Polyps in the uterus are a fairly common disease that can occur in women of any age.
The formation looks like a rounded growth on a stalk, resembling a fungus, ranging in size from several millimeters to several centimeters.
A polyp appears on the endometrium lining the uterus, or in its canal.
In this article we will talk about methods for diagnosing polyps in the uterus and, in particular, whether they can be seen on an ultrasound. From it you will learn what are the features of ultrasound examination of this pathology.
What is a polyp
Polyp is a pathological growth of tissue above the endometrium in the inner layer of the endometrium of the uterus.
Such neoplasms are of the following types :
- glandular;
- fibrous;
- glandular-fibrous.
The glandular type is characterized by the fact that it consists of glandular tissue. This pathology is more common in women of reproductive age. Fibrous polyp consists of connective tissue and is diagnosed mainly in postmenopausal women. The mixed structure, as the name implies, has glandular-fibrous formations.
Lack of treatment can lead to the following consequences :
- malignancy of the neoplasm;
- infertility;
- miscarriage and frozen pregnancy;
- development of anemia.
IMPORTANT!
The risk group includes overweight women with a history of hypertension and endocrine disorders.
Symptomatic manifestations
depend on the number and size of tumors.
With small polyps, as a rule, there are no signs of their presence, and they can only be detected during a routine examination in a gynecological office.
Large formations are characterized by the following symptoms:
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- heavy menstrual bleeding;
- irregular periods;
- anemia;
- discharge streaked with blood after sex;
- discomfort, pain in the lower abdomen;
- uterine bleeding during menopause.
As a rule, symptoms appear when the formations in the uterus become multiple or large in size.
In order to detect or prevent the disease in a timely manner, as well as to take the necessary measures to treat it in a timely manner, a woman should systematically visit a gynecologist and undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Differential diagnosis of fibroids
Ultrasound is the main method for diagnosing myomatous tumors, the so-called gold standard. But this disease can manifest itself in different ways: bleeding, pain of different localization, difficulties with urination and defecation. Therefore, there are still risks of confusing a benign tumor with other pathologies.
Most often, when diagnosing, it is necessary to differentiate fibroids from:
- uterine sarcoma (malignant tumor);
- ovarian tumors;
- cancer of the uterus;
- inflammation of the uterine appendages;
- uterine bleeding;
- miscarriage;
- internal endometriosis;
- pregnancy;
- in rare cases - from hydatidiform mole.
To distinguish myomatous nodes from a malignant tumor on ultrasound, it is important to consider the following criteria.
| Criterion | Differences |
| Presence of anechoic areas | Much more common in sarcoma |
| External contours | Simple fibroids have clearer |
| Dimensions of the tumor | In a myomatous tumor it is usually within 26-50 mm, in a sarcoma - more than 51 mm |
| Velocity of arterial and venous blood flow (Dopplerography is used) | In sarcoma it is noticeably higher |
In other cases, differential diagnosis is carried out on the basis of a routine examination, additional studies, laboratory tests, etc.
So, to recognize cancer, they use hysterosalpingography, hysteroscopy, and diagnostic curettage. The age factor plays an important role - cancer usually develops later than myomatous nodules.
Ovarian tumors (benign) can be easily detected separately from the uterus by palpation. If diagnosis is difficult (in the presence of adhesions or ovarian cancer), a trial laparotomy is used. An X-ray of the pelvis is also used.
With uterine bleeding, the uterus is slightly enlarged in size, the surface is quite smooth (in comparison with a myomatous tumor). With hydatidiform mole, general signs of pregnancy occur; the uterus rapidly enlarges, which does not happen with fibroids.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnostic measures may consist of several stages. A patient can hear about polyposis by visiting a gynecologist for a routine examination.
If polyps are localized in the cervical area, the doctor will be able to identify them during a gynecological examination using mirrors. For more detailed diagnostics, special hardware devices and methods are used.
When polyps are identified, histology of the formations is necessarily carried out, which will help to identify the nature and structure of the cells that formed them.
Diagnostics includes the following activities:
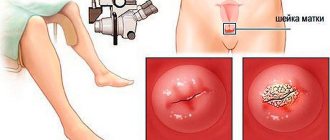
- standard gynecological examination . Polyps are round or cluster-shaped and bright red (less often pink). In this case, a separate place is occupied by examination of the cervix; it is usually thickened and hypertrophied. If the polyp has a dark or even purple tint, this indicates a circulatory disorder. The formation is elastic and soft to the touch;
- Cerviscopy is an instrumental examination of the cervix using a hysteroscope, which is equipped with a video camera. This method allows you to correctly assess the patient’s condition, without causing any harm to the body, and even the smallest neoplasms and necrosis of endometrial tissue can be detected. Cerviscopy allows you to study the polyp not only size-wise, but also structurally. To identify or refute the development of cancer cells, tumor tissues are sent for a biopsy;
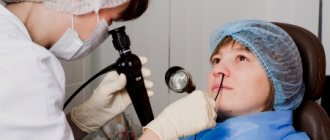
- colposcopy - allows you to assess the condition of the vaginal opening and its walls. For the procedure, a special device is used - a colposcope - an optical device with a built-in binocular and a lamp for illumination;
- Ultrasound . When diagnosing polyposis on the cervix, there is a risk of developing formations on the internal mucous membranes of the uterus. In such cases, the neoplasm is thoroughly studied by ultrasound. The specialist receives detailed information about the thickness of the endometrium, its structural changes, multiplicity and size of the polyp. The advantage of ultrasound of the uterus is that this diagnostic method allows you to additionally assess the condition of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, which will be taken into account by the gynecologist in the subsequent treatment of the patient;
- hysteroscopy . This method is typical for microsurgical (minimally invasive) interventions to obtain detailed information about the condition of the uterine cavity. In this case, a special optical device is used - a hysteroscope. This method allows not only to identify tumors, but also to remove them at the same time. Next, the excised tissues are sent for laboratory study of the structure and nature of the cells;
- Metrography , an X-ray examination of the uterine cavity using a contrast agent, can also visualize polyps All uneven outlines will be visible in the image, including polyps.
Expert opinion
Dmitrieva Elena Yurievna
Gynecologist-endocrinologist, 40 years of experience
Polyposis in the uterine cavity can be suspected after collecting an anamnesis and examination in a gynecological chair. Ultrasound diagnostics will help confirm the diagnosis, but it should be carried out 3-5 days after the start of a new menstrual cycle, otherwise it is not possible to distinguish a thickened endometrium from a polyp. Hysteroscopy and curettage of the uterine cavity can also help. These procedures can be considered therapeutic, because during their implementation polyps are also removed.
Extra options
The gynecologist interprets all studies. To make an accurate diagnosis, determine the stage of development of the pathological process and the presence of complications, not only an ultrasound image is taken, which shows the polypous formation, but the general condition of the uterine cavity is also taken into account.
During a transvaginal ultrasound, to obtain a detailed picture of the condition and functioning of the female reproductive organ, the doctor conducts the following additional studies:
- the size of the uterus, its echogenicity, the degree of homogeneity of the structures, the ratio of the uterus to its cervix;
- examination of the ovaries and appendages.
Using ultrasound through the abdominal cavity, the following is examined:
- appendages;
- bladder.
Only based on the condition of all organs of the reproductive system can an accurate diagnosis be made and an effective treatment regimen outlined.
An ultrasound examination is performed at the time of diagnosis, before scheduled surgery to remove pathological formations on the endometrium and at the end of the recovery period.
What does pathology look like on ultrasound?
If there is a suspicion of polyps in the uterus, the doctor needs to differentiate the disease from other pathologies:
- endometrial tumors;
- myomatosis;
- cyst;
- erosion or foci of inflammation.
A characteristic feature of a polyp, in contrast to a tumor formation of any nature, is the presence of a stalk and a body (mushroom-shaped). If the polyp is located in the cervical canal, then the leg is necessarily present, since the organ has an anatomically elongated shape.
How well are polyps visible on ultrasound? Are there any special features?
On ultrasound, the polyp is characterized by some features:
- rounded shape;
- clear contours;
- expansion of the cervical canal and uterine cavity;
- moderate deformation of the mid-transverse part of the M-echo;
- the presence of endometrial cysts near the base of the pedicle of the formation.
NOTE!
Ultrasound signs of polyps differ slightly in location, size and shape, so this study can only accurately confirm the fact of abnormal growth of the endometrium. The most informative method for determining the characteristics of a polyp and its structural features is considered to be histological examination.
Preparation for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs depends on which method will be used:
- abdominal examination . The day before your scheduled procedure, you should not consume foods that cause increased gas formation. The procedure is performed with a full bladder;
- transvaginal ultrasound . This diagnostic method does not require filling the bladder; on the contrary, it is done after emptying before the procedure;
- intrauterine diagnostics . Does not require any special measures. However, it is advisable that the bladder be emptied immediately before the test.
The photo below shows an ultrasound image of a polyp in the uterus.
Possible dangers
When polyps are detected in the uterus, it becomes necessary to remove them due to the fact that they are dangerous to the woman’s health.
Among the possible troubles that a woman may encounter are:
- Uterine bleeding. If therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, the polyp develops internal small vessels. But due to the fact that its walls do not have a dense structure, there is a possibility of injury. Because of this, bleeding may occur even in the middle of the menstrual cycle. They are completely insignificant and the woman will not notice it. But even small blood losses, when repeated systematically, “threaten” to manifest as anemia. However, large polyps when injured lead to quite heavy bleeding. It will not stop on its own.
- The possibility of conception becomes difficult. The larger the tumors, the more serious the possible problems. A fertilized egg will not be able to penetrate inside the uterus and, naturally, gain a foothold there. On its way there will be a polyp, which is a mechanical obstacle.
- Complications may also arise when carrying a child. If there are polyps, miscarriages and placental abruption may occur. The pregnancy itself may be ectopic.
- The polyp may appear as a source of infection. If a pathological agent enters the uterine cavity, then it will “begin” its destructive effect near the polyp. This effect occurs due to the fact that the polyp shell is not able to resist infection.
These possible complications can lead to major health problems for the woman. Because of this, there is a recommendation from gynecologists to remove detected formations immediately after their identification.
Treatment methods
The main method of getting rid of polyps in the uterus is endoscopic removal. The formations are removed during hysteroscopy. As a rule, the procedure is carried out 2-3 days after the end of menstruation. This is due to the fact that during this period the endometrial layer is thin and polyps are clearly visible. Excision is performed with an electric loop, then the tear site is cauterized.
If the polyps are small, the specialist may prescribe conservative therapy - taking hormonal medications .
Such drugs reduce the production of estrogen, while the level of progesterone increases. As a result, the hormonal causes of polyposis are eliminated, and the neoplasms dry out and leave the uterine cavity with menstrual bleeding.
IMPORTANT!
As preventive measures against relapses and monitoring the effectiveness of the therapy, it is necessary to be under constant supervision of a specialist.
When the growth of polyps is caused by endometrial inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed.
In case of multiple formations, treatment is supplemented by endometrial curettage of areas of growth of formations. After the procedure, the injured areas are disinfected with a special solution, and the tissue of the removed polyps is sent for histological examination.
When should an ultrasound examination be performed?
The structure of the female internal genital organs undergoes significant changes under the influence of cyclically changing hormonal levels. This also affects the visualization of pathological changes. What a uterine polyp looks like on an ultrasound also depends on the day of the cycle for which the study is performed. The optimal period for diagnostics for this pathology is the second phase of the cycle, when the endometrium is at its maximum thickness. If you do an ultrasound in the first phase of the cycle, it is almost impossible to see formations up to 5 mm in size.
Symptoms
Cervical polyp has the following symptoms:
- spotting that occurs during or after sexual intercourse;
- general malaise;
- progressive anemia;
- mucous discharge from the genital tract;
- weight loss;
- menstrual irregularities;
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
- infertility.
Often, a cervical polyp does not cause any symptoms and is discovered during a routine examination by a gynecologist.
Reasons for development
The exact causes of cervical polyps have not yet been established. Most doctors are inclined to believe that neoplasms arise due to hormonal imbalances.
However, there are a number of factors that contribute to the development of cervical polyps. These include:
- inflammation of the cervix;
- excess of the hormone estrogen, which is responsible for the growth of endometrial tissue;
- progesterone deficiency;
- hereditary predisposition;
- abortions;
- diabetes;
- excess weight;
- traumatic injuries to the cervix.
Pregnant women are also at increased risk. This is due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, which can lead to the growth of epithelium in the cervix and provoke the development of hyperplasia and metaplasia.