CT scan of the jaw is an x-ray method for studying the condition of the bone and soft tissue structures of the lower part of the facial bones. CT scan of the upper jaw or CT scan of the lower jaw can detect diseases of the joints, ligaments, maxillary sinuses, bone tissue and teeth. However, this examination should not be confused with a dental CT scan, which is a targeted method of scanning the dentition of the jaw area.
CT scan of the upper and lower jaw has a number of advantages in comparison with x-rays of the jaw area and MRI of the jaw joint:
- minimal time spent on CT scanning, in contrast to the longer MRI of the temporomandibular joint;
- higher image quality and detail compared to radiography;
- absence of pain and discomfort;
- issuing results on the same day.
The high quality of reproduced images is ensured by layer-by-layer scanning of the selected area in sections up to 1 mm thick.
The main disadvantage of computed tomography of the jaw is the presence of radiation exposure to the body. On average, it ranges from 1-3 mSv per scanning session.
Free diagnostic consultation
If in doubt, sign up for a free consultation. Or consult by phone
+7
All about diagnostics
Indications and contraindications
Computed tomography of the jaw is prescribed for the following indications:
- Injuries to the teeth, upper and lower jaw.
- Anomalies in the development of the jaw apparatus and teeth.
- Upcoming maxillofacial surgery.
A CT scan of the upper jaw is prescribed for:
- The presence of foreign bodies in the nose or ear canals.
- The presence of polyps, cysts and other similar pathologies in the paranasal sinuses.
- Suspicion of the development of a tumor in the maxillary sinuses, in the soft tissues of the jaws and in bone structures.
- Damage or congenital defects of the nasal septum.
A CT scan of the lower jaw is prescribed in the following cases:
- Congenital or acquired pathologies of the mandibular joint.
- Suspicions of the development of hidden caries.
- Control after root canal filling.
- Dental implantation.
- Jaw fracture.
- Disease of the salivary glands.
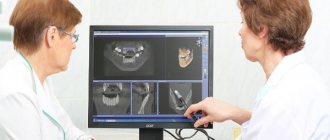
Child 16 years old. Secondary deforming arthrosis of the right TMJ. Deformation of the facial skeleton due to underdevelopment of part of the body, branches and processes of the lower jaw on the right. Multislice computed tomograms: a, b – 3D reconstructions
Contraindications for diagnostics:
- The patient's age is up to 14 years (relative contraindication; in emergency cases, a CT scan of the jaw is performed for younger children).
- Limit values for annual radiation exposure during radiography (indicated in a special table in the patient’s medical record).
- The presence of electronic devices and metal objects (splints, staples, etc.) in the patient’s body.
- Renal failure (relevant for CT with contrast).
- Allergic reactions to contrast agent.
- Pregnancy and lactation.
- Claustrophobia.
- Mental illnesses.
- The patient is overweight.
Features of the procedure
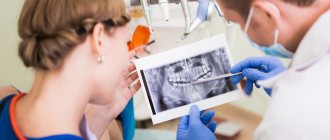
Computed tomography of the jaw is a procedure that allows you to conduct research without penetrating the organ. The device for carrying out the procedure is called a tomograph. Its work is based on X-ray radiation: rays are directed at the area under study at different angles, after which they fall on special high-sensitivity sensors. The radiologist receives information in the form of clear images, which are processed into three-dimensional pictures.
Dentists face difficulties in diagnosing diseases of the dental system due to its structure, and CT allows you to see all elements that are inaccessible to visual inspection, for example the TMJ (temporomandibular joint).
What does a CT scan of the upper and lower jaw show?
Computer examination of the jaw apparatus reveals:
- Quality of dental canal filling. The number of dental canals in a particular tooth.
- Oncological diseases: tumor foci, metastases.
- Osteomyelitis, deep caries, pulpitis.
- Abnormal development of the jaw area.
- Anomalies of the dentition.
- Pathological gum pockets and their depth.
Multislice computed tomograms: a-e – 3D reconstructions; e – MPR in oblique-sagittal projections
CT scan of the upper jaw and maxillary sinuses shows:
- Pathological changes in the maxillary sinuses.
- Perforation and/or curvature of the nasal septum.
- Pathology in the development of the alveolar processes of the jaws.
- Pathologies of the inner and middle ear, as well as anomalies of the external auditory canal.
A CT scan of the jaw for dental implantation determines:
- Condition of the jaw bone.
- The presence of dystrophy of the jaw bones and the degree of bone destruction.
- The thickness of the jaw bone (if implantation is planned in the lower jaw).
Contraindications to CT scan of the jaw
There are a number of contraindications for which the procedure is not recommended.
These include:
- weight more than 150 kg or girth more than 150 cm (the device is designed for a load of up to 150 kg);
- pregnancy (the risk of developing defects in the fetus increases);
- lactation period (during the procedure, rays can directly affect the composition of a nursing woman’s milk);
- severe mental illness (during the procedure the person must be at rest);
- the presence of metal objects in the area of interest, as they can reduce the information content of the results;
- children under 5 years old;
Using Contrast
A contrast agent is a special pharmacological preparation based on iodine radionuclides. Contrast is used to study tumor lesions in more detail at an early stage of development. An iodide drug administered intravenously to a patient is distributed throughout the body by the bloodstream. Areas affected by cancer cells intensively accumulate radionuclides, which, when X-ray waves pass through this area, make the boundaries of the pathological area clearer.
Dentistry uses a contrast marker to determine the degree of destruction of the bone structures of the jaws. Contrast is not used to examine teeth. The upper jaw is examined with contrast if there is a suspicion of a tumor in the nasal sinuses or in the ear area.
Preparatory stage
CT scanning of the upper and lower jaw according to the basic, naive protocol does not require special preparation. If a CT scan of the jaw with contrast is prescribed, the diagnosis is usually carried out with a 2-hour break in food. If the patient suffers from renal failure, tests to determine the level of creatinine in the blood are preliminarily prescribed before contrast tomography. This way, the doctor can assess the possible risks of developing nephropathy after administration of a contrast agent. Before entering the CT room, it is better to change into comfortable clothes and remove all jewelry.
Advantages of this method
Computer examination of the jaw apparatus is more accurate and reliable compared to other types of diagnostics, although it is prescribed much less frequently than radiography. The advantages of computer scanning include the following capabilities:
- Get a two-dimensional image of the jaw, and if necessary, a 3D tomography of the teeth is prescribed, which allows you to examine the problem area in detail from all sides.
- The image obtained from the tomograph consists of several layer-by-layer images, which enable the doctor to assess the degree of tissue damage.
- The tomograph is equipped with an automatic processing function for the resulting images, which allows you to obtain clear, easily readable images.
- The radiation from the tomograph is quite high, but the capabilities of the device allow a complete examination of the problem area in one session. The x-ray machine will need much more time for this, therefore, the radiation exposure during x-rays will be no less than with CT, with more modest results.
What is the essence of the procedure
CT is based on the action of x-rays. For this reason, during the examination, the body is exposed to radiation. The resulting image directly depends on the ability of a particular tissue to transmit x-rays. If necessary, a contrast agent is used for diagnosis. The device resembles a donut in appearance. There is a moving couch inside. Inside the device there is built-in lighting, ventilation and two-way communication.
It is important to remain still during a CT scan. Otherwise, the pictures will be blurry and ineffective. In such a situation, repeated diagnostics will be required.
CT scan of the jaw is done using a special machine
The apparatus for examining the jaw has a slightly different design. Diagnostics is carried out in a vertical position. The face is fixed on a special stand.
During tomography, the body receives a minimal level of radiation exposure, so the diagnosis is safe.
How is a jaw examination performed?
The patient is placed on the moving table of the tomograph. If a CT scan with contrast is prescribed, the doctor injects a contrast agent into the patient’s vein before starting the diagnostic procedure. Then the table slides inside the device, and the diagnostician sets the desired operating mode on the tomograph.
The tomograph scanner begins to rotate around the table, taking layer-by-layer images at high frequency. Data from the scanner is sent to a computer, where it is processed automatically. Diagnostics lasts from a few seconds to 3 minutes. The duration depends on the task at hand. On average, a computed tomography scan of one jaw along with the issuance of a report takes about 30 minutes.
Contraindications
A CT scan of the jaw can be performed on an adult patient if there is a referral from a doctor or on personal initiative. For children, due to the presence of radiation exposure to the body, computed tomography is performed strictly on the direction of a doctor and exclusively for strict medical reasons.
When scheduling a CT scan, patients should consider the following contraindications:
- the patient is pregnant at any stage;
- The age of the subject is up to 3 years.
Is contrast used?
Contrast is often required to determine the exact location of the tumor. An iodine-containing substance is introduced into the body. This tool will significantly improve visualization.
CT is used to diagnose a jaw fracture
A procedure with contrast is not required if:
- fractures;
- osteomyelitis;
- congenital anomalies.
When using contrast, you need to take some tests in advance. 4 hours before the diagnosis you need to stop eating. It is also necessary to follow the same recommendations that are needed for a standard CT scan.
Diagnostics takes 30-40 minutes. This is due to the fact that after administering the substance, you will need to wait a few minutes for the product to spread throughout the body and reach the desired area.
Preparing for the examination
No preparatory measures are required for CT scanning. There is no need to change your diet or medications. The usual way of life also remains. But if it is necessary to administer a contrast agent, the doctor may ask you to refuse food the day before. However, such manipulations are rarely carried out.
It is recommended to take the results of the previous examination with you if you undergo one. This will allow the doctor to more accurately adjust the equipment. Clothing must be chosen without metal objects (buttons, rivet snaps) so that the information is not distorted. All metal jewelry, glasses, hearing aids, and removable dentures are removed.
The doctor must be warned about all-metal and non-removable metal-ceramic crowns if they are present in the oral cavity. Then the device settings are changed to reduce the likelihood of distortion of the result.
Is preparation necessary?
No specialized training is needed. This diagnostic method does not require dietary changes or therapeutic fasting. The most important thing to do is to remove any metal elements and jewelry.
All metal bracelets must be removed before examination.
Metallized elements make diagnostics difficult. The pictures will be overexposed and the device may malfunction. Such an examination will be ineffective. You also need to first lay out any electronic devices and removable medical structures.
The patient must take all medical documentation with him. This will allow the doctor to review your medical history and make sure there are no contraindications. In this case, the examination will be completely safe.
Hearing aids and dentures are removed in advance. You should come to the examination in comfortable and loose clothing. There should be no foreign metal elements on it.
Why is the CT method better than others in diagnosing these diseases?
Benefits of CT
- Dentists or maxillofacial specialists can obtain complete information about the shape of the jaw, its size, assess the density of bone tissue, the location of the nerve canals, and the condition of the paranasal sinuses.
- Unlike 2D X-rays, which overlay images of tissue, 3D jaw CT provides distortion-free images and precise measurements down to fractions of a millimeter of jaw and tooth structures.
- An accurate three-dimensional image and analysis of the area where the implant is planned to be installed allows you to select the most optimal positioning of the implant, especially if there are areas with rare bone tissue
What is the result of CT scan
CT allows you to see the following deviations from the norm:
- tumors and bleeding;
- foreign bodies likely present;
The image can be used to assess the unevenness of the dentition
- bone damage;
- nerve damage;
- pinched nerves;
- uneven teeth;
- signs of inflammation in soft tissues;
- damage to dental structures;
- fluid accumulation;
- neoplasms.
Using CT, you can simulate the results of implantation. Diagnostics is effective for both minor and significant pathological processes.