Since childhood, we have been accustomed to the procedure of taking blood from a finger. The reason is that it is one of the most common diagnostic measures. After all, almost every pathogenic change in our body will be reflected in the composition of the blood. Material is taken from the finger for a general (general clinical) study. The procedure is mandatory both for various preventive medical examinations, checks before vaccination, and for diagnosing a number of diseases. It is interesting for the person being examined to know what a finger prick blood test shows before the doctor’s conclusion. We will present information that will help lift the veil of secrecy.
What kind of research is this?
What does a finger prick blood test show? First of all, sufficient data for the doctor to assess the functional state of the patient’s vital systems. This is a blood sample taken from a capillary - the smallest vessel that is responsible for gas exchange between local tissues. Note that the sample may differ in some respects from the material taken from the vein.
A finger prick blood test is considered one of the most economical, simple and accessible today. A sample of material for research can be submitted to almost any clinic.
What does a finger prick blood test show? This is a quick diagnosis of various types of pathologies. Carried out by a specialist based on a number of indicators:
- Blood sugar concentration.
- Hemoglobin content.
- Platelet count.
- Leukocyte count.
- Determination of blood clotting.
- ESR is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
What does a finger prick blood test show first of all? In domestic medicine, it is valued for information about blood glucose, blood cell ratio, and hemoglobin concentration.
Basic analysis data and their norm
Norms depend on age and gender. All biofluid indicators have a wide range of values, so doctors use definitions such as normal and reference values. The normal amount indicates the absence of pathologies, and the reference amount indicates the average indicator of this blood value for the population.
The concentration rate according to the table is as follows (woman/man):
| Index | Men | Women |
| Hemoglobin cells | 125-140 g/l | 135-160 g/l |
| Red blood cells | 3.6-4.6 g/l | 4-5 g/l |
| ESR | 0-20 mm/hour | 0-20 mm/hour |
| Platelet cells | 180-320x109/liter | 180-320x109/liter |
| Sugar level | 3.4-5.6 mmol/l | 3.4-5.6 mmol/l |
Prothrombin time – 10-16 seconds. Leukocyte cells:
- 45-75% neutrophilic;
- 0-5% eosinophilic;
- 0-1% basophilic;
- 20-40% lymphocytic;
- 3-9% monocytic.
When assessing blood parameters, the gender, age and individual characteristics of the patient are taken into account. “Normal” only indicates the basic, general range.
What diseases does the study help identify?
What does a complete finger blood test show? The study helps to identify the presence of a fairly wide range of diseases and pathologies:
- Anemia. It is determined by a doctor by the lack of iron, red blood cells, and hemoglobin in the blood mass. Or by the ratio of hemoglobin and blood cells.
- Problems with blood clotting. The number of platelets and the time spent by the body on this process are assessed.
- Leukemia. The development of a dangerous disease is indicated by the appearance of abnormal blood cells in the material sample.
- Diabetes. The results of a finger prick blood test alone are not enough to make such a serious diagnosis. However, the test helps monitor blood glucose levels. It is often performed independently by the patient using a special device.
- Inflammation, allergies, infectious diseases. Diagnosed based on the ratio of ESR and leukocytes.
- Genomic, chromosomal, gene pathologies.
A child over one year old must donate blood on an empty stomach or can be fed
A general blood test for children over one year old is taken on an empty stomach - this is an unbreakable rule. It applies to both children and adults. The attending physician needs real indicators of how the patient’s body works.
If there is a suspicion of an infectious process, inflammation, or exacerbation of a chronic disease, then this is exactly what the doctor will confirm or refute through analysis. If the patient is getting better, this should be visible in the study results.
Example: a child was fed before the study, food components, when absorbed into the blood, caused a change in its composition, affecting viscosity, leukocyte formula, the ratio of proteins, fats, and more. In the transcript, the doctor sees signs of an inflammatory process that are not actually there. Therapy is prescribed that is unnecessary and dangerous for the patient. This outcome will not please any parent.
It’s good if the doctor finds out the reasons for the false readings. If not, then additional examinations and procedures may be prescribed, which is tiring for the baby and ineffective in general.
An exception is made only for young patients suffering from diabetes mellitus and pancreatitis (we recommend reading: features of diabetes mellitus in children and treatment). Long breaks between meals and donating blood on an empty stomach are contraindicated for them. Before blood tests, such children are recommended to eat a small portion of cereal porridge with water, fresh vegetables or crackers, and cheese.
The conclusion is simple - all other categories of children (over 1 year old) undergo a general blood test strictly on an empty stomach, subject to simple rules
Children are prepared in advance for the procedure and its importance is explained. To make everything go smoothly, the visit to the laboratory is made early in the morning.
Then the baby can and should be fed.
Preparing for the test
Taking a blood sample from a finger prick does not require any special preparation for the procedure. The general consensus is that the procedure is best performed early in the morning and on an empty stomach. Only clean drinking water without impurities and gas is allowed. But doctors testify that a general clinical analysis is completed within a day.
Why is it important to abstain from eating for 8-12 hours? The diet can affect the results, especially if it is fatty, spicy, canned food, sausages, sauces, spices, etc.
It is not recommended to smoke less than an hour before the procedure. More than a day must pass after drinking alcohol. If you took sunbathing, went for physical therapy, or had an X-ray examination, do not forget to warn a specialist about this.
How to prepare properly?
The analysis will show a reliable result only if you prepare for it correctly. Is blood donated on an empty stomach or not? Treatment rooms in government institutions are open strictly in the morning. You cannot have breakfast before taking blood. In private clinics you can donate blood at any time.
The main principles of preparing for blood collection are as follows:
- The day before, he recommends avoiding foods rich in fats.
- You should not drink alcohol 1-2 days before donating blood.
- Immediately before visiting the treatment room, you should refrain from smoking,
- It is recommended to avoid stressful situations and physical activity the day before,
How is blood drawn?
Let's analyze a general finger blood test as an event for the patient:
- The specialist selects a finger to take a sample. As a rule, it is nameless. Why? He participates less than others in the patient’s physical activities.
- The puncture site and adjacent areas of the skin are treated with a special antiseptic (disinfecting) solution.
- The skin is pierced with an applicator or blade.
- The first drop of blood is usually removed with a cotton swab. The subsequent ones in the required volume are collected with a special tube.
- Blood samples are placed by a specialist on a glass slide in a test tube.
- The puncture site is treated with an antiseptic, alcohol solution, and a tampon is applied to it.
As a rule, the procedure does not take more than 2 minutes. Modern applicators help to perform it as painlessly as possible for the patient.
Which finger is best to take blood from?
Why is it common to take blood from the ring finger? The choice is due to the fact that this finger bears less physical stress. Injury to the damaged area of skin is unlikely. You can also take blood from your middle or index finger. This is practiced if plasma donation is carried out on a regular basis.
Any damage to the skin can lead to the spread of infection. The anatomical location of the index, middle and ring fingers eliminates the possibility of infection spreading to the hand due to the presence of an internal septum. Infection from the little finger or thumb spreads faster.
Important indicators
What tests does blood from a finger test show? These are the following indicators:
- Plasma cell level. They are responsible for the production of antibodies in response to the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Leukocyte formula. The number of each of the five types of leukocytes in the blood of the subject. Important here are neutrophils, monocytes, responsible for attacking and absorbing harmful microorganisms. Eosinophils are responsible for the production of immunity, and lymphocytes identify and remember antigens - foreign elements.
- The number of white blood cells responsible for protecting the human body from viruses and infections.
- Thrombocrit. The ratio of the volume of blood mass to the number of platelets it contains.
- ESR. Assessment of the ratio of protein fractions of blood plasma.
- Platelets. The situation with the cells responsible for blood clotting.
- Reticulocytes. The content of “embryos” of red blood cells in a blood sample, which “grow up” under the influence of a certain hormone.
- Red blood cells. The volume of red cells in the blood is the bulk of its mass.
- Color index. This section demonstrates the saturation of red blood cells with hemoglobin.
- Hemoglobin. An important element responsible for transporting oxygen to all cells in the body. In addition, it takes carbon dioxide from them and delivers it back to the lungs.
Types of fencing tools
It would be good to know in advance how the biofluid is taken for analysis. The level of pain depends on the device. Typically, this role is performed by a scarifier for collecting blood. This is a very thin plate of steel with a sharp tip. When donating, the fingertip is punctured and the biofluid comes out.
For children, a special device is used that reduces pain to a minimum. It's called a lancet. The piercer is a special needle, located in a unique way, that presses evenly on the finger. Using the lancet is easy. The device works by contacting the skin or by pressing a button.
It is easy to take from newborns. The laboratory technician uses the Komarik kit for a painless test. The set includes four disposable needles. The mechanism makes it possible to prick with a needle painlessly so that the baby does not feel anything. Advantages of a lancet over a scarifier:
- Quick to use.
- No risk of bruising.
- No pain.
- Possibility of use at home.
Externally, the device does not cause fear, which leads to reliable results.
What does a deviation from the norm indicate?
Let's look at some deviations from the norm:
- Increased levels of hemoglobin and red blood cells. Diseases of the heart, lungs, dehydration, pathologies of the hematopoietic organs, and the renal system are suspected.
- Reduced levels of red blood cells and hemoglobin. Leukemia, anemia, large-scale blood loss. Lack of certain vitamins or iron.
- Deviations from the norm in the color indicator. Diagnosis of one or another type of anemia. Increased - deficiency of folic acid, vitamin B12. Decreased - lead poisoning, iron deficiency, anemia during pregnancy.
- Reticulocytes. Their norm is monitored during treatment with iron, vitamins B12, folic acid - to stabilize the course. Spontaneous elevated levels indicate hemolytic anemia, malaria, autoimmune diseases, metastases of a cancer tumor in the bone marrow. Spontaneous decreased levels are a consequence of kidney disease.
- A high platelet level indicates a recent operation, removal of the spleen, or heavy physical activity. Low level - lupus erythematosus, anemia, congenital blood diseases. Sometimes this is a consequence of prematurity or a recent blood transfusion.
- A high ESR rate is a consequence of the inflammatory process and infection. In women, it indicates the beginning of menstruation, also typical from the 5th week of pregnancy.
- An increased level of white blood cells is observed after injuries, burns, operations or vaccinations. If it is observed constantly, it may indicate oncology or an inflammatory process. A low number indicates leukemia or infection.
- Now the leukocyte formula. Elevated levels of neutrophils and lymphocytes indicate infection, monocytes indicate a tumor, autoimmune diseases, basophils indicate chickenpox, tuberculosis, influenza, and eosinophils indicate helminthic infection and allergies. A low level of neutrophils indicates anemia, lymphocytes - autoimmune pathologies, lymphocytes - an immunodeficiency state, eosinophils - purulent infections, basophils - Cushing's syndrome, monocytes - oncohematological pathology.
- The presence of plasma cells in the blood indicates the presence of viral infections. An exception is for children - single indicators in their blood do not indicate the disease.
What does a general blood test show, detailed, main indicators
Let's find out what a general blood test shows and why it is taken. A general hematological blood test is an important diagnostic criterion that reflects the response of the hematopoietic system to the action of physiological and pathological factors.
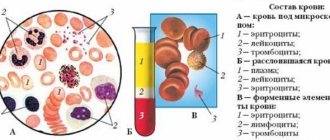
CBC is of great importance in establishing a diagnosis, especially in diseases of the hematopoietic organs. The UAC covers the study of the following indicators:
- hemoglobin (Hb) level
- red blood cells
- leukocytes
- platelets
- color index
- leukoformula calculation
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate
If necessary, clotting time and bleeding duration are examined. In many laboratories, analysis is carried out on hematology automatic analyzers. They immediately determine up to 36 parameters.
Hemoglobin, functions and clinical significance
Hb is a blood pigment and is the core component of the red blood cell. Its role is to transport O2 from the lungs to organs, tissues and remove carbon dioxide.
The hemoglobin level performs the main function in the diagnosis of anemia of various etiologies. At the same time, his performance decreases.
An increase in Hb concentration occurs with erythremia, symptomatic erythrocytosis, congenital heart disease, and cardiopulmonary failure. An increase in Hb is combined with an increase in the number of red blood cells. With acute blood loss, there is a significant decrease in Hb to 50 g/l. The minimum pigment content in the blood compatible with life is 10 g/l.
If you have problems with back pain, I suggest you find out what spinal osteoporosis is, symptoms and treatment, Nordic walking with poles is also very useful, the benefits and harms of which are revealed in the article - follow the link.
Red blood cells, physiological role in the body
Red blood cells occupy the main share in the mass of blood cells and contain hemoglobin. The main function is the transfer of O2 with the assistance of Hb. In addition, red blood cells participate in:
- in the absorption of lipids, amino acids, toxins
- in enzymatic processes
- when regulating the acid-base balance of the body
- in regulating plasma ion equilibrium
A decrease in the number of red blood cells is one of the signs of anemia. In addition to anemia, red blood cells decrease when the volume of blood in the bloodstream increases, for example during pregnancy.
An increase in the number of red blood cells (erythrocytosis) is characteristic of erythremia. CBC in newborns will show erythrocytosis during the first 3 days of life. In adults, erythrocytosis is observed during fasting, profuse sweating, and climbing to altitude.
Leukocytes: their physiological role in the body
The number of leukocytes (L) in the bloodstream is an important diagnostic criterion. They perform important functions - protective, trophic and others. An increase in the number of leukocytes more than 10 × 10 9 / l (G/l) is called leukocytosis .
Most often, leukocytosis occurs as a consequence of acute infections caused by cocci. Therefore, the CBC will definitely show inflammation, pneumonia, and blood cancer. Leukocytosis is typical for:
- leukemia of various courses, malignant tumors
- inflammatory, purulent, acute infectious processes
- uremia
- myocardial infarction
- toxic poisoning, severe blood loss, shock, extensive burns
CBC in acute appendicitis will show an increase in the amount of L. Leukocytosis is characteristic of tubal pregnancy, splenic rupture, and acute gout.
A decrease in the number of leukocytes below 3.5 g/l is called leukopenia . A tendency to leukopenia occurs among the healthy population and is often hereditary, but may depend on exposure to external environmental factors (solar radiation).
Sometimes it occurs during fasting, when tone decreases, or during sleep. Leukopenia is typical for:
- infections caused by viruses and bacteria - typhoid fever, endocarditis, salmonellosis, measles, influenza, rubella
- lupus erythematosus
- hemoblastoses
- stomatitis in adults and children (read more by following the link)
The appearance of leukopenia is associated with inhibition of cell maturation and the release of L from the hematopoietic organs and their redistribution in the vascular bed.
Leukocyte formula
The diagnostic value of calculating the leukoformula is enormous in many pathological conditions. It can be used to judge the severity of the situation and the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy.
Leukocytes include cells of the lymphocytic, monocyte, and granulocytic series. To find out their number, use the calculation of the leukocyte formula - the % content of different types of leukocytes:
- band and segmented neutrophils
- eosinophils
- monocytes
- basophils
- lymphocytes
Neutrophils perform bactericidal and virucidal functions. They are capable of phagocytosis in capillaries and participate in all stages of inflammation. Therefore, an increase in the number of neutrophils will show inflammation in the body. Neutrophilia (above 8×10 9 /l) is present in any suppurative process, sepsis.
Eosinophils have a detoxifying effect. They are found in large quantities in tissue fluid, intestinal mucosa, and skin.
An increase in the number of eosinophils (eosinophilia) in the blood indicates an allergy in a child and an adult, the presence of worms in the body. Infection with parasites is the basis of long-term eosinophilia. Sometimes it is caused by protozoa.
Eosinophilia accompanies connective tissue diseases - polyarteritis, rheumatoid arthritis, tumors, especially with metastases and necrosis.
Eosinopenia (decrease) is typical for an infectious-toxic process in the postoperative period. And it indicates the severity of the condition.
Basophils have anticoagulant properties. Involved in inflammatory and allergic processes. Basophilia occurs when an allergic reaction to food, medication, or foreign protein. For oncology - chronic myeloid leukemia, myelofibrosis, erythremia, lymphogranulomatosis.
Characteristic of ulcerative colitis, treatment with estrogen. Basophilia is likely during ovulation and pregnancy, with lung cancer, anemia of unknown origin, and iron deficiency.
Monocytes have the ability to phagocytose. They actively phagocytose (absorb) cell debris, small foreign bodies, malaria plasmodia, and mycobacterium tuberculosis.
With tuberculosis, monocytosis is observed in the blood - an increase in the number of monocytes. Monocytopenia is observed with hypoplasia of hematopoiesis.
Lymphocytes are important for immunity. In addition, lymphocytes take part in the fight against infection and also perform a trophic function at sites of inflammation and wounds. Lymphocytosis is possible with infectious mononucleosis, tuberculosis, and syphilis.
Platelets - physiological role, clinical significance
A formed element of blood, participates in the processes of hemostasis. Thrombocytosis (increased tr number) can be observed under physiological conditions after physical exertion, due to stimulation of the nervous system. Thrombocytosis occurs when:
- injuries with muscle damage
- burns, asphyxia, after blood loss and removal of the spleen
- leukemia – erythremia, myeloid leukemia
Thrombocytopenia (decreased tr number) in physiological conditions occurs during menstrual blood loss in women, after histamine. In pathological conditions, thrombocytopenia occurs when:
- idiopathic platelet purpura
- toxic intoxications
- infectious-toxic conditions - sepsis, meningococcus, scarlet fever, diphtheria, typhus
- toxic-allergic conditions – the effect of medicinal and food allergens
- parasitic and infectious diseases
- diseases of bone marrow hematopoiesis, leukemia, myeloma
In this case, the autoimmune factor is of great importance - the formation of antibodies to one’s platelets.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
An increase in ESR can occur under physiological conditions - during pregnancy, during fasting, when eating dry food, after vaccination, when taking certain medications.
Changes in ESR in pathology have diagnostic and prognostic meaning . And it serves as an indicator of the effectiveness of the treatment. ESR increases with:
- infections and inflammations
- purulent processes
- rheumatism
- kidney diseases, liver diseases (including bile stagnation)
- myocardial infarction, malignant tumors, anemia
Reduced ESR levels occur during processes accompanied by blood thickening. Sometimes observed with neuroses, epilepsy, anaphylactic shock, and erythremia.
Total red blood cell volume (hematocrit)
Hematocrit (Ht) is the ratio of plasma to formed elements. An increase in Ht occurs with heart defects and is accompanied by cyanosis and erythrocytosis.
A decrease in hematocrit is typical for various anemias in the second half of pregnancy.
Color index
Color or color index is the relative amount of Hb in a red blood cell. A decrease in this value occurs with iron deficiency.
An increase in the color index is observed with anemia, deficiency of Vit B12 (cyanocobolamine), and folic acid. Accompanies cirrhosis of the liver, thyroid disease, occurs during therapy with cytostatics, taking contraceptives, and using anticonvulsants.
Negative consequences
Such a harmless procedure for some categories of patients is fraught with the following:
- Severe pain due to careless puncture, individual high sensitivity of the subject.
- Unpleasant sensations persist at the puncture site for several hours.
- In a tenth of cases, hematomas and subcutaneous bleeding are possible. However, they do not require intervention and resolve on their own.
- Individual reaction - dizziness, nausea, weakness.
- A shock procedure for many young patients.
- There is a small risk of local infection during puncture.
Normal blood laboratory tests
An important stage in assessing the result of OAC is to establish the difference between pathology and the norm. To do this, it is necessary to define normal indicators - these are indicators found in healthy people. They may differ depending on gender.
| Index | Normal values | |
| men | women | |
| Hemoglobin, Hb | 125 - 170 g/l | 105 – 155 g/l |
| Red blood cells, Er | 3.8 – 5.5 T/L | 3.5 – 4.9 T/l |
| Leukocytes, L | 3.8 – 9.5 G/L | |
| Hematocrit | 40 – 50 % | 38 – 47 % |
| ESR | 1 – 10 mm/h | 2 – 12 mm/h |
| Platelets, tr | 150 – 380×10 9 /l | |
| Leukocyte formula: When assessing test results, it must be remembered that deviations outside the normal range do not necessarily indicate the presence of a disease. When interpreting the results, it is necessary to find out whether the deviations are physiological in nature. We should not forget about the variability of the norm associated with personal characteristics. When interpreting the results, it is necessary to take into account many factors: age, gender, concomitant diseases, medications, living conditions and much more. Therefore, a doctor should do this. | ||
Comparison with venous blood collection
You now know what a clinical finger blood test shows. Let's compare it to examining a venous blood sample. The latter method will have the following advantages:
- More accurate results.
- Wider range of diagnostics.
But there are also disadvantages compared to testing blood from a finger:
- To take a sample, you need the help of a qualified specialist. Therefore, the method is not available for regular home monitoring of blood sugar by patients themselves.
- More painful procedure.
- The event is more labor-intensive for medical personnel.
- It is impossible to collect blood from the inner elbow crease several times a day.
Thus, a finger prick blood test is an effective study designed to tell a lot about a person’s state of health. Its implementation is simple for both the subject and the laboratory assistant.
Why are they considered painless?
First of all, the child is not afraid of the injection, since he does not see the needle itself. In addition, the needle is very small, so there is virtually no pain from puncturing the skin. The diameter of the needle in lancets for children is 0.25-0.8 mm, and its length is 1.2-1.8 mm. Such needles are very tiny and the skin is injured to a minimum.
As a result, the puncture is practically painless and heals very quickly. And these are important factors when choosing a device that is used to take blood from children under one year old, as well as from children who are very afraid of injections.
To draw blood using a lancet, you need:
- Unscrew and remove the protective cap from the scarifier.
- Place the body of the device firmly against the child’s finger.
- Using gentle pressure on your finger, withdraw the required amount of blood.
All lancets used for collecting capillary blood for clinical analysis in childhood are disposable, so they must be disposed of after use. Repeated use is impossible, even if you want to do this - as soon as a blood sample is taken, the needle is retracted into the body and immediately blocked. This is done for the safety of patients to eliminate the risk of infection. In addition, the blood collected through the needle does not come into contact with the environment, so the test result will be very accurate.
If we are talking about a blood sugar test performed at home for a child with diabetes, then the lancet will be slightly different. For this purpose, a universal device is used that is inserted into a glucometer. Thanks to this, the consumption of needles is reduced.
The used automatic lancet, which was used to collect blood from a child’s finger for clinical analysis, should not be thrown into the trash bin along with other garbage immediately after the procedure. If a child is infected with any infection, such a lancet can act as a source of disease.
Like other waste materials that have been in contact with human blood, lancets are classified as hazard class B. Such medical waste must be disinfected before disposal. Lancets can be autoclaved and once sterilized they are considered non-hazardous waste and can be thrown into any trash bin.
Lancets, which are used to painlessly take blood samples from children, are represented by the following models:
1. Automatic lancets Medlance Plus from the Polish company HTL-Strefa Inc. They are presented in several types with different body colors - lilac devices are suitable for children (needle penetration depth is 1.5 mm), and blue ones are universal (with a needle 1.8 mm long).
2. Lancets from Qlance. This Chinese manufacturer offers devices for children with a penetration depth of 1.8 mm. In a purple lancet, the needle diameter is 0.45 mm, and the volume of blood taken is up to 100 μl. In a blue lancet, the needle has a diameter of 0.8 mm. With this device, 100 to 150 μl of blood is collected.
3. Automatic lancets MR. These are also Chinese-made devices with a triangular thin tip. For children, lancets with a puncture depth of 1.8 mm are produced - pink and yellow.
4. Scarifiers of the Vitrex Sterilance Lite II series. Children can draw blood with orange lancets from this brand, the puncture depth of which is 1.8 mm.
5. PROLANCE lancets. This company's assortment includes lancets with a puncture depth from 1.4 to 1.8 mm in blue, blue, yellow and green, also differing in needle diameter.
6. Mini Collect lancets. Purple lancets from this manufacturer with a puncture depth of 1.25 mm are intended for children.
7. Acti-Lance devices. The needle of this company's purple lancet pierces the baby's skin to a depth of 1.5 mm. You can also use the universal blue Acti-Lance lancet with a puncture depth of 1.8 mm.
8. Bd Microtainer lancets. Lilac devices pierce the child's skin to a depth of 1.5 mm, and pink ones - to a depth of 1.8 mm. The range also includes lancets for infants up to one year old, which can be used to draw blood from the heel.
Most mothers who encounter the use of lancets in private clinics for the first time are satisfied with this device. They note that children really don’t cry or worry when they take blood from their finger using a lancet. The procedure itself is very quick and babies tolerate it very well, and no marks are left on the finger.
The only drawback of lancets for taking blood for general analysis is their absence in many clinics, so mothers must buy these devices themselves. However, they can be easily purchased at medical equipment stores or on the Internet, and are relatively cheap. For example, Qlance or MR lancets cost only 5-6 rubles apiece, and for an automatic Medlance lancet you need to pay 15-20 rubles.