Every woman is required to undergo a gynecological examination at least once every six months; many diseases and problems can occur unnoticed and asymptomatic. The same situation arises with regard to the problem of the appearance of accumulation of free fluid in the pelvis in women, the causes of which can be manifestations of various diseases. You should not be afraid of this; in most cases, this process does not lead to serious illnesses, but you should not ignore this topic.
What does fluid in the pelvis mean?
In 95% of cases, free fluid in the pelvis is formed during the process of the release of the egg into the fallopian tube, as a result of which the mature follicle ruptures. As soon as menstruation ends, a small amount of fluid forms in the follicles and can enter the space behind the uterus. This is an absolutely normal process, but if after a couple of days the indicator has not decreased, this means that free fluid in the pelvis is a symptom of pathologies that need to be diagnosed in the near future.
Causes
Possible reasons for the presence of fluid in the pelvis may be:
- Ectopic pregnancy. As the embryo develops in the fallopian tubes, they begin to become deformed and bleed. As a result, the discharge enters the pelvis, which is the pathology diagnosed on ultrasound.
- Endometriosis. During menstruation, inflamed endometrial tissue begins to bleed and the discharge enters the pelvis.
- Abortion or spontaneous miscarriage. After an abortion, the fallopian tubes, like the uterus itself, are quite severely injured, which leads to the presence of blood in the retrouterine space.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms. Violation for this reason is associated with rupture of the cyst and the release of fluid to the outside.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system. The pathological condition in this case is associated with inflammatory processes of internal organs, which lead to a violation of tissue integrity.
- Ascites. This disorder leads to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, which can be caused by liver pathologies and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. This disorder, leading to the appearance of fluid in the pelvis, unlike the others, can also be observed in men.
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the causes of the accumulation of free fluid localized in the pelvis, and involves treatment of the underlying disease or pathology accompanied by the formation of effusion. Solving a problem may involve several directions, and they are discussed separately below.
In the absence of timely measures, the development of peritonitis is likely - inflammation of the abdominal cavity , which often leads to death. Excessive internal bleeding can result in severe blood loss, shock, and death.
Drug therapy
Medical conservative treatment includes the use of the following groups of drugs:
- NSAIDs – non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed for inflammatory diseases and severe pain.
- Antibiotics are indicated for bacterial infections and are selected individually after identifying the causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to the active substances.
- Preparations based on enzymes (Longidaza, Wobenzym) have anti-inflammatory, antiplatelet, anti-edematous and fibrinolytic effects, eliminating inflammation, resolving internal hematomas, removing breakdown products and metabolites and improving intercellular metabolism.
- Hormonal drugs are recommended for gynecological diseases accompanied by hormonal imbalances. Selection is carried out individually by a gynecologist.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed to restore and maintain the body.
Surgical treatment
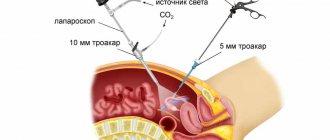
Surgical treatment is indicated in the absence of the effect of conservative methods, a rapid increase in fluid volumes and the presence of neoplasms. Surgeries are performed for cysts and their ruptures, malignant tumors, ectopic pregnancy, and peritonitis. Treatment can be carried out using the standard method using an abdominal incision or laparoscopically, in which several punctures are made.
Folk recipes
Folk remedies are used after consulting a doctor and usually as an auxiliary method in addition to the main treatment. Recipes used:
- Daily douching with decoctions of chamomile, calendula, coltsfoot, and nettle. The procedures help eliminate inflammation of the female genital organs.
- Baths with mustard. Add a small amount of mustard powder to the water and immerse yourself in it for 15-20 minutes.
- The viburnum decoction is prepared as follows: a glass of berries is poured into a liter of water, boiled for 10 minutes, taken three times a day, a glass.
- Drink one glass of celery juice three times a day.
In the retrouterine space
During ovulation, free fluid in the pelvic region of the small pelvis in women is not a cause for concern, but if, on a repeat ultrasound after ovulation (2-3 days), the fluid has not gone away, then this will be a sign of such pathological conditions as:
- Ectopic pregnancy. In this case, the woman is immediately sent to surgery and the operation is performed.
- Internal bleeding occurs when the space behind the uterus fills with blood. The woman is also being prepared for surgery, since the condition is considered extremely dangerous to life and health.
- Endometriosis. This disease is associated with the growth of the inner layer of the uterus during menstruation. Too much blood is released, which enters the posterior cavity of the uterus. The endometrium descends and can lead to the appearance of a cyst.
- Ascites. It can provoke the appearance of both benign and malignant neoplasms.
How to treat abdominal ascites using traditional methods?
A doctor can advise you to turn to traditional methods of treating such a serious condition as ascites only in anticipation of the additional effect of diuretic herbs and plants. The effect really improves when combined with medications.
The most popular recipes with folk remedies:
- decoction of birch leaves and buds;
- collection of raspberries, lingonberries, currant leaves, rose hips;
- juniper berries, nettle leaves, linden blossom;
- parsley and bearberry;
- apricot compote (contains essential potassium).
Ready-made diuretic mixture can be purchased at the pharmacy
Plants are effective in the initial stages if the patient follows a diet and regimen. But it is not recommended to arrange a hot steam room with birch leaves or wraps for the patient. This can worsen the condition of the cardiac system.
In the ovary
The appearance of fluid in the ovary contributes to the development of serious diseases and pathologies, such as inflammation of the internal genital organs, against the background of which an ovarian cyst can form. The previous stage is the occurrence of hydrosalpinsk, i.e. the formation of fluid in the fallopian tubes, which leads to adhesions. Most often, the disease is asymptomatic for the first months, but after some time a woman may notice the following symptoms:
- change in the menstrual cycle, which is expressed first in hypomenorrhea, and then vice versa, in heavy discharge;
- unpleasant smell of discharge, the color may change to pale yellow, pale green, in some cases it has bloody spots;
- painful urination, as with cystitis;
- decreased sexual desire, painful, unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse;
- bloating, which may indicate the appearance of neoplasms;
- an increase in basal and general body temperature, which indicates the onset of inflammatory processes in the body.
We recommend additional reading: How to quickly and effectively relieve swelling from the legs at home
In any case, urgent treatment is necessary; if the cyst bursts, peritonitis will begin and the woman will face long treatment in the hospital and months of rehabilitation. Delayed treatment can lead to infertility.
Additional symptoms
The norm of liquid, which does not cause concern, is up to 10 ml. If up to 50 ml is detected, this condition requires observation and consideration of other clinical symptoms. More than 50 ml of liquid indicates pathology.
A small amount of effusion may go unnoticed, and the woman’s sensations and well-being will not worsen. Inflammatory exudate causes irritation of the peritoneum and pain. Symptoms are more pronounced if inflammation has developed in the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
The woman has:
- increased body temperature;
- signs of intoxication;
- pain radiating to the lower back;
- weakness, increased fatigue.
Exudate may be a consequence of an ovarian tumor. It often develops in women after 40 years of age and does not produce additional symptoms for a long time. There may be a disruption in the menstrual cycle, an enlarged abdomen, and later pain.
A rupture of the fallopian tube occurs with a clear clinical picture during an ectopic pregnancy. The blood irritates the pelvic peritoneum, so the woman feels acute pain in the abdomen. Heavy bleeding leads to a decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia and a pre-fainting state.
Large blood loss causes hemorrhagic shock. He requires emergency medical care and a blood transfusion.
Pregnancy is indicated by a previous delay of several days. Many women already have time to confirm their condition using a rapid test, and abdominal pain and bleeding come as a surprise.
In old age
During the period when a woman’s reproductive function stops, the endometrial walls stop renewing themselves, which affects the walls of the uterus and cell membranes. Hormonal changes can lead to the development of serozometra, i.e. accumulation of free fluid in the pelvis. But there are also accompanying factors that influence the appearance of serozometers:
- previous operations, in particular frequent curettages, in 45% of cases with the onset of menopause lead to the appearance of free fluid in the pelvic area;
- promiscuous frequent sexual intercourse, which leads to vaginal dryness, and as a consequence to microtraumas;
- passion for cigarettes and alcohol leads to disruption of the vascular system and hormonal imbalances;
- fasting and strict diets can provoke illness because the body does not receive the necessary substances for proper functioning;
- a sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity disrupts blood flow and contributes to hormonal problems;
- self-medication with hormonal drugs, without examination and a doctor’s prescription, you should not use them, since instead of being beneficial, they can cause irreparable harm to a woman’s health.
Is it possible to predict how long a patient will live?
The prognosis for the course of the pathology depends on how likely it is to cope with the main cause that caused it. Unfavorable factors for determining how long people suffering from various diseases live with ascites are:
- elderly patients;
- tendency to hypotension;
- a significant drop in albumin level, according to a blood test to 30 g/l or lower;
- concomitant diabetes mellitus;
- reduced glomerular filtration in the kidneys;
- development of peritonitis;
- cancerous tumor as the cause of pathology.
According to statistics, 50% of patients with ascites live no more than two years. And when resistance to diuretics develops, half die within 6 months of observation. Ascites is a symptom of decompensation. This already indicates that the body has tried all its strength. No matter how much we strive to defeat it, there are still no conditions and no opportunity to replace the “tired” organs.
Diagnostics
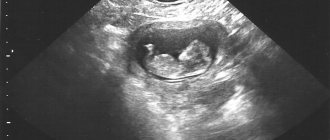
Diagnosis and treatment are prescribed strictly according to the instructions of the attending physician. First of all, the patient will be sent for an ultrasound to detect fluid in the pelvis. Also, an ultrasound examination can confirm or exclude an ectopic pregnancy, which facilitates further diagnosis. Next, the patient is referred to a gynecologist (in most cases), or another doctor, depending on the cause of the disease. The doctor will definitely refer the patient for tests to determine the exact cause and prescribe adequate treatment.
Anamnesis collection includes:
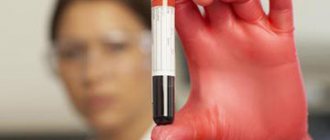
- detailed blood test;
- cytological analysis from puncture to determine tumor markers;
- examination for the presence of erosive tissue lesions;
- catheterization, with a large amount of liquid;
- hysteroscopy to determine the condition of the uterine cavity.
What factors increase the risk of ascites?
The risk group includes individuals who have the highest likelihood of developing major diseases leading to ascites:
- alcohol abusers;
- smokers;
- drug addicts;
- survivors of acute hepatitis and those suffering from chronic forms;
- after a blood transfusion;
- those in need of hemodialysis support for renal filtration;
- those who are fond of tattooing;
- having excess body weight, obesity;
- patients with diabetes mellitus;
- with signs of impaired protein and fat metabolism according to blood tests;
- those who are keen on trendy diets for weight loss;
- having a hereditary burden of oncological pathology.
Read more about the features of ascites in liver cirrhosis in this article.