Ekaterina Smolnikova
Practicing endocrinologist (10 years of experience). He has extensive experience working in private and public clinics in Russia.
Ask a Question
Last updated - June 9, 2020 at 08:15
For diabetic patients, not only insulin levels are important, but also C-peptide levels. C-peptides, what are they and what is the normal level in the blood? The literal meaning of this expression is “connecting peptide.” Based on the level of this element, one can judge the reasons for the decrease in blood sugar and evaluate how hormone therapy affects insulin synthesis.
How is the analysis carried out?
The peculiarities of taking a C-peptide test for a patient differ little from a conventional biochemical blood test.
To test for peptides, blood is taken from a vein, and since food directly affects insulin production, blood is donated on an empty stomach. Eating should be 6-8 hours before the test.
Prohibited before the study:
- drink alcoholic beverages;
- smoke;
- take hormonal medications (if they are not vital for health);
- eat chocolate or other types of sweets.
Important! If it is impossible to refuse medications that provide important body functions on the day of the test, you should warn the laboratory technician about the presence of foreign substances in the blood. . Sometimes a fasting test does not provide accurate data, so the doctor prescribes stimulating measures for more accurate test results
Such measures include:
Sometimes a fasting test does not provide accurate data, so the doctor prescribes stimulating measures for more accurate test results. Such measures include:
- a regular breakfast containing light carbohydrates (white bread, bun, pie), which increases the production of insulin and, accordingly, C-peptides;
- glucagon injection is an insulin antagonist (the procedure is contraindicated in people with hypertension) and increases blood glucose levels.
The patient receives results no earlier than 3 hours after blood collection. This period may increase because the C-peptide test is not performed in all clinical laboratories and may need to be transported to a more qualified research center. The standard waiting time is 1-3 days from the date of analysis.
On the day of the test, you should refrain from using all types of medications. If refusal poses a threat to life or health, you must consult the doctor who prescribed these medications.
Normal content
The peptide norm ranges from 0.26 to 0.63 mol/l, although other units of measurement are used in the analysis. The concentration of the substance is calculated in nanograms per milliliter of blood, in this case the norm is 0.9-7.1 ng/ml. Such a significant gap in the normal indicator scale is due to the fact that people have different indicators:
- body weight;
- age;
- chronic diseases;
- various types of infections (ARVI, Influenza);
- hormone levels.
The peptide content is the same in men and women. The fasting norm is 0.78-1.89 ng/ml.
Increased level
The level is elevated if the value is more than 0.63 mol/l (more than 7.1 ng/ml). Increased levels of peptides are observed when:
- diabetes type 1 and 2;
- adrenal dysfunction;
- endocrine system disorders;
- excess weight (obesity);
- hormonal imbalance (in women due to taking contraceptives);
- a surge of hormones (typical of the male sex during puberty);
- insulinoma (malignant formation);
- pancreatic diseases;
- liver cirrhosis.
Important! Elevated levels of c-peptides should not be ignored, as they may indicate life-threatening diseases.
Reduced level
The level of C-peptides is reduced if the value is less than 0.26 mol/l (less than 0.9 ng/ml).
A reduced peptide content indicates complications of type 1 diabetes, such as:
- diabetic retinopathy (damage to the blood vessels of the retina);
- dysfunction of the nerve endings and blood vessels of the legs (risk of developing gangrene and amputation of the lower extremities);
- pathology of the kidneys and liver (nephropathy, hepatitis);
- diabetic dermopathy (red spots or papules with a diameter of 3-7 cm on the legs).
We also recommend reading the article: "".
Indications for testing
Prescribed in the following cases:
- for diagnosing diabetes;
- to monitor and adjust drug treatment for diabetes;
- for various liver diseases;
- to monitor the hormonal state of the body after pancreatic resection;
- for diabetes in overweight adolescents;
- for infertility caused by polycystic ovaries;
- for the diagnosis of hypoglycemia;
- for diagnosing endocrine tumors of the pancreas;
- to monitor the condition of the fetus and pregnant women with diabetes.
A test for c-peptide is usually prescribed when elevated sugar and glycosylated hemoglobin have already been detected several times. With the help of this protein, the type of diabetes is determined as quickly and accurately as possible, the intake of sugar-lowering medications is adjusted, and a hormone-producing tumor is diagnosed.
What to do if c-peptide deviates from the norm
If a deviation in the level of c-peptide from the norm is recorded for the first time, additional studies should be carried out to accurately determine the cause. Perhaps the amount of peptide is affected by taking hormonal drugs, and after they are discontinued everything will return to normal. Also, the decrease in the amount of peptide caused by a stressful situation is eliminated after rest.
If this factor is excluded, then additional examination is prescribed. Using ultrasound and MRI, it is possible to detect a pancreatic tumor, metastases, and liver condition. If liver cirrhosis or kidney pathology is suspected, a biochemical blood test, kidney and liver tests are additionally performed.
If the cause of the increase is the use of medications to lower sugar levels, the dosage should be adjusted or the medication discontinued. If the pancreatic tumor recurs, the doctor urgently decides on repeat surgery and chemotherapy.
Causes of reduced cepeptide levels
A decrease in the level of c-peptide in the blood can occur for various reasons. If the indicators are significantly lower than normal, this may indicate the following pathologies:
Article on the topic:
What do elevated platelets in women indicate? Causes, symptoms and treatment
- Artificial hypoglycemia caused by the administration of a large dose of insulin.
- Hypoglycemia resulting from drinking large amounts of alcohol.
- Presence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (type 1).
- Condition after resection of the pancreas.
- Severe emotional stress.
Purpose of analysis
The C peptide indicator, the norm and deviation of which are determined only after blood tests, is one of the methods of differential diagnosis. Laboratory testing of c-peptide and insulin is prescribed to patients by an endocrinologist to exclude or confirm non-insulin-dependent or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Insulin in the human body is of paramount importance, but despite this, an analysis for the content of active insulin is not always carried out due to low efficiency. After insulin is produced, it penetrates into the liver structures, where it is first absorbed. After this, insulin penetrates into the general bloodstream.
Typical blood sugar measurement
Often tests, due to the complex mechanisms of insulin transport throughout the body, show low levels of the hormone. Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to almost reliably determine the amount of insulin in the blood. Analysis is prescribed for the following conditions:
- liver diseases of any origin;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- suspicion of developing insulinoma;
- determining the effectiveness of insulin therapy;
- obesity, sudden weight changes;
- feeling of constant thirst;
- an increase in the volume of daily diuresis;
- somatotropin (pituitary adenoma).
Important! C-peptide does not reflect the amount of glucose that comes into the body from food, unlike an insulin test, so excess sugar will not be reflected in the tests. Analysis for c-peptide content is an accessible way to assess the production of your own insulin
Hormone analysis: features
The importance of the hormone in the human body is difficult to underestimate. It is believed that it is a central substance that takes an active part in carbohydrate and energy metabolism.
However, testing for this hormone is rarely recommended in medical practice, and this circumstance is based on many reasons. First, when insulin is produced, the hormone first goes to the liver, where a little is absorbed by the internal organ.
And only after such a chain does it enter the human circulatory system, as a result of which it cannot fully reflect its specific level of synthesis by the pancreas. Secondly, insulin is the body’s “response” to the consumption of glucose-containing foods, so it can increase after eating.
Based on such information, we can say that C-peptide indicators are as reliable and correct as possible. Since it does not pass through the liver, it is in no way related to the level of sugar in the blood that comes with food.
There are a number of situations when it is necessary to analyze this indicator:
- To determine whether there are metastases after surgical removal of a pancreatic tumor.
- Determination of the level of beta cell activity in order to select adequate therapy based on the results of the study.
- To determine the mediated insulin level against the background of inactivating antibodies, which change the values downward. It is also recommended for severe pathologies of liver function.
New information: Which blood sugar test is more accurate: from a finger or from a vein?
The level of C-peptide is of no small importance, so in the vast majority of cases it is recommended for the following pathologies:
- For type 1 diabetes, when protein is below normal.
- For type 2 diabetes mellitus, when the levels are higher than normal.
- Gestational form of diabetes in women during pregnancy. In this option, the doctor tries to clarify the likely risk for the baby’s intrauterine development.
- The patient's condition after surgery in the pancreas.
- Autoimmune diseases that impair the functionality of the pancreas.
- Benign pituitary gland formations.
- Infertility, polycystic ovary syndrome.
The level of C-peptide allows you to determine the likely factors of hypoglycemia. The hormone will be high if the patient takes pills to lower blood sugar, which are synthetic.
The level of the hormone may be reduced after drinking large quantities of alcohol, as well as against the background of constant use of insulin-containing drugs in the treatment of diabetes.
Prospects for the use of protein in the treatment of diabetes
Some medical data suggest that the parallel administration of the peptide and insulin to patients with insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes avoids some complications of diabetes, in particular, such as diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy and angiopathy.
It has been proven that as long as a person has at least a small amount of this protein in the blood, this reduces the risk of transition from non-insulin-dependent diabetes to insulin-dependent. It is quite possible that in the future the patient will be given c-peptide injections to help get rid of the dangerous disease.
Many medical studies clearly state that a low-carbohydrate diet with a carbohydrate content not exceeding 2.5 bread units significantly reduces the body's need for insulin in insulin-dependent diabetes. This suggests that even type 1 diabetes can be kept under control and only maintenance doses of insulin administered.
So, c-peptide is an important protein that indicates the condition of the pancreas and the risk of developing diabetes complications.
For what conditions and diseases is analysis prescribed?
Diseases for which analysis is prescribed:
- diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2;
- various liver diseases;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- pancreatic tumors;
- pancreatic surgery;
- Cushing's syndrome;
- control of hormone treatment for type 2 diabetes.
Insulin is important for humans. This is the main hormone involved in carbohydrate metabolism and energy production. The test that determines the level of insulin in the blood is not always accurate.
The reasons are as follows:
- Insulin is initially produced in the pancreas. When a person’s sugar rises, the hormone goes first to the liver. There, some of it settles, and the other part performs its function and reduces sugar. Therefore, when determining the level of insulin, this level will always be less than what the pancreas synthesized.
- Since the main release of insulin occurs after eating carbohydrates, its level increases after eating.
- Incorrect data is obtained if the patient has diabetes mellitus and is treated with recombinant insulin.
In turn, C-peptide does not settle anywhere and enters directly into the blood, so this study will show real numbers and the exact amount of the hormone secreted by the pancreas. In addition, the compound is not associated with glucose-containing foods, meaning its levels do not increase after eating.
C-peptide and diabetes mellitus
Until recently, doctors believed that cepeptide was not needed for the body to function. This substance was used only to determine the type of diabetes. It has now been established that injections of c-peptide in combination with insulin can prevent the occurrence of diabetic complications, such as vascular hardening, damage to the retina, and impaired liver and kidney function. However, many doctors consider this theory unproven, that is, there is no absolute data on the relationship between complications and cepeptide levels.
Protein levels do not always decrease in diabetics. If the pancreas is still functioning, then the amount of peptide will not deviate greatly from the norm. The peptide in diabetic patients is always measured in relation to glucose levels. The following conditions are possible:
- High c-peptide and normal glucose levels . This indicates that the patient has prediabetes or has developed insulin resistance. In this situation, insulin injections are not yet indicated, since the body is able to cope on its own. The patient is prescribed a low carbohydrate diet.
- Increased cepeptide and sugar. This means that the patient has advanced type 2 diabetes. Strict adherence to a low-carbohydrate diet is required to delay or minimize the use of insulin injections.
- Low c-peptide and high sugar. What does it mean? This can happen with insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes or advanced form of type 2 diabetes. Only insulin injections will save the situation.
C-peptide for type 2 diabetes
In type 2 diabetes, C-peptide may be increased, normal, or decreased. The following explains what to do in all these cases. Regardless of your test results, learn the step-by-step treatment plan for type 2 diabetes. Use it to control your disease.
If C-peptide is elevated, you can try to keep your blood sugar within normal range with a low-carb diet and physical activity, without insulin injections. About
How is the analysis carried out?
To obtain correct results for the level of C-peptide in the blood, the test can be performed in two ways. At the first stage of the examination, a “hunger” test is prescribed. However, this type of analysis does not always provide a reliable picture.
In some diagnosed patients, fasting C-peptide levels may not be impaired. In this case, to obtain an objective picture, it is necessary to do a stimulation test.
This type of research can be carried out using three methods:
- The patient is asked to drink a certain amount of glucose, after which blood samples are taken two hours later.
- Before collecting the material, the patient is given an injection of an insulin antagonist - glucagon.
Advice! This stimulation option has many contraindications, so it is used infrequently.
- The material is collected two hours after the patient eats a certain amount of carbohydrate food.
Advice! To stimulate insulin production, you need to get 2-3XE carbohydrates. This amount is contained in a breakfast consisting of 100 grams of porridge, a slice of bread and a glass of tea with the addition of two pieces of sugar.
How to prepare?
In order to properly take a blood test for C-peptides, you need to prepare for it. Necessary:
- stop taking medications that may affect the test results, having previously discussed this issue with your doctor;
- stop consuming fatty foods and alcoholic beverages at least 24 hours before sampling;
- If a “fasting” test is prescribed, then you should avoid eating any food 8 hours before sampling.
How is the procedure done?
To obtain material for research, it is necessary to donate blood from a vein, that is, to perform a venipuncture. The blood is placed in a labeled tube - empty or filled with gel.
After the material is collected, the patient can lead a normal lifestyle. If a hematoma appears in the area of venipuncture, absorbable compresses are prescribed.
What influences the result?
The study shows the functioning of the pancreas, so the main rule is to maintain a diet.
Basic recommendations for patients donating blood for C-peptide:
- 8 hour fasting before donating blood;
- you can drink non-carbonated water;
- you should not drink alcohol a few days before the test;
- reduce physical and emotional stress;
- do not smoke 3 hours before the test.
The norm for men and women is the same and ranges from 0.9 to 7.1 mcg/l. The results do not depend on age and gender. It should be remembered that norm results may differ in different laboratories, so reference values should be taken into account. These values are the statistical average for this laboratory and are established after examining healthy people.
Video lecture on the causes of diabetes:
Blood test norm for diabetes mellitus
The norm of c peptide is up to 5.7%. The norm in women during pregnancy is usually exceeded. If the indicator goes off scale, then this indicates that the endocrine system is disrupted and suitable therapy is required in order to maintain the health of the pregnant woman and baby.
If the sugar intensity is higher than expected, there is a danger of excessive intrauterine growth of the fetus and excess body weight. This condition leads to premature birth and injury to the child or injury to the mother during childbirth.
This is why it is so important to control your sugar levels. Only then will the safety of mother and baby be guaranteed
A biochemical blood test, c-peptide, the decoding of which shows what standard the child has. The child’s standard is determined individually by the doctor. Although there are standards:
- from 0 to 2 years – not higher than 4.4 mmol/l;
- from 2 to 6 years – not higher than 5 mmol/l;
- school age – not higher than 5.5 mmol/l;
- adults – up to 5.83 mmol/l;
- elderly – up to 6.38 mmol/l.
Blood is taken from a child in the same way as from older people. It is taken into account that in children, when analyzed, the substance is slightly lower than normal, since the hormone is eliminated from beta cells into the blood system after eating food. The norm of c-peptide in a healthy population varies from 260 to 1730 pmol per 1 liter. blood serum.
Those who took tests on an empty stomach or after lunch, the results are different. Sweet foods increase the level of peptide in the blood. If the test was taken early in the morning, then its value changes within 1.89 ng/ml.
Normal sugar levels in adults are 3.2-5.5 mmol/l. This parameter is standard when taking fasting blood from a finger stick. After donating blood from an artery, the sugar level rises to 6.2 mmol/l. What are the dangers of an increased parameter? If the parameter increases to 7.0 mmol, then this threatens pre-diabetes. This is a situation in which monosaccharides are not absorbed. On an empty stomach, the body knows how to control sugar levels; after eating carbohydrate foods, the parameter of insulin produced does not coincide with the standard.
There is an express test that allows you to independently determine your blood sugar level. A special measuring device will accurately and quickly perform analysis under any conditions. This option is convenient for those who suffer from diabetes. If the drug is stored incorrectly, there may be errors in the readings.
For a more accurate diagnosis, you can use the services of the Invitro laboratory. Such clinics are equipped with modern and high-quality equipment from well-known manufacturers. There you can get tested during your visit, or call a special service at home.
While there are many such clinics, each clinic uses different research methods and also uses different units of measurement. It is advisable to use the services of the same clinic for accurate results.
Invitro Laboratory provides free SMS messages about the readiness of tests. This is an advantage of this laboratory. It is worth considering the standards that are indicated on the form, since the standards in each laboratory are slightly different.
Different parameters of the norm of the substance c-peptide
For men and women, there is no special distinction in terms of c-peptide levels. If the body works normally, then the level of peptide C should correspond to the values in the table, which are taken as a basis by laboratories:
| Units | Indicators of normal c-peptide in women and men |
| micronanograms per liter (mg/l) | from 0.5 to 1.98 |
| nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml) | from 1.1 to 4.4 |
| pmol per liter (pm/l) | from 298 to 1324 |
| micromoles per liter (mmol/l) | from 0.26 to 0.63 |
The table shows different units of measurement for the c-peptide norm, because different laboratories for research analyzes use their labeling as a basis.
There is no uniform norm for c-peptide in children, because when taking a blood test on an empty stomach, the results may give underestimated values due to the fact that c-peptide enters the blood only in the presence of glucose . And on an empty stomach, neither c-peptide nor the hormone insulin can enter the blood. For children, only the doctor decides which c-peptide indicators should be considered normal and what should be considered a deviation from the norm.
The patient can independently understand whether c-peptide is normal after receiving the test results. Each laboratory writes down the normal limits on a form in specific units of measurement. If the result obtained is lower or higher than the c-peptide norm, then you should look for the cause of the imbalance and take measures to normalize it, if possible.
How to get tested
Donating blood for C-peptide involves following a number of preparatory procedures. They are necessary to ensure the most accurate result.
So, the rules for preparing for analysis imply:
- Delivery of material on an empty stomach. This means that the last meal should be at least 8 hours before visiting the laboratory, but drinking clean water will even be beneficial;
- It is better to eliminate alcohol and smoking even earlier;
- Also, the day before, you should not subject your body to heavy physical activity;
- Similarly, psychological stress also falls under the previous paragraph. Everyone knows that severe stress or shock affects general hormonal levels and other indicators of the body;
- It is advisable not to use any medications on the eve of donating blood. If they cannot be excluded, then the patient must notify his attending physician about which medications he took;
- Another rule applies to children under 5 years of age. Before analysis, it is recommended to give them 100-150 ml of drinking water.
It happens that a patient is prescribed a C-peptide test not on an empty stomach, but, on the contrary, with the existing load of glucose on the metabolism. But this procedure is rarely performed and mainly only for pregnant women. It involves taking a glucose solution before donating blood.
Reference values
Important! Standards may vary depending on the reagents and equipment used in each particular laboratory.
That is why, when interpreting the results, it is necessary to use the standards adopted in the laboratory where the analysis was carried out. You also need to pay attention to the units of measurement. Commonly accepted units of measurement: pmol per 1 liter of biomaterial.
Alternative units: ng per 1 ml with the following conversion: pmol/l = ng/ml * 333.33.
Norms of C-peptide in the blood:
- 260 - 1730 pmol/l.
- 1.1 - 4.4 ng/ml.
- 0.9 - 1.2 µg/l.
This range is based solely on the test performed on an empty stomach.
Factors influencing the result
- Violation of the rules for preparing for analysis;
- Eating before the test;
- Male pattern obesity;
- Taking medications: hormones (progesterone, estrogen, oral contraceptives);
- ethinyl-estradiol;
- danazol;
- glucocorticoids;
- chloroquine;
- sulfonylurea, etc.
Important! The interpretation of the results is always carried out comprehensively. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on only one analysis.
Characteristics of the substance and its effect on the human body
In a healthy body, a lot of chemical reactions occur every second, which allow all systems to work harmoniously. Each cell is a link in the system. Normally, the cell is constantly renewed and this requires a special resource - protein. The lower the protein level, the slower the body works.
C-peptide is a substance that is part of the chain of events for the synthesis of natural insulin, which is produced by the pancreas in special cells designated as beta cells. Translated from the English abbreviation “connecting peptide,” the substance is called “connecting or binding peptide” because it connects the other molecules of the substance proinsulin.
What is the role of c-peptide and why is it so important whether its content is normal or whether an imbalance has arisen:
- In the pancreas, insulin is not stored in its pure form. The hormone is sealed in a parent base called preproinsulin, which contains c-peptide along with other types of peptides (A, L, B).
- Under the influence of special substances, the L group peptide is separated from preproinsulin and a base called proinsulin remains. But this substance is not yet related to the hormone that controls blood glucose levels .
- Normally, when a signal is received that blood sugar levels are elevated, a new chemical reaction is triggered, in which C-peptide is separated from the chemical chain of proinsulin . Two substances are formed: insulin, consisting of peptides A, B and group C peptide.
- Through special channels, both substances (C peptide and insulin) enter the blood and move along an individual route. Insulin enters the liver and undergoes the first stage of transformation. Part of the hormone is accumulated by the liver, while the other enters the systemic circulation and is transformed into cells that cannot function normally without insulin. Normally, the role of insulin is to convert sugar into glucose and transport it inside cells to give the cells nutrition and energy to the body.
- C-peptide moves freely along the vascular bed with the blood flow. It has already fulfilled its function and can be disposed of from the system. Normally, the entire process takes no more than 20 minutes and is utilized through the kidneys. Apart from the synthesis of insulin, c-peptide has no other functions if the beta cells of the pancreas are in normal condition.
When C-peptide from the proinsulin chain, an equal amount of the protein substance C-peptide and the hormone insulin are formed. But, being in the blood, these substances have different rates of transformation, that is, decay.
Laboratory studies have proven that under normal conditions, c-peptide is detected in human blood within 20 minutes from the moment it enters the bloodstream, and the hormone insulin reaches zero within 4 minutes.
During normal functioning of the body, the content of c-peptide in the venous blood flow is stable. It cannot be affected by insulin introduced into the body from the outside, nor by antibodies that reduce cell resistance to the hormone, nor by autoimmune cells that distort the normal functioning of the pancreas.
Based on this fact, doctors assess the condition of people with diabetes or who have a predisposition to it. In addition, other pathologies in the pancreas, liver or kidneys are detected based on the c-peptide norm or level imbalance.
An analysis for c-peptide and its norm is relevant when diagnosing diabetes mellitus in preschool children and adolescents, because this pathology occurs quite often due to childhood and adolescent obesity.
Features of the analysis
The analysis is carried out:
To indirectly determine the amount of insulin with inactivating antibodies, which change the indicators, making them less. It is also used for severe liver dysfunction.
To determine the type of diabetes mellitus and the characteristics of pancreatic beta cells to choose a treatment strategy.
To identify tumor metastases of the pancreas after its surgical removal.
A blood test is prescribed for the following diseases:
Type 1 diabetes mellitus, in which protein levels are low;
Type 2 diabetes mellitus, in which the indicators are higher than normal;
The state of postoperative elimination of cancer in the pancreas;
Infertility and its cause – polycystic ovary syndrome;
Gestational diabetes mellitus (the potential risk for the child is specified);
Various disorders due to deformation of the pancreas;
Somatotropinoma;
Cushing's syndrome.
In addition, this analysis allows us to identify the cause of the hypoglycemic state in diabetes. This indicator increases with insulinoma and the use of synthetic hypoglycemic drugs.
The level is reduced, as a rule, after consuming large amounts of alcohol or against the background of the administration of exogenous insulin on an ongoing basis.
A study is prescribed if a person complains:
for constant thirst,
increase in the volume of urine excreted,
weight gain.
If a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus has already been made, then the analysis is carried out to assess the quality of treatment. Incorrectly selected treatment is fraught with complications: most often in this case, people complain of blurred vision and decreased sensitivity in the legs. In addition, there may be signs of kidney malfunction and arterial hypertension.
Venous blood is taken for analysis. The patient must not eat food for eight hours before the test, but can drink water.
It is advisable not to smoke for at least 3 hours before the procedure and not to undergo heavy physical activity or be nervous. The result of the analysis can be known after 3 hours.
Results of modern research
Modern science does not stand still, and the results of recent studies indicate that C-peptides are not only a by-product in the production of insulin. That is, this substance is not biologically useless and plays a certain role, especially in people suffering from various types of diabetes.
Some scientists are talking about the fact that the simultaneous administration of insulin and peptide for type II diabetes significantly reduces the risks of possible complications, including:
- renal dysfunction;
- damage to the nerves and/or blood vessels of the extremities.
A relatively small amount of the peptide in the patient’s blood can reduce the risk of dependence on constant doses of insulin. Who knows, perhaps in the foreseeable future there will be special peptide drugs that help fight and overcome diabetes. To date, all possible risks and side effects of such therapy have not yet been taken into account, but various academic studies are successfully continuing.
A low-carbohydrate diet, in which the consumption rate does not exceed 2.5 bread units, is considered an excellent way out of the situation. Such a constant diet helps reduce dependence on the regular use of sugar-lowering medications, as well as insulin.
In addition, we should not forget about general hygiene measures, which include regular walks in the fresh air, unconditional abandonment of all bad habits, avoidance of stress, regular visits to sanatoriums that specialize in the treatment and prevention of endocrine diseases.
Useful video
Watch the video about diabetes:
Autoimmune diabetes is characterized by the fact that it has type 1 and type 2 symptoms. It is also called latent, or one and a half. The reasons may be heredity. Often detected in adults after 30 years of age. Treatment of diabetes begins with pills and diet, but often switches to insulin injections.
You can figure out what types of diabetes there are and determine their differences by what a person takes—whether he is insulin dependent or on pills. Which type is more dangerous?
Diabetes may be suspected if there are accompanying symptoms - thirst, excessive urine output. Suspicion of diabetes mellitus in a child can only arise during a coma. General examinations and blood tests will help you decide what to do. But in any case, you will need a diet.
If type 1 diabetes is established, treatment will consist of administering insulin of varying durations. However, today there is a new direction in the treatment of diabetes - improved pumps, patches, sprays and others.
Often, patients with problems of the hypothalamus, adrenal glands, and thyroid gland become obese due to hormonal imbalance. It is also provoked by stress, surgery, and radiation therapy. Obesity also occurs after hormonal pills. Depending on the cause, therapy is selected - drugs for the underlying disease, pills and diet for obesity.
source
General information
One of the components of the secretion of the endocrine segment of the pancreas, which determines the production of insulin, is C-peptide. Analysis of its concentration in blood serum serves as the main criterion for determining the presence/absence of diabetes mellitus (DM), as well as pancreatic cancer.
C-peptide is a fragment that is formed when proinsulin is broken down into insulin. That is, the concentration of C-peptide in the blood completely reflects the process of insulin production in the body. But at the same time, the C-peptide remains biologically inactive and does not perform any regulation on its own.
After production, insulin is released into the portal blood flow (portal circulation) and enters the liver. This stage is called the “first pass effect”. And only after this the hormone enters the systemic circulation in smaller quantities. That is why the concentration of insulin in venous blood plasma does not demonstrate the level of its primary production in the pancreas. In addition, some physiological conditions (stress, fasting, inhalation of nicotine tar, etc.) directly affect the concentration of the hormone.
Important! C-peptide bypasses the “first pass” phase, so its blood levels remain relatively stable. . The ratio between insulin and C-peptide is not always constant; it can shift in one direction or another against the background of pathologies of internal organs (kidneys, liver, gastrointestinal tract)
How to test for C-peptide
In the pancreas, the production of proinsulin occurs around the clock, and when glucose is released into the blood, it is significantly accelerated. Therefore, more accurate, stable results are obtained by fasting testing. It is necessary that at least 6, maximum 8 hours pass from the last meal to donating blood.
It is also necessary to exclude in advance the influence of factors on the pancreas that can distort the normal synthesis of insulin:
- do not drink alcohol for a day;
- cancel training the day before;
- 30 minutes before donating blood, do not get tired physically, try not to worry;
- do not smoke all morning before the test;
- don't take medicine. If you cannot do without them, warn your doctor.
After waking up and before donating blood, only clean water without gas and sugar is allowed.
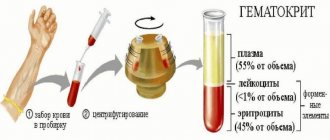
Blood for analysis is taken from a vein into a special tube containing a preservative. The plasma is separated from the blood elements by centrifuge, and then the amount of C-peptide is determined using reagents. The analysis is simple and takes no more than 2 hours. In commercial laboratories, results are usually ready the next day.
Fat Burning Peptides
The eternal problem of humanity is how to lose weight without doing anything. Indeed, today peptides are used not only in professional sports, but also among ordinary people who want to be slim and beautiful. Substances in this group act as activity stimulants. This, in turn, stimulates the burning of fat mass and the removal of excess fluid. We have already said that these are dietary supplements that are traditionally used in professional sports. They increase the production of adrenaline, the very substance that is responsible for the body working at the limit of its capabilities. At the same time, athletes know that high loads are accompanied by serious nervous exhaustion and pain, since muscle fibers tend to be injured. All these points are also leveled out after you start taking these substances.
Today, there are two large groups of peptides:
- The first is structural, which have an impact not immediately, but gradually. They supply the body with a shock dose of amino acids, accelerate muscle growth and dry out the body. As a result, you get pure muscle mass without fat.
- The second group is functional. Reviews from those who have taken peptides (injections) confirm that this particular group can effectively reduce the body’s fat reserves. Under their influence, appetite decreases and the rate of fat breakdown increases, and the immune system is strengthened. Of course, in order for weight loss to be effective, it is necessary to make some efforts, increase sports activity and change your diet.
Features of c-peptides
C peptide - what is it? C-peptide (literally “connecting peptide”) is a clear indicator of the body’s production of natural internal insulin. C-peptide is a complex protein compound that characterizes the functioning of beta cells of the pancreas and the production of proinsulin. Secreted by the pancreas along with endogenous insulin. With a certain biochemical interaction, the protein is broken down into c-peptide and insulin. The level of connecting peptide is considered a marker of natural insulin. Thus, when this protein compound is detected in the blood, the production of endogenous insulin occurs naturally, and the level of c-peptide shows how much insulin is produced.
The initial basis of the protein is preproinsulin, consisting of 110 amino acids. All of them are connected by A-peptide, L-peptide, B-peptide and C-peptide. L-peptide, separating in a small proportion from preproinsulin, cuts off the C-peptide compound and binds the A and B groups. Insulin and c-peptide are released into the blood simultaneously in the same volume, which makes it possible to record the volume of insulin in the blood based on the level of the protein compound. Despite the total amount of volume released into the blood, the blood levels of both components differ. Such differences are due to the speed of “life” of the components in the blood. So, insulin lives about 4 minutes, and c-peptide 18-20 minutes. The speed of life fully affects the concentration of c-peptide in the blood, which is almost 5 times higher than the concentration of insulin.
The need for C-peptide analysis
A study of the level of C-peptide in the blood is most often prescribed if, after diagnosing diabetes mellitus, it is difficult to determine its type. Type 1 diabetes begins due to the destruction of beta cells by antibodies, and the first symptoms appear when most of the cells are damaged. As a result, insulin levels are reduced already during the initial diagnosis. Beta cells can die gradually, most often in young patients, and if treatment is started without delay . As a rule, patients with residual pancreatic functions feel better; complications begin later. Therefore, it is important to preserve beta cells as much as possible, which requires regular monitoring of insulin production. With insulin therapy, this is only possible with the help of C-peptide tests.
Type 2 diabetes in the initial stage is characterized by sufficient insulin synthesis. Sugar rises due to the fact that its utilization by tissues is disrupted. An analysis for C-peptide shows the norm or its excess, as the pancreas increases the release of the hormone to get rid of excess glucose. Despite the increased production, the sugar to insulin ratio will be higher than in healthy people. Over time, with type 2 diabetes, the pancreas wears out, proinsulin synthesis gradually decreases, so C-peptide gradually decreases to normal and below it.
The analysis is also prescribed for the following reasons:
- After resection of the pancreas, to find out how much hormone the remaining part is capable of producing, and whether insulin therapy is needed.
- If periodic hypoglycemia occurs, if diabetes mellitus is not detected and, accordingly, treatment is not carried out. If glucose-lowering drugs are not used, glucose levels may drop due to a tumor that produces insulin (insulinoma - read about it here).
- To resolve the issue of the need to switch to insulin injections in advanced type 2 diabetes. Based on the level of C-peptide, one can judge the safety of the pancreas and predict further deterioration of indicators.
- If hypoglycemia is suspected to be artificial. People who are suicidal or have mental illness can inject themselves with insulin without a doctor's prescription. A sharp excess of the hormone over C-peptide indicates that a hormone injection was given.
- For liver diseases to assess the degree of accumulation of insulin in it. Chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis lead to a decrease in insulin levels, but do not affect C-peptide levels.
- Identification of the onset and duration of remission in juvenile diabetes mellitus, when in response to treatment with insulin injections the pancreas begins to synthesize its own.
- For polycystic disease and infertility. Increased insulin secretion may be the cause of these diseases, since in response to it the production of androgens increases. It, in turn, interferes with the development of follicles and prevents ovulation.