PCR analysis for chlamydia is one of the most effective methods for identifying pathogenic microorganisms Chlamidya pecorum, Chlamydia psittaci in the human body and making a correct diagnosis. With the help of an external examination and clarification of complaints from the patient, it is impossible to differentiate sexually transmitted infections, and only laboratory tests help determine the type of pathogen. Some types of chlamydia diagnostics may produce a false negative result. The polymer chain reaction technique is highly reliable and allows doctors to diagnose even a latent form of the disease.
What is it about
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) was invented in the 1970s. Improvements in technology have increased the accuracy of the results. The method is highly sensitive, so it will show the DNA of the pathogen even with small sample volumes. For this reason, PCR for chlamydia is preferable to antibodies. When conducting a study on chlamydia, conditions are artificially created in which the infection multiplies, growing to volumes that allow visual detection. The technique does not lose effectiveness even when the pathogen grows slowly.
Chlamydia trachomatis, which causes chlamydia, is common, but the course of the disease does not affect the quality of life for a long time, and changes are not noticed. Those few signs that appear during sluggish processes are ignored by patients or confused with other disorders. PCR for chlamydia determines exactly whether infection has occurred and how large the extent of the damage is.
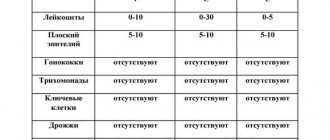
The material for the laboratory assistant is a scraping taken from the urethra and cervix. Hemotest and other research options are accurate in 20% of cases. The correct result is obtained only using PCR.
What is chlamydia and why should it be diagnosed?
Chlamydia is a special type of microorganisms that occupy an intermediate position between bacteria and viruses. They belong to intracellular parasites that multiply in the cells of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system. By destroying infected cells, chlamydia becomes a source of constant inflammation, causing a decrease in immunity and the development of various diseases of the genitourinary tract.
In men, chlamydia is most often asymptomatic, worsening the general well-being of the patient and increasing the risk of developing other diseases of the genital organs. But in women, chlamydia infection can lead to infertility, recurrent miscarriage, or infection of the fetus during pregnancy.
Chlamydia: features
PCR as a method for diagnosing chlamydial infection has been common since the 90s. The specificity of the technology is in identifying the pathogen living inside another cell. But antibodies, widely used to detect a number of diseases, are not always able to detect the presence of intracellular infection.
Without treatment, chlamydia provokes secondary diseases of the female reproductive system, the inability to bear fruit and conceive a child.
Chlamydia are parasites that depend on the respiration of host cells. Provoke development:
- genital infections;
- psittacosis;
- diseases of the respiratory system.
Chlamydia is common in humans and animals. For example, cats suffer from eyes, gastrointestinal tract and lungs. Diagnosis is made using the same polymerase reaction.
Among humans, the most common form is caused by genital pathogens. Chlamydia provokes disorders of the urinary system, leads to the development of inflammatory processes in the pelvic cavity and the formation of adhesions.
Typical complications in women:
- endocervicitis;
- urethritis;
- cervical erosion;
- arthritis;
- netting process in the pelvic cavity;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- frequent miscarriages;
- infertility.
In men they observe:
- cystitis;
- proctitis;
- prostatitis.
What does infection lead to?
Chlamydia trachomatis are parasites located intracellularly in the epithelium of the genitourinary tract. Such parasitism leads to prolonged infection, since the disease does not manifest clinical symptoms.
Antibodies to chlamydia appear in the body. This leads to damage not only to the urogenital tract, but also to the joints, heart and internal organs. Infection occurs instantly through unprotected sexual contact if one of the partners is infected. Next, the parasites penetrate the epithelium and multiply intensively.
An acute infection occurs, which is often accompanied by painful symptoms:
- burning sensation when urinating
- pain in the lower abdomen
- decreased libido
- unpleasant discharge from the genital tract
- discomfort during sexual intercourse
- general intoxication (rare)
But not only the genitourinary tract is affected. Problems with the organ of vision and joints often occur.
With long-term persistence of chlamydia, contractures of large joints may develop, which leads to a sharp decrease in the quality of life. In addition, chlamydia is often associated with infertility and impotence. Therefore, identifying microorganisms is an important goal for maintaining health for many years.
Diagnostics
A chlamydia smear using the PCR method is an accurate way to determine whether the pathogen is present in the body. The technology is microscopic and involves obtaining biological material and further reproduction in laboratory conditions.
The polymerase chain reaction is carried out when receiving:
- urethral smear;
- prostate secretion;
- cervical smear;
- vaginal tissue.
At home, the polymerase reaction is carried out using a rapid test. You can buy one at the pharmacy, the biological material is urine. The reliability of this option is less than a laboratory test for chlamydia, but if the result is positive, there is no doubt - it’s time to go to the doctor.
An effective diagnostic method to detect infection
Determination of pathogens of infectious or parasitic diseases by blood is considered the most accurate and safe for patients of different ages, gender and position. The PCR method helps confirm the disease as soon as possible in cases of development:
- HIV (human immunodeficiency virus);
- hepatitis class B and C;
- parasitic diseases (ureaplasmosis and trichomoniasis);
- fungal diseases such as candidiasis;
- mononucleosis;
- detect papilloma virus;
- tuberculosis.
The polymerase reaction method is used in modern medicine as one of the most effective ways to diagnose chlamydia.
Before analysis
Preparation for submitting biomaterial is the key to the accuracy of the result. Remember, although the method is effective, failure to follow the recommendations leads to incorrect results.
Preparatory measures:
- 1-3 days before the delivery of biomaterials, sexual intercourse is excluded;
- the last urination occurs 3-4 hours before sampling;
- testing for chlamydia is taken 3-4 days after the cessation of menstrual bleeding;
- douching is unacceptable 24 hours before visiting a doctor;
- exclusion of medications (primarily antibiotics), except those prescribed by a doctor, 7 days before the delivery of biomaterial.
Rules for preparing for the procedure
To obtain the most reliable result, the patient must take a responsible approach to preparing for the study.
For taking a smear from women, the following rules apply:
- last urination 3 hours before taking material
- ideal period – from the 5th day of menstruation
- If there is copious bloody discharge, it is better to postpone the examination
- hygiene measures at least 2 hours before taking a smear
- douching is prohibited
- It is advisable to abstain from drinking alcohol 48 hours in advance, unless otherwise advised by your doctor.
How to get tested for men?
For men, the rules differ due to the physiological characteristics of the structure of the genital organs.
Last urination at least 2 hours before the test.
It is not advisable to drink alcohol 72 hours before the procedure. After any instrumental examinations, such as cystoscopy, at least 5 days must pass.
A swab from the throat is usually taken in the morning on an empty stomach; it is not advisable to eat or drink water, since chlamydia can be washed away. Analysis of synovial fluid does not require special preparation. Since the material is obtained directly in the doctor’s office.
Blood is not usually used for PCR. constitute cases when the generalization and spread of microorganisms through the blood or lymph is suspected.
The hemotest only confirms the presence of antibodies, while PCR involves determining the chlamydia DNA itself. The ELISA method is used to detect antibodies, but it is less informative.
Features of the polymerase chain reaction
PCR analysis for chlamydia in the laboratory is carried out on various biomaterials. If previously they used tissues of the genital organs and urinary system, now doctors give an accurate diagnosis using saliva, seminal fluid, and urine. The sampling is carried out with a universal probe using gynecological speculum.
Having taken an analysis for chlamydia using the PCR method, the working instrument is placed in a protected container, filled with transport liquid, and hermetically sealed. Why is this necessary? The reaction is highly sensitive, specific and accurate, so the penetration of foreign bacteria, infections and viruses is unacceptable. When examining the obtained materials in the laboratory, part of the DNA characteristic of chlamydia is isolated. The result is prepared in 6-8 hours. Accuracy and speed are guaranteed by automation of the laboratory process.
Where and how to get tested for PCR for chlamydia
Biological material is collected in laboratories or clinics and then sent for research.
Today, some paid diagnostic institutions offer the service of collecting samples at home. PCR analysis does not require a large volume of material, and this is also one of the advantages of the method. Various types of liquid media are used for testing.
In men, in order to detect chlamydia, urethral secretions, semen, and urine are collected. In women, scrapings from the urinary or cervical canal, urine and synovial fluid are taken.
To carry out the analysis, laboratory technicians only need 15 ml of venous blood. Modern centers use a vacuum system that prevents the penetration of bacteria into samples, which increases the effectiveness of the PCR technique.
Pregnancy
Is it possible to undergo PCR testing for chlamydia while pregnant? How to donate biomaterials in an “interesting situation”? The technology is the same as that used for non-pregnant women. Doctors recommend undergoing testing at the stage of planning a child, but there are situations when the need arises after conception.
During pregnancy, a chlamydia test allows you to find out whether there is a high risk of infection of mother and child at the same time. There is an opinion that the collection of biomaterial harms the fetus. This is a stereotype that has no basis. A smear is obtained from the cervix. In this case, the gynecologist’s working instrument (probe, speculum) does not enter the uterus and does not harm the amniotic sac. The process is safe and painless.
PCR for chlamydia during pregnancy
In order to detect the presence of chlamydia in the amniotic fluid of pregnant women, a small volume of amniotic fluid is collected. This method carries certain risks for the fetus, so it is carried out for serious reasons. The doctor makes a puncture in the peritoneal area to remove material. The procedure is carried out under the mandatory supervision of ultrasound equipment.
All pregnant women at the antenatal clinic are prescribed tests to detect chlamydia. For these purposes, a hemotest is performed using the PCR method. Such diagnosis is of great importance during this period, since the presence of chlamydia in a woman’s body can affect the course of pregnancy and the intrauterine development of the child.
Blood is drawn from a vein. In some cases, the doctor may additionally prescribe an enzyme immunoassay. This is necessary to clarify the stage of the infectious disease. A treatment regimen for chlamydia in pregnant women is drawn up by an obstetrician-gynecologist, taking into account the form of chlamydia.
results
Chlamydia PCR gives one of two results:
- Negative when the material does not contain infectious traces.
- Positive. Possible even in cases where antibodies in other studies have shown the absence of the pathogen. This is due to the sensitivity of the technology. This result indicates the presence of infection in the studied cells. The result is qualitative; no conclusions can be drawn about the quantity.
If the result is positive, the doctor determines how to clarify the diagnosis and what treatment is required.
Difficulty in making a diagnosis
Even if a patient exhibits several symptoms, a specialist will not be able to make a final diagnosis without additional research.
Laboratory methods for diagnosing chlamydia are the most effective. The diagnosis and doctor’s prescription will depend on their results.
What tests will be prescribed for a man if he is suspected of having chlamydia depends on the attending physician.
IMPORTANT! Even with the use of the latest equipment, chlamydia is easier to detect in its acute form. Additional tests may be needed to identify the chronic form of the disease.
Carrying out PCR
Material for the laboratory is obtained with a plastic probe or gynecological brush. The resulting substances are collected in a conical sealed one and a half milliliter test tube, and the unoccupied space is filled with a pinkish medium.
The tubes are disposable, sterile. Materials for testing for chlamydia are obtained from the urethra and cervix. It is unacceptable for the smear to contain blood, so the scraping is taken carefully.
The study of biomaterial is carried out by amplification. The process gives an accurate result in 6-8 hours. In this case, the DNA sequence is copied by DNA polymerase. At each cycle, a primer is introduced. The change of cycles is ensured by temperature conditions.
High sensitivity is the advantage of PCR for chlamydia in comparison with ELISA and immunofluorescence testing.
The reaction occurs in three stages:
- raising the temperature to 94°C turns the DNA molecule into a single-stranded one (denaturation);
- short synthetic fragments bind to specified sections of protein chains (annealing);
- New DNA is synthesized when heated to 70-72°C (polymerization).
Accuracy is guaranteed by eliminating cross-reactions.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
This type of analysis of samples to determine the presence of HUM genes (chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma) is one of the most accurate and fastest.
Its advantages include:
- The test method allows achieving high sensitivity of the analysis (at least 95%).
- It can be used at all stages and forms of the disease: latent (hidden, asymptomatic), chronic, acute period of the disease.
- Allows you to determine whether the patient is a carrier of the disease.
- A huge range of possibilities for collecting material for research.
- High speed of obtaining data and results after analysis. Usually, the result is given within one to two days, but if there is an urgent need, the test result can be obtained on the day the sample is taken.
- This type of analysis is “direct”. It detects exactly the disease factor that is the cause.
- Availability of analysis. If the patient has suspicions or symptoms, it can be performed on their own initiative, without waiting for a doctor’s referral.
- Allows you to detect and identify not only the disease itself, but also concomitant or diseases with similar symptoms. Almost all urogenital infections and diseases of HUM have such properties.
Despite many positive aspects, this test has a number of disadvantages:
- Must be carried out in laboratories with a high degree of sanitary standards. These are strictly required to avoid false positive results due to sample contamination. The chance of getting an erroneous result is about 5%.
- The result is difficult to interpret. To accurately diagnose and process data, you must have a medical education. The study should be evaluated by a qualified specialist in immunology and infectious diseases.
- High cost of the test. It is determined by the need to install expensive equipment and hire highly qualified specialists to study, conduct and verify the result.
Summing up
Despite the prevalence and danger of chlamydia, PCR detects the disease in active and latent forms. It is recommended to do a study at the first symptoms of infection and after treatment of the disease.
Do not hesitate to go to the doctor if you suspect sexually transmitted infections! It is important for a woman, especially an expectant mother, to monitor her health and contact the clinic in a timely manner. Remember, advanced chlamydia leads to serious organ damage and infertility. By taking a PCR test, a woman not only finds out the presence of chlamydia in the body, but also receives accurate data about other pathogens, including hidden ones.
Read
Also:
- Female sex hormones: interpretation of tests, norm and deviations
- Progesterone: on what day of the cycle should I take hormones?
- Why you can’t donate blood or be a donor during your period
- How is treatment and bacterial culture carried out: ureaplasmosis and mycoplasmosis in women
What is PCR analysis and in what cases is it prescribed?
The question of what kind of examination this is and what preparation is needed interests many patients who have been prescribed a PCR test. The essence of the method is to produce copies and multiply fragments of the DNA chain of a pathogenic pathogen. To speed up this process, laboratories use a group of enzymes that activate the construction of new genetic chains. As a result, the material increases many times over, making it easier to detect bacterial DNA. A laboratory worker conducts a study under a microscope, comparing the samples obtained with a standard produced at a research institute.
Diagnosis using the PCR method is carried out for such conditions as:
- pregnancy;
- detection of chlamydia in a partner;
- infertility of unknown etiology;
- presence of symptoms of sexually transmitted infection;
- suspected HIV, hepatitis, tuberculosis.
Currently, a pregnant woman can be tested for chlamydia. Many obstetricians and gynecologists strongly recommend getting tested, since the baby may become infected at birth.
How can chlamydia be detected?
To detect chlamydia, several types of tests are performed, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages
Attention! The most accurate is PCR, which determines the presence of the disease using RNA antibodies. This method can detect even the initial stage of chlamydia
This method will require a smear or blood.
Diagnostic methods
- ELISA detects the presence of the disease even in the early stages; even after 10 days the presence of the disease can be detected. This method also works well in determining the chronic stage of chlamydia.
- RIF gives any results only if chlamydia is present and is in an acute stage. All other stages are not detected using this method, especially this makes it difficult to determine early chlamydia. In addition, it will require a lot of material.
- Cultural culture determines with a 90% probability not only the fact of the presence of the disease, but also the type of bacterium itself, which allows you to select the most appropriate antibacterial therapy. The only disadvantage of this method is the time - it will take about a week.
Symptoms
The vast majority of men become infected after sexual intercourse. In a significant proportion of patients, chlamydia occurs without symptoms. For the rest of the sick, the first symptoms may appear only after fourteen days from the moment of infection.
An advanced form of the disease can provoke the development of serious diseases, so it is important to consult a specialist in time.
The presence of infection can be determined by the following symptoms:
- constant body temperature within 37.2 - 37.5 degrees, accompanied by increased fatigue and general weakness of the body;
- the presence of glassy, watery, mucopurulent discharge from the urethra. Such discharge is more noticeable after sleep;
- feeling of itching, burning during urination;
- spotting during ejaculation, at the end of the urination process;
- swelling, redness of the external opening of the urethra;
- pain in the groin, scrotum, lower back;
- burning sensation, discomfort felt in the area of the head of the penis;
- In rare cases, a symptom of chlamydia is pain during bowel movements.
Chlamydia is difficult to diagnose. It is almost impossible to determine the disease on your own.
Rapid tests sold in pharmacies have extremely low accuracy. They may not detect the disease, despite the presence of chlamydia in the body.
If the symptoms described above occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Chlamydia in men: consequences of the disease
Chlamydia is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the modern world. Despite this, it can have very serious consequences for the patient. In some cases, everything ends in infertility or disability.
Chlamydia is difficult to cure . Even in patients who have completed the full course of treatment, the disease may reappear after some time. Both women and children, as well as men, are susceptible to the disease.
ATTENTION! If not treated promptly, chlamydia can cause a number of specific diseases.
One of the consequences of chlamydia is epididymitis. Chlamydia is the main causative agent of this disease. Often in patients with epididymitis, urethritis also appears.
In this case, the man’s epididymis may swell, which causes pain. Typically, pain is felt on only one side of the scrotum.
Homosexuals infected with chlamydia may suffer from proctitis, which is accompanied by pain in the rectum.
With chlamydia, men may develop Reiter's syndrome. Seventy percent of men with Reiter's disease were found to have chlamydia.
Brief information about the pathogen
Chlamydia are pathogenic microorganisms of extremely small sizes (about 300 nanometers), and they exist mainly inside the cells of the human body. In the systematic series, they occupy a position between bacteria and viruses.
These microorganisms exist in two morphological forms: elementary bodies - a form necessary for survival outside cells, and reticular bodies - an intracellular form of life.
In the cell of its host, chlamydia develops and exists for about three days, after which the cell is completely destroyed, and the microorganisms spread through the intercellular substance to other areas of the affected tissue. It is very rarely possible to take a fragment of material for analysis at the moment pathogens emerge from cells, and therefore the usual microscopic technique for studying scrapings and smears is low-informative.
Statistics have very impressive figures: during sexual intercourse without the use of barrier methods of contraception, infection with chlamydia occurs in ninety cases out of a hundred; about half of sexually mature men and women in the modern world are infected with this pathogen. At the same time, the asymptomatic course of the disease and the intracellular existence of the pathogen cause infertility, impaired fetal development, miscarriage and cause some autoimmune somatic diseases - for example, arthritis.