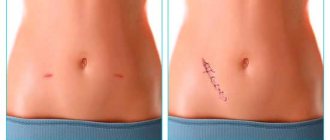
Removal of an umbilical hernia by laparoscopy is considered an effective method of eliminating pathology. The main advantages of this type of surgical intervention include a low risk of complications and relapses, as well as a short recovery period. During the operation, no large incisions are made, but several punctures are made. Due to the low tissue trauma, there is no severe pain during the recovery period.
Removal of an umbilical hernia by laparoscopy is considered an effective method of eliminating pathology.
Indications
Surgery is the only way to treat umbilical hernias in adults and children over 5 years of age. A planned operation is necessary for an uncomplicated hernia, since over time the protrusion and hole in the abdominal wall will increase. Because of this, displacement of internal organs may occur. Laparoscopy is used for small protrusions, which can be easily reduced in the supine position.
For a strangulated hernia, this type of surgical intervention is used if no more than 3 hours have passed since the organ was clamped. Laparoscopy is performed in the absence of intoxication and inflammation of the peritoneum.
Preparing for surgery
Before removing a hernia, you need to undergo an examination.
The patient must undergo a blood test (general, biochemical, coagulogram) and urine. Before laparoscopy, an electrocardiogram and fluorography are performed.
Experts recommend stopping drinking alcohol 2 weeks before surgery. At the same time you need to start taking vitamins.
A few days before the hernia is removed, patients are prescribed a diet. You will need to exclude fatty meats, legumes, and brown bread from your diet. Fruits and vegetables are allowed to be eaten without peeling. 8 hours before surgery, you are prohibited from eating or drinking. Before surgery, you will need to take an enema and empty your bladder.
Before surgery, you will need to take an enema and empty your bladder.
Hernia therapy
There are many conservative methods for treating this anomaly of the body. But there are also radical ways to solve the problem, including an operational method. However, surgical treatment remains the most effective. Most often, laparoscopy is performed for inguinal hernia in men.
Hernia removal is performed under general or local anesthesia. During surgical manipulations, the hernial sac is removed, the inguinal canal is strengthened, and plastic surgery is performed using muscle tissue or artificial polypropylene grafts (the so-called “mesh”). If the surgical intervention is successfully completed, the rehabilitation process begins. After an inguinal hernia operation in men, some restorative and preventive measures are provided to maintain the patient’s normal vitality. This includes the outpatient period, diet, exercise therapy.
Technique
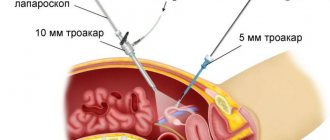
Laparoscopic (endoscopic) hernioplasty is performed inside the abdominal cavity under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes 3 punctures, the size of which ranges from 5 to 15 mm. Carbon dioxide is then released into the abdominal cavity to improve vision. A laparoscope with a video camera that displays the image on a monitor and other instruments are inserted into the punctures.
At the first stage of the operation, the doctor dissects the hernial sac and examines the protrusion. Then, in the absence of complications, the prolapsed organ is reduced into the abdominal cavity. After this, the tissues forming the bag are tightened and cut off.
At the next stage of the operation, the hole through which the internal organs protruded (hernial orifice) is strengthened.
During the operation, the umbilical ring is sewn together in children. In adults, plastic surgery of the defect is performed using a mesh-shaped endoprosthesis.
Thanks to the use of an implant, the possibility of a secondary appearance of an umbilical hernia is reduced. The mesh is fixed to the anterior abdominal wall. Over time, it is tightened with connective tissue and the existing hernial opening is eliminated. The operation is completed by suturing the puncture sites.
For small hernias, the patient is left in the hospital for 1-3 days. All this time he is under the supervision of a doctor. You can get out of bed and move carefully on the day of laparoscopy. In the first few days, you may experience discomfort and pain in the puncture area. This is considered the norm.
For small hernias, the patient is left in the hospital for 1-3 days.
Concept of laparoscopy
Laparoscopic hernioplasty of inguinal hernia is a modern method of surgical intervention in which the necessary manipulations are carried out through small punctures in the skin under endoscopic control.
The main tool for the intervention is the laparoscope - a tube equipped with magnifying glasses, attached to a video camera.
During the procedure, the patient's abdominal area is filled with carbon dioxide, due to which the skin is inflated, which makes it possible to perform a hernia repair.
The surgeon removes the hernia with special microscopic instruments. The surgical field is illuminated using an optical cable equipped with a halogen or xenon lamp. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and takes no more than an hour.
Advantages of technology
Surgery to remove an inguinal hernia (a pathology more common in men) using a laparoscope has a number of advantages compared to open surgery:
- Small puncture diameter. Wounds heal quickly and do not leave large scars.
- Minimal trauma to the soft tissues of the abdominal cavity when removing the hernial sac.
- Rare formation of adhesions in the postoperative period.
- Short periods of the patient's stay in the hospital.
- Minimum pain.
- Rapid restoration of the intestines and digestive system.
- Rehabilitation takes less time than with open surgery.
Within a few hours after removal of the hernia, the patient gets out of bed and takes a small amount of water and food. If no complications arise during the postoperative period, the patient is discharged home after a few days. Patient reviews of hernia laparoscopy are most enthusiastic.
Flaws
Despite the many positive aspects, laparoscopy has its disadvantages. The mechanism of the intervention is more complex than when performed using an open technique. The surgeon must have the necessary knowledge and experience.
Another disadvantage is the limited movement, and the fact that when performing medical manipulations with the help of instruments, it is not always possible to accurately calculate the force of pressure.
That is, the doctor has no tactile sensations, because the surgeon touches the organs not with his hand, but with an instrument whose length reaches 20-30 cm.
The big disadvantage of laparoscopy is the high cost of the method. The cost of the operation is quite high, so not many people can afford it.
In what cases is the method used?
Laparoscopic surgery is one of the popular methods of surgical intervention. Indications for use are the following patient conditions:
- The presence of a hernial protrusion less than 20 cm.
- Possibility of using general anesthesia.
- Absence of pathologies of internal organs.
- The patient’s desire to avoid scars is especially important for girls and women.
- Hernia in a child.
- The need to perform the operation in a short time.
- Patients whose work involves intense physical activity.
The decision to prescribe a method is made by doctors at a medical consultation after making a diagnosis and carefully studying the person’s medical record. For strangulated hernia and other complications, laparoscopy is not used.
The anatomy of the abdominal cavity is so complex that it is not possible to find a dead section of intestine using laparoscopic tubes. In such cases, the patient is indicated for open surgery.
Contraindications
Removal of an inguinal hernia by laparoscopy has a number of serious general and local contraindications. Common ones include:
- pregnancy;
- presence of contraindications to general anesthesia;
- infection of the peritoneal organs;
- obesity;
- hypertension;
- renal and liver failure;
- purulent peritonitis.
Among the local ones there are:
- development of phlegmon;
- infringement;
- intestinal obstruction;
- the diameter of the hernial protrusion is more than 15 cm;
- reappearance of hernia after laparoscopy.
On the day of the operation, the patient is prohibited from eating and drinking. The patient is prescribed drug therapy aimed at preventing complications and reducing the risk of wound infection.
Execution technique
The duration of laparoscopy for inguinal hernia takes no more than an hour. Removal of the formation is carried out under general anesthesia, which is selected by the anesthesiologist in advance.
Excision of an inguinal hernia is performed using small punctures through which the surgeon inserts a trocar (special tube). During the removal of inguinal hernias, three such tubes are used.
The first is inserted in the umbilical region, and microscopic video equipment is passed through it. Subsequent punctures are performed directly in the groin area, and manipulators are inserted through them.
Using micro-instruments, it is possible to fix a special implant in the area of the hernial opening and apply sutures to fix it.
This type of technique is called tension-free hernioplasty. Tension plasty involves suturing the patient’s own tissues by superimposing them on top of each other.
Laparoscopy has no age restrictions. In the absence of contraindications, the method is used in children and adults.
Possible complications
Laparoscopy is well tolerated by patients, complications occur extremely rarely. Among them are:
- damage to the vessels of the anterior abdominal wall;
- injury to soft tissues with a Veress needle or trocar;
- development of internal and external bleeding;
- violation of the integrity of large vessels in the area of the surgical field;
- damage to the spermatic cord;
- injury to internal organs (extremely rare).
Immediately after the operation, the patient experiences minor bruising, soreness, numbness, or, conversely, increased sensitivity of the skin.
Sometimes, due to technical difficulties in accessing the hernial sac, the intestinal walls are damaged, which provokes disruption of the digestive process and the development of inflammation.
If the correct methodological approach is used, there are no complications after the operation.
Features of rehabilitation
The recovery period after excision of a hernia using laparoscopy does not require a long time. After the operation, the patient experiences a feeling of discomfort and slight pain.
This cannot be avoided, since wound healing takes time.
The patient must strictly adhere to the recommendations of the attending physician. It is important to monitor the cleanliness of the dressing and visit the hospital in a timely manner for a preventive examination of wounds. If bleeding, suppuration or other complications occur, you should visit a doctor unscheduled.
The speed of recovery directly depends on the type of human activity. For patients involved in physical work, the rehabilitation period may take several months. If after the intervention the patient is at rest, the healing time of the sutures takes no more than a week.
To quickly recover and avoid negative consequences, you must follow a diet. The patient is advised to exclude from the diet foods that lead to increased gas formation. It is undesirable to consume strengthening products, carbonated water, and alcohol.
Last but not least are sports activities. After the sutures have healed, it is recommended to perform daily exercises aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles. Physical education will help prevent relapse of pathology and will have a positive effect on overall well-being.
Laparoscopy is a common and effective method of surgical treatment of hernias and other diseases of the abdominal cavity. With proper use of the technique, in most cases the operation is successful, relapse of pathology and complications occur quite rarely.
Source: https://proods.org/pahovaya/laparoskopiya-pahovoj-gryzhi.html
Rehabilitation
An important part of rehabilitation are:
- Nutrition. Eating is allowed the next day after the hernia is removed. Dishes should be liquid or semi-liquid (low-fat soups, purees, boiled porridges). In the first 2-3 weeks, the patient needs to adhere to a diet, excluding from the diet foods that contribute to gas formation, bloating and constipation. The following items are prohibited: baked goods, fatty meats, soda, and legumes. It is allowed to eat foods that improve intestinal motility - stewed vegetables, fruits, cereals.
- Fixation of damaged tissues at puncture sites. After surgery, experts recommend wearing a bandage to eliminate the risk of muscle divergence. They walk in it until the damaged tissue is restored. The bandage is removed during rest and at night.
- Exercise stress. After removing a hernia, you should not lift objects that weigh more than 3-5 kg. Physical therapy is prescribed after scars have formed at the puncture sites. With its help, it will be possible to speed up tissue healing. A set of exercises is selected by a doctor.
After removing a hernia, you should not lift objects that weigh more than 3-5 kg.
During the rehabilitation period, it is worth abandoning strength and aerobic exercise, because due to an increase in internal abdominal pressure, the stitches may come apart. You can return to training only after the mesh implant has adhered to the tissues. This takes from 2 to 6 months. You should consult your doctor before resuming exercise.
After surgery, you need to maintain your shape. Gaining weight can lead to problems with your stitches.
Technical aspects of operations
The operation was performed under ETN. Position the patient on his back in the Trendelenburg position and tilt the operating table to the left by 150. In this position, the internal organs shifted upward, freeing the groin area. The surgeon and video assistant were located at the head of the patient. The monitor was installed at the patient's feet to the right of the table. The operating nurse with the instrument table was located to the left of the operating table. The operation was performed using three punctures. The first one, for the laparoscope, was made in the navel area, and the other two punctures were made along the outer edges of the rectus abdominis muscles at the level of the navel. In this case, a 12 mm trocar for the hernia stapler was inserted on the left, and a 5 mm trocar for scissors and a dissector was inserted to the right of the midline. The surgeon used a two-handed technique, and an assistant provided visualization of the surgical field using a laparoscope. Only at the stage of fixing the mesh, the assistant helped to hold the mesh with an instrument through the right trocar, while simultaneously ensuring visibility with the laparoscope. After revision of the groin areas and clarification of the diagnosis, the operation began with a dissection of the peritoneum in the right groin area. The side on which work should begin, with bilateral lesions, does not matter, and the choice of order depends only on the desire of the surgeon. The peritoneal incision was made in a semi-oval shape above the inguinal rings. The peritoneum was bluntly dissected down to the beginning of the hernial sac. Tissue preparation in the area of the medial ring was carried out to the pubic bone. With oblique inguinal hernias, isolating the hernial sac presents certain technical difficulties due to the rather dense fusion of the peritoneal layer with the elements of the cord. During separation, we always monitored the integrity of the vas deferens and the choroid plexus of the cord. With direct hernias, as a rule, we did not experience such difficulties. The peritoneum was exposed to the level of the femoral fossa. Hernioplasty was performed according to the Corbitt technique (15). A mesh prosthesis with a dissected outer edge was placed in the projection of the inguinal rings. The lower leg of the mesh was placed under the isolated spermatic cord. This provided an additional point of support and contributed to a more dense placement of the mesh in an anatomical area with complex relief. The mesh was fixed with a hernia stapler through a 12 mm trocar. The staples were applied along the outer upper contour of the mesh, fixing it to dense structures. When applying staples, we avoided “critical zones” in the area of passage of the lower epigastric vessels, in the area of the “fatal triangle”, in the locations of the branches of n. Ilioinguinalis, n. Genitofemoralis, lateral fevoral cutaneus n. etc. Without closing the peritoneum, a similar operation was started on the opposite side.
Complications
During laparoscopy and after surgery, the risk of complications is minimal.
However, the possibility of health problems due to surgery cannot be completely excluded. Possible complications include:
- Suppuration and inflammation of punctures. If infection is present, antibiotics are prescribed.
- Edema. Most often occurs when using an endoprosthesis. This is how the body reacts to the implant. Additional treatment if swelling occurs is not required. This complication resolves on its own within a few weeks. If swelling appears, you will need to do an ultrasound to rule out another hernia.
- Neuralgia. Manifested by loss of sensitivity and burning sensation in the surgical area. It goes away on its own after six months.
- Hemorrhage at the surgical site. This complication also goes away on its own. In case of extensive hemorrhages, the affected area is opened.
Advantages and disadvantages of laparoscopy for inguinal hernia
Before hernioplasty, the patient should learn the advantages and disadvantages of the procedure. Laparoscopic hernioplasty for a hernia in the groin has the following advantages:
- reduced risks of relapse;
- after laparoscopy the risk of complications is negligible;
- dynamic tissue regeneration;
- no unsightly scars;
- shortened rehabilitation period.
But when choosing between laparoscopy and abdominal surgery to remove an inguinal hernia, the patient must also take into account the disadvantages of the procedures. Laparoscopic removal has a major disadvantage - not everyone can afford such a procedure, due to its cost. In addition, this manipulation has all the risks that arise when using general anesthesia. It is also not so easy to find a truly experienced surgeon who has mastered this technique to the maximum.
Contraindications
Laparoscopy of umbilical hernia has a number of contraindications. The operation is not performed on children under 5 years of age, because before this age, the umbilical hernia can close on its own due to muscle strengthening. Contraindications to surgery are also:
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
- The size of the hernia is too large.
- Obesity.
- Pregnancy.
- Oncology.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Reviews
Anna, 31 years old, Barnaul: “I got an umbilical hernia due to pregnancy. I didn’t want to remove it, because there was no discomfort, but the doctor convinced me. She agreed to undergo surgery to avoid complications. The hernia was removed laparoscopically. In my case, the surgeon had to make 5 punctures. The hernial opening was closed with a special mesh. The entire operation took less than an hour.
After the laparoscopy, I was left in the hospital for 3 days. They injected analgesics, because The place where the implant was installed hurt. It took me 2 months to fully recover. There were no special problems after the operation. Within a year, the scars became almost invisible.”
Elena, 27 years old, Moscow: “I removed an umbilical hernia in a paid clinic. The cost of the operation was about 50 thousand rubles. It included: removal of a hernia, installation of a French implant and hospital stay. Within a few hours after the laparoscopy, I was able to get up and walk around the room. I felt good. Painful sensations arose, but were tolerable. I stayed in the clinic for 1 day. 2 months have passed since the operation. I feel great."
Rules of behavior in the postoperative period
If the operation was completed without any complications, the patient can leave the clinic in a few days. On average, the postoperative period lasts from 1 to 7 days. 3-4 hours after surgery, the patient is allowed to move independently. This helps avoid adhesions and restores normal blood circulation. In some cases, wearing a special corset is indicated, especially if a complication such as “operated spine syndrome” is observed.
In the first days, dizziness, nausea, and acute pain are possible. These consequences of the operation are in most cases eliminated with medication. Complete recovery of the body takes about a month. If you follow your doctor's recommendations, the period may be shorter. Generally accepted rules:
- It is better to start eating no earlier than 6-8 hours after completion of the operation (portions should be minimal, the consistency should be puree or liquid);
- if the body temperature at the initial stage does not exceed 37 degrees, it does not need to be brought down by medication or other means;
- you need to treat the stitches from the first day; after about 2 weeks you can apply an ointment that resolves scars;
- It is recommended to avoid heavy lifting and serious physical activity for a month (light exercise is allowed).
Remember, the earlier a spinal hernia is diagnosed and operated on, the easier the surgical intervention, the more reliable the result and the shorter the rehabilitation period. Don't put off until tomorrow what needs to be done today!