No complex preparation is required for laparoscopy. Before the operation, the doctor must check the patient's condition to ensure that there is no possible risk of complications. The patient needs to undergo tests, for which the doctor gives directions. Without them, the patient will not receive permission for laparoscopy.
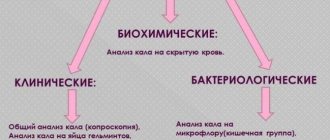
List of tests for laparoscopy
Basic tests before laparoscopy, the results of which are needed for admission to surgery:
- Complete blood count (CBC).
- Biochemical analysis.
- General urinalysis (UCA).
- General smear on the flora.
- Coagulogram.
- Test for HIV, hepatitis B and C.
- Wasserman reaction (test for syphilis).
- Oncocytology.
- Electrocardiogram.
- Ultrasound.
- Blood type, Rh factor (to eliminate errors and be safe during laparoscopy).
Depending on the presence of other diseases or the purpose of laparoscopic surgery, the doctor decides what additional tests and studies need to be performed.
Preoperative preparation may include visits to other specialists to evaluate contraindications. For diseases of the cardiovascular, respiratory, endocrine and gastrointestinal systems, the patient is first sent to see other doctors to confirm or refute contraindications.
Additional research:
- Fluorography.
- Examination of stool for the presence of helminths.
Each general test (blood, urine, smear) is valid for 2 weeks . After the expiration of the period, the patient must be tested again. A smear for oncocytology and stool for helminths are valid for a year. The Wasserman reaction, blood test for HIV and hepatitis are valid for 3 months. The validity period of an ECG is 1 month, fluorography is 11 months.
Particular attention is paid to the number of platelets and the content of prothrombin, fibrinogen, bilirubin, urea, glucose, and total protein in the blood.
General blood analysis
Clinical analysis (CBC) is a diagnostic method in which blood is taken from the ring finger. The goal is to identify anemia or inflammatory disease.
The main indicators that pay close attention before laparoscopy (including diagnostic):
- leukocytes. A decrease in indicators indicates leukopenia, an increase indicates any inflammatory disease in the body.
- hemoglobin. A decrease in indicators indicates insufficient oxygen supply to the body, an increase indicates heart defects, smoking and dehydration.
- red blood cells. A decrease indicates pregnancy, anemia, blood loss, destruction of red blood cells, and an increase is observed with neoplasms, polycystic disease, and hormonal disorders.
- platelets. A decrease in indicators indicates a diseased liver, bacterial infections, anemia, hemolytic disease, immune and hormonal diseases. An increase is observed after operations, with cancer, benign tumors, and inflammation.
- ESR. A decrease in indicators indicates an increase in albumin (a group of proteins), bile acids, and circulatory failure. An increase is observed with a decrease in albumin, red blood cells, an increase in fibrinogen, as well as in infectious and inflammatory diseases, liver and kidney damage, fractures, postoperative periods, and endocrine disorders. If a woman is found to have an increase in ESR, it is necessary to undergo a gynecological examination and check the gastrointestinal tract system.
- hematocrit Low levels indicate a deterioration in blood viscosity and anemia. An increase is observed with dehydration, lack of oxygen, and congenital heart defects.
The doctor evaluates all indicators and discrepancies from the norm. For example, if leukocytes, red blood cells, ESR and platelets are elevated, and other indicators are within normal limits, then we will talk about the presence of an inflammatory process and neoplasms, due to which laparoscopic treatment methods are planned. If red blood cells, platelets, and hematocrit are low, and other indicators are within normal limits, then the patient most likely has anemia.
Interpretation of biochemical blood test. Click to enlarge
Blood chemistry
This diagnostic method before laparoscopy allows us to judge the functioning of all organs. The main goal is to check the condition of the heart, endocrine system, liver and kidneys. It reveals:
- Total protein. A decrease indicates starvation, liver disease and serious bleeding of an acute and chronic nature. Increase – about dehydration, oncology, acute infections.
- Bilirubin. A decrease indicates the use of certain groups of drugs, alcohol and coffee, and coronary heart disease. Increase – about hepatitis, acute infections and viruses, tumors and cirrhosis of the liver, anemia, inflammatory diseases.
- Urea. A decrease indicates fasting or strict vegetarianism, pregnancy, poisoning with toxic substances, and impaired liver function. Increased – kidney disease, cardiovascular failure, severe blood loss, excess protein intake.
- Fibrinogen. A decrease indicates the formation of microthrombi, toxicosis, hypovitaminosis, poisoning, and liver cirrhosis. Increase – about pregnancy, heart attack, diabetes, pneumonia, tuberculosis, oncology and infectious diseases.
- Glucose. A decrease indicates poor nutrition, starvation, excessive stress, bad habits, malignant tumors, excessive consumption of baked goods, fast food and sweets. An increase occurs with diabetes mellitus, pancreatitis, cancerous tumors, diseases of the endocrine system, and metal poisoning.
Analysis of biochemistry results provides an almost accurate picture of the patient’s body condition.
General urine analysis
Normal urinalysis results. Click to enlarge
OAM is the simplest and most painless diagnostic method before laparoscopy, with the help of which acute and chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system and other inflammatory diseases are determined. Together with blood tests, the overall picture will allow you to better understand the functionality of the body.
The main values of TAM, which are given attention before performing a laparoscopy operation:
- Amount of urine. A decrease is observed in the initial stages of acute renal failure, polycystic disease, and chronic kidney disease. Increased in diabetes mellitus, acute renal failure, heavy drinking.
- Color. A specific color change, depending on the shades, is caused by urolithiasis, tumor decay, red blood cells in the urine, liver disease and consumption of coloring foods.
- Transparency. Cloudy urine is characteristic of cystitis and pyelonephritis.
- Smell. Harshness or a specific odor is observed with hereditary diseases, increased acidity or diabetes.
- Reaction. High acidity indicates previous infectious diseases.
- Protein. An increase in the amount is observed with inflammation and kidney disease.
- Glucose. Presence in urine indicates diabetes mellitus.
- Leukocytes. Indicate an inflammatory process in the body.
A general urine test is necessary to assess the functioning of the genitourinary system and kidneys.
It is important to know
In the abdominal cavity, in addition to diagnostic procedures, the laparoscopic technique is used for therapeutic purposes: drainage of the abdominal cavity, cholecysto-, gastro-, colonostomy, appendectomy and others.
In gynecology, laparoscopy as a surgical approach is widely used in the treatment of many diseases: infertility, uterine fibroids, adnexal adhesions, polycystic ovaries.
With invasive interventions, which include laparoscopy, there is always a risk of developing certain consequences (purulent infection, bleeding). To minimize the likelihood of complications, an examination is carried out with tests to make sure that the patient does not have acute infectious diseases, heart disease, lung disease, or a tendency to bleed.
A standard set of studies has been developed that are mandatory before any operation. The doctor decides what additional tests need to be taken before laparoscopy, depending on the purpose of the procedure (diagnostic, therapeutic).
General smear
A flora smear is a method for diagnosing diseases and assessing the state of the microflora of the vagina, urethra and cervical canal. The goal is to identify infections and inflammations. Analysis shows:
- Leukocytes. Enlargement is a sign of inflammation or pregnancy.
- Lactobacilli. A decrease in their number is a symptom of bacterial vaginosis.
- Yeast. A high rate indicates thrush.
- Key cells. Enlargement is a sign of gardnerellosis.
- Leptothrix. Occurs when mixing infections: bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis, chlamydia and trichomoniasis.
- Mobiluncus. The appearance in the results is a sign of candidiasis or bacterial vaginosis.
- Trichomonas. The appearance is a symptom of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Gonococci. The appearance is a sign of gonorrhea.
- Escherichia coli. An increase in the number indicates the onset of bacterial vaginosis, neglect of intimate hygiene, and stool getting into the smear.
- Staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci. Enlargement is a sign of infection.
A flora smear assesses the general condition of the reproductive organs.
Decoding the coagulogram. Click to enlarge
Pros and cons of laparoscopy
In modern gynecology, laparoscopy is perhaps the most advanced method for diagnosing and treating a number of diseases. Among its positive aspects is the absence of postoperative scars and postoperative pain, which is largely due to the small size of the incision. Also, the patient usually does not need to comply with strict bed rest, and normal well-being and performance are restored very quickly. In this case, the period of hospitalization after laparoscopy does not exceed 2 - 3 days.
During this operation, there is very little blood loss and extremely little trauma to body tissue. In this case, the tissues do not come into contact with the surgeon’s gloves, gauze napkins and other means that are inevitable in a number of other operations. As a result, the possibility of the formation of the so-called adhesive process, which can cause various complications, is minimized. In addition, an undoubted advantage of laparoscopy is the ability to simultaneously diagnose and eliminate certain pathologies. At the same time, as mentioned above, organs such as the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, despite surgical intervention, remain in their normal state and function in the same way as before the operation.
Coagulogram
This test before laparoscopy examines the blood clotting system, regulated by the endocrine and nervous systems. The goal is to determine how the operation will go, whether the surgeon will be able to stop the bleeding and save the patient in an unforeseen situation. Particular attention before the operation is paid to the following indicators:
- PT and INR. A decrease in readings may be a sign of thrombosis. Increased – liver diseases, intestinal dysbiosis, amyloidosis, nephrotic syndrome, etc.
- APTT. Shortening the value is a sign of increased coagulability. Lengthening – insufficient coagulation, severe liver disease, etc.
- PTI. A decrease is observed with increased coagulability during pregnancy, thrombosis, cirrhosis, and hepatitis. Increased – deficiency of blood factors, vitamin K, etc.
- Fibrinogen. A reduced amount is a symptom of congenital deficiency, liver disease, bone marrow damage, prostate cancer, etc. An increased amount is observed during infections, injuries, stress, menstruation, heart attacks, pregnancy, lung cancer, and also in the postoperative period.
- RFMK. An increase occurs with sepsis, thrombosis, shock, complicated pregnancy, etc.
Not all doctors are able to decipher this analysis.
How to properly prepare for laparoscopy
The main goal of research before laparoscopy of ovarian cysts, interventions in the gallbladder and other organs is to identify hidden pathologies that can lead to complications in the postoperative period. In addition, it is important to bring the body into a state in which the doctor can perform surgical procedures with minimal difficulty.
In order for the studies to show a reliable result, and the body to be ready for intervention, preparation for laparoscopic surgery begins with correcting the patient’s diet:
- Foods that cause fermentation in the intestines and flatulence are removed from the menu - all types of cabbage, black bread and fresh milk, vegetables and fruits that contain a lot of fiber, as well as legumes. Such restrictions are especially important if laparoscopy is performed on the abdominal organs.
- At least a week before laparoscopy, avoid alcohol, strong coffee, and energy drinks. These products thin the blood and may cause bleeding during and after the procedure.
- The day before surgery, you are allowed to consume only clear broth, fermented milk drinks and water. Eating should be stopped at least 16 hours before surgery. Stop drinking 6-8 hours before laparoscopy.
- The evening before the operation, the doctor may advise you to do a cleansing enema and, if necessary, repeat the procedure in the morning 2-3 hours before the intervention.
As for taking tests for laparoscopy, they should be taken no earlier than 2 weeks before the scheduled procedure. Many studies also require preparation: following a diet 2-3 days before collecting biological material, taking tests on an empty stomach, etc.
Cytological smear analysis
Oncocytology is a method for diagnosing oncology in the reproductive organs. The goal is to detect the presence of cancer cells or other viral diseases.
Abnormalities in the analysis do not always imply the presence of cancer. A positive result may be a consequence of pathologies:
- HPV;
- chlamydia;
- trichomoniasis;
- gonorrhea;
- fungal diseases.
If infections are found, therapy is prescribed, after which the test is repeated to monitor the dynamics.
Types of laparoscopy for ovarian cysts
Laparoscopic surgery is a direction that is dynamically developing in modern medicine. In the presence of an ovarian cyst, there are three main types of laparoscopic operations:
- Resection is a method that minimizes the traumatic effect on healthy ovarian tissue. The essence is to cut the ovarian membrane, isolate and remove the formation.
- Enucleation - during surgery, the cystic formation is placed in a special plastic container. This prevents rupture of the formation in the abdominal cavity, as well as the potential spread of the tumor process. The surgeon carefully removes the cyst without affecting the ovarian tissue.
- Ovariectomy of the ovary is a method of removing the cyst along with the ovary. It is used for large formations, as well as suspected malignant process. The doctor isolates the ovary and fallopian tube, ligates and removes them in a special container.
When choosing the type of laparoscopy, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital take into account
nature, size and location of the ovarian cyst. With timely diagnosis of the disease, it is possible to apply organ-preserving treatment, which is especially important during reproductive age.
Electrocardiogram and ultrasound
An ECG is prescribed to study the heart's function in order to assess the patient's readiness for laparoscopy. Contraindications to laparoscopic surgery are diseases of the heart, respiratory system, liver and kidneys.
If surgery is prescribed due to diseases of the female organs, a pelvic ultrasound is performed. In other cases, an abdominal ultrasound may be prescribed.
No matter how many studies the doctor prescribes, they are carried out as soon as possible. CBC, coagulogram, Wasserman reaction, analysis for Rh factor, blood group, HIV and hepatitis - the material is taken from a vein once, checked for all the necessary indicators, and this already means that half of the tests have been passed.
Methodology
5 days before the day of surgery, it is advisable to adhere to a diet with limited foods that contribute to increased gas formation in the intestines, namely, eat less cabbage, legumes, and black bread.
On the eve of the operation, a cleansing enema is performed, and if necessary, also in the morning.
12 hours before the intended intervention, you should not take food or water.
Next about the intervention itself:
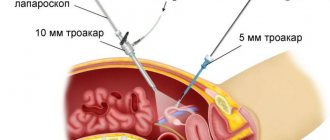
- To perform the laparoscopy itself, general anesthesia is required.
- After the patient has been put under anesthesia, the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide, thus achieving the best view of the abdominal organs and providing a large space for manipulation.
- A telescope with a camera and a special illuminator and manipulative instruments are inserted through small holes on the anterior abdominal wall.
- After the surgeon has carried out all the necessary manipulations, the instruments are removed from the abdominal cavity, and the holes for their insertion are sutured.
Hysteroscopy differs from laparoscopy in its technique. The hysteroscope is inserted into the uterus through the vagina. Laparoscopy is an invasive method of examining the uterine cavity and neighboring organs by puncturing the abdominal wall. Laparoscopy is always performed under general anesthesia, and hysteroscopy under local anesthesia.
Hysteroscopy is an internal examination of the organ; laparoscopy allows you to examine the outer surface of the uterus and adjacent organs.
In what cases are internal and external examinations of the uterus performed?
Hysteroscopy (internal diagnostics) is prescribed for:
- detection of papillomas and growths on the mucous membrane;
- identifying the causes of irregularities in the menstrual cycle;
- removing the old coil and mucous residues after cleaning;
- identifying the cause of miscarriages;
- endometrial studies;
- complications of pregnancy;
- research into the causes of other pathologies.
Diagnostics are also prescribed after an unsuccessful IVF protocol, periodic uterine bleeding, and congenital anomalies of the reproductive organs.
Laparoscopy is prescribed for:
- diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy;
- research into the causes of ovarian pathology;
- studies of neoplasms on the outer shell of the organ;
- performing organ perforation;
- other gynecological problems.
After the operation is completed, the puncture area is sutured; the stitches must be removed after 12-14 days in the hospital. Both procedures are carried out after examination of the tests in the laboratory. Since laparoscopy involves the introduction of anesthesia, preliminary preparation is necessary - refusal of food on the eve of diagnosis.
Contraindications to laparoscopy and hysteroscopy:
- malignant neoplasms;
- severe obesity;
- adhesions after previous abdominal operations;
- hernia.
Is there a risk of complications after surgery? Complications can appear after any surgical manipulation of internal organs, it depends on the severity of the existing pathology and the characteristics of the woman’s body. However, the statistics of complications is small.
In order not to provoke trouble after both procedures, you should not use tampons during menstruation, take hot baths or steam in a sauna. Douching and any manipulation of the genitals without the approval of a gynecologist are prohibited. These restrictions must be adhered to until your health is fully restored.
Diagnostic laparoscopy in gynecology is used to determine the causes of the disease. Often diagnosis is combined with treatment. How long laparoscopy in gynecology lasts is determined by the type of disease and the qualifications of the surgeon.
Operations in gynecology that are performed laparoscopically:
- determining the causes of infertility;
- detection of the source of prolonged pelvic pain;
- removal of a cyst, tumor;
- treatment of endometriosis;
- Fallopian tube ligation;
- elimination of ectopic pregnancy;
- restoration of patency of the fallopian tubes;
- removal of the uterus and appendages;
- elimination of adhesions;
- ovarian apoplexy;
- torsion of the cyst.