The appendix is a miniature worm-like appendage of the cecum, a unique organ whose purpose has been revealed relatively recently. Being an integral part of the immune system, the appendix “lures” certain harmful formations into its lymphoid tissue and destroys their structure, thereby ensuring the safety and protection of the entire organism.
If a person is subjected to prolonged exposure to various toxins, the appendage, “working tirelessly” on internal invisible cleansing, can fail, then an inflammatory process occurs - appendicitis. Since it is quite difficult to see and recognize its first signs, ultrasound comes to the aid of people - a modern diagnostic method that allows you to identify a dangerous disease at an early stage of development.
Is it possible to reliably see appendicitis on an ultrasound?
To diagnose appendicitis, clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods are used. An experienced doctor can make a diagnosis based on complaints and examination of the patient in 50% of cases. In other cases, the manifestations of the disease may be hidden, or the patient’s complaints resemble other pathologies.
In such cases, X-ray diagnostics were previously used, which helped differentiate atypical forms of appendicitis. With the development of ultrasound, it began to be used when the clinical picture was in doubt and it was necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms. These include:
- acute or chronic cholecystitis;
- ovarian cyst rupture;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- acute pilonephritis;
- cystitis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- Crohn's disease;
- omental infarction;
- mesenteric lymphadenitis;
- carcinoid , etc.
Many of these pathologies give a clear picture on ultrasound, and this makes it possible to exclude inflammation of the appendix. But whether it is possible to determine whether there is appendicitis using an abdominal ultrasound depends on several factors, including the following:
- location of the cecum;
- presence of gases in the intestines;
- thickness of the subcutaneous fat layer.
Also, the patient’s individual sensitivity to pain plays a role during the examination, since it is carried out without preparation, the cecum normally contains a certain amount of gases, and the diagnostician uses dosed compression and pressure with a sensor to improve visualization.
This technique allows you to displace gases from the cecum, because they do not allow ultrasound to pass through, thereby creating an acoustic window for searching and studying the appendix.
A number of advantages and disadvantages
The widespread use of ultrasound in domestic medicine began in the 80s of the last century. The advent of ultrasound made it possible to abandon X-ray radiation, which can cause harm to the body, and make diagnostics completely safe for all people, including pregnant women.
In addition to ultrasound, MSCT (multispiral computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are considered safe, but only ultrasound can be called the most affordable diagnostic method: every clinic has an ultrasound machine, and if the procedure is paid for, the cost of ultrasound will be an order of magnitude lower than for tomography.
Ultrasound does not require any preparation and has no restrictions or contraindications. It is absolutely painless and takes only a few minutes. The patient receives the results of the examination immediately, so quick confirmation of the diagnosis will allow immediate treatment to begin if necessary.
When perforated:
- The walls of the process are thickened to varying degrees. The structure is discontinuous and layered.
- The echogenicity of the fluid around the appendix increases. It is surrounded by an inflamed omentum.
- Between the intestinal loops there are one or more abscesses.
Inflamed appendix:
- When pressed, air is not removed from it. The tubular structure ends blindly.
- In cross section it looks like a target.
- The width of the walls of the filled process exceeds 3 mm, and the diameter is 6 mm.
It can sometimes be difficult to identify acute abdominal pathology in people who are obese or in pregnant women. Excessive gas formation also impairs good visualization of organs, making diagnosis difficult. Therefore, if the examination is planned, the patient needs to exclude gas-forming foods from the diet one day before.
Diagnostic laparoscopy of the abdominal cavity
- High level of information content (about 90–92%).
- Obtaining reliable results about the patient’s condition.
- There is no need for any surgical intervention.
- Accessibility for citizens with an average level of income.
- Low cost.
- Speed of procedure (from 15 to 30 minutes).
- Possibility of making a diagnosis even with an unusual location of the appendix.
- Lack of special preparation.
It should also be noted that ultrasound shows the true cause of physiological discomfort, which, at first glance, resembles appendicitis. If other organs are affected, sonography will most likely reveal this.
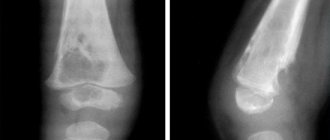
The image shows the state of the rectal process in a state of inflammation (left) and normal (right)
Since official medicine does not have accurate data regarding the effects of ultrasonic vibrations on humans, it is impossible to declare with absolute certainty that there is no danger to health. However, inflammation of the appendage of the cecum is exactly the case that requires urgent diagnosis using an echography device: only it, at the stage of exacerbation, is able to detect appendicitis on ultrasound in time.
If we talk about obvious shortcomings, then we can focus on two significant flaws:
- Not every doctor has the opportunity to identify a dangerous disease, so there is a practice of so-called linking to the appropriate specialist.
- It is practically impossible to carry out the study through the abdominal wall of a patient if he has significant excess body weight.
In case of dangerous complications of appendicitis, such as sepsis, perforation, gangrenization, urgent surgical intervention is necessary. When symptoms are pronounced, doctors rely on the overall clinical picture. But if the symptoms are not so pronounced, or the appendicitis itself is atypical, then delay in surgical intervention can cost the patient’s life. In these cases, they resort to ultrasound examination of the appendix.
Examination of the appendix using ultrasound allows you to accurately differentiate the symptoms of appendicitis and signs of other diseases
The procedure allows you to determine the current condition of the patient. Moreover, almost half of abdominal diseases have symptoms similar to acute appendicitis. Interestingly, the location of the appendix itself is often completely different, which significantly affects the nature of the pain and the course of inflammation. Ultrasound helps to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe correct and timely treatment.
Even before the 1980s, barium X-rays were used to examine the appendix. Ultrasound is much safer, especially for pregnant women and children. Many experts highlight computed tomography as the most accurate research method. Ultrasound examination is in no way inferior to it, but much cheaper and more accessible. In emergency situations, they resort to ultrasound, due to faster acquisition of data on the patient’s condition.
The use of ultrasound is especially convenient in diagnosing inflammation of the appendix in children and pregnant women. Due to its anatomical features, it is quite difficult to diagnose appendicitis using classical research methods. In addition, children themselves often cannot explain coherently and clearly where exactly it hurts. This makes it difficult to make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
But there are also disadvantages to this examination method. For example, due to bloating, improper preparation for an ultrasound, or the patient being overweight, the examination may not show some areas of the abdominal cavity on the monitor screen. In any case, the surgeon makes the final diagnosis and prescribes treatment, but ultrasound is only a way to collect data.
What is appendicitis, symptoms of acute appendicitis
The disease is registered in 10% of children over 5 years of age and people under 40 years of age, although the possibility of development in the elderly cannot be ruled out. The vermiform appendix of the cecum is located in the region of the right iliac fossa and the inflammatory process in it is called appendicitis. The disease begins acutely, with diffuse abdominal pain, then it gradually takes on a focal character and is localized in the lower right part of the abdomen.
Since the appendix can have a length from 0.5 to 25 or more centimeters, be located retrocecally or descend into the small pelvis, in 50% of cases the clinical picture of the disease differs from the classic form of appendicitis. Symptoms can also be erased in children, pregnant women, and the elderly.
The main complaints of patients are the following:
- pain does not always have a clear localization, can radiate to the navel, spine, subsidence and then re-development of severe pain often indicates perforation and the development of peritonitis;
- temperature usually does not exceed 38 degrees Celsius;
- nausea and vomiting, as well as loss of appetite, can mask the pathology as infectious toxic diseases;
- diarrhea, more common in children, together with fever is an important prognostic sign in children who cannot accurately describe their complaints.
Patients also have dry mouth, a coated tongue, and specific symptoms of appendicitis.
Causes of appendicitis
The causes of acute appendicitis are complex, they are poorly understood by doctors and have not been fully investigated. It is assumed that the appendix has its own microflora inside. Under normal conditions, these bacteria cannot penetrate mucous and lymphoid tissue. They do not harm the body.
Factors contributing to a decrease in immunity, an increase in the activity of the microflora of the appendix and the development of acute appendicitis may be different. These include:
- Mechanical reasons. The lumen of the appendix is blocked by feces. Excessive growth of lymphoid tissue. Excessive mucus production. “Lazy” intestines and frequent constipation. Also, the appendix can be pinched during pregnancy, various hernias, tumors and cysts.
- There may be a fecal stone in the inflamed appendix on the ultrasound picture of appendicitis (Fig. 3).
- Heredity. Sometimes it manifests itself after a generation.
- Diet. One of the main factors contributing to the development of appendicitis. Low fiber content in consumed foods, fried and smoked foods, and baked goods reduce intestinal immunity and impair its functioning. Therefore, it is necessary to eat right, eat more vegetables and fruits, and, if possible, limit your consumption of fast food.
- Infections. Infectious lesions of various cocci and bacilli, which can cause an inflammatory process in the appendix.
- Impaired blood flow. Vascular diseases and blood clots increase the chances of developing appendicitis. In this case, the disease bypasses the initial stages and proceeds in a complicated form.
Will an ultrasound show appendicitis or not, and how is the diagnosis carried out?
It is not always possible to see appendicitis on an abdominal ultrasound, especially if it has a retrocecal location. The search starts from the ileocecal angle, where it originates. Despite the fact that its dimensions can vary greatly, the diameter of the organ should not exceed 6 mm, and the wall thickness should not exceed 3 mm. It is the increase in diameter and wall thickness that is the first sign of inflammation.
To find the appendix, the doctor presses a probe on the area being examined to force gases out of the cecum. Also, during the inflammatory process, the appendage swells, which affects its flexibility and mobility. Fluid oozes around it, so when pressure is applied, its cavity does not collapse, and on the cut it looks like a target, due to periappendiceal effusion.
Effusion can also be found in the abdominal cavity, for example, in the pouch of Douglas in women. The tissues surrounding the process become hyperechoic and denser. This is due to their infiltration by leukocytes and macrophages.
In the future, with the development of the disease, perforation of the wall of the appendix and the release of contents into the abdominal cavity are possible, with the formation of purulent cavities. Ultrasound shows discontinuity of the wall and a hypoechoic formation adjacent to the process.
At an early stage of the development of the disease, it is informative to conduct a duplex scan, which shows increased blood flow in the organ. Transvaginal ultrasound is also used in women to detect appendicitis with an atypical low location.
But in some cases, it is not possible to see appendicitis if it is located behind the cecum. Difficulties in diagnosis also occur with chronic appendicitis, when, due to a sluggish inflammatory process, an infiltrate is formed around the appendix, which is a conglomerate of tissues of nearby organs, fatty tissue, and adhesions.
Doctor's opinion
“I believe that the appointment of ultrasound as a quick method of secondary diagnosis of appendicitis is very justified. Before an operation, even an urgent one, there is always a need to clarify the patient’s condition “from the inside”: anatomy and topography, presentation, shape of the appendix and other criteria.” Ivanov I.G., surgeon of the highest category, Tver.
“Ultrasound is prescribed only at the early stage of inflammation, when the clinical picture is noticeably erased and resembles the course of multiple diseases (including pathologies with distantly radiating pain). Progressive appendicitis is diagnosed based on examination and palpation - this is always enough.” Kurev A.D. surgeon-urologist, Saratov.
Features of the procedure in childhood
When diagnosing appendicitis in children, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is used most often, since in childhood the disease is atypical, and the child cannot always explain what is bothering him or where the pain is localized. The vermiform appendix is involved in the formation of immunity, so removal of appendicitis in children should be carried out only after the diagnosis has been clarified using ultrasound.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in most cases shows a disease such as appendicitis, so it is used for primary and differential diagnosis. No special preparation is required to conduct the examination. It is performed transabdominally, less often transvaginally. Ultrasound is a simple, inexpensive and informative technique used in the diagnosis of appendicitis.
Features of diagnosis in women
Due to the physiological structure of women, pain characteristic of appendicitis can be caused by an ectopic pregnancy, inflammation of the appendages or the right ovary. As a result, it is very difficult to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe an effective treatment regimen based only on data from laboratory tests and palpation.
The study allows us to reliably distinguish appendicitis from gynecological diseases
It has been statistically revealed that women are more often susceptible to inflammation of the appendix than men. The physiological structure is to blame for this.
Firstly, the female organs of the genitourinary system are almost in contact with the gastrointestinal tract. This is how inflammation in the genital organs is transmitted to the bladder, urethra and even the intestines.
Secondly, during menstruation, blood circulation increases, the uterus “swells”, moves other organs and puts pressure on the appendix. Therefore, complex therapy is possible. Expectant mothers are especially at risk. The growing uterus puts pressure on other internal organs, disrupting normal blood circulation.
Pregnant women attribute most of the pain that occurs in the abdominal area to their “interesting position.” This is usually the case, so the symptoms of appendicitis are not immediately recognized. Moreover, in the later stages of pregnancy the appendix itself moves upward, i.e. its location changes, which affects the general symptoms of appendicitis and the nature of the pain.
For acute abdominal pain during pregnancy, ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity in general, and the appendix area in particular, is indicated.
The causes of inflammation of the appendix in pregnant women are not fully understood. According to one version, the growing uterus puts pressure on other organs, moving them. As a result, the lumen between the appendix and the intestine becomes clogged, which disrupts blood circulation, leading to inflammation. It turns out that pregnancy itself often provokes appendicitis. According to statistics, among women, acute appendicitis is diagnosed more often in pregnant women.
The main signs of appendicitis in pregnant women:
- pain in the upper abdomen or navel area, gradually moving to the lower right area;
- diarrhea, nausea, vomiting;
- heat;
- lack of appetite;
- pale skin;
- sweating
Sometimes pregnant women notice pain not only above the uterus, but throughout the entire abdomen, as well as increased pain when lying down on the right side. When the process is located low, the pain radiates to the legs, and the nature of such pain varies greatly, so an ultrasound examination is required.
However, the threat remains in the postoperative period. Antibiotics are indicated; expectant mothers are prescribed general tonics and sedatives, because all experiences are transferred to the baby.
Young children often cannot describe the nature and intensity of pain. They cry, are capricious, pull their legs to their stomach. All this makes it difficult to make a diagnosis. Most often, school-age children are susceptible to this disease.
Due to the physiological characteristics of children, inflammation of the peritoneal organs is often added to appendicitis, which threatens the development of appendiceal peritonitis. Inflammation is provoked by viruses, infections, congenital pathologies of the appendix, and the entry of feces, foreign bodies, pus, and parasites into the lumen of the appendix.
The child is not always able to describe the nature of the pain; this is where a safe ultrasound examination comes to the rescue
As a result, swelling of the mucous membrane of the appendix occurs, increased tension in its walls, proliferation of pathogenic flora, venous stagnation, and impaired arterial circulation. The inflammation itself in children is much more acute and faster than in adults. Appendicitis in children is even provoked by acute respiratory viral infections, tonsillitis, otitis media, measles, sinusitis, dysbacteriosis, gastritis, constipation and overeating.
Sometimes resection of the appendix is contraindicated for various clinical indications. Such cases are less common, but they do occur. As a result, appendicitis is treated with antibiotics, without surgery. It is not possible to completely cure the appendix, and appendicitis becomes chronic. During the period of exacerbation, treatment in a hospital under the vigilant supervision of doctors is indicated.
Carrying out the procedure
If pain is mild, or if the pain area is located in an atypical location, the analysis is carried out in the following way:
- Study of the apex of the cecum.
- Detection of iliac vessels.
- Study of the iliac muscle.
- Study of the place behind the cecum.
- Analysis of the condition of the peritoneal and pelvic organs.
- Especially for women, the right ovary is examined.
The final diagnosis is made by the doctor. There is not always enough data to make an adequate diagnosis. Some cases require additional tests, diagnosis using MRI, laparoscopy or CT. Conclusions are drawn based on the results of all types of research.
Ultrasound is often prescribed after removal of the appendix, especially if complications occur or a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition, allowing one to see the internal source of the complication.
Carrying out in women
The female body is structured somewhat differently. Therefore, the appearance of pain characteristic of appendicitis may indicate gynecological problems in the form of inflammation of the appendages or ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, a doctor cannot make a correct diagnosis only on the basis of palpation of the peritoneum and the results of blood and urine tests. This is exactly the option where ultrasound is indispensable.
During the procedure, a clear source of pain is visible. An examination of the peritoneal and pelvic organs reflects the condition of the appendages and appendix, allowing one to diagnose the exact cause of the ailment. The procedure when examining female patients is performed more often due to the structural features of the female body. The internal reproductive structure of women, the organs of the urinary system are in close contact with the digestive ones. As a result, inflammatory processes in the gynecological parts of a woman’s body spread to the genitourinary system or intestines.
In addition, during menstruation, a woman’s uterus swells, increases in volume and displaces other organs in the abdominal cavity. During pregnancy, the uterus enlarges many times; in addition to displacement, it compresses and disrupts blood circulation in the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to inflammatory processes. In this case, ultrasound remains a relevant research method that can show an accurate picture.
Features of the procedure in childhood
Children are not always able to describe the symptoms of an attack and cannot indicate where the pain is located. Conducting an ultrasound examination in children is a safe and quick way to determine the cause of pain and an accurate diagnosis. The attack itself develops much faster in a child than in adults.
This is due to the physiology of the child’s structure and the course of metabolic processes. An attack can be triggered by ARVI or tonsillitis, poor diet, dysbiosis, or gastritis. An ultrasound will show the source of inflammation and the cause of its development.
In some cases, removal surgery is contraindicated and antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Appendicitis gradually becomes chronic. The described point requires a mandatory ultrasound examination two or three times a year to monitor the condition of the appendix. This is necessary because the disease in a chronic condition can occur covertly and lead to aggravating consequences for human health.
Ultrasound diagnostics is an informative, safe, accessible method for identifying pathology in acute appendicitis. The procedure will help the doctor differentiate the ailment from other diseases, see inflammatory processes, exclude or determine the presence of problems in neighboring abdominal organs. Diagnostics can make it possible to establish the correct diagnosis, and if there is insufficient data, it is supplemented by laboratory tests, MRI or CT.
It is important to take good care of your health, monitor your physical fitness and well-being, and seek help in a timely manner if you feel unwell. A strong immune system will allow you to maintain health, prevent the development of pathological conditions and complications, and ensure a speedy recovery from illnesses. Well, if the body malfunctions and medical attention is required, modern research methods in the form of diagnostics using ultrasound will help make an accurate diagnosis and identify the true cause of the disease.