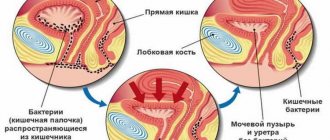
At an appointment with a coloproctologist, the doctor must conduct an external examination of the anus and palpation of the lower parts of the rectum. If, as a result, there remains uncertainty about the identified structural changes, anoscopy is prescribed. The doctor explains in advance what kind of study this is and what its significance is, in order to avoid unnecessary stress on the patient and fear of the procedure.
Anoscopy is a technique widely used to visualize suspicious formations in the rectum. The use of a modern anoscope allows you to examine the inner surface of the rectum in the final section at a depth of no more than 10–14 cm. The doctor detects non-palpable structural abnormalities, the exact location, and the nature of the changes. As a result, a decision is made to use other endoscopic diagnostic methods to more accurately determine the cause and essence of the pathology.
It is recommended to undergo an anoscopy examination annually not only if indicated, but also for preventive purposes after the age of forty. This helps to identify the asymptomatic phase of hemorrhoids and rectal tumors.
Why is an anoscopy necessary?
Often, rectal diseases make a person so embarrassed that he repeatedly postpones a visit to a specialist. This is the main problem of the sick. By the time the decision is finally made to go for an examination, the disease process is already quite advanced and treatment is difficult. Diseases of the rectal area are best treated immediately after they are diagnosed, and anoscopy exists precisely for this. In general, visiting a proctologist should be at least once a year.
When examining rectal abnormalities, the results of anoscopy (endoscopy of the anus) are very important to confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis. This diagnostic method is also needed to obtain material for analysis. Obtaining materials can be in the form of a smear or scraping from the rectal mucosa. The use of anoscopy is also justified for assessing mucosal damage, for administering a drug, or for carrying out any therapeutic procedures.
If the nodes are located higher, then sigmoidoscopy (rectoscopy) is also performed. Rectoscopy makes it possible to conduct a deeper examination - up to 35 cm in depth, which allows you to examine the mucous surface along the entire length of the rectum and distal portion of the sigmoid colon.
Also, if anoscopy is insufficiently informative, an anal colonoscopy can be performed - an examination that allows you to examine the entire large intestine - from the anus to the cecum.
Video on the topic:
Anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy: what are the differences?
In addition to anoscopy, proctology uses other instrumental diagnostic methods with a similar principle - sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy. These studies have different goals:
- with anoscopy, the doctor can examine the inner surface of the anus and the rectal mucosa to a depth of 15 cm;
- during sigmoidoscopy, the entire rectum and distal sigmoid colon are examined to a depth of 35 cm;
- During colonoscopy, the entire large intestine up to the cecum is accessible for visual inspection.
All three diagnostic procedures are instrumental studies used in proctology, but they allow you to examine the intestines in different areas. So, the most thorough examination is a colonoscopy.
Indications for anoscopy
In addition to the mandatory completion of this examination for both men and women, it is also prescribed when the following symptoms occur;
- Discharge with mucus, blood or pus;
- Hemorrhoids (single or multiple);
- Inflammation (infectious) of the intestinal mucosa;
- Constipation (chronic or long-term);
- Painful sensations in the sphincter and rectum area.
Anoscopy is also prescribed for suspected cancer, for polyps, condylomas and other neoplasms.
Differences between anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy
Both anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy are used to diagnose diseases of the rectum. However, the power of these studies varies. Anoscopy measures only 8-12 centimeters of the anal canal. This segment includes the anorectal region, where hemorrhoids are most often found. But damage to the rectum can also be at a higher level. In this case, the diagnostic capabilities of anoscopy to identify a pathological defect will not be enough.
If necessary, doctors conduct a more detailed examination - sigmoidoscopy. It allows you to assess the condition of the rectal mucosa over 20-25 centimeters. A deeper examination can reveal additional complications of the disease, for example, the source of bleeding from the intestines.
The study plays an important role in the diagnosis of rectal cancer, which is often located in the colorectal area. Using sigmoidoscopy, you can detect anal fissures that are located quite high. Early detection of these defects is very important, since correct and timely treatment allows you to get rid of them with the help of medications, while advanced cases require surgical intervention. The study is carried out if thrombosis of hemorrhoids is suspected, especially in the presence of internal hemorrhoids.
In general, sigmoidoscopy and anoscopy differ in the scope of diagnostic capabilities. Anoscopy is usually used as a method of primary diagnosis of hemorrhoids. Sigmoidoscopy is a more advanced procedure, so it is used to detail data and clarify the diagnosis.
Preparation for anoscopy
Before carrying out this procedure, be sure to cleanse the intestines using a microenema.
This procedure can be done at home. Usually two enemas are given - one in the evening and one in the morning before visiting the doctor. Medicines such as Microlax or Fortrans (a drug for cleansing the intestines) are also used as additional stimulants. Also, before an anoscopy, you should not eat fatty foods or foods that may produce gases when digested. Only a light breakfast is allowed before the procedure.
You should know that anoscopy is a fairly simple procedure. It is carried out in any of three positions, at your choice:
- On all fours, leaning on your elbows;
- Using a gynecological chair, lying on your back;
- Lying on your left side (pulling your legs bent at the knees towards your chest).
Progress of the study
Anoscopy is a simple and painless diagnostic procedure. As a rule, it does not cause severe discomfort to the patient. Its duration is about 20 minutes and depends on the goals.
To make the insertion of the anoscope as painless and natural as possible, the patient must take the appropriate position. There are three options for the examination position:
- using a gynecological chair (the patient lies on his back);
- the patient lies on the couch on his left side, and then brings his knees closer to him;
- the patient kneels, leaning forward with emphasis on the elbow joint.
The proctologist lubricates the anoscope with a special composition that facilitates its insertion, and then inserts the device into the rectum 12 cm and conducts diagnostics.
Anoscopy usually does not require the use of painkillers. However, manipulations such as taking mucosal material for histology, as well as doping polyps, require the use of anesthesia. It is possible to use local anesthetics and administer sedatives.
Palpation and anoscopy
Before performing an anoscopy itself, the doctor performs an examination and palpation on the patient to clarify important details. To perform palpation, the proctologist puts on disposable gloves, which are necessarily covered with an anesthetic (pain-relieving) gel (or ointment). Only after this can the proctologist insert a finger into the anus. This technique allows you to assess the condition of the anus, coccyx and sacrum. The doctor checks the presence of nodes, their condition, as well as the condition of the rectal muscles. Palpation allows the doctor to understand whether it is possible to reduce the nodes into the intestine in the future.
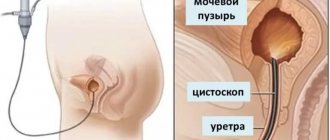
For anoscopy, the doctor uses an optical device equipped with illumination - an anoscope. Anoscopes are available in single-use and reusable types; they are made of plastic or metal. An anoscope is a smooth rod with a diameter of no more than 1 cm. This device allows you to examine up to 10 cm of the internal tissue of the anus and the distal rectum.
Before directly inserting the device, the doctor moistens the tip of the anoscope with a special oil or gel, and then moves it into the anus in a circular motion. After reaching the required depth, the doctor pulls out the mandrin (a rod that imparts rigidity during insertion) and examines the surface of the mucosa; the whole procedure does not last long - no more than 20 minutes. This data allows you to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
If, in addition to a routine examination, it is necessary to take tissue particles for analysis or to dope a polyp, then the procedure takes a little longer. To reduce the feeling of discomfort, the patient may be offered local irrigation with an anesthetic or a sedative.
After the procedure is completed, the anoscope is removed from the rectum slowly and carefully, while observing the condition of the anal folds. This method allows you to identify hemorrhoids, condylomas, fissures, polyps, tumors and inflammations in the rectum itself and at the border with the anus.
In the case of video anoscopy, an optical device built into the device displays the image on the monitor. This recording can be saved and viewed for a more detailed study, and even taken a photo of the areas of interest to the mucous membrane. This version of the procedure is very suitable for those patients who experience severe discomfort during this type of computer diagnostics - they will not have to experience them again.
Anoscope sizes
The choice of anosops by diameter is quite wide, and all manufacturers offer a large range of sizes, so for advice on choosing, see below. As for the length, most manufacturers have everything more or less standard; the working part for all is approximately 65-80 mm.
The only thing I would like to note is that some manufacturers, including Heine and Welch Allyn, offer a class of instruments that is very mysterious to me, for example, which they call a “proctoscope.” Proctoscopes are approximately 130 mm long. Those. the result is such a “under-rectoscopy”, with the help of which it is inconvenient to carry out manipulations in the anal canal (too long), on the one hand, and you cannot do a full-fledged rectoscopy, on the other hand. Apparently, the idea of using them is the pathology of the mid-ampullary part of the rectum, when the anoscope is too short, and the standard rectoscope, on the contrary, is too long. But, in my opinion, the problem is somewhat far-fetched. I have never used such a tool in my life and have not experienced any particular inconvenience due to this.
Contraindications for anoscopy
Although there are no absolute contraindications for this diagnostic study, there are times when the procedure can simply be postponed for some time. Examples of such cases include:
- Cracks in the anal passage (in the acute stage);
- Narrowing of the intestinal lumen;
- Chemical or thermal burns of the rectum;
- Tumors on the anus leading to stenosis;
- Acute inflammatory processes.
In these situations, anoscopy is postponed for the duration of treatment, but if the situation is critical, then it is done using painkillers.
Anoscopy capabilities
Despite the fact that the anoscopy method is quite simple, it is very popular in proctology, and its results are considered especially important. The anoscopy procedure is necessary for the following purposes:
- Confirmation (or refutation) of the diagnosis;
- Taking tissue samples for analysis;
- Assessment of the condition of the mucous membrane;
- Administration of drugs.
Examination with an anoscope allows you to notice emerging Crohn's disease, the beginning growth of polyps, and identify hemorrhoids. Anoscopy also makes it possible to verify the correctness of the diagnosis or refute it, as well as confirm the presence or absence of:
- Anal fimbriae;
- Cracks in the anus;
- Incomplete rectal fistula;
- Cancerous neoplasms.
In surgical proctology, the anoscope device itself is used to perform such manipulations as:
- Electrocoagulation;
- Infrared coagulation;
- Sclerotherapy.
Why do the research?
The results of anoscopy are of great importance in the diagnosis of rectal pathologies. Its use makes it possible to carry out manipulations with the aim of:
- confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis;
- take material (a piece of mucous membrane, a smear) for subsequent analysis;
- administer medicine;
- assess the degree of damage to the rectal mucosa;
- carry out medical procedures.
Proctologist explains the procedure of anoscopy to a patient
This diagnosis makes it possible to detect the occurrence of internal hemorrhoids, polyps in the initial stages of development, and symptoms of Crohn's disease. The procedure also makes it possible to identify pathologies such as fistulas, tumors, cracks, and condylomas.
Only with the help of anoscopy is it possible to carry out such a therapeutic manipulation as administering a medication directly to the site of inflammation. In addition, surgical interventions such as sclerotherapy, infrared and electrocoagulation and others are performed under videoscopic control.
Complications during anoscopy
As already mentioned, anoscopy is a fairly simple procedure and in most cases goes without complications. But there is still a possibility of their appearance. One of the reasons for the occurrence of complications may be the inexperience of the doctor. If, when taking a tissue sample, the doctor makes a careless movement to the side, he can damage the mucous membrane, which will lead to bleeding. This leads to the second reason, again due to the inexperience of the proctologist. If all the doctor’s movements are sharp and careless, then it is possible to pierce the wall of the large or small intestine, and the consequence of this will be the merging of the contents of this organ with everything around it.
Lack of treatment and proper care can lead to blood poisoning and even death.
Differences between anoscopy and other diagnostic methods
Endoscopy, being the most important direction in diagnostics at present, is used in the study of various types of diseases. It is the ease of implementation and accuracy in making diagnoses that makes it so universal for different areas of medicine. Endoscopy methods provide a chance not only to detect the onset of the disease, but also to take materials for analysis.
In addition to anoscopy, there are a couple more procedures that are similar in principle, but different in the areas of study of the intestines - anoscopy, colonoscopy and rectoscopy. The main differences are as follows:
- During an anoscopy, the doctor examines the lower part of the rectum and anus;
- Colonoscopy provides a better look at the entire large intestine;
- Rectoscopy examines the inside of the rectum and the lower part of the sigmoid colon. This method is divided into several types - anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy and proctoscopy, chromorectoscopy (examination with a flexible endoscope).
What other types of endoscopy are there? Modern endoscopy uses its methods in various fields of medicine. For example, versoscopy is a method of examining the uterine cavity using, again, an optical device, otoscopy is a method used to examine the ear, etc.
Video on the topic:
Procedure
- The patient is placed in a position in which it is convenient to examine the anal area: either lies on his side with his legs drawn to his stomach, or sits in a gynecological chair.
- The doctor conducts a preliminary digital examination of the rectal area to assess the patient’s readiness for the procedure and to detect contraindications to the examination from the rectum.
- After a digital examination, an anoscope, an endoscopic device that has lighting and optical technology, is inserted into the rectum through the anus.
- The device moves inward using slow circular movements to a depth of approximately 8 cm.
- The obturator is removed from the anoscope, after which a sequential examination of the intestinal mucosa is carried out.
During the manipulation, the doctor can assess the condition of the rectum and anal canal, detect pathological changes in their walls (hemorrhoids, neoplasms, inflammatory processes).
When the anoscope is inserted, the patient does not feel severe pain; only slight discomfort is felt when the device is inserted through the anus. Therefore, the procedure does not require the use of local anesthesia.
Reviews
When I was being prepared for rectal endoscopy, I was very nervous. But the doctor explained everything correctly and said that the procedure was not scary and quick. Everything went really quickly and I was almost not nervous.
List of references: https://dr-paramonov.ru/news/articles/anoskopiya/ https://medbiospectr.ru/patient/section/razlichiya_mezhdu_anoskopiey_i_rektoromanoskopiey/ https://www.yamed.ru/services/proktologiya/anoskopiya/ https ://www.smclinic.ru/professional-services/diagnostika-v-proktologii/anoskopiya/ https://medongroup-spb.ru/blog/anoskopiya/ https://www.mediccity.ru/directions/208 www. gkb-31.ru/articles/anoskotpiya/ https://www.fdoctor.ru/anoskopiya/ med.vesti.ru/doc/maryana-abritsova/na-osmotre-u-proktologa-chto-takoe-anoskopiya/ Author's notes articles based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/09/2020