Unfortunately, not all women manage to get pregnant “easily and simply”, without delays and problems. Various gynecological diseases become an obstacle to motherhood, and in such cases medicine comes to the rescue. Laparoscopic surgery, which can be performed both because of the inability to get pregnant, and because of the treatment of any gynecological pathology, is one of the methods that helps to become a mother. But on the other hand, patients who have undergone this manipulation have a lot of questions: when can they get pregnant, what is needed for this, whether the operation will cause infertility, and others.
Laparoscopy: what's the point?
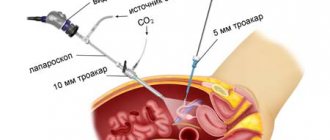
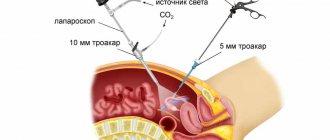
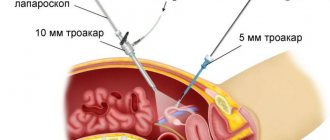
Laparoscopy, which translated from Greek means “looking at the womb,” is a modern surgical method, the essence of which is to perform surgical operations through three small holes (up to 1.5 cm). Laparoscopy is used to operate on the abdominal and pelvic region. Laparoscopy is widely used in gynecology, as it allows you to reach both the appendages (tubes and ovaries) and the uterus.
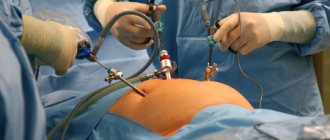
The main laparoscopic instrument is the laparoscope, which is equipped with lighting and a video camera (everything that happens in the pelvis is displayed on a television screen). Various laparoscopic instruments are inserted through the other 2 openings. To provide surgical space, the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide. As a result, the abdomen swells, and the anterior abdominal wall rises above the internal organs, forming a dome.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
First of all, it is worth noting that with laparoscopic access, the surgeon sees much wider and more accurately the organs on which he operates due to multiple optical magnification of the given area. Other advantages should be noted:
- low trauma to organs (they do not come into contact with gloves, air and gauze swabs);
- minor blood loss;
- short periods of hospital stay (no more than two to three days);
- there is practically no pain (except for a feeling of distension in the abdomen in the first or second days after the operation, until the gas is absorbed);
- absence of rough scars, except for the places where the holes were sutured;
- quick rehabilitation period (does not require bed rest);
- low probability of formation of postoperative adhesions;
- the possibility of simultaneous diagnosis and surgical treatment;
The disadvantages of laparoscopy include:
- requires general anesthesia, which is fraught with various complications;
- requires specially trained surgeons;
- the impossibility of performing some operations laparoscopically (large tumor sizes, operations involving suturing of blood vessels).
Examination before laparoscopy
Before laparoscopy, as before any other surgical operation, it is necessary to undergo a certain examination, the list of which includes:
- examination of the patient on a gynecological chair;
- complete blood count (with platelets and leukocyte count);
- general urine analysis;
- blood clotting test;
- blood chemistry;
- blood group and Rh factor;
- blood for hepatitis, syphilis and HIV infection;
- gynecological smears (from the vagina, cervix and urethra);
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- fluorography and electrocardiography;
- spermogram of the husband in case of laparoscopy for infertility.
Laparoscopic surgery is prescribed for the first phase of the cycle, immediately after the end of menstruation (approximately 6–7 days).
Preparation
Before laparoscopy, the patient undergoes a medical examination, her anamnesis and medical record are studied, and basic tests are taken:
- blood, urine;
- coagulogram;
- biochemistry;
- RV, HIV, hepatitis;
- FLG, ECG;
- ultrasonography (transvaginal or abdominal);
- colposcopy;
- cervical smears for oncocytology and microflora.
If based on the results there are suspicions of other diseases, then an additional examination is prescribed. This may be a polymerase chain reaction (PCR), MRI, or biopsy. If PCR shows an infection, then laparoscopy is postponed until recovery, since acute or chronic inflammation from the acute stage is a temporary limitation to the procedure. If magnetic resonance imaging reveals metastases or a primary cancer site of a different location (not in the reproductive area), then a completely different approach is chosen for treatment. Pregnancy can occur after successful elimination of non-metastatic cancer or a benign tumor. Biopsy material from the suspicious area is taken during the laparoscopy itself.
You need to prepare as for any intervention: do not eat foods that increase gas formation, and cleanse your intestines with an enema the day before. The timing of the planned implementation is 7-10 days before the expected ovulation.
You have questions?
You can contact the leading specialists of the AltraVita clinic
Indications for use
Laparoscopy is performed for both planned and emergency indications. Indications for immediate laparoscopic surgery are:
- ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy;
- rupture of an ovarian cyst;
- torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst;
- necrosis of the myomatous node or torsion of the subserous node of uterine fibroids;
- acute purulent inflammatory diseases of the appendages (tubo-ovarian formation, pyovar, pyosalpinx)
But, as a rule, laparoscopic operations are performed as planned (not all clinics are equipped with special equipment). Indications for them are:
- Fallopian tube ligation as a method of contraception;
- temporary sterilization (clamping of the fallopian tubes with clips);
- various tumors and tumor-like formations of the ovaries (cysts);
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- genital endometriosis (adenomyosis and ovarian endometriosis);
- uterine fibroids (multiple nodes for myomectomy, removal of pedunculated subserous nodes, amputation of the uterus if its size is small);
- tubal infertility, intersection of adhesions in the pelvis;
- abnormalities of the internal genital organs;
- removal of the ovary/ovaries or removal of the uterus (amputation and extirpation);
- restoration of patency of the fallopian tubes;
- chronic pelvic pain of unknown etiology;
- diagnosis of secondary amenorrhea.
Ovarian cyst: is it possible to plan a baby?
Ovarian cyst is a disease that occurs in many women of childbearing age. Most often, cysts appear in patients with menstrual irregularities. The cyst can be functional or organic. Functional cysts disappear on their own after several cycles or are eliminated with hormone therapy. It is not dangerous to plan a child with such a cyst. Even if treatment has been carried out, you will not have to wait several months. If the cyst does not disappear within about two months, laparoscopy is required. Most types of cysts cannot be gotten rid of without surgery. It is imperative to remove the cyst before planning a pregnancy. The least dangerous cysts, which most often go away without treatment, include corpus luteum cysts.
Important! If a cyst is found in the ovaries, it is important to understand its type, size and effect on the body of a woman thinking about pregnancy. The most dangerous for those planning a pregnancy is an endometrioid cyst.
Often, after unsuccessful removal of an endometrioid cyst, women experience infertility. This formation in the ovaries has a negative impact on the reproductive system, which leads to an irregular menstrual cycle. The appearance of an endometrioid cyst is caused by an inflammatory process, so it often affects nearby internal organs. Over time, the endometrium grows into the ovarian tissue, which leads to scarring and disturbances in the process of egg production. Surgical removal of endometrioid ovarian cysts is the only treatment method. If laparoscopy is used for elimination, patients have an increased chance of becoming pregnant. After the operation, a rehabilitation period is required, including hormone therapy. There is no need to rush into conceiving a child, even with a removed endometrioid cyst, because this formation may appear again. Pregnancy, which is considered the best preventative method for this pathology, allows you to prevent relapse. Pregnancy after an ovarian cyst is possible, but a consultation with a gynecologist is first necessary.
We recommend you find out: What is an endometrioid cyst of the left ovary
Contraindications
Laparoscopic surgery, like laparotomy, has a number of contraindications. Absolute contraindications are:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system in the stage of decompensation;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- coagulopathies (hemophilia);
- kidney and liver failure;
- malignant diseases of the pelvic organs greater than grade 2 plus the presence of metastases;
- shock and coma of any etiology.
In addition, laparoscopic surgery is prohibited for “its own” specific reasons:
- incomplete and inadequate examination of spouses in the presence of infertility;
- the presence of sexual and general acute and chronic infectious diseases or in case of recovery less than 6 weeks ago;
- subacute or chronic salpingoophoritis (surgical treatment is carried out only for acute purulent inflammation of the appendages);
- pathological indicators of laboratory and additional examination methods;
- 3 – 4 degree of vaginal smear purity;
- obesity.
Laparoscopy: when can you get pregnant?
And finally, the climax of the article has come: when can you plan a pregnancy or even “get active” after laparoscopic surgery? It is not easy to answer this question unambiguously, since much depends not only on the diagnosis for which the operation was performed, but also on concomitant gynecological diseases, any difficulties during the operation and in the postoperative period, the woman’s age and the presence/absence of ovulation before the operation .
After tubal obstruction (tubal-peritoneal infertility)
If laparoscopic surgery was performed for obstruction of the fallopian tubes (dissection of adhesions), then doctors, as a rule, allow planning a pregnancy no earlier than 3 months later .
What explains this? After laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes and dissection of the adhesions that are tightening them, the tubes themselves are still in a state of edema for some time, and in order to return to normal, they need some time. The swelling subsides after about a month, but the body also needs rest to recover after the operation and to “regulate” the functioning of the ovaries.
It is undeniable that the less time has passed since the separation of adhesions, the higher the chances of conception, but. Against the background of swollen, hyperemic and “shocked” tubes, the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy is high, which is why doctors recommend waiting. And so that the wait is not painful, combined oral contraceptives, usually monophasic, are prescribed for a three-month period. Such a prescription of hormonal pills serves not only the purpose of preventing “inopportune pregnancy,” but also to give the ovaries a rest, which, after stopping the pills, will begin to work (ovulate) in an enhanced mode.
After cyst removal
After laparoscopy for an ovarian cyst, pregnancy should also not be rushed. Laparoscopic removal of an ovarian cyst is performed very carefully; only the ovarian cyst itself is removed, leaving healthy tissue behind.
In most cases, ovarian function is restored within a month. And yet, doctors advise delaying the desired pregnancy for at least 3, and preferably 6 months .
For this period, oral monophasic contraceptives are usually prescribed, which protect against unplanned conception, allow the ovaries to rest and normalize hormonal levels. If the pregnancy occurs earlier than the agreed upon date, then problems with its course are possible, so you should not delay visiting a doctor and registering.
After polycystic disease
Polycystic ovary syndrome is characterized by the presence of many small cysts on the surface of the ovaries. The operation can be performed in three ways:
- cauterization - when multiple incisions are made on the ovarian capsule;
- wedge resection - excision of part of the ovary along with the capsule;
- decortication - removal of part of the compacted ovarian capsule.
After such operations for polycystic disease, the ability to conceive (ovulation) is restored for a short period (maximum one year). Therefore, planning a pregnancy should begin as early as possible (about a month after the operation , when sexual rest is canceled).
After an ectopic pregnancy
After laparoscopy for an ectopic pregnancy, doctors categorically prohibit getting pregnant for six months (it doesn’t matter whether a tubectomy was performed or the fertilized egg was removed from the tube and preserved). This period is necessary to restore hormonal levels after an interrupted pregnancy (as well as after a miscarriage). You should protect yourself for 6 months by taking hormonal pills.
After endometriosis
Laparoscopy of endometriosis consists of either removing the endometrioid cyst or cauterizing endometrioid lesions on the surfaces of organs and peritoneum with simultaneous dissection of adhesions. Pregnancy has a beneficial effect on the course of endometriosis, as it inhibits the process of growth of lesions and the formation of new ones. But in any case, doctors recommend planning a pregnancy no earlier than after 3 months .
As a rule, laparoscopic surgery is supplemented by the prescription of hormonal therapy, the duration of which can last for six months. In this case, pregnancy can be planned after completing the course of hormone therapy.
After uterine fibroids
If a laparoscopic conservative myomectomy was performed (that is, removal of myomatous nodes while preserving the uterus), the uterus needs time to form “good” wealthy scars. In addition, the ovaries also need to “rest” in order to function effectively in the future. Therefore, pregnancy planning is allowed no earlier than 6–8 months after surgery. During this “rest period”, it is recommended to take oral contraceptives and regular ultrasound examination of the uterus (to check the healing process and the consistency of scars).
Pregnancy that occurs earlier than the agreed term can cause uterine rupture along the scar, which can lead to its removal.
Treatment of ovarian cancer during pregnancy
The choice of therapy and its effectiveness entirely depend on the stage at which the tumor is detected, as well as what type it is. The earlier the disease is detected, the more effective the treatment will be. The main methods of therapy are the following:
- Surgical intervention. If the disease is detected in the first stages, then they do not even resort to complete removal of the organ; only the neoplasm can be excised. If the disease has taken on a more aggressive form, then in addition to complete removal of the left and right ovaries, uterine body and omentum, they resort to other treatment methods, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy;
- Chemotherapy is the most common type of treatment for ovarian cancer. The disadvantage of this therapy is that along with cancer cells, healthy cells also die, which affects the patient’s well-being;
- Radiation therapy is used only when the two previous methods are not suitable for the sick person. The effect of treatment occurs after a long time;
- Immunotherapy is used to stimulate the body to produce healthy cells that can fight cancer cells. Most often, this type of therapy is used in combination with radiotherapy and chemotherapy;
- A palliative technique is more likely not a treatment, but a relief of the condition of a seriously ill person, when the disease can no longer be cured. Used in the last stages of the disease. The essence of the therapy is that the patient is injected with potent painkillers in order to alleviate his suffering.
Along with therapeutic procedures, the doctor recommends strictly following a certain diet, since nutrition is very important during treatment.
A person loses a lot of energy during the therapies used, so a balanced diet is very important for patients. If the disease has been overcome, you still cannot relax, as relapses are possible. For the first two years, the patient should be examined by a gynecological oncologist every three months. After two years - once every six months. It is not for nothing that specialists at the Yusupov Hospital focus on early diagnosis of ovarian cancer. With a common process in the first two trimesters, recommendations for the management of patients consider it rational to neglect pregnancy, and in the third, to urgently perform a cesarean section. According to the experience of doctors at the Yusupov Hospital, not everyone agrees to surgical treatment. Therefore, our doctors develop a management plan for patients, taking into account age, trimester, extent of the process, and select the most favorable timing and treatment methods. The work is carried out with the involvement of doctors of related specialties. “Miracles” have already happened many times within the walls of the Yusupov Hospital and the most difficult patients received a second chance for recovery.
Yusupov Hospital provides assistance around the clock. You can make an appointment by phone or online.
Make an appointment
Author
Alexey Andreevich Moiseev
Head of the Oncology Department, oncologist, chemotherapist, Ph.D.
Laparoscopy: chances of pregnancy
There is a chance of pregnancy within a year after laparoscopic surgery in 85% of women. How long after laparoscopy is pregnancy possible (by month):
- after 1 month, 20% of women report a positive pregnancy test;
- 20% of patients become pregnant within 3–5 months after surgery;
- within 6 to 8 months, pregnancy was registered in 30% of patients;
- by the end of the year, the desired pregnancy occurred in 15% of women.
However, there are still 15% of women who have undergone laparoscopy and never become pregnant. In such situations, doctors recommend not to delay the wait, but to resort to IVF. After all, the longer the time passes after the operation, the less likely the chances of conceiving a child become.
Why doesn't pregnancy occur?
Many women fail to conceive a baby after removal of an ovarian cyst, since there are factors that prevent natural fertilization:
- poor quality of the operation;
- other pathologies were identified;
- non-compliance with doctor's recommendations;
- frequent nervous shocks.
It is recommended to maintain a positive attitude and do something you enjoy and enjoy. It is better not to focus on pregnancy, since sometimes conception does not occur due to psychological factors.
To increase the possibility of fertilization, after sexual intercourse, a woman should lie on her back for 10-15 minutes. This will prevent semen from leaking out.
It has been established that after laparoscopic surgery, conception occurs in 85% of patients. 15% become pregnant after 30 days, and 20% after 6-12 months.
It is necessary to follow the doctor's advice, since further conception and the period during which this process can be carried out depends on the individual characteristics of the human body.
Rehabilitation after laparoscopy
After laparoscopy, rehabilitation of the body occurs much faster than after laparotomy (an incision in the abdominal wall). By the evening, the woman is allowed to get up and walk, and discharge is carried out after a couple of - three days. You are also allowed to start eating on the day of surgery, but meals should be small and low in calories.
Sutures, if they were applied, are removed on 7–8 days. As a rule, there is no pronounced pain, but in the first days you may be bothered by bursting pain in the abdomen due to the gas introduced into the abdominal cavity. After its absorption, the pain disappears.
For 2–3 weeks, it is recommended to limit heavy lifting (no more than 3 kg) and physical activity, and sexual rest should be observed for about a month.
Types of surgery
Let's consider the types of operations to remove an ovarian cyst:
- Puncture. Under general anesthesia, a needle is inserted through the vagina or abdominal cavity. With its help, the entire contents of the tumor are extracted. The entire procedure is carried out exclusively under ultrasound control. This operation is contraindicated for polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Laparotomy. The tissues of the abdominal wall are dissected with a scalpel. This operation has a long postoperative rehabilitation. Therefore, it is carried out only when other methods are impossible.
- Laparotomy is a very dangerous operation. Often accompanied by complications. During the procedure, the patient is also given local anesthesia. A laparoscope equipped with a video camera, as well as surgical instruments, are inserted through punctures in the abdominal cavity.
- If surgery is necessary for pregnant women due to a ruptured or twisted cyst, local and regional anesthesia may be used. It is needed so as not to harm the fetus. Leads to a successful pregnancy.
- Laparoscopy is the most commonly used in medical practice. The main and only aspect is the preservation of the largest amount of healthy tissue of a woman. This increases the chance of future conception and significantly reduces the risks of hormonal imbalances.
Basic surgical techniques for removing ovarian cysts:
- if the affected area is large, then the ovary is completely removed. Typically this technique is used in laparoscopy and laparotomy;
- Aspiration is used to remove the contents of cysts. Using a needle, the internal contents of the cyst are pumped out, and ethyl alcohol is injected to replace it. This is done to reduce the size of the tumor. Typically, this method is used for endometrioid and dermoid cysts. It can be carried out with various types of surgical intervention;
- cauterization of the cyst - coagulation. For this purpose, a laser, high-frequency electric current, argon plasma and radio waves are used. Used during laparoscopy, in rare cases during laparotomy;
- clipping It is usually performed if there is a suspicion of malignancy of the neoplasm and a dermoid cyst. Used if the formation is pedunculated. Area of application: laparotomy and laparoscopy.
After the cyst, the woman’s body recovers and is ready for pregnancy after four months from the date of surgery (without complications). Menstruation can begin either after a few days or after several months. The first and second cases are the norm. The functioning of the ovaries and tissues improves gradually; the production of eggs may not begin immediately. If pregnancy occurs earlier than four months, you need to register with a gynecologist to monitor changes in the body.
Menstrual cycle after laparoscopy
After undergoing laparoscopic surgery, in most cases, menstruation comes on time, which indicates the normal functioning of the ovaries. Immediately after the operation, moderate mucous or bloody discharge may appear, which is considered normal, especially if the intervention was performed on the ovaries.
Minor bleeding may continue for three weeks with the transition to menstruation. Sometimes there is a delay in menstruation from 2 - 3 days to 2 - 3 weeks. If the delay is longer, you should consult a doctor.
Menstruation after an ectopic pregnancy, which was removed by laparoscopy, occurs on average within a month, plus or minus a few days. In the first days after laparoscopic removal of an ectopic pregnancy, slight or moderate bleeding appears, which is absolutely normal. This discharge is associated with the rejection of the decidua (where the embryo should have attached, but did not attach) from the uterine cavity.
Recommendations for a quick pregnancy
For some diseases (adhesions in the fallopian tubes, polycystic ovary syndrome), a woman needs to conceive a child as soon as possible, since a relapse of the disease is possible after 2-3 months. But most often, the expectant mother has no time limits, but she wants to get pregnant in the near future. There are 4 rules that will help a woman conceive a long-awaited child after undergoing surgery:
Calculate ovulation
There are 2-3 days in the menstrual cycle when the egg is ready to merge with the sperm. In order not to miss ovulation, a woman is recommended to use the calendar method or a special test.
Have sexual intercourse once every 2 days
When intimacy is too frequent, sperm do not have time to accumulate in the required quantity.
Lead a healthy lifestyle
When planning a child, you should follow proper nutrition and avoid nicotine and alcohol.
Preparing for pregnancy after laparoscopy
In order to increase the chances of conception and reduce the risk of possible complications of the desired pregnancy, you first need to undergo examination:
- mandatory visit to a gynecologist;
- general clinical tests (blood, urine), biochemistry and blood sugar as indicated;
- PCR tests for sexually transmitted infections (if detected, mandatory treatment);
- smears from the vagina, cervix and urethra;
- determination of hormonal status (according to indications) and correction of disorders;
- Ultrasound of the reproductive system;
- genetic consultation (preferably for all married couples).
It is possible that a more extensive examination will be needed, for example, a colposcopy or ultrasound of the mammary glands, which is decided by the doctor observing the woman.
During pregnancy planning, it is recommended to follow a number of rules:
- taking folic acid for at least three months before the planned pregnancy;
- completely give up bad habits, including for the future father;
- lead a healthy and active lifestyle (walks in the fresh air, moderate physical and sports activities);
- review your diet in favor of a healthy and fortified diet;
- avoid stressful situations if possible;
- calculate or determine the days of ovulation (using a special ovulation test) and “be active” during this period.
Reasons for unsuccessful attempts to conceive
After surgical intervention, the long-awaited conception occurs. But it happens that after a year or a year and a half, patients fail to get pregnant. This happens due to a poorly performed operation and failure to follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
If the patient has questions about prescribed medications, or experiences a deterioration in health, you should immediately consult with your doctor.
Doctors advise having a positive mood. If a woman is in a good emotional state after surgery, the chances of conception increase. You should not fall into depression, this can only worsen your condition. It is recommended to find a hobby you like and surround yourself only with cheerful events.
According to statistics, women who believe in a quick conception and easy bearing of a baby achieve what they want much faster. And the most important thing is that a neoplasm is not an end to motherhood. Medicine has been successfully eliminating this disease for many years.
How does pregnancy proceed after laparoscopy?
If you follow the terms after which pregnancy is permitted and recommendations during the planning period, pregnancy, as a rule, proceeds without complications. All deviations from the normal course of the gestation period are not associated with the laparoscopic operation performed, but with the reason for which the operation was performed.
For example, when pregnancy occurs after ovarian laparoscopy earlier than 3 months, the risk of early miscarriage increases due to a failure of the hormone-producing function of the ovaries. Therefore, in this situation, the doctor will most likely prescribe progesterone drugs and antispasmodics to prevent miscarriage. The development of other complications of gestation cannot be ruled out:
- intrauterine infection due to chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- polyhydramnios (as a result of infection);
- placenta previa (after removal of fibroids);
- fetoplacental insufficiency (hormonal dysfunction, infection);
- incorrect position and presentation of the fetus (uterine surgery).
Useful video about the progress of laparoscopy
We recommend reading : Is it possible to induce menstruation if there is a delay?
Author
Irina Kuleshova
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the second qualification category. Graduated from Vitebsk State Medical University of the Order of Peoples' Friendship. She has experience working in antenatal clinics, gynecological departments, and maternity hospitals. All articles by the author
I like!
Course of labor
The previous laparoscopic operation is not an indication for a planned cesarean section, so the birth is carried out through the natural birth canal. The only exceptions are those operations that were performed on the uterus (removal of fibroid nodes or reconstruction of the uterus due to developmental anomalies), since after them scars remain on the uterus, creating a danger of its rupture during childbirth. Complications of childbirth that are possible are associated with the presence of gynecological pathology for which laparoscopy was performed, and not with the operation:
- anomalies of generic forces;
- prolonged labor;
- early postpartum bleeding;
- postpartum subinvolution of the uterus.
Laparoscopy for uterine fibroids
Laparoscopic interventions on the uterus are performed for small fibroids with the presence of subserous nodes.
This type of surgery is contraindicated if:
- from 12 weeks of pregnancy;
- the presence of a large number of nodes and their low location.
After myomectomy, conception can be planned under the strict supervision of a doctor. Only a specialist will give recommendations on possible timing.