A thyroid biopsy is perhaps the only final method of assessing the condition of the gland. Assessment in terms of the presence or absence of malignancy of the neoplasm.
When asked the question of whether it is worth doing a thyroid biopsy, one is left surprised at the medical illiteracy. The patient cannot independently go to the medical center and express the desire to have a biopsy.
Only a doctor and only if there is a reason can send you for the procedure. It should be kept in mind that a thyroid biopsy is an invasive procedure. As a rule, before it is recommended to undergo it, the patient undergoes a simpler diagnosis. But when making a final diagnosis based on the accuracy of the result, there is no substitute for a biopsy
About the procedure
Biomaterial is collected for subsequent analysis by inserting a thin needle into the thyroid gland, which is not a painful procedure.
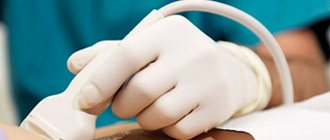
General or local anesthesia is not used because the patient reacts more painfully to the administration of analgesic drugs than to the biopsy procedure itself. Some medical institutions use special creams with an anesthetic, but doctors are of the opinion that this is rather a psychological component of preparation for the procedure. Today, blind biopsy is practically excluded. Puncture analysis is performed using an ultrasound machine. This helps to maintain continuous control over medical procedures. A clear image on the monitor allows the doctor to accurately insert the needle into the tumor and minimize the risk of damage to tissues and adjacent organs.
The time range of a puncture biopsy is about a quarter of an hour.
Schematic drawing of a fine-needle biopsy, which is performed only by a qualified specialist
The name fine-needle biopsy comes from the instruments used - thin needles, 23-21G in diameter. Such needles are used not only to make the procedure easier for the patient (reducing pain and fear), but also because little blood penetrates into the thin needle, which improves the quality of the biomaterial taken for analysis.
Is it possible to use ultrasound instead of a biopsy?
Ultrasound and biopsy are complementary methods. Carrying out a biopsy of the thyroid gland significantly increases the information content of ultrasound examination of nodules in the thyroid gland (thyroid gland).
Biopsies are used for differential diagnosis of nodular neoplasms of the thyroid gland (clarification of the malignant or benign etiology of the disease).
For thyroid biopsy, fine needle aspiration biopsy is used. This research method is indicated when ultrasound reveals palpable nodules with a diameter of more than 1 centimeter.
If nodules with a smaller diameter are detected, a puncture biopsy of the thyroid gland may be indicated if there is a suspicion of thyroid cancer (if suspicious symptoms are detected on ultrasound).
It should be noted that during a biopsy of the thyroid gland, a scattered group of cells is examined, and not a section of gland tissue, therefore this type of biopsy refers to the cytological diagnostic method, and not to the histological biopsy.
Needle biopsy of the thyroid gland consequences
Taking a puncture in some cases leads to the development of various complications. For example:
Dizziness. It is noted in osteochondrosis, especially in the cervical spine
To prevent this symptom, and also to prevent the patient from losing consciousness, it is recommended to get up slowly and carefully after the operation.
Temperature increase. She should be back to normal in a day, so there is nothing to worry about.
Hematoma
Bruising may occur if capillaries or vessels lying in the path of the needle were touched during surgery. To reduce the manifestations of a hematoma, after removing a thin needle, the puncture site should be fixed with a cotton swab.
Cough. This consequence occurs after a biopsy, when the node being examined is located near the trachea. The symptom usually does not last long and gradually goes away on its own.
Thyrotoxicosis syndrome. A complication occurs when the patient experiences severe anxiety. His heart rate increases, his palms sweat, and he becomes overly nervous. A calm explanation from the doctor about the details of the study, as well as the psychological preparation of the patient himself, will help here. You will receive more detailed information about hyperthyroidism by reading the article.
The described side effects usually do not require medical intervention and go away on their own over time.
However, there are cases when emergency assistance from a specialist is needed, such moments include: bleeding, inflammation at the puncture site, very high temperature, etc. In this case, for consultation and examination, you should contact the specialist who performed the operation.
The purpose of a biopsy is to determine, based on the analysis, whether the tumor is benign or malignant. So the result can be one of two things. Sometimes the analysis can be uninformative. In this case, it is necessary to re-sample the material, i.e. the procedure is repeated.
If the thyroid biopsy response shows a benign sample, then further observation by an endocrinologist is required. A colloid nodule, as a rule, does not develop into cancer.
It is much worse if the analysis confirms a malignant tumor - thyroid cancer. This diagnosis requires removal of the thyroid gland or part of it, it all depends on the stage of development of the malignant neoplasm and the degree of damage to the organ. You can learn about the features of diagnosing thyroid cancer from the article.
You can often hear that after a biopsy, malignant tumor cells begin to grow more rapidly and worsen the condition. But this fact has not been scientifically confirmed.
Puncture of the thyroid gland, when performed correctly, is considered a simple, but very informative procedure.
Indications for the procedure
Not all people with thyroid nodules undergo a biopsy procedure. Most formations do not cause discomfort or health problems and are often not detected throughout a person’s life.
Puncture of the thyroid gland is performed only in cases where a tumor is detected by palpation or during ultrasound examination. The doctor recommends additional diagnostics.
According to medical instructions, thyroid puncture should be performed in the following cases:
- if the size of the nodes detected in the patient exceeds 10 mm;
- in the presence of cysts;
- when painful sensations appear during palpation in the area of the cervical lymph nodes;
- if neoplasms are detected in the thyroid gland and at the same time symptoms and laboratory test results suggest cancer;
- if a person has been exposed to ionizing radiation;
- if any of the patient's close relatives suffered from thyroid cancer.
Depreciation of the thyroid biopsy procedure
In fact, today this is the only method for diagnosing thyroid cancer with sufficient accuracy. An absolutely accurate method is intraoperative histological examination, for which there are also certain indications, and it is not performed on everyone.
During the puncture, cells are removed that make up the wall of the thyroid follicles, where cancer may be hidden. This material is then applied to a glass slide and examined under a microscope.
No other study has such accuracy, since here the histologist sees these same cells and can distinguish normal cells from atypical ones.
Evaluation of the results of the procedure
Deciphering the received material takes approximately 7 days. The accuracy of the results is more than 90%.
Research shows:
- how informative was the puncture;
- the presence of atypical cells in the thyroid gland;
- benign nodes;
- intermediate stages, possible tumor development.
The smaller the nodes from which the material is taken, the greater the likelihood of incorrect or negative results. Therefore, a puncture biopsy is usually not performed for small neoplasia.
The results of the tests are given to the patient on a special form, which reflects the main information:
- node location;
- tumor size;
- general condition of the node.
Diagnosis scheme
There are several categories of diagnostic results:
- Uninformative indicators. A repeat biopsy is necessary.
- Benign neoplasm. In such cases, the patient is recommended to undergo annual examinations.
- The appearance of follicles for unknown reasons. The most difficult conclusion, since the development of several diseases of the organ tissue is possible. A repeat biopsy is required, and sometimes the thyroid gland is partially removed.
- The likelihood of poor quality education. Examinations are carried out by an oncologist.
- Proven malignant tumor.
Safety of the procedure
A thyroid biopsy is completely safe. There may be some pain in the neck area for a few days, but this is normal. Small hematomas may also appear at the injection sites, so it is necessary to press the cotton swab firmly for several minutes. If the gland is slightly enlarged, then the injection is given into the isthmus. In this case, there is a possibility of a puncture of the trachea and the patient may cough violently. Then the puncture is delayed a little. Many people think that a biopsy of the thyroid gland can provoke the transformation of a nodule into a malignant tumor, but in world practice, not a single such case has been recorded. There is also an opinion that a biopsy can provoke the spread of the tumor, but this is also not confirmed.
The video shows the process of taking thyroid cells for cytological examination
Practical advice
After receiving the cytological examination protocol, you must pick up the slides with your material. It would not be a bad idea to have them examined by a specialist from another clinic, especially in cases where surgery was prescribed based on the results of a thyroid biopsy and subsequent cytological examination.
There is no need to neglect the prescribed examination - timely identification of nodes and appropriate treatment will help to avoid serious problems in the future. A thyroid biopsy will help detect cancer at an early stage, which will greatly facilitate treatment. Nowadays, scientists have found that oncology can be inherited. Therefore, in families where cancer has occurred, it is recommended to undergo preventive examinations from time to time.
It must be remembered that the effectiveness of cytological examination is somewhat lower than the effectiveness of histological examination of glandular tissue, performed at the time of surgery. When conducting a histological examination, a whole piece of an organ is taken and the exact structure of the pathological focus is studied, while when performing cytology, only a suspension of cells obtained from the organ is examined, therefore the diagnostic efficiency is somewhat lower, but this study does not require surgery on the organ.
Lumps on the neck, shortness of breath, sore throat, dry skin, dullness, hair loss, brittle nails, swelling, puffiness of the face, dull eyes, fatigue, drowsiness, tearfulness, etc. - this is all a lack of iodine in the body.
If the symptoms are obvious, your thyroid gland may no longer be able to function normally. You are not alone, according to statistics, up to a third of the entire population of the planet suffers from problems with the thyroid gland.
How to forget about thyroid diseases? Professor Vladimir Trofimovich Ivashkin talks about this here.
Consequences of thyroid removal in women and men
Removal of the thyroid gland may be necessary if a tumor is diagnosed or the goiter is significantly enlarged. The operation itself is not classified as complex, so there is no need to panic prematurely.
Thyroid diseases are one of the most common reasons for visiting a doctor these days. According to statistics, thyroid diseases rank second after diabetes in terms of the number of people affected. Speaking of specific figures, 665 million people in the world suffer from goiter and 1.5 billion people are faced with thyroid problems due to iodine deficiency. Every year these numbers increase, so undergoing routine examinations is more justified and advisable than ever. In most cases, problems with the thyroid gland mostly affect older women, although the number of men with similar diseases is also large.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Many factors can disrupt a person’s normal health, but the worst influence is the poor environmental situation. Among the triggers that can provoke thyroid diseases, it is worth noting:
- constant emotional stress;
- unfavorable working conditions (chemical production);
- pathological changes in the hypothalamus;
- autoimmune diseases;
- unbalanced diet;
- infectious diseases that were left without proper treatment;
- uncontrolled use of medications.
Separately, I would like to mention that problems with the thyroid gland can be inherited. If one of your relatives suffered from thyroid disease, then there is a high probability that over time the disease will affect you too. If you have a genetic predisposition to the disease, after 35 years of age, be sure to undergo preventive examinations with an endocrinologist.
The thyroid gland plays an important role, as it is responsible for the production of hormones that are involved in all metabolic processes in the body. Externally, it is a small organ weighing about 20 g. It is located in the front of the neck and consists of two lobes and an isthmus.
It is quite simple to calculate thyroid diseases, since they, like all diseases, have a number of symptoms that can be a good reason to visit a doctor. Typical signs of thyroid problems include the following:
- increased fatigue;
- drowsiness;
- anxiety for no apparent reason;
- irritability;
- indifference to sexual relations;
- constipation;
- chilliness;
- frequent cramps during the day;
- attacks of nausea on an empty stomach;
- weight gain;
- hair loss and baldness in men;
- increased sweating and body temperature;
- peeling of the skin and dry mouth;
- high cholesterol;
- high blood pressure;
- sleep disorders;
- painful menstruation in women;
- hoarseness in the voice.
Most often, the patient discovers problems with the thyroid gland himself, noticing a small swelling in the neck area where there should not be any. Sometimes swelling in the neck can be accompanied by an enlargement of the eyeballs, which seem to begin to protrude from their usual location.
If you notice at least 2 points from the above list, you should immediately consult an endocrinologist. In the early stages, almost all thyroid diseases can be cured with medications without surgery.
Preparing for surgery
Removing the thyroid gland is a rather serious undertaking that requires preliminary diagnosis. Before surgery, the patient must undergo a series of tests, which include:
- analysis of thyroid hormone levels;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and lymph nodes in the neck;
- biopsy of lymph nodes and thyroid gland;
- laryngoscopy;
- computed tomography of the neck and some parts of the chest;
- thyroid scintigraphy;
- genetic research.
After confirming the diagnosis and if drug therapy does not help, the patient must decide on the date of the operation. There is an opinion that surgery on the thyroid gland is best performed in the summer months. By and large, when exactly to perform the operation does not make any difference, the main thing is that it is carried out in a timely manner.
Immediately before the operation, upon admission to the hospital, the patient must undergo a clinical and biochemical blood test, urine test, blood group test, a coagulogram, a chest x-ray and, if necessary, additional clinical studies. After all the studies, a control examination of the patient is carried out by a therapist and an anesthesiologist. A consultation with the surgeon who will perform the operation is mandatory. Sometimes the patient needs a conversation with a psychologist.
Surgical technique
If removal of the thyroid gland is inevitable, then the surgeon first needs to decide on the method of intervention. Today there are several options:
- removal of a cyst or isolated node while preserving most of the gland;
- removal of one lobe of the thyroid gland while preserving the isthmus and the second lobe of the organ;
- resection of the gland with preservation of a certain part of the organ and adjacent parathyroid glands;
- complete removal of the gland with lymph nodes.
The reason for the intervention plays a significant role in choosing the surgical procedure to remove the thyroid gland. Removal of this organ has a number of indications, including:
- oncological neoplasms;
- toxic and diffuse goiter;
- adenoma;
- retrosternal goiter;
- large goiter.
In order to avoid the possible consequences that the removal of the thyroid gland will cause, you need to take seriously the choice of the medical institution where the operation will be performed and the doctor who will perform it. It is important to follow all the doctor’s instructions during the period of rehabilitation after surgery.
Possible consequences include suppuration and bleeding of the sutures, as well as paresis of the parathyroid glands and recurrent nerve. If removal of the thyroid gland does not cause any consequences in women, then subsequent pregnancy and childbirth are quite possible. The main thing is to immediately inform the doctor about your condition, since he is obliged to adjust the hormone and monitor your condition throughout the entire period of pregnancy. Removing the thyroid gland also has virtually no consequences for men, you just have to pay attention to physical activity. Extensive physical activity is, of course, prohibited, but moderate exercise will be beneficial. Professional athletes will still have to give up their careers.
According to surgical statistics, the operation to remove the thyroid gland itself is not complicated, so it is not a reason for assigning disability. If, in the postoperative period, certain complications arise that lead to limited capabilities of a person, then the patient can undergo examination to be assigned a group.
The surgical intervention is performed under general anesthesia and lasts approximately 2 hours. After the operation, the patient is transferred to the ward. The first day you are not allowed to get out of bed. If a drainage was inserted into the patient during the operation, it is removed the next day and systematic dressings are performed. In general, the patient's hospital stay, if there are no complications, is 3 days.
Features of the postoperative period
After thyroid surgery, people can live long and fulfilling lives. Of course, replacement therapy and long-term rehabilitation are required, but most people were able to return to their previous lives. The only inconvenience after surgery on the thyroid gland is that the patient will have to take the drug Thyroxine for the rest of his life. It is a kind of analogue of the hormone that the thyroid gland produces. The task of the treating endocrinologist is to select the correct dosage of the medication in accordance with the weight and individual characteristics of the patient who has undergone surgery. Hormone levels are monitored once a month, and the dosage of the drug is adjusted approximately once a year.
If surgery was performed due to cancer, then in addition to the hormone, the patient will be prescribed radioactive iodine.
It is necessary to avoid possible relapse and prevent the formation of metastases.
After removal of the thyroid gland, the patient will initially experience a number of inconveniences, such as:
- voice disorder;
- weakness;
- hypocalcemia;
- a sore throat;
- discomfort in the back of the neck;
- swelling in the incision area.
In most cases, if the operation was successful, then all of the above symptoms will go away on their own after 3 weeks. Because your thyroid gland was removed, there should be no consequences, just a small scar.
Proper nutrition
As for the diet in the postoperative period, it does not exist as such; the only requirement is proper nutrition. You need to increase the amount of fruits and vegetables in your diet, and also avoid coffee, fatty and smoked foods. People who have undergone surgery are strictly prohibited from fasting.
Only such a decoction will trigger REGENERATION of the thyroid gland
The goiter will disappear in 3 days! This remedy has become a sensation in the treatment of the thyroid gland!
If you have been given a disappointing diagnosis and have been prescribed surgery, do not panic, modern medicine has made great progress in the treatment of the thyroid gland, and 98% of operations on it are successful. Remember that the main thing is not to ignore the body’s initial signals and immediately seek qualified help. Timely treatment is the key to a quick recovery and return to normal life.
Consequences of thyroid biopsy
Currently, the puncture is performed with a thin needle, which does not cause much discomfort to the person.
However, a thyroid biopsy is not such a simple procedure, therefore, as with any other intervention, unpleasant consequences may occur.
- Hematoma. Often, when a doctor performs a procedure, he can catch and injure small capillaries, vessels, and muscles that cover the organ itself. In order not to damage larger arteries, specialists use ultrasound of the esophagus, but with small ones it is more difficult. To prevent bruising after the puncture, immediately after the needle is removed, a cotton swab is pressed tightly to this place. It will prevent a hematoma from appearing and reduce pain in the future.
- Sometimes it happens that after a biopsy, the patient may have a fever in the evening, up to about 37 degrees. This shouldn't be scary; it doesn't happen often.
- Cough. This consequence of puncture may appear if the neoplasm that was examined is located in close proximity to the trachea. Usually the cough goes away on its own quickly enough and does not cause any concern.
- Very often, after this procedure, a person may experience dizziness. This is not uncommon among those who are overly impressionable. In addition, this consequence often appears in patients with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Therefore, after the examination, you need to get up very slowly and carefully so as not to lose consciousness.
- Thyrotoxicosis syndromes may often appear. This occurs as a result of excessive worries. Your palms may begin to sweat, nervousness may appear, and your heart rate may increase. To prevent this from happening, it is best to talk to your doctor before the procedure, find out exactly all the necessary information, and then relax and let the specialist conduct the biopsy in a calm state.
These complications and consequences are not considered severe and do not require intervention from doctors. However, sometimes it happens that you cannot do without the help of specialists.
- Bleeding. If a person has poor blood clotting or is taking medications that thin the blood, then it is necessary to inform the doctor about this before the procedure.
- Symptoms of fever and very high temperature is also a serious complication.
- In a good way, after some time there should not be any traces left at the puncture site. If this place begins to swell, then you should consult a doctor.
- If the specialist does not have much experience, then during the procedure large arteries and trachea may be affected.
- If a patient has difficulty swallowing after a biopsy, this also indicates possible complications.
- It also happens that the medical staff simply did not properly process their instrument before performing the puncture. As a result, a person may get some kind of infection. If you experience neck pain, sometimes so severe that it is difficult to even turn your head, or if your lymph nodes become enlarged, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid even more serious problems.
In any case, if any unpleasant symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. There are widespread rumors that after such an operation, malignant tumor cells begin to grow faster. However, this fact has not been scientifically confirmed. Therefore, there is no need to be afraid.
If a doctor prescribes this procedure, then, first of all, it is worth deciding on the choice of a specialist. You can talk to friends, look for reviews of clinics on the Internet. There is no need to run to the first doctor you come across. Indeed, in addition to the fact that he may perform a biopsy poorly, unpleasant consequences may arise. And future life will depend on the results. In addition, you should not be afraid of this procedure. All serious complications can arise mainly as a result of the unprofessionalism of doctors. But in general, this procedure is quite tolerable. And completely safe for the human body. It cannot precipitate any other diseases. Therefore, there is no need to refuse if the doctor nevertheless decides to take the test in this way.
Patient reviews
A biopsy examination of the thyroid gland is a fairly common procedure, so you can easily find reviews from those who know about it first-hand.
Maria, 29 years old: “My story, like most, began with an ultrasound. As a result of the examination, they discovered a mass in my right lobe. It turned out to be quite large - 2.7 cm. After that I was sent for a biopsy. Of course, I was worried that it would be painful, but in fact it was just unpleasant, but quite tolerable. I was given two needles under ultrasound guidance. They covered the injection site with a plaster and asked me not to get it wet for a couple of hours, although an evening shower was allowed. After the procedure, there was some discomfort in the neck when turning the head, but after a couple of days it went away. I had no bruises or swelling at the puncture site. The result showed that I have a benign tumor, but it cannot be treated with medication. And sooner or later the operation needs to be done.”
Yulia, 24 years old: “I have done TAB more than once and have a rather sad first experience. During the initial analysis, a puncture was taken from me with a regular 20 cc syringe. I survived this execution normally, and at the end they didn’t even cover the puncture site with a plaster because it had run out. The answer was ready within 1 hour - everything is fine, nothing to worry about. So another 2 years passed, but when we started thinking about having a child, I decided, just in case, to undergo surgery and get rid of the tumor. When I went to another clinic for surgery, they redid the biopsy and this time everything looked completely different. In addition, malignant cells were discovered. In response to my questions, how did it happen that 2 years ago everything was supposedly fine, but now it’s like this, the doctor said that the first tests were done negligently. So my conclusion is that don’t be afraid of the procedure, but where to do it, carefully collect information.”
A thyroid biopsy is not prescribed for all patients who have nodular goiter. For this there must be clear indications. Those who are prescribed it may be very afraid of the needle puncture itself or the future result, and therefore choose to live in ignorance. And yet, if the procedure is recommended by the attending physician, then you should not refuse it. A timely biopsy is the key to a correct diagnosis and timely selection of effective treatment.
How is a biopsy sample taken?
Fine needle biopsy is performed on an outpatient or inpatient basis. The manipulation takes about half an hour. Before the biopsy, the patient's thyroid gland is examined using an ultrasound machine.
The procedure for collecting a biopsy sample during a fine-needle biopsy is similar to taking blood from a vein. No preparation is required to carry it out. During biopsy sampling, the person lies with his head thrown back.
When the specialist inserts a needle into the patient’s throat, the latter must precisely follow all the doctor’s commands.
The accuracy of hitting the desired node depends only on the doctor’s skill level. In fact, the procedure is not complicated, and any health care worker who has at least minimal experience in taking a biopsy from the thyroid gland can handle it.
You should be mentally prepared from the very beginning for the fact that the doctor will insert a needle into your throat several times.
There is no need to worry - the reason for repeated injections is not the poor qualifications of the specialist, but the inability to obtain the required amount of material in one puncture.
No anesthesia is required before the procedure, as tissue sampling is painless. Moreover, cytologists say that general anesthesia can negatively affect the outcome of the study.
The patient's throat is treated with a local anesthetic. Those who are overly nervous can take a sedative immediately before the test (with the doctor’s permission).
To stop bleeding, just apply a cotton swab to the puncture site for five minutes.
One of the complications of fine needle biopsy of the thyroid gland is puncture of the trachea. Its immediate symptom will be a cough that begins right during the procedure.
When the trachea is punctured, the doctor stops taking the biopsy. The research can only be continued after some time.
Patients with problems in the cervical spine may feel dizzy after a fine-needle biopsy, so there is no need to get up from the couch immediately after removing the needle from the throat - it is better to lie down for at least a few minutes.
Recognition of the procedure as necessary
Most scientists, as well as the World Health Organization, have recognized the need for such a procedure. Scientists point out that formations, even of the smallest size, if there are several of them, have the most adverse effect on the human body, therefore, clarifying their nature is the responsibility of every doctor who is faced with such a problem in a patient. People who seek help with such a problem are under the supervision of a doctor. The latter prescribes tests for the content of hormones, such as thyroid-stimulating hormone, triiodothyronine, thyroxine, and so on. Periodic ultrasound examinations are also prescribed, usually such procedures are performed 3-6 times a month, in addition, patients need to independently monitor their condition.
Another way to check for malignancy
Radioisotope scanning is another way to check the condition of nodes. It does not exclude a biopsy, but is a preliminary step before it. In medical terminology there are 2 concepts: hot and cold nodes. Thyroid cells absorb iodine, which is part of the gland. When radioactive iodine is administered to a patient, images of the thyroid gland may result in 2 images. If the glandular nodule consists of cellular material that for some reason does not absorb iodine, then a bluish image will be obtained and it will be a cold nodule. If iodine is actively absorbed, the image will produce a bright orange image, this will be a hot node.
It is quite difficult to determine the benign quality of the nodes from these images, but if we talk about probabilities, then if the node is hot, the probability that it is malignant is much lower than if the picture is the opposite. Since radioisotope scanning does not give a clear answer, doctors still end up resorting to the final type of diagnosis in the form of a thyroid biopsy.
Contraindications for thyroid biopsy
The procedure for collecting a tissue sample with a thin needle is absolutely harmless and, as a rule, goes without complications. The worst thing that can happen during the procedure is a puncture of a vessel located close to the node being examined, after which a little blood will come out.
The diameter of the needle is so small that the pain from the puncture is practically not felt - this is the feedback left by most patients. For an experienced specialist, 2–5 seconds are enough to take a tissue sample.
Insufficiently informed people believe that after inserting a needle into a benign node, it can degenerate, but such a transformation is completely excluded.
Video:
The thyroid gland has the following proven feature - a benign nodule does not turn into malignant.
A malignant compaction is initially of an oncological nature. If, at the beginning of the growth of a node, malignancy mechanisms are not embedded in it, then the pathology will never turn into a cancerous tumor.
There are cases when, two or three years after the biopsy, cancer is still discovered in a node that was previously benign.
The reason for this could be three things:
- the first time the tissue sample was taken from a very small node, and the doctor did not hit the syringe in the right place;
- the laboratory violated the technology for studying the sample due to insufficient qualifications of laboratory technicians;
- the error occurred at the stage of deciphering the biopsy, that is, the cytologist made a mistake.
Advice: whatever the result of the biopsy, it would be a good idea to conduct additional examination of the biopsy sample, especially if surgery is prescribed based on the test results. To do this, you need to take the glasses with your material from the laboratory and send them for research to another clinic.
After a fine-needle biopsy, a bandage is applied to the throat, which can be removed after a few hours.
For comparison: if the biopsy sample was taken using the method of core needle biopsy, then the bandage can be removed only after a day.
If pain persists after the procedure, you can take a painkiller. For 24 hours after TAPB, you should not be physically active or wet your neck with water.
Video:
If, due to a poorly performed biopsy, an infection enters the body, this will be expressed in the following symptoms:
- swelling of the skin at the puncture site;
- temperature increase;
- fever;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- redness of the throat;
- painful swallowing.
In such cases, you must return to the medical facility. To relieve inflammation, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
Having received a form with the results of a biopsy, which indicates that the node is likely to be malignant, you should not panic, but act immediately.
Modern medicine successfully treats thyroid cancer. The prognosis for this disease with early diagnosis is favorable in 95% of cases.
Method of performing TAB of a thyroid nodule in our clinic
The manipulation is carried out only under ultrasound control, which makes it possible to quite accurately localize the location of the node and the needle entering it. Carrying out FNA under palpation control does not provide such accuracy. It is not for nothing that the described technique is called fine-needle biopsy, since it uses the thinnest needles. Thanks to this, less blood gets into the smear, which improves the quality of cellular material for cytology; The intensity of pain decreases, and there is no need to use additional anesthesia.
The injection itself takes a few seconds from an experienced doctor, and the injection is barely felt. However, if the patient complains of increased sensitivity of the skin, then additional superficial anesthesia with special creams is performed. In this case, the product is applied to the skin 1 hour before the procedure, this reduces pain sensitivity, but does not affect the accuracy of hitting the node.
The entire preparatory process takes about 10 minutes:
- patient registration,
- an explanatory conversation with him before the procedure,
- and other organizational issues.
As you can see, they take much longer than the injection itself.
How is a needle biopsy of the thyroid gland performed?
- 1. The patient is placed on his back with a pillow to promote neck extension.
- 2. The skin over the thyroid gland is treated with an antiseptic;
- 3. The working area is delimited by sterile material.
- 4. Initially, an ultrasound of the thyroid gland is required, which allows you to determine how many and which nodes need to be punctured, and to localize them correctly.
- 5. Then a puncture is performed.
- 6. After 15 minutes, the patient is free and can engage in normal activities.
In our Clinic, special attention is paid to issues of sterility, patient safety issues in terms of infection with infections such as HIV and hepatitis, which are transmitted with traces of blood due to ineffective processing of instruments.
Most medical facilities that perform FNA use immersion of the probe in an antiseptic solution after the FNA procedure to disinfect the ultrasound probe. But usually, given the experience of our doctors, such treatment is not enough to completely disinfect the sensor due to the high resistance of infectious agents to many disinfectants. Special attachments used in a number of clinics for guiding the needle during a biopsy make it easier for the needle to enter the node, but at the same time their subsequent sterilization by autoclaving is significantly more complicated.
Our clinic specialists do not use anything like this. They hold the sensor, protected by a disposable protective cover, in their free hand, and with the other hand they puncture the node with a thin needle. The used cover is disposed of. But the sensor remains intact. After the procedure is completed, the injection site is pressed with a sterile ball, the need for which disappears after 5 minutes. Application of anesthetic cream and fine needles; Carrying out absolute sterility of the manipulation at all its stages is the key to the safety of this procedure.
Biopsy process
Immediately before TAB, an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland is performed to accurately determine the location of the nodes. The procedure is performed with the patient lying horizontally on the couch. The main condition is the correct fixation of the head and neck using a special roller. Supporting the cervical spine on the bolster provides the best access to the protruding thyroid gland.
The patient's neck area is treated with an alcohol-containing antiseptic. The instrument for collecting the biopath is an empty syringe equipped with a thin and long needle. The doctor uses an ultrasound sensor to find the tumor. The puncture can be performed in two ways:
- using a needle attachment. A specialized attachment for the ultrasound sensor helps to determine the location of the formation as accurately as possible. A thin needle passes directly through the nozzle, the doctor punctures the skin and enters the needle directly into the node. In this case, sterility measures must be strictly observed, since the nozzle is a reusable instrument that comes into direct contact with the patient’s blood;
- without guide nozzle. Carrying out a biopsy without a special attachment requires a highly qualified doctor and experience in performing such manipulations. Because in this case, the doctor identifies the node with the help of a sensor with one hand and, holding it, inserts the puncture needle by touch with the other hand. This type of diagnosis is called “hands-free”.
In essence, puncture of the thyroid node is the drawing into a syringe of a substance that is located in the tissues and cells of neoplasms. The walls of the node have the greatest information about the presence of cancer cells, so it is preferable to obtain biomaterial from this part. During the biopsy, the patient must remain completely static and avoid swallowing movements.
After pumping out the required amount of biopath, the needle is removed, the puncture site is wiped with an antiseptic again, and a gauze napkin is fixed on it with a plaster. To obtain complete information and in the presence of several space-occupying formations, the puncture is taken several times in different areas. To prevent bleeding, the bandages should be pressed and held for several minutes (as after an intravenous injection).
The resulting biomaterial from the Spitz is squeezed onto a special laboratory glass and sent for further analysis. After a quarter of an hour, the patient can lead a normal life. On the first day after the puncture, doctors recommend avoiding sports and not washing or getting the puncture area wet.
The doctor will tell you before the procedure how to prepare and how the manipulation will take place.
Carrying out
The operation proceeds as follows:
- The patient is positioned on the couch with his head on a pillow.
- Using palpation, the doctor determines the location of the node.
- A very thin needle is inserted into the existing formation, and a small part of the gland is drawn through it, which has suspicious dynamics. In some cases, several punctures are performed to take the necessary analysis from different parts of the node. Actions are controlled; an ultrasound machine is used for these purposes, which makes it possible to exclude careless actions, puncture or damage the esophagus, blood vessels and arteries.
- The needle is removed, the puncture is covered with a cotton swab and adhesive tape.
- After a while (15-20 minutes), the patient gets up from the couch.
- The collected material is sent for laboratory testing.
The total duration of the puncture is up to 20 minutes, of which the collection of the contents of the node is about 3 minutes. The sensations for the patient are not very pleasant, but tolerable.
Fine needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid gland
The procedure is often abbreviated TAPB or TAB. During this procedure, material is taken for analysis to determine the cellular composition. Fine-needle biopsy of thyroid nodules is the most reliable and accurate method for determining cancer of this organ. It is necessary to hit the needle directly into the knot with an accuracy of a millimeter; it is difficult to do this blindly. The puncture is carried out while monitoring the process with an ultrasound machine.
Many people are concerned about how a thyroid puncture is done, because this is an invasive procedure; a thin needle penetrates into the organ. The main questions of patients are: how long does this intervention last, is it painful. No special preparation is required for the puncture. The sequence is as follows:
- The patient lies down on the couch and a pillow is placed under his head. The doctor palpates the neck and finds a node. The patient is asked to swallow saliva several times.
- The doctor inserts a thin, long needle into the thyroid nodule. The accuracy of the manipulation is ensured by an ultrasound machine. The needle is connected to an empty syringe. The contents of the node are absorbed into it.
- The needle is removed and the resulting material is applied to laboratory glass. Typically, 2-3 injections are given in several areas of the node. This is done for the objectivity of the results; the biological material must be diverse.
- After collecting the material, the puncture site is covered with a sterile sticker. After 10 minutes, the subject can go home. You can wash and be physically active after 2 hours.
Including preparation, the procedure will take approximately 20 minutes, the puncture itself lasts no more than five. No anesthesia is required. A cytologist will conduct a microscopic analysis of the material to study the cellular composition. Possible conclusions based on the research results:
- Colloidal node. This is a formation that does not have an oncological nature. Such a nodule does not degenerate into a tumor.
- "Hashimoto's thyroiditis" or autoimmune. There are inflammatory changes in the tissues of the thyroid gland, and the node is part of them. But it's not cancer.
- Follicular tumor. 85% of such formations are adenomas. In other cases, carcinomas are possible.
- Carcinoma: papillary, medullary, squamous cell, anaplastic. Lymphoma. Such conclusions mean that the node is a malignant tumor.
- The material is not informative. With this result, repeated sampling of the material is required.
Thyroid puncture is performed in specialized clinics. The cost of the procedure consists of such components as:
- Doctor visit;
- direct puncture;
- ultrasound control;
- analysis of results, cytological examination.
The cost differs from the clinic, the range is 2000 – 4500 rubles. The price is affected by:
- the “brand” of the clinic, its fame;
- doctor's qualifications;
- medical facility equipment.
What is a biopsy
A puncture biopsy of the thyroid gland is a method of collecting biological material and its histological and morphological examination. This procedure allows you to reliably diagnose the presence of malignant tumors.
Methods of examining the thyroid gland, such as visual examination and palpation, do not allow one to determine the nature of the nodule. Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) reveals unclear boundaries of the formation and its heterogeneous structure. But this does not give precise confidence that the detected lump is malignant. The doctor can only assume the development of cancer. To make a correct diagnosis, a biopsy of the thyroid nodule is required.
What is a biopsy and how is it taken? This procedure can be performed in several ways: open and puncture (fine-needle biopsy):
- When using an open technique, biological material is taken through a specially made incision. This method is invasive, so it is used infrequently, if there are contraindications to biopsy and there is no accurate result using the puncture method;
- fine-needle biopsy of the thyroid gland is performed under ultrasound control. This method of collecting material for research is the most accurate.
Based on the results of an open or puncture biopsy, the doctor plans further treatment measures and decides whether the patient requires surgical intervention or whether conservative treatment is sufficient. A correctly performed thyroid biopsy is a very important stage of the examination.
Patients who are prescribed a needle biopsy of the thyroid gland often jump to the conclusion that this procedure will necessarily be followed by surgery. This opinion is not always true. Previously, surgeons preferred active treatment tactics and many patients diagnosed with thyroid nodules were recommended to undergo surgery. It was the emergence of informative and accurate examination methods, such as fine-needle biopsy of the thyroid gland, that made it possible to reduce the number of operations and reduce the number of complications: metabolic disorders, problems with the vocal cords.
The role of biopsy in the range of diagnostic methods cannot be overestimated. Its main advantages:
- differs in information content;
- easy to implement;
- well tolerated by most patients;
- does not require the use of complex and expensive equipment.
Thanks to these features of the method, thyroid puncture is successfully performed in many endocrinological centers.
Does cancer develop after a node biopsy?
The answer is simple, like everything brilliant in this world. Thyroid cancer will not develop in a colloid node, because this can never happen. When the growth of a node begins, it is already growing, carrying oncology or not having it in its composition. While the node is small, even if there is cancer there, then basically it does not yet have the qualities of cancer that we imagine.
Therefore, according to WHO recommendations, not all nodes are subject to examination, but only those larger than 1 cm in diameter and smaller nodes with obvious signs of cancer according to ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
If a thyroid nodule has been punctured and a colloid goiter is found there, it means that cancer will not develop in it in the future, this is a fact.
"How so? - you say, - my friend (relative, friend) had a biopsy, and a few years later the node began to grow, and upon repeated puncture they discovered thyroid cancer."
In fact, such situations do occur, but it only gives the impression that cancer has developed after the puncture. Thyroid cancer has this peculiarity - it grows slowly and the likelihood that it will grow to a large size in a few years is extremely small. In fact, the cancer was there from the very beginning and it was simply not detected during the first procedure.
There are actually three reasons why this happens:
- Extremely small size of the cancer tumor at the time of puncture of the node. She was physically impossible to detect. In order to detect it, it would require not a puncture, but a histological examination, i.e., examination of the tissue of the node, which is only possible with surgical removal of the node itself. But going for surgery for every nodular goiter is the wrong tactic.
- Incorrect fine-needle biopsy technique. Punctures are often performed without the use of ultrasound diagnostics, which significantly reduces the effectiveness of the method.
- Skipping pathology by a cytologist in the laboratory. Indeed, it is possible to carry out the procedure perfectly, but due to the low qualifications of the cytologist, false negative results may be obtained. In this case, if you doubt the qualifications of the specialist, take the glass with the material to an independent laboratory.
It is encouraging that such false negative thyroid biopsies occur in 5% of cases.
With warmth and care, endocrinologist Dilyara Lebedeva
Interpretation of terms in biopsy results
The volume and quality of information in the conclusion depends on the technical equipment of the laboratory and the qualifications of the pathologist. Typically, a transcript of a thyroid biopsy includes two sections - a description of the biomaterial (what the doctor sees under a microscope) and conclusions indicating a specific diagnosis.
Below is a breakdown of the most commonly used terms that can be found in the conclusion:
- Adenoma is a benign tumor of the cells that line the follicles. It is distinguished by preserved histological architecture and the presence of a capsule.
- Amyloid is the deposition of abnormal protein due to chronic inflammation or tumor growth. A typical sign of medullary cancer.
- Giant cells are large inflammatory cells containing a large number of nuclei. Usually found in a chronic inflammatory process, including in response to foreign bodies (for example, during puncture) and in granulomatous diseases (tuberculosis, sarcoidosis).
- Hyperplasia is a synonym for the word “overgrowth”.
- Hurthle cell proliferation is an increase in the number of specific Hurthle cells often found in thyroid cancer.
- The dominant node is the largest nodular formation in goiter.
- Infiltration (literally “impregnation”) is the penetration of inflammatory and other cells into the thickness of the organ.
- The capsule of the node is dense tissue surrounding the nodular formation.
- Ashkenazi cells ( Hurthle ) – see “Hurthle cell proliferation”.
- Colloid edema is deposits of colloid between thyrocytes (normally it is located only inside the follicles).
- The colloidal type of structure is a characteristic of nodular goiter, when the nodes are represented predominantly by colloid.
- Colloid is a protein mass containing thyroglobulin, the main source of the hormones T3 and T4.
- The normoplastic type of structure is a nodular goiter, which under a microscope looks like a normal thyroid gland.
- The parenchymal type of structure is again a characteristic of a goiter, but in this case the nodes are represented mainly by cells, as well as small follicles, practically devoid of colloid.
- Proliferation is another synonym for the word "growth".
- Psammoma bodies are small layered structures containing calcium that can be associated with cancer.
- Sanderson's pads are areas of the follicular epithelium that protrude into the follicle in the form of a thickening. Proliferation option.
- Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid gland. Can be acute or chronic. Depending on the clinical and morphological picture, Hashimoto's, Riedel's and de Quervain's thyroiditis, as well as a number of other options, are distinguished.
- Thyrocytes are also follicular cells and epithelial cells. The main cells of the thyroid gland.
- Fibrosis is the proliferation of connective tissue.
- Hasimotization is an outdated term meaning the presence of lymphoid infiltrates in the thickness of the thyroid gland (a sign of chronic inflammation) without Hürthle cells.
A clear sign of cancer is atypical cells, which can be encrypted under words such as carcinoma, neoplasia, neoplastic cells, cells with atypical mitoses or bizarre.
Indirect signs of a malignant neoplasm are amyloid deposits, Hurthle cell proliferation, thickened capsules of nodes and psammoma bodies.
TAB results
The substance extracted from the thyroid nodule is sent for microscopic analysis to a cytologist. When assessing structural changes in tissue and cellular composition, the doctor uses color indicators. The reliability of the results is more than 96%. The results of the analysis of the contents of nodes are classified into four main groups:
- Colloidal node. A benign neoplasm that is not prone to transformation into cancer and does not require surgical intervention. With colloid nodes, it is necessary to balance the level of iodine in the body. This is easily achieved through diet correction and vitamin and mineral supplements.
- Inflammation of the thyroid gland of autoimmune, syphilitic or tuberculous etiology (thyroiditis). It is not related to malignant processes, but requires additional diagnostics for differentiation and special treatment.
- Compensated or decompensated follicular neoplasia. The disease can be malignant or benign. Determining the nature of the tumor is possible only through surgery, followed by studying the extracted biomaterial.
- Carcinoma or cancerous tumor. There are several types of thyroid cancer. Squamous cell and papillary carcinomas are considered less dangerous. The rapidly metastasizing and aggressive types include medullary and anaplastic. In any case, the cancer requires immediate surgical removal. With timely treatment and the absence of metastases in adjacent organs, the prognosis is 94–96% favorable.
The location of the node in the thyroid gland can be palpated in most cases.
Benign formations in the thyroid gland do not have a tendency to degenerate into cancer. Oncological nature is always inherent from the very beginning. If hyperplasia (a benign tumor) was determined, and a few years later the patient is diagnosed with cancer, it means that during the first study medical errors were made: the doctor passed the needle past the node and the puncture was taken from the gland tissue, the microscopy technology of the biopath was violated, when decoding the results the doctor interpreted them incorrectly or the tests were mixed up.
Nodes of benign origin do not pose a serious danger, but require constant monitoring by an endocrinologist. Neoplasms tend to grow, which can significantly complicate the patient’s life.
Additionally
The results (results) of the analysis can sometimes be uninformative; in percentage terms, this figure is about 20% of all studies. This situation occurs when there is insufficient amount of biomaterial and requires a repeat puncture biopsy. In case of a secondary uninformative study, to determine the nature of the nodules, surgery to open the thyroid gland is recommended.
Only in this way can the condition of the gland be assessed and material removed for laboratory analysis. By decision of the doctor, auxiliary tests for hormones (calcitonin, thyroglobulin, patharhormone) may be prescribed. The biomaterial is obtained by flushing from a manipulation needle. The patient receives a protocol with the results of FNA in 10-15 days.
The choice of treatment tactics (conservative or surgical), as well as the prescription of medications and special nutrition, is the prerogative of the endocrinologist. The thyroid gland is part of a complex endocrine system; in order to avoid serious consequences, it is forbidden to self-medicate.
Important advice from endocrine surgeons
“Determine calcitonin in the blood before performing TAB!”
Calcitonin is a tumor marker for the most malignant and dangerous tumor of the thyroid gland - medullary carcinoma. Even a slight increase in calcitonin is a reason for a biopsy of all detected nodes even less than 1 cm in size. In our institution, the doctor will certainly perform such a puncture if this indicator is elevated. It is necessary to donate blood ONLY in a specialized laboratory of the North-Western Endocrinology Center. No preparation is required for the test.
Thanks to this tactic, patients with medullary cancer ranging in size from 3 and 6 mm were operated on at our institution, and their lives were saved. In terms of the number of diagnosed medullary cancer in Eastern Europe and Russia, the North-Western Center for Endocrinology and Endocrine Surgery is the leader.
Early detection of this type of cancer and prompt surgical treatment is the only way to defeat the disease and give yourself a future life!