A low level of white blood cells in the blood is called leukopenia. Since these cells are responsible for the functioning of the immune system, their decrease leads to a decrease in the body's resistance. A sharp decrease in the indicator that persists for a long time is extremely dangerous. The immune system during this period can be affected by any infection. Treatment of the disease will also be difficult due to the lack of immune cell support. A decrease in the level of leukocytes manifests itself under the influence of physiological and pathological reasons, but poses a danger to the body regardless of the etiology.
Leukopenia - what is it?
Leukopenia is a low level of leukocytes in the blood, namely a decrease in the indicator to a threshold of 1.5 * 109/l.
If there are no leukocytes in the blood, agranulocytosis is diagnosed. The incidence of severe disease is 1 case per 100 thousand population. Attention!
There is a congenital form of leukopenia. The frequency of its manifestation is 1 case per 300 thousand people.
A lack of leukocytes is dangerous not only for children, but also for adult patients. The mortality rate is 4-40%, depending on the form of the disease, severity and associated complications. A particularly dangerous form is leukopenia acquired by the patient as a result of chemotherapy. This therapy is often used in oncological processes. The appearance of leukopenia in cancer worsens the prognosis for recovery due to the lack of immune protection of the patient.
Having considered the statistical data, it is necessary to clarify that the disease is more often detected in older women. Doctors associate this feature with the onset of menopause. Low levels of leukocytes in the blood of women are often the result of uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives or antidepressants, sedatives. Despite this feature, the risk of the disease in men cannot be excluded.
Normal for women
In healthy people, the level of leukocytes is in the range of 4-9 × 106/l. A low level of cells is a signal for extensive research and careful study of the altered leukocyte formula.
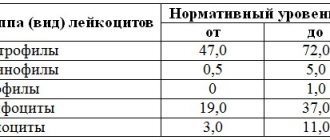
Table: LF norms for women
| Index | Neutrophils | Lymphocytes | Monocytes | Eosinophils | Basophils | |
| PY | SY | |||||
| Normal value, % | 1-6 | 47-72 | 19-37 | 3-11 | 0,5-5 | 0-1 |
In the study, it is necessary to pay attention not only to the concentration, but also to the ratio of groups of leukocytes. This analysis allows us to identify the “weak link” of immunity and find out the causes of leukopenia.
Causes of low leukocytes in the blood
Leukocytes are blood cells that protect the body from the activity of bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microorganisms. They provide resistance to various diseases, so their reduction or absence is dangerous. In cases where there is a shortage, absence, or concentration of blood cells that exceeds the norm, you need to undergo an examination and determine the cause.
Physiological reasons
Physiological leukopenia is rarely observed. The disorder occurs in no more than 10% of Europeans who do not have functional or organic bone marrow disease. In this condition, the values do not fall below 2*109/l.
A reduced number of leukocytes in the blood is manifested by:
- during night sleep due to activation of the vagus nerve;
- after visiting a bathhouse, sauna, or a long stay in a hot bath;
- under stress.
The main reason for the deviation is the migration of formed components to other zones of the vascular bed.
Pathological causes
The number of leukocytes often decreases under the influence of various diseases and conditions:
- taking medications (chemotherapy, sedatives, hormonal pills);
- autoimmune diseases, against which cells independently attack healthy tissues in the body;
- congenital or acquired lesions of the bone marrow, which reduce its functional activity;
- acute viral diseases;
- malignant oncological processes;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- acute intoxication with toxic substances;
- liver damage;
- damage to the hematopoietic organs;
- helminthiasis;
- HIV;
- tuberculosis.
If a child has low white blood cells, the cause may be many diseases:
- viral and bacterial activity;
- acute allergic reactions;
- blood poisoning;
- genetic lesions of the bone marrow.
Attention! Often the cause of leukopenia in a child is a hereditary predisposition. Doctors say that the lesion is transmitted from mother to child.
Why is a decrease in white blood cells dangerous?
A decrease in the number of white blood cells in the blood often occurs without symptoms, especially if their number is slightly below normal. In this case, the development of the disease is detected only clinically, as a result of laboratory tests. Such a change cannot be ignored. It often indicates the progress of serious problems.
If you do not respond to such a signal from the body in a timely manner, the inflammation will take a generalized form and a chronic course. Against this background, the concentration of blood cells drops critically, and the condition itself takes on an advanced form, in which the prognosis for recovery becomes unoptimistic. The prolonged presence of leukocytes in a concentration in the blood below normal indicates the development of agranulocytosis, leading to blood poisoning.
Considering the reasons for changes in the content of blood cells in the blood, we can conclude that the basis for the development of the disorder is often oncology, AIDS, HIV or tuberculosis. Such diseases can be successfully treated if detected at an early stage; if time is lost, the prognosis is unfavorable, which is why low white blood cell counts cannot be ignored.
Main causes of leukopenia
Low white blood cells in an adult or child are not always associated with pathology. If the analysis shows a slight deviation from the norm, this may be caused by taking certain medications. This deviation is observed during a course of treatment with antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as medications for thyrotoxicosis. Leukopenia of drug origin is considered physiological, it is not associated with diseases. However, a decrease in leukocytes should be reported to your doctor; it may be necessary to adjust the dosage or discontinue the medication.
It often happens that leukocytes are low due to pathology. Leukopenia is not a separate disease, but can be a symptom of various ailments. The reasons for this deviation can be divided into the following groups:
- lack of substances that affect the production of leukocytes;
- death of white cells or a decrease in their number in the bloodstream during infections and poisonings;
- disruption of the hematopoietic system;
- diseases of internal organs leading to leukopenia.
Let's take a closer look at each of these factors.
Types of leukopenia
In the modern medical classification there are the following types of leukopenia, they are discussed in the table:
| According to the nature of the flow | By time of appearance | By severity | |||
| Acute | Up to 3 months | Congenital | Kostmann's syndrome, cyclic neutropenia | Lightweight | 1-1,5*109 |
| Chronic | Progresses over 3 months | Acquired | Under the influence of factors such as the activity of fungi, viruses, bacteria | Average | 0.5-1*109/l |
| Heavy | Less than 0.5*109/l | ||||
If the concentration of blood cells in the blood decreases to less than 0.5*109/l, this means that agranulocytosis develops.
Features of leukopenia in women
The reasons for the decrease in the proportion of blood cells in women may not only be inflammatory processes. The female body can independently turn on protective mechanisms that provoke both a decrease and an increase in the content of blood components.
Attention! A decrease in leukocytes in a woman’s blood during pregnancy is normal, especially if there is a Rhesus conflict between mother and fetus. In the case of such a deficiency, the picture normalizes after childbirth. The condition does not require correction.
Deviation from the norm can be provoked by prolonged use of painkillers and antispasmodics on the days of menstrual bleeding. Gynecologists report that the disorder is often detected in women who uncontrollably take contraceptives.
Often the reason for changes in marks is poor nutrition, and this factor specifically affects the female gender. This is due to the fact that girls, more often than men, neglect the need for adequate nutrition in favor of diets. Against this background, vitamin deficiency with a lack of vitamin C and B appears.
White blood cells are low in a child
A general blood test is an important marker of a child’s health because it allows a preliminary diagnosis or confirmation of health status. An important indicator is the concentration of leukocytes, the norm of which varies depending on the age of the child. The disease in a child is diagnosed when the indicator decreases by 2 * 109/l from the norm for age.
List of main reasons:
- Lack of vitamins and microelements, namely: vitamin B and C, iron, iodine, zinc, selenium and protein.
- Destruction of blood cells as a result of the activity of pathogenic flora.
- Destruction of leukocytes and other blood components as a result of toxic effects.
- Bone marrow disorders.
- Genetic diseases.
Violation of the blood formula often accompanies the following processes:
- viral infections;
- lack of vitamins;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- hypotension;
- purulent and septic processes;
- tumors;
- systemic, autoimmune diseases;
- transferred radiation exposure;
- acute allergic reactions.
The cause of development in children often lies in an incorrectly defined treatment regimen for the underlying disease. Leukopenia can be the result of long-term use of antibacterial, hormonal, anticonvulsant drugs, or drugs that enhance immunity. The prescription of any drug must be agreed with the pediatrician; the consequences of self-medication can be irreparable.
What causes leukopenia
The reasons for the drop in the number of white cells are conventionally divided into 5 categories, which we will consider in more detail later in this article:
- Low intake of elements into the body for the production of leukocytes;
- Bone marrow pathologies (formation of new bodies);
- Intoxication;
- Diseases of internal organs and systems;
- Taking pharmaceutical drugs.
Lack of essential nutrients in the diet
To produce white cells, the human body needs the following vitamins and minerals:
- Thiamine (vitamin B1);
- Cobalamin (vitamin B12);
- Folic acid (vitamin B9);
- Copper;
- Iron.
If food products lack these elements, tests reveal a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells in combination with leukopenia (the body needs the same microelements and vitamins for their production).
Leukocytes drop below normal gradually, so if the indicator drops to the lower normal value, the doctor advises you to adjust the diet. If the process does not slow down after optimizing the diet, then the reasons lie in other factors or in the inability to absorb the necessary substances from food. The process is accompanied by developing anorexia and exhaustion of the body.
Bone marrow diseases
The primary reasons why the analysis shows that leukocytes are low are hidden in diseases of the bone marrow. The damaged organ produces few leukocytes, and this is reflected in the blood count. Leukopenia is caused by:
- Congenital asymptomatic bone marrow pathologies;
- Malignant tumors and precancerous conditions – myelosarcoma, myelofibrosis;
- Spread of metastases from foci of malignant tumors into the bone marrow.
The tumor, penetrating the bone marrow, replaces normal hematopoietic tissue, in which white blood cells, among others, are formed. This causes their number to become lower in the bloodstream.
Intoxication
Very often, leukocytes are low after a person is intoxicated (the bone marrow stops performing its functions for a while - it seems to “turn off”). The reasons may be drug abuse, alcohol abuse; exposure to radioactive radiation; food intoxication; poisoning with arsenic, toluene, heavy metals, mercury, benzene and similar substances. The amount of white elements in the blood becomes less if a person has undergone radiation and chemotherapy.
Diseases of internal organs and systems
During inflammatory and purulent diseases, if they occur locally, white blood cells may be completely absent from the bloodstream. This situation means that protective bodies rush to the site of the pathogenic process to carry out their function, while their number in the body as a whole can even increase due to intensive formation. Cells are reduced, down to zero, if they are completely destroyed in the process of performing their function (during its life, one cell destroys several pathogens and dies). This situation can occur if the body is attacked by viruses or bacteria.
Autoimmune diseases (immune cells destroy healthy cells of the body) provoke a decrease in the number of white cells, they destroy themselves. With HIV infection, the body's immune response is practically absent, and the mechanisms of production of cells of the protective system - leukocytes - are disrupted.
Diseases of internal organs can provoke a decrease in the number of white blood cells:
- Increased production of thyroid hormones;
- Pathologies of the spleen and liver (a kind of “base” for blood components);
- Gastrointestinal dysfunction (gastritis, colitis);
- Kidney failure.
Medicines that affect the number of white blood cells
The white cells of the circulatory system drop significantly below the minimum numbers when taking certain medications. These include analgesics (painkillers), sulfonamides, cytostatics, barbiturates, drugs against seizures, antiallergic medications, antidepressants, drugs with interferon, chloramphenicol, amidopyrine and some other pharmaceutical groups.
Symptoms of low white blood cells in the blood
If leukopenia has a physiological etiology or is mild, there are often no symptoms. The clinical picture becomes clear after the process takes a chronic course.
The violation is characterized by:
- increase in body temperature to 37-38 degrees;
- chest pain;
- tachycardia;
- hyperhidrosis;
- loss of appetite;
- joint pain;
- headache;
- increased size of lymph nodes;
- predisposition to colds.
The list of such symptoms does not allow one to accurately determine a violation of the leukocyte formula. To determine the diagnosis, you need to undergo a laboratory examination and visit specialized specialists. If the change is associated with the activity of viruses, the help of an infectious disease specialist and an immunologist is needed.
Attention! When determining a diagnosis, it is necessary to establish the reason for the decline in grades. It is important to eliminate the risk of developing cancer, bone marrow diseases, tuberculosis and HIV.
Lack of substances necessary to create new white blood cells
If leukocytes are slightly reduced or their indicator is rapidly approaching the lower limit of normal, one can suspect that the body lacks elements that ensure the synthesis of blood components.
The most common cause is a lack of the following substances:
- selenium;
- protein;
- arachidonic acid;
- folic acid;
- ascorbic acid;
- thiamine;
- iodine;
- copper;
- iron;
- cobalt;
- zinc.
Restoring the leukocyte formula in this case is simple. The patient is advised to change his own diet and balance it. You can get vitamins and microelements not only from food, but also from vitamin-mineral complexes.
Death of leukocytes in the body
There is a situation when the human body creates blood cells, but they die in the blood. This happens when pathogenic agents are introduced. Some leukocytes are directed to the source of infection and leave the vascular bed - this will affect the test results, therefore you should not donate blood for testing for ARVI and other diseases. Concentrations can also be reduced due to intoxication of the body. The reason for this is the destruction of blood cells as a result of exposure to toxic compounds.
Bone marrow dysfunction
All leukocytes mature in the bone marrow until they are released into the bloodstream. Any injuries or damage to this organ can cause changes in the leukocyte formula. The cause of bone marrow failure may be:
- poisoning of the body with poisons, alcohol;
- autoimmune diseases;
- tumor development;
- metastasis to the bone marrow;
- use of radical treatment methods.
A decrease in white blood cells due to impaired bone marrow function is quite rare, but this possibility cannot be excluded. CT or MRI as a diagnostic tool will help eliminate such a risk.
Signs of a decrease in leukocytes
Symptoms indicating that there are not enough white cells in the bloodstream are most often absent. But since the immune system is gradually depleted, then:
- the body begins to pick up infections one after another;
- weakness and low tolerance to stress appear;
- the temperature jumps to 38 degrees and above;
- Fever and chills are inevitable.
In the first few days of leukopenia:
- there are no inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx;
- no cough or wheezing;
- there may be an increase in the size and density of the tonsils, spleen and lymph nodes;
- there is a pronounced proliferation of opportunistic microflora, harmless to a healthy person. Fungal infection, herpes viruses, and cytomegalovirus are active.
All this is the result of intoxication, which the leukocytes did not eliminate in time, since their level is lower than necessary.
The danger is that with a significant decrease in the number of white cells, some ailments can quickly cover the entire body and create a real threat to life (septic shock).
Leukopenia is often caused by chemotherapy or radiation. After the sessions, characteristic signs associated with damage to the liver, spleen, intestinal tissue and bone marrow appear. These symptoms are:
- ulcerative stomatitis with death of affected tissues;
- swelling of the oral mucosa develops;
- constant diarrhea caused not by ingested food, but by necrotic processes in the intestines.
Norm
Normal values vary depending on the age and gender of the patient. The accepted indicators are presented in the table:
| Age | Indicator (*109 U/l) |
| Newborns up to 3 days | 7 – 32 |
| Up to 1 year | 6 – 17,5 |
| From 1 to 2 years | 6 – 17 |
| From 2 to 6 years | 5 – 15,5 |
| From 6 to 16 years | 4, 5 – 13,5 |
| 16 – 21 years old | 4,5 – 11 |
| From 21 to 60 years (men) | 4,2 – 9 |
| From 21 to 60 (women) | 3,98 – 10,4 |
| 60 and older (men) | 3,9 – 8,5 |
| 60 and older (women) | 3,7 – 9 |
You should not try to interpret the results of the study yourself. The reasons for misrepresentation of information may be different. It is worth remembering that laboratories now use different research methods, so the results may differ significantly.
Decreased white blood cells among children and adults
The normal white blood cell count among children is:
Up to a year: 9.2-18.8 *109/liter;
1-3 years: 6-17*109/liter;
script async src="//pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js">
3-10 years: 6.1-11.4*109/liter;
Teenagers: 4-8.9*109/liter.
Low white blood cells are dangerous because they can lead to the development of serious pathologies, for example, sepsis; tuberculosis and others (from the above chapter).
In this case, the disease may be accompanied by fever, weakness, bleeding gums, headache, and pale skin.
To normalize the level of leukocytes, the pediatrician studies not only the test results, but also pays attention to the individual characteristics of the body and the age of the patient. If a pathology is suspected, the pediatrician prescribes an examination by a hematologist, neurologist, or infectious disease specialist.
Treatment most often includes taking medications, diet, taking vitamins and other methods, which you will read more about in the next chapter.
But a reduced number of leukocytes is not always associated with the disease. It is worth highlighting other reasons for this decrease:
- large amount of physical activity;
- severe stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- recovery period after influenza, rubella, measles;
- lack of vitamins;
- low pressure.
Leukopenia among adult patients
In men , the leukocyte norm is 4.5-11*109/liter. A decrease in indicators indicates that the body is in an exhausted state and the immune system cannot cope with the viruses and bacteria that have entered the body.
However, most patients do not pay attention to the symptoms of leukopenia, since they regard the symptoms as simple overwork. Meanwhile, leukopenia is rapidly developing. To confirm leukopenia, the patient must take a general blood test and, if there is a significant deviation, immediately consult a doctor.
Important! With age, the number of white blood cells decreases.
In female , a decrease in leukocytes occurs more often than in men. The leukocyte norm among women ranges from 3 to 10*109/liter. Minor failures occur for a number of reasons:
- Binge eating.
- Menstruation.
- Chronic illness.
- Ovulation.
- Taking contraceptives.
- Climax.
- Strict diet.
- Frequent stress.
- Change of climatic conditions.
A significant decrease in leukocytes contributes to the development of pathologies discussed in the previous chapter.
A special group of patients are pregnant women . Most often, a decrease in leukocytes is observed due to toxicosis. In this case, the doctor may prescribe a vitamin complex to the woman.
But if the temperature rises, the body is exhausted, or headaches, it is worth taking a blood test again, because low white blood cells can cause the development of one of the following diseases: influenza; malaria; viral hepatitis; gastritis; renal failure; rubella.
All such pathologies negatively affect the health of mother and child. Therefore, a pregnant woman must follow all doctor’s instructions, including: regularly undergo examination; take the necessary tests; follow the doctor's recommendations; diversify your diet; walk more.
For more information about leukocytes, watch the following video:
.
Diagnostics
The following diagnostic procedures will help identify leukopenia:
- general blood test with determination of platelets and red blood cells;
- analysis for blast cells of bone marrow and peripheral blood;
- determination of antinuclear antibodies;
- determination of rheumatoid factor;
- liver tests;
- allergy tests;
- bone marrow puncture.
Attention! The doctor can supplement the examination regimen with other manipulations and tests.
ethnoscience
If leukocytes are low in an adult, you can resort to using traditional methods of treatment. Such drugs should be taken in conjunction with medications selected by a doctor, following the dosage regimen. Medicinal plants can be a source of allergic reactions, so before you start taking them, you need to refute the risk of an immune response.
- Green bean juice. Take 2 tbsp. l 3 times a day.
- Infusion of wormwood and propolis. Dry the horsetail herb and grind it in a coffee grinder. Pour 2 tbsp. l of dry raw materials 500 ml of boiling water and leave for 2 hours, then strain. Take the product 3 times a day before meals, add 20 drops of propolis tincture to a glass of water before taking.
- Take oat decoction regularly. Brew 2 tbsp in 500 ml of boiling water. l grains and leave for 3 hours, covered with a towel. Take the strained medicine 3 times a day, 100 ml. Store the rest in the refrigerator.
Attention! The listed recipes cannot be considered as a treatment regimen. Correction methods are selected by the doctor; auxiliary techniques can be used after a preliminary consultation.
Treatment methods
What to do if leukocytes in the blood are low? The most important method of increasing the number of white cells in the blood is to follow a therapeutic diet. The diet should be enriched with B vitamins, amino acids, choline, proteins, while limiting the consumption of carbohydrates.
The following products should be present in the diet:
- Grenades;
- Raw vegetables, herbs, fruits, berries, in particular red ones;
- Chicken eggs;
- Seafood;
- Oats, buckwheat;
- Legumes;
- Beet juice;
- Dry red wine;
- Walnuts;
- Caviar.
Drug treatment:
- Multivitamin complexes: folic acid, thiamine, pyridoxine.
Folic acid, 1 tablet twice a day;
- Agents that stimulate the production of white cells: methyluracil, pentoxyl, leucogen.
Leukogen, 1 tablet 3 – 4 times a day;
- Means to strengthen the immune system: tincture of Eleutherococcus, Echinacea.
Eleutherococcus tincture, 20 – 30 drops per glass of water;
- Agents that enhance the production of leukocytes by the bone marrow: filgrastim, leucomax.
Leukomax, 1 capsule three times a day;
- Immunostimulants - to strengthen the immune system: comedon, immunal, estifan.
Immunal, 1 tablet 3 – 4 times a day.
The medications and course of treatment are prescribed by the doctor!
Diet
The basis of the patient’s diet should be the following products:
- hot dishes with vegetable, meat or fish broth;
- compotes, juices, fruit drinks from natural fruits;
- fermented milk and dairy products;
- steam cutlets, meatballs, meatballs;
- fruits vegetables;
- porridge and pudding;
- fish.
Meals should be fractional, the body should not experience hunger. To do this you need to eat 5-6 times a day. The calorie content of the diet for a woman is 3000 kcal, for a man – 3300-3500 kcal. If leukocytes are reduced, strict diets should be abandoned - this is the basic rule, nutrition should be complete, but proteins should predominate in the diet.
How to prevent low white blood cells
When there are few leukocytes in the blood, but their concentration does not fall below the limit, methods for preventing leukopenia will help. The list of main recommendations includes:
- normalization of diet;
- refusal to use GCS and hormonal contraceptives;
- complete rest;
- restoration of the emotional background.
People with a predisposition to blood diseases should undergo periodic examinations to minimize the risk of health problems.
How to increase white blood cells at home
To normalize well-being, a complex effect is necessary. First of all, you need to see a doctor and undergo an examination. Treatment can be selected only after determining the causes of the disease.
Attention! If the reason for the decrease in leukocytes in the blood of an adult patient is a violation of the bone marrow, attempting home treatment is prohibited.
Normalizing your diet will help you feel better. The diet must be complete. If it is difficult to create a diet on your own, it is better to visit a nutritionist, because this point is key and the effectiveness of the medication regimen depends on it.
Function and types of leukocytes
Like all other cells in the body, leukocytes or white blood cells have their own personal responsibilities. Moreover, their function is very important for ensuring normal human life, and it consists in protecting him from pathogenic microbes and various toxins. Leukocytes are the first to react to the introduction of pathogens into the body, and concentrate around them, that is, they surround them in a peculiar way.
Then they are neutralized and subsequently absorbed, dying in the process. In a healthy person, in most situations, the reaction to the ingress of foreign agents is very violent and is accompanied by a rapid increase in leukocytes in the blood, as they rush to do their job.
This means that the immune system is strong enough and the defense system is functioning at the proper level. In such patients, before the introduction of pathogens, the white blood cell count in the blood test will most likely be within the normal range.
In order for the immune system to function at the proper level, new ones are constantly produced to replace dead white cells, thereby maintaining the balance of blood components. If at some stage of synthesis disturbances occur, then their content becomes less than normal, which leads to a deterioration in the body’s protective capabilities.
Reference! A long-term and significant decrease in leukocytes is dangerous because it increases the likelihood of developing many diseases, because the body becomes very vulnerable even to simple infections.
Lifestyle of a patient with leukopenia
In general, the lifestyle of a patient diagnosed with leukopenia does not differ from the rhythm of life of a healthy patient. The only point that you need to pay close attention to is protecting the body from the activity of viruses and bacteria, because against the background of leukopenia, immunity is significantly reduced.
Good nutrition is also necessary. If a person feels unwell or lacks strength, he needs to give up active physical activity. Walking in the fresh air is beneficial.
When leukocytes in the blood are low, it is worth undergoing a full examination. The reason for this change is a variety of diseases that progress in a latent form. Since leukopenia leads to a decrease in immunity, all viral, bacterial and fungal diseases will be especially severe and therefore can cause irreversible consequences.