eating large amounts of food have an enlarged stomach.
- It is a reservoir for the accumulation and digestion of food, passing the first stage of assimilation of nutrients.
The stomach is a complete organ with several layers of muscles. Thanks to the contraction of the latter, food moves through the organ and further into the intestines.
The pancreas is located slightly lower under the stomach. She:
- participates in the process of food digestion,
- produces juice to break it down,
- ensures metabolic processes in the body, namely protein-carbon and fat.
The spleen provides hematopoiesis for adults and fetuses in women. It is located behind the stomach. In appearance it is a non-hollow dense hemisphere.
Spleen:
- responsible for the production of lymphocytes
- accumulates platelets
- traps harmful substances and bacteria and filters them
- participant in the body's metabolic processes
- first aid for red blood cells and platelets with damaged membranes
The third category is the liver, gall bladder.
The liver is a vital human organ. It consists of 2 lobes, of which the right one is much smaller than the left one.
The liver has the task of neutralizing poisonous and toxic compounds and then removing them from the body. And:
- maintaining lipid balance
- absorption of cholesterol and glucose
- removal of excessive amounts of vitamins and internal metabolic substances
The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped sac that is located under the right lobe of the liver.
MORE ABOUT: Endometrium thickness norm by day of cycle: Extension and implantation of endometrial follicles, stimulation of ovulation | Tags: endometrium, day, cycle, norm, thickness
Its task is to accumulate bile coming from the liver and send it to the intestines. It helps to efficiently digest food at all stages of its movement, starting from the stomach.
On both sides are the kidneys and adrenal glands.
The buds are shaped like beans.
- Located behind the abdominal organs closer to the lumbar area.
- The right kidney is smaller than the left. The weight of one varies between 100-190 grams, and the size is about 10 cm.
- The purpose of the kidneys is to filter and secrete urine and regulate chemical processes.
The adrenal glands are paired glands, representatives of the endocrine system. Responsible for regulating hormone levels:
- adrenaline
- sexual - androgens
- corticosteroids
- cortisone and cortisol
- norepinephrine
The adrenal glands help a person adapt to new living conditions and cope with stressful situations.
A diagram will help you visually remember the location of the abdominal organs.
abdominal organs: diagram with inscriptions
schematic representation of the structure of the internal organs of the pelvis in a woman
Since people are divided into two groups based on gender, our set of pelvic organs is not the same.
In the small pelvis there are:
- bladder and rectum - common
- uterus and ovaries - in women
- prostate gland and testicles - in men
Let's look at the first two in a little more detail.
The bladder falls on the pubic area. When empty it seems to spread out, but when filled it has the shape of an oval container.
Its task is to accumulate fluid from the kidneys and remove it from the body through the ureters.
The rectum is a continuation of the large intestine. It is located vertically down the far wall of the pelvis.
Its task is to collect and remove waste material after the digestion process.
Between the bladder and rectum are:
- uterus in women
- prostate gland in men
A diagram showing the location of the pelvic organs is presented below.
diagrams of the structure of the internal organs of the pelvis in men and women
So, we looked at the anatomical location of human internal organs and got acquainted with their main tasks and activities.
Study the structure of your body consciously. Learn to listen to his needs and live in harmony with him!
The structure of the human body is unique. The coordinated work of each organ ensures vital activity. Each region consists of a specific set of organs.
Humans are the most complex organism on our planet, capable of performing several functions simultaneously. All organs have their responsibilities and carry out their work harmoniously: the heart pumps blood, distributing it throughout the body, the lungs process oxygen into carbon dioxide, and the brain processes thought processes, others are responsible for a person’s movement and his life activities.
Anatomy is the science that studies the human structure. She distinguishes between the external (what can be observed visually) and internal (hidden from view) structure of a person.
Human structure based on external features
The external structure is the parts of the body that are visible to the human eye and can easily be listed:
- head - the upper round part of the body
- neck - part of the body connecting the head and torso
- chest - front part of the body
- back - back of the body
- torso - human body
- upper limbs - hands
- lower limbs - legs
The internal structure of a person consists of a number of internal organs that are located inside a person and have their own functions. The internal structure of a person consists of the main, more important organs:
- brain
- lungs
- heart
- liver
- stomach
- intestines
main internal organs of a person
A more detailed listing of the internal structure includes blood vessels, glands and other vital organs.
It can be noted that the structure of the human body is similar to the structure of representatives of the animal world. This fact is explained by the fact that, according to the theory of evolution, man descended from mammals.
Man developed together with animals, and scientists often notice his similarity with some representatives of the animal world at the cellular and genetic level.
A cell is an elementary particle of the human body. The accumulation of cells forms the tissue that actually makes up the internal organs of a person.
All human organs are united into systems that work in a balanced manner to ensure the full functioning of the body. The human body consists of the following important systems:
- The musculoskeletal system provides a person with movement and maintains the body in the required position. It consists of a skeleton, muscles, ligaments and joints
- The digestive system is the most complex system in the human body; it is responsible for the digestion process, providing a person with energy for life.
- Respiratory system - consists of the lungs and airways, which are designed to convert oxygen into carbon dioxide, oxygenating the blood
- Cardiovascular system - has the most important transport function, providing blood to the entire human body
- Nervous system - regulates all functions of the body, consists of two types of brain: the brain and the spinal cord, as well as nerve cells and nerve endings
- The endocrine system regulates nervous and biological processes in the body
- The reproductive and urinary systems are a number of organs that differ in structure in men and women. Have important functions: reproductive and excretory
- Integumentary system - provides protection for internal organs from the external environment, represented by the skin
- The pelvis consists of two pelvic (or innominate) bones, the sacrum and the coccyx.
- The entrance to the small pelvis is located at the level of the sacral promontory and the upper edge of the pubic bones.
- The exit from the small pelvis is formed by the pubic arch, the ischial spines, the sacrotuberous ligament and the coccyx.
- The closed space between the inlet and outlet is called the true pelvis, with the inlet plane being at right angles to the outlet plane.
- The female true pelvis differs from the male one in that it is shorter, has smoother surfaces, a wider angle of convergence of the lower rami of the pubic bones and a wider plane of exit of the small pelvis.
- There are gynecoid, android, platypeloid and anthropoid forms of the female pelvis.
MORE ABOUT: High blood pressure after alcohol - what to do and how to lower blood pressure after a hangover
Pelvic shapes
Dimensions of the female pelvis
To predict the birth process and prevent complications, much attention is paid to size. But it is possible to measure a large basin as accurately as possible, but there is no way to calculate the dimensions of a small one, so they follow from the dimensions of a large one. It is necessary to have information about them in order to determine whether they correspond to the circumference of the head of the newborn fetus.
The female pelvis is endowed with an inlet, a cavity and an outlet. There are straight, transverse, oblique right and left sections of the pelvis.
The exit from it is covered in women by a bottom consisting of three layers of muscle tissue covered with a connective tissue membrane. The pelvic floor performs many necessary functions.
The pelvic floor serves as a support for the genital organs located inside and facilitates their correct placement. It also holds other internal organs. During labor, the muscular layers of the woman's pelvic floor are stretched and form a tube that continues the bone canal.
The female pelvis is measured with an instrument called a pelvis.
Pelvic floor muscles
Pelvic floor muscles in men
The pelvic floor muscles form a dome-shaped structure, similar to a hammock. They are responsible for supporting the pelvic organs, bowel and bladder function, and sexual function. The pelvic floor muscles are made up of 3 layers and have a complex relationship with the surrounding pelvic bones, fascia, ligaments and nerves.
The superficial layer consists of the bulbospongiosus muscle, the ischiocavernosus muscle, the superficial transverse perineal muscle and the external anal sphincter. This layer of muscle is involved in ejaculation, urination and rectal emptying.
You can read about the anatomy of the pelvic floor muscles in women here.
The next layer is the so-called urogenital diaphragm, which consists of the deep transverse perineal muscle and the urethral sphincter. This layer is responsible for holding urine when intra-abdominal pressure increases (for example, when coughing or sneezing).
The deepest layer includes the pubococcygeus, puborectalis, pubourethral, iliococcygeus and ischiococcygeus muscles. These muscles are especially responsible for supporting the pelvic organs and the continence mechanism.
Pelvic organs
The organs of the human body have their own special structure and location. It is necessary to have an idea of where the main organs are located in order to be able to determine which one is causing pain before visiting a specialist. The pelvis is the location of a large number of vital organs of the human body.
The organs of the female pelvis, like those of the male, are concentrated in the plane formed by its bones. In medicine, they are divided into general ones, which include the bladder and rectum, as well as into purely female and male ones.
The bladder, shaped like a turnip, is located behind the junction of the pubic bones, separated from them by fiber. When this organ is filled, it comes into contact with the abdominal wall. The size of the bubble can vary depending on the degree of its fullness.
The main task of the rectum is the accumulation and removal of digestive waste from the human body.
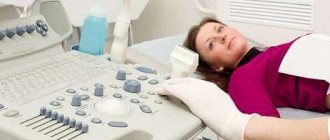
What can an ultrasound doctor see if you are not pregnant?
- Condition of the vagina;
- Condition of the uterus. Its structure, size, position, tissue structure, presence or absence of neoplasms in the cavity;
- The condition of the ovaries, or rather the position, size, presence of follicles in them and their maturation; the presence or absence of neoplasms, adhesions and constrictions;
- The position and size of the bladder, the presence or absence of stones or deposits inside the bladder;
- The position, size, structure of the intestine, as well as the presence or absence of tumors inside.
Ultrasound is prescribed during the period of preparation for pregnancy (through the abdominal wall or transvaginally), in the presence of complaints, often with chronic diseases in order to monitor the state of women's health. Also, ultrasound examinations of the pelvic organs are included in the calendar of mandatory examinations of pregnant women:
- In the first trimester, at 9-10 weeks. Allows you to see the fertilized egg, determine its size, and also distinguish the presence of genetic abnormalities;
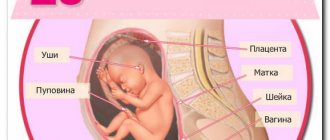
- In the second trimester, at 16-20 weeks. On this ultrasound, you can already see the baby’s gender, body structure, the presence of major organs, the number of limbs, etc. The most important thing is that the ultrasound shows the condition of the placenta and umbilical cord, as well as blood flow and the amount of amniotic fluid;
- In the third trimester, from 32 to 34 weeks. On the third ultrasound, you can already see the features and structure of the face, the fetus is so large.
Ultrasound also monitors the condition of scars on the uterus resulting from cesarean section or other surgical interventions.
If necessary, additional examinations are prescribed during pregnancy - MRI diagnostics, CTG, Dopplerometry, etc.
Anatomy of the genital organs
The genital organs of the female pelvis carry out the processes of fertilization and the birth of a new life, thanks to them the production of sex hormones occurs in the fair sex. These organs are located outside and inside the pelvis.
The externally located genital organs include the pubis, covered with a layer of fat and hair, the labia majora and minora, and the clitoris:
- The clitoris is one of the small, but especially sensitive and important organs.
- The labia minora are the folds located between the labia majora and the opening of the vagina; they may be visible outside the labia majora and be a deeper color. They are able to become larger at the moment of sexual desire.
- The labia majora are located on the sides of the genital slit. Their skin is covered on the outside with hair and contains sweat and sebaceous glands. Inside they are covered with the thinnest pinkish skin.
- Under the labia majora and minora there is an opening designed to drain urine from the body. Underneath it there is an opening to the vagina, which is covered by the hymen in innocent girls.
Internal organs
These genital organs are located inside the female pelvis, therefore they are called internal:
- Vagina. It is a muscular elastic tube of a certain length.
- The uterus, which is a muscular organ and includes the body and cervix. Her body is located in the very center of the woman's pelvis. The orifices, located in the upper corners, are the points of attachment of the uterus to the tubes.
The walls of the uterus are lined with endometrium. Under the influence of sex hormones, it waits for an egg that has undergone fertilization, and if it does not appear, it leaves the uterus, causing menstrual bleeding.
The purpose of a woman’s uterus is to be a receptacle for the fetus, where its development occurs.
The female pelvis is home to the ovaries, which are located on either side of the uterus. They produce and contain many eggs that mature here. Ripe eggs are sent to the fallopian tube, where sperm can await them. If fertilization has occurred, the egg travels through the tube into the body of the uterus.
Effective ways to examine female organs inside the pelvis
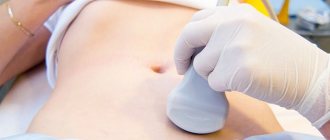
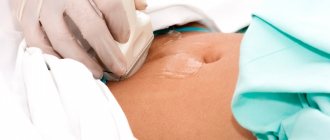
Most often, ultrasound is used to examine the female reproductive organs and identify pathological processes. It allows you to most accurately examine each of them, making the correct diagnosis. This method is also effective for confirming pregnancy.
Most often, the attending physician (gynecologist or therapist) refers to this procedure due to the following complaints: pain in the lower abdomen, menstrual irregularities, delays, heavy or scanty bleeding, pathological discharge from the vagina, suspected malignant or benign formations, cysts, endometriosis. Ultrasound also helps identify kidney stones. This type of diagnosis is used for diseases of the genitourinary tract.
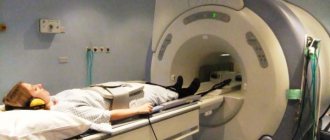
MRI of the pelvic organs in women
Recently, magnetic resonance imaging has become one of the most popular diagnostic methods. With its help, it is possible to study the female pelvis and obtain comprehensive information about the condition of all organs of the human body. MRI cannot have any harmful effects on the body, although it has certain limitations.
Carrying out an MRI of the pelvic organs in women makes it possible to study in detail the condition of the internal organs and identify the presence of pathological processes in them in the early stages of development. It can significantly facilitate the diagnosis of diseases and assist in selecting the right course of treatment.
When performing an MRI, a person who has assumed a horizontal position is placed in a special tomograph chamber. This is where a specific area of the body is scanned.
In the field of gynecology, safety plays a special role, since health problems can have a harmful effect on the development of the baby, even if the woman is not expecting a child at the time of diagnosis.
Detection of female diseases
- Characteristic features of the structure of the uterus (bicornuate, saddle-shaped, with a partial septum, etc.);
- Dense round or oval formations - fibroids or vaginal cysts;
- Changes in the walls of the uterus - possible oncological problems, inflammatory processes;
- An increase in the size of the ovaries is often one of the signs of polycystic disease;
- Changes in the structure of tissues and walls of the uterus - possible endometriosis;
- The presence of foreign inclusions in the bladder cavity - stones and sand.
An ultrasound reveals some signs of the disease; if there is suspicion, the doctor conducts an additional examination and prescribes a number of tests. During the course of the inflammatory process in the pelvic cavity, adequate treatment is prescribed. Inflammation inside the bladder, uterine cavity, tubes or ovaries is always painful and is often accompanied by discharge. Vaginal diseases make sexual intercourse uncomfortable, and serious diseases can be fatal.
It is recommended to do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs for women of childbearing age at least once a year and immediately if there are complaints.