Colposcopy is considered a non-traumatic type of diagnosis, which is of great importance in the early diagnosis of cervical pathologies. This examination is often carried out on pregnant women, and almost always patients worry whether such an intervention will complicate the period of bearing the baby.
Gynecologists say that colposcopy during pregnancy is absolutely safe. Moreover, it allows timely detection of conditions that can negatively affect the development of the fetus, the process of gestation and directly the process of childbirth.
Why is colposcopy prescribed during pregnancy?
As a rule, in gynecology, colposcopy is used even in the absence of complaints, in order to identify hidden diseases. However, more often it helps to identify the true cause of unpleasant symptoms:
- discomfort in the vagina, leucorrhoea;
- irregular, scanty bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle;
- chronic pain in the pelvis and lower abdomen;
- pain during sexual intercourse and immediately after it.
They try to perform a colposcopy before planning a pregnancy. If conception occurs unplanned, diagnostics may be prescribed to identify previously undetected pathologies that could affect the course of pregnancy.
During colposcopy, the doctor is able to see even minor changes on the cervix: erosions, foci of inflammation, endometriosis and dysplasia. They often prevent a woman from becoming pregnant, but even if this is successful, they can cause complications:
- premature opening of the cervix;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- premature birth;
- intrauterine infection and so on.
During pregnancy, this type of study is prescribed even if a previous procedure showed the presence of abnormalities. According to indications, colposcopy of the cervix is performed at the initial stage of gestation to ensure that there is no progression of the previously diagnosed disease, and then the diagnosis is repeated at intervals of 3 months.
Important! Pregnancy is accompanied by hormonal fluctuations and changes in the vaginal microflora, which is why previously “dormant” gynecological problems can receive an impetus for rapid development.
Is it safe to perform colposcopy on pregnant women?
Some women are concerned about their condition and do not know whether colposcopy can be done during pregnancy. Of course, the ideal option is to carry out the manipulation before conception and collect all the information regarding the patient’s health and her characteristics, but in any case, the procedure will not harm the expectant mother and her child.
Colposcopy in any trimester is prescribed only after the doctor has reviewed the woman’s medical history and test results.
The colposcopic method is aimed at identifying inflammation and more severe changes that, without treatment, pose a danger to the body during pregnancy.
A pregnant woman can undergo colposcopy throughout the entire period of pregnancy; early or late pregnancy does not play a special role in this case; the main thing is to listen to the recommendations of the gynecologist and properly prepare for the examination.
After passing a basic smear to determine the microflora, a woman must, 48 hours before the procedure, exclude sexual contact and local methods of treatment, such as a suppository, douching.
On the day of the manipulation, it is necessary to carry out cleansing care of the genitals using the usual product. Since the colposcope is not inserted into the vagina, but is placed in front of the patient, there is no risk to the woman’s body.
When is Ginipral prescribed for pregnant women?
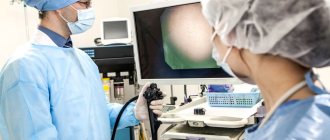
This is what a colposcope looks like
Is it possible to do a colposcopy in the early stages?
Many patients are afraid to undergo colposcopy during pregnancy, especially in the early stages, believing that it can lead to miscarriage or other problems. In practice, this probability is extremely low, because during the examination there is no direct impact on the cervical canal. The doctor delicately examines the cervix and conducts the necessary studies without injuring the mucous membranes.
Good to know! Even if abnormalities requiring a biopsy are detected, biological material is not collected in the first weeks of pregnancy. The only thing that can be done to make a diagnosis is to take a scraping of the epithelium.
For a woman during early pregnancy, there will not be a significant difference between a standard examination and colposcopy. Since when registering, in any case, she will have to undergo an examination, take smears for flora and gonorrhea, determine the so-called background of the vaginal microflora and oncocytology, there is definitely no need to worry about the harm of colposcopy.
Features of the procedure during pregnancy
The technique of colposcopy for pregnant patients complies with generally accepted standards. No special preparation is needed for diagnosis using this method. It is recommended that a woman stop having sex, using vaginal suppositories, and douching 3 days before the examination.
Before the examination, the woman lies down in a chair, the doctor inserts a gynecological speculum into the vagina, and then endoscopic equipment. With its help, the cervix is examined with a magnification of 10 or 40 times. The specialist notes the detected changes and records them in the protocol.
As a rule, during pregnancy, colposcopy is performed without the use of reagents and separation of a mucosal fragment. The problem is that the cervix is covered with viscous discharge from the first days of gestation. It may interfere with normal visualization of the epithelium, so colposcopy during the first trimester may be of little value. If this happens, the doctor prescribes a repeat diagnosis at 30 weeks of pregnancy. During this period, mucus separates from the outer covering of the cervix, but still fills the cervical canal.
Important! The mucus covering the cervix may contain particles of epithelium, so the gynecologist carefully takes a scraping for analysis, without penetrating the cervical canal and without injuring the mucous membranes.
If a previous diagnosis revealed abnormalities, and atypical cells were found in smears, the doctor may decide to perform an extended colposcopy for pregnant women in the first half of gestation. To do this, you will need to remove the mucous secretions with a special sponge moistened with an acetic solution, after which the necessary tests are carried out: treating the epithelium with Lugol, iodine solution or acetic acid.
From the second half of gestation, colposcopy for pregnant women is performed only in the usual way without tests. The fact is that the cervix is intensively supplied with blood from the 20th week of gestation, and even delicate touches can provoke bleeding of the mucous membranes. If this happens during the examination, Monsel paste is applied to the surface of the cervical canal.
What is colposcopy?
Colposcopy is a low-traumatic method of endoscopic examination, the purpose of which is to examine the cervix using a device - a colposcope. The role of colposcopy can hardly be overestimated: this method accurately diagnoses gynecological diseases such as erosion, precancerous conditions and cervical oncology.
Colposcopy is one of the mandatory examinations in obstetrics, especially if there are indications for it. Most often, mild diseases detected during pregnancy cannot be treated, so the results of the study will remain relevant for the woman after childbirth. But, given the current tension in cancer pathologies in the world, sometimes colposcopy during pregnancy can reveal precancerous and cancerous lesions of the cervix. Of course, these conditions disrupt the normal course of pregnancy and prevent natural childbirth - in such cases, a caesarean section is performed.
Colposcopy is performed routinely for pregnant women. A referral for examination is issued by a gynecologist. Most women are worried when they are recommended to undergo this test, but in fact, conducting it does not mean that the expectant mother has any serious pathology. It can be prescribed not only if gynecological problems are suspected, but also if there is relative well-being in order to make sure that nothing can interfere with natural delivery and complications will not arise during childbirth.
Features of the procedure after childbirth
If diagnostics reveal abnormalities during pregnancy, gynecologists recommend colposcopy after childbirth. In addition, the examination is indicated for women who have suffered injuries during the birth process. It is done after postpartum discharge stops. They usually last up to 6-8 weeks.
In terms of technique, the procedure is no different from that performed before and during pregnancy, however, the diagnostic capabilities become more extensive: after delivery, the doctor can safely take a biopsy and treat the cervix with the solutions necessary to identify pathologies.
Is the procedure dangerous: possible consequences
Most pregnant patients believe that colposcopy is harmful to the pregnancy process itself and may pose a threat to the baby. When prescribing a diagnosis, women worry whether colposcopy is required, and whether it is possible to do without it. In fact, this is not so: the procedure is not dangerous if carried out in the absence of contraindications to its implementation. These are:
- bleeding in early pregnancy;
- increased uterine tone in the second and third trimester;
- acute inflammatory and infectious processes in the pelvic organs;
- intolerance to reagents used for extended colposcopy.
If they are present, the doctor may refuse colposcopy during pregnancy and reschedule it to a later date. In uncomplicated conditions, as well as after pregnancy-preserving therapy, the procedure can be performed. However, the gynecologist must assess the possible consequences and risks for the health of the expectant mother and the developing fetus.
Another cause for concern in pregnant women is scanty or heavy discharge after colposcopy. They worry about 30% of expectant mothers who have been diagnosed. Experts say that this is normal and does not always signal complications. The exception is foul-smelling greenish or bloody discharge. If they appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How long after colposcopy can you get pregnant?
As a rule, pregnancy after cervical colposcopy occurs if there are no problems with conception before it is performed. The method does not affect the ability to conceive in any way, so it can be planned almost immediately after the diagnosis. The exception is cases where it was necessary to take a biopsy from the cervical canal. Gynecologists advise planning pregnancy in the next cycle to allow the tissues to fully recover.
Important! If colposcopy reveals advanced erosion, a precancerous condition and malignant degeneration, you should plan pregnancy only after appropriate treatment and rehabilitation.
Can it cause a miscarriage?
Standard colposcopy of the cervix during pregnancy is not able to affect the course of pregnancy if the woman has not previously experienced a threat of miscarriage. During the examination at any stage of gestation, there is no traumatic effect on the cervical canal, so there is no risk to the fetus. According to gynecologists, only a carelessly performed biopsy, which was done in the early stages of pregnancy, can cause a miscarriage. This happens if a woman comes to the appointment without yet knowing about the conception that has occurred. If she is already registered for pregnancy at the antenatal clinic, a biopsy is not performed.
Indications for testing
Colposcopy during pregnancy on the cervix is performed if, during a routine examination by a gynecologist, the doctor discovers erosion of the cervix or other pathological changes in the female genital organs. The procedure is necessary to make the correct diagnosis and select the correct treatment. Some experts recommend that all women undergo this examination once a year.
Colposcopy helps diagnose 7 diseases of the female genital organs:
Erosion
Visible when examined with a colposcope as a smooth or fine-grained red area with vessels in the form of loops. The danger of this pathology is that it can malignize (become malignant into cancer). Colposcopy of the cervix during pregnancy helps to detect erosion in time; against the background of hormonal changes, the risk of its malignancy increases.
Pseudo-erosion
During colposcopy, this pathology looks like red voluminous circles. Pseudo-erosion can be a physiological reaction of the body to pregnancy, but more often it is a marker of infectious diseases and hormonal imbalance.
Polyps
They are distinguished by a shiny surface when examined with a colposcope. It is a consequence of hormonal changes or chronic inflammation.
Papilloma
During colposcopy, it looks like a voluminous growth of a pinkish tint with blood vessels. After applying acetic acid it turns pale. It is a precancerous condition.
Attention!
Colposcopy helps to identify many diseases of the cervix and vagina in a timely manner, prescribe the correct treatment and prevent malignancy or other complications.
Cervical endometriosis
During colposcopy, it looks like a pink or purple growth, bleeds when pressed, and does not change color when treated with acetic acid. This pathology occurs as a result of the spread of the uterine epithelium to its cervix. Endometriosis can transform into a malignant tumor.
Leukoplakia
When examined with a colposcope, it looks like light, uneven films that separate from the mucosa. Malignizes into cervical cancer if left untreated.
Cancer
It comes in various shapes and sizes, usually looks like swollen protrusions, and has blood vessels. This formation does not react to acetic acid and iodine.
A woman should consult a gynecologist and undergo a colposcopy if she experiences the following symptoms:
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- the appearance of blood from the vagina outside of menstruation;
- discomfort in the vagina;
- constant pain in the pelvis;
- itching, rash on the labia.