Vaginal microflora is a complex biosystem that includes a whole complex of microorganisms. To assess its condition, calculations are carried out in both quantitative and qualitative terms.
The bacterial composition can change as the female body matures and is greatly influenced by sex hormones.
All flora can be divided into several types:
- Obligate flora, without which the existence of normobiocenosis is impossible. This includes, first of all, lactobacilli or Dederlein bacilli. They represent the majority of the vaginal landscape, both in percentage and quality. To maintain the desired pH, it is required that lactobacilli comprise at least 98% of all bacteria. It is due to their vital activity that an acidic environment of the mucous membrane is created. Bifidobacteria can also be included in this group; their number is usually insignificant.
- Opportunistic flora includes a large group of microorganisms, which consists of cocci, as well as other bacteria. These are mainly streptococci, staphylococci, enterobacteria, etc. In small quantities they do not manifest clinically, but with an increase in content they manifest themselves in most cases as a clinical inflammatory process.
- Absolute pathogens include, first of all, pathogens of sexually transmitted infections. If it gets on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, it leads to the development of a pathological process and subsequently leads to the development of serious complications. This group should primarily include gonococci and trichomonas; these are the main microorganisms detected in a smear and requiring treatment.
- A small group of flora representatives are mushrooms. They are represented by the genus Candida and are found in small quantities in the vagina. But with an increase in quantity they lead to the development of an inflammatory process.
What smears can be taken?
Diseases of the female reproductive system are dealt with by a specialized branch of medicine - gynecology.
There are many reasons for patients to apply: undergoing a medical examination for employment, pregnancy, painful or unpleasant cramping sensations in the lower abdomen, itching or burning, thrush, heavy menstruation or discharge of unknown origin.
A general smear or microscopy is performed during a preventive examination or during pregnancy planning. The result is the study of the cervical and urethral canal, vagina, and in virgins - the rectum.
Papanicolaou cytology analysis makes it possible to timely detect the papilloma virus, precancerous conditions of the epithelium, and cervix. It is recommended that all females with hereditary cancer diseases and those over 21 years of age undergo a Pap test.
A bacteriological research method, bacterial culture in women, is recommended if there is a suspicion of an inflammatory process, a disorder of the microflora, which was caused by opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms.
PCR is carried out in the form of an analysis for infections transmitted mainly through sexual contact. Provides complete information about the bacterial composition of the internal microflora.
The effectiveness and reliability of the method is 98%.
When results may deviate from the norm
After receiving the results of the study, women do not always see satisfactory or ideal indicators. This raises the question of why the data is not normal.
Gynecologists identify a number of reasons:
- The presence of inflammation of a specific and nonspecific nature.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Puberty period.
- The onset of menopause.
- Carrying a child.
Deciphering a smear analysis in gynecology allows you to assess the condition of the organs of the genitourinary system. The study is applicable to identify some inflammatory, infectious, and bacterial diseases. Thanks to this, it is possible to start treatment in a timely manner and prevent the pathology from becoming chronic.
Author: Chernyshova Victoria
Article design: Mila Friedan
Preparing for a smear test
Before prescribing an examination, the gynecologist or laboratory employee is obliged to warn the patient about how to properly take a smear for flora, what can and cannot be done before the procedure.
Preparation for a microscopic examination involves avoiding strong antibiotics 2 weeks before the expected analysis and visiting the bathroom the day before. You should try not to go to the toilet 2 hours before the test.
It is better to do diagnostics not before, but during menstruation and in the first two days after.
To increase the sensitivity of the test, microflora culture is carried out in the absence of treatment with antibacterial drugs and douching. Be sure to follow a special diet 2-3 days before the bacteriological analysis: limit foods that provoke fermentation or intestinal upset.
Refrain from sexual intercourse with your partner and do not wash yourself 24 hours before data collection.
3-5 days before the prescribed PCR diagnosis, taking any antibacterial and contraceptive drugs is prohibited. It is necessary to avoid sexual intercourse for 36 hours. It is advisable not to shower the day before the PCR and on the eve of the test. The material is taken during menstruation and for 1-2 days after its end.
Decoding the results obtained
Microscopy of glasses with biomaterial allows you to obtain important data about a woman’s health.
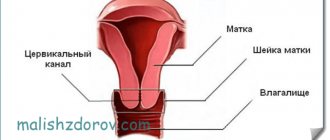
To indicate the localization of material collection, the letters of the Latin alphabet are used: V, C and U. The letter V stands for the vagina, C for the cervical canal, U for the urethra. To understand the interpretation of the data obtained during the study, you should understand what microorganisms can be identified when analyzing a smear for flora.
How to take a smear from women
The technique for collecting material is usually carried out in the morning in the gynecology department or directly in the laboratory itself. Taking vaginal discharge and areas for examination is prescribed only for women who are sexually active. In girls, it is taken more carefully from the lateral vault of the vagina to prevent damage to the hymen, and from the intestines, secretion.
All manipulations take place on a gynecological chair. At this time, the specialist introduces a special mirror depending on the age and physiological characteristics of the patient. If the organs are not yet formed, size XS is used, girls will need a mirror S. After labor, examination instruments with a diameter of 25-30 mm, sizes M, L are used.
The material is collected with a spatula or spatula, brush, applied to a glass slide or placed in a test tube for further transfer of the results to the laboratory.
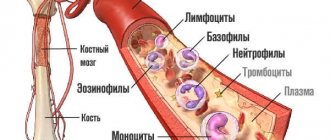
What do leukocytes indicate during microscopy of a gynecological smear?
White blood cells are a sign of inflammation. There are generally accepted standards for their quantity. However, they are very conditional. Because the number of white blood cells in the vagina varies from woman to woman.
Differences are due to individual characteristics.
In addition, in the same woman, the number of leukocytes can normally change based on:
- days of the cycle (during ovulation there are more of them)
- sexual activity
- contraceptive methods
- hygiene, etc.
When deciphering the results of a smear, the doctor tries to assess the ratio of leukocytes and vaginal epithelial cells. Normally, their number is the same.
Therefore, even if there are more leukocytes than the quantitative norm (more than 10 in the field of view), it is likely that there is no inflammation if:
- no complaints or objective symptoms
- There are fewer leukocytes than epithelial cells
The assessment is carried out only in those areas of the preparation where leukocytes are distributed evenly between epithelial cells. If there are 2-3 times more leukocytes, this is a sign of inflammation.
Microflora smear: interpretation
It is impossible to independently draw a conclusion about how good or bad a smear is without the appropriate knowledge. Using special notations, it is very easy to decipher a microscopic examination of a smear. Depending on the location of the biological material taken, they are distinguished: vagina - “V”, cervix - “C” and urethra - “U”.
Gram-positive rods, “Gr.+” and the absence of coccal flora. The result is “++++”. It is observed quite rarely, most often it is a consequence of intensive antibacterial therapy. Norm: “++”, “+++” rods, the number of cocci does not exceed “++”.
Gram-negative bacteria gonococci - “Gn”, trichomonas vaginalis - “Trich”, yeast of the genus “Candida”. Corresponds to diseases such as gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and candidiasis.
The presence of key cells and E. coli, if they are listed in the microflora, indicates that the patient has bacterial vaginosis.
What does a urogenital smear show?
The purpose of taking an analysis is primarily to diagnose infectious diseases.
In women, the state of the vaginal microflora is also assessed.
Using a smear from the urogenital tract, you can identify:
- signs of urethritis, vaginitis, colpitis;
- pathogens of sexually transmitted infections;
- causative agents of nonspecific inflammation of the urogenital tract;
- signs of vaginal dysbiosis in women.
This research method is not the most informative and accurate.
It is largely subjective, since the results depend on the human factor.
However, microscopic examination of a urogenital smear remains one of the most commonly used methods in venereology, gynecology and urology.
Because this way of identifying infections:
- simple;
- inexpensive;
- fast.
Microscopic examination is an indicative examination.
The doctor uses its results to plan additional diagnostic measures.
Flora smear: normal in women
All patients, without exception, from the age of 14 until the onset of menopause, correspond to the same standard, obtained as a result of laboratory microscopic examination.
Leukocytes. Providing protection for the body from penetrating viruses, bacteria and infections, they can be in the field of view, but should not exceed the indicator in the vagina - 10, in the cervix - 30, urethra - 5.
Epithelium. A moderate amount of epithelial tissue is normal. A high number indicates possible inflammation, while a too low number indicates insufficient production of the hormone estrogen.
Slime. A small amount or no quantity is allowed. The maximum daily rate of secretion from the glands of the cervical canal is 5 ml.
Gram-positive rods, “Gr.+”. Lactobacilli and Doderlein bacilli must be present in large quantities. They are responsible for the body's immune response to foreign bodies. They should not be in the cervix and urethra.
“Gr.-”, gram-negative, anaerobic rods are not detected.
Gonococci with the symbol “gn”, Trichomonas, chlamydia, key and atypical cells, fungi, yeast, Candida are absent. If they are detected in the results, the patient is prescribed additional testing for gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, bacterial vaginosis, and thrush.
Why are leukocytes in the smear elevated?
Flora smear
The main reason for detecting a large number of leukocytes in a smear is considered to be the presence of infections. Bad (pathogenic) bacteria can enter the female body through sexual intercourse, unprotected sexual intercourse, as well as through household contact with a carrier of infections (STIs - sexually transmitted infections). Also, the cause of elevated white blood cells may be the presence of herpes viruses, papilloma, cytomegalovirus, HIV. A large number of leukocytes in a smear does not always mean the presence of a sexually transmitted infection; this can be a consequence of trauma to the genital organs during sexual intercourse, after childbirth, in chronic and acute forms of kidney disease, in diabetes mellitus, as well as in tumors. In any case, if elevated leukocytes are detected in the smear, further examination by the attending physician is required.
- Infections that cause an increase in white blood cells on a smear:
- Gonococci - lead to the disease gonorrhea
- Spirochete pallidum (syphilis)
- Klebsiella (granuloma inguinale)
- Chlamydia (chlamydia)
- Gardnerella (garderellosis or bacterial vaginosis)
- Koch bacillus (tuberculosis)
- Fungi Candida albicans (thrush or candidiasis)
- Protozoal infection (trichomoniasis)
- Mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas (mycoplasmosis and ureaplasmosis)
- Reasons for increased leukocytes in a smear:
- Colpitis (inflammation in the vagina)
- Cervinitis (inflammation of the cervix)
- Endometritis (inflamed uterine mucosa)
- Urethritis (inflammation of the urethra)
- Cystitis (kidney disease)
- Andexitis (inflamed appendages)
We should also talk about such a concept as vaginal dysbiosis (gardnerellosis). Normally, in a woman’s vagina, 98% of all bacteria are beneficial lactobacilli. And only 5% are other microorganisms, which are called opportunistic. The immune system and beneficial bacteria control and inhibit the growth of opportunistic bacteria. However, against the background of ongoing diseases or inflammation, this ratio of beneficial and harmful bacteria is disrupted, the number of harmful bacteria increases and dysbiosis occurs.
- Causes of vaginal dysbiosis:
- Hormonal disorders, hormone intake
- Taking antibiotics
- Kidney diseases
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Decreased immunity
- Use of spermicidal drugs
- Taking cytostatics
- Poor intimate hygiene
- Allergic reactions to intimate hygiene products
- Stress
- Anal, oral and vaginal sex in one sexual act
When these causes are eliminated, vaginal dysbiosis goes away quite quickly, and the vaginal flora returns to normal.
Smear purity:
| Index | Description |
| 1 - complete absence of problems (rare) | Acidic environment No pathogenic microbes No blood cells Lactobacilli and Dederline bacilli present |
| 2 - moderate deviations, in most% of women | Acidic environment cocci - units leukocytes - up to 10 epithelium - up to 5 |
| 3 - inflammation, discharge, itching | Alkaline environment Coccus bacteria and fungi present Lactobacilli are reduced Leukocytes are moderately increased |
| 4 - infectious disease | Alkaline environment Abundant number of pathogenic bacteria Lactobacilli are absent Leukocytes are greatly exceeded |
Smear for purity level
To avoid complications during pregnancy, pregnant women are advised to determine the degree of purity of the gynecological smear. Normally, in a healthy woman, 95-98% of the vaginal microflora consists of Bacillus vaginalis or Lactobacillus bacillus Doderlein. They produce lactic acid, which helps maintain acidity levels.
Pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms are not able to survive in such conditions. But under the influence of various factors, such as sexual activity, menopause, the menstrual cycle and decreased immunity, microflora indicators can change.
- Level 1 vaginal cleanliness is normally pH 3.8-4.5. The environment is acidic. Leukocytes and epithelial cells - no more than 10.
- 2nd degree. Slightly acidic environment: pH=4.5-5. There is a slight increase in gram-positive cocci and Candida fungi.
- 3rd degree. Pathogenic microorganisms are activated, mucus appears, and epithelial indicators exceed the norm. Neutral acidity level, pH=5-7. There are over 10 leukocytes. Mucus, key cells are present, gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms multiply in favorable microflora conditions.
- At the last, 4th degree , purity is low. pH values reach 7.5. Doderlein's rods are either completely absent or found in single quantities. The vagina is filled with pathogens.
Norm of analysis indicators by woman’s age
Gynecological analysis of a smear of the obtained biological material is carried out as prescribed by a doctor in childhood and adolescence. The norms for a healthy child are shown in the table.
| Indicators assessed | 1-5 years | 6-10 years | 11-15 years | 16-17 years old | Teenagers who are sexually active |
| Leukocytes | 0-2 | 3-5 | 5-7 | To 10 | To 10 |
| Slime | 1-2 | 1-2 | 1-2 | 1-2 | 1-2 |
| Epithelium | 1-3 | 4-6 | 5-6 | To 10 | To 10 |
| Flora | Coccus + | Coccus + | Mixed | Rod | Rod |
Norm for smear analysis in gynecology (read the explanation below)
The indicated parameters correspond to the number of visible cells of certain microorganisms that fall into the field of view when studying the material under a microscope. In women of reproductive age and older age, the norms depend on where the mucus was obtained from.
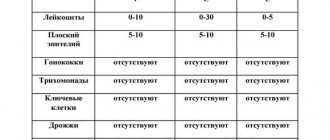
| Indicators | Vagina (V) | Cervical canal (C) | Urethra (U) |
| Leukocytes | 0-10 | 0-30 | 0-5 |
| Flat epithelium | 5-10 | 5-10 | 5-10 |
| Gonococci | None | None | None |
| Trichomonas | None | None | None |
| Key cells | None | None | None |
| Yeast | None | None | None |
| Microflora | Multiple Dederlein rods (gram-positive) | Absent | Absent |
| Slime | Moderate amount | Moderate amount |
In patients of reproductive and childhood age, not only the quantitative content of certain cells differs, but also the list of parameters by which the condition of the organs of the genitourinary system is assessed.
Bacteriological research
The variety of composition, in addition to Lactobacillus bacillus Doderlein, which is an integral part of the vaginal microflora of the woman being examined, does not begin to be studied immediately. Sowing the collected biological material onto a specially created favorable environment for its subsequent growth, development and reproduction takes time.
Bacteriological culture of flora can be assessed through a microscope, provided that the number of representatives of microorganisms increases.
- 0 class. Observed during treatment with antibiotics. The pathogen is absent.
- I class. The number of bacteria does not increase or increases moderately.
- II class. Mixed nature of microflora. Up to 10 colonies of bacteria Gardnerella vaginalis or Mobiluncus, the causative agents of gardnerellosis, are detected.
- III class. There are about 100 colonies. The microflora is predominantly inhabited by Gardnerella and Mobiluncus. Symptoms of bacterial vaginosis appear.
- IV class. Lactobacilli are absent, immunity is weakened. Diagnosis of acquired infectious disease - aerobic vaginitis.
Cytological examination
The probability of detecting areas of altered epithelium, papilloma virus and oncological tumors is quite high after 30 years of age and the beginning of sexual activity.
Therefore, gynecologists recommend taking a smear for cytology or a PAP test. The starting material for cytological examination is: the cervical canal, the vaginal part of the cervix.
The correct interpretation of the PAP test depends on the presence or absence of cancerous, atypical cells.
- NILM. The clinical picture is without features, CBO. Leukocytes and bacteria are released in small quantities. Primary candidiasis or bacterial vaginosis is possible. The epithelial layer is normal.
- ASC-US. Atypical areas of unknown origin were found in epithelial tissue. A repeat analysis is carried out after 6 months to look for chlamydia, dysplasia, and human papillomavirus.
- LSIL. To confirm a precancerous condition caused by atypical cells, a biopsy and colposcopy are prescribed. Weak signs of changes in the epithelium.
- ASC-H. Pronounced damage to the squamous epithelium. 1% of patients are diagnosed with the initial stage of cervical cancer, the remaining 98-99% have grade 2-3 dysplasia.
- HSIL. Concomitant symptoms preceding cancer of the squamous epithelium and cervix were identified in more than 7% of the women examined. 2% have cancer.
- AGC. Atypical condition of the glandular epithelium. Diagnosis: cervical or endometrial cancer, advanced form of dysplasia.
- AIS. Squamous cell carcinoma, cervical cancer.
Microscopy results in men
Male indicators are analyzed identically (by the number of cells in the field of view). Pathogenic microorganisms (gonococci, trichomonas), as well as opportunistic Candida fungi and Gardnerella bacteria should not be present.
Normal values
| Index | Leukocytes | Slime | Epithelium | Coccus bacteria |
| Norm | 0-5 | Moderately | 5-8 | Single inclusions |
The reason for the increase in leukocytes is the inflammatory process in the urogenital tract. If a large number of epithelial cells are detected, it presumably indicates the formation of stones in the bladder (urinary ducts). The abundance of mucus is caused by inflammation of the prostate gland or urethra. The presence of sperm is a sign of dysfunction of the seminal ducts or prostate.
PCR analysis
The molecular biological method of PCR diagnostics is distinguished by its high sensitivity and reliability of the data obtained. By creating earlier samples of the isolated and copied DNA section, comparisons are made with the resulting biological material.
Testing for infections using PCR makes it possible to quickly find the causative agent of a disease in the female genital organs by obtaining a positive or negative result.
The polymerase chain reaction facilitates the determination of chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, thrush, trichomoniasis, HPV, HIV, and the search for the causes of difficult pregnancy and hormonal disorders.
The disadvantages of PCR are cases of false data due to incorrect tests and possible mutation of the pathogen's DNA.