0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.10.08
22 707
Blood analysis
Every woman dreams of becoming pregnant and giving birth to a healthy child, but this process is preceded by multiple tests and health checks of the mother and father. A separate and especially important topic is the different Rh factors of parents during pregnancy. Once conception has occurred, parents must take care not only of their health, but also of the development of their baby.
Pregnancy test
Both the expectant mother and her husband should know about their Rh factor. The probability that the fetus can inherit the Rh factor of one of the parents is 50%. Of course, we are not talking about cases where both husband and wife have the same (Rh-) or (Rh+) blood.
The danger arises only when the wife is Rh negative and the husband is Rh positive. Only then does the likelihood of incompatibility between the blood of the child and the mother increase. This condition is called Rhesus conflict, but with the capabilities of modern medicine, even this problem can be solved with timely diagnosis.
What is the Rh factor?
Rh factor (Rh factor) is a blood protein that is found on the surface of blood cells - red blood cells.
If this protein is present, then this means that the person has a positive Rh factor, but if it is not there, then it is negative. Rh factor is determined by antigen. There are five main antigens, but it is the D antigen that indicates Rh. 85% of the world's population have positive Rh factors. How to determine your Rh factor? It is enough to donate blood from a vein just once. This indicator does not change throughout life. The Rhesus status of the embryo is formed already in the first trimester of pregnancy. Determining this indicator is very important for the expectant mother, since in the case of an Rh-negative mother and an Rh-positive child, various pregnancy complications are possible. In this case, it will be especially important to follow the doctor’s instructions, avoid infectious and colds, as well as stress. Also on various websites there are so-called calculators that determine the Rh factor of the unborn child. It must be remembered that blood is donated on an empty stomach. A rapid Rh test can be taken at any independent laboratory where blood is taken (for example, Invitro). The price depends on the price list of the clinic itself. You can find out about the cost of the analysis immediately before delivery. You can also donate blood and find out your Rh factor for free if you become a donor. To do this, you need to fill out a form to register yourself as a blood donor at the appropriate institution.
The Rh factor also plays a big role in blood transfusions. A transfusion involves two people: the recipient (the one who receives the blood) and the donor (the one who donates the blood). If the blood is incompatible, the recipient may experience complications after the transfusion.
The most common myth among couples is that blood type (like the Rh factor) is inherited from a man. In fact, the inheritance of the Rh factor by a child is a rather complex and unpredictable process, and it cannot change during life. But it is worth remembering that in rare cases (about 1% of Europeans) a special type of Rh factor is determined - weakly positive. In this case, Rh is determined either positive or negative. This is where questions arise on forums: “why did my Rh minus change to plus?”, and legends also appear that this indicator may change. The sensitivity of the testing method plays an important role here.
An equally popular search on the Internet is “horoscope by blood type.” For example, in Japan, great attention is paid to deciphering blood type. Believe it or not - it's up to you.
In the world there is such a thing as a medical tattoo, photos of which can be easily found on the Internet. What do these tattoos mean and what are they for? Its designation is quite pragmatic - in case of a serious injury, when an urgent blood transfusion or surgery is required, and the victim is not able to give the doctor information about his blood type and Rh. Moreover, such tattoos (a simple application of the blood type and Rh factor) should be in places accessible to the doctor - shoulders, chest, arms.
What to do
Pregnant women are wondering what to do if a Rhesus conflict has been detected. Experts advise undergoing all examinations and tests in a timely manner. Isoserological incompatibility can be treated if diagnosed in a timely manner. The period from 21 to 31 weeks is considered the most dangerous - during this time the pregnant woman’s blood is regularly taken for analysis. There are several main diagnostic methods.
Analysis
Rh factor conflict can be determined using laboratory tests. Pathology is determined based on the results of tests taken by the woman. Material taken from the vein helps determine the group and Rp affiliation. After a woman is registered, she must donate blood three times to determine her group:
- first appearance;
- at 30 weeks of pregnancy;
- before the birth of the child.
If antibodies are detected in the blood of a pregnant woman, she should donate blood monthly. The dynamic titer is determined first. Experts determine the rate of growth and formation of antibodies.
Diagnostic measures also include:
- Ultrasound;
- invasive diagnostic method;
- non-invasive diagnostic method.
Important information: Table of food products for women according to the 2nd (second) blood group positive (negative) and diet (menu) for weight loss for men
Ultrasound examination can be used to monitor the child's condition. GNB can be recognized by primary signs at 19-20 weeks (second screening). If there is no suspicion of a conflict, the next procedure is carried out at 33-34 weeks. If the condition of the fetus is satisfactory and sensitization was identified earlier, then ultrasound screening is carried out once every 14 days. If a child is confirmed to have HDP, an ultrasound is performed every 2-4 days.
Signs that indicate pathology on ultrasound:
- enlarged placenta (0.5-1 cm);
- enlarged spleen and liver;
- polyhydramnios;
- expansion of the vein in the connecting canal (umbilical cord).
Ultrasound examination can reveal the edematous form of HDP. The fetus has an enlarged liver and spleen, and bloating of the abdominal cavity is clearly visible. The limbs swell, the heart is also enlarged. Invasive methods for determining pathologies include:
- amniocentesis;
- cordocentesis.
Amniocentesis is carried out at 16 weeks. Analysis of amniotic fluid allows us to identify abnormalities. Cordocentesis is considered the most accurate method for determining the severity of HDP. Blood from the umbilical cord is taken at 18 weeks. Through the procedure, blood can be transfused in utero. The material obtained through collection makes it possible to determine the level of bilirubin and hemoglobin.
Non-invasive methods include a modern procedure that allows the Rhesus of the unborn child to be determined from the mother’s blood. The material contains fetal red blood cells, which are responsible for the formation of the Rp conflict.
Treatment
Blood group conflict during pregnancy cannot be specifically treated due to the lack of drugs that can change the composition of the blood. It is impossible to get rid of antibodies in the blood by taking medications. Rhesus is a conflict, the treatment of which must be carried out in a timely manner, requiring control over the well-being and lifestyle of the pregnant woman. Individually selected therapy will help minimize the risk of developing pathologies in the fetus.
During 9 months of pregnancy, a woman must take a course of medications three times. The dosage regimen and regimen are determined by a specialist. These include:
- vitamin and mineral complexes;
- calcium-containing medications;
- iron supplements;
- medications that improve metabolism.
If the condition of the child in the womb is assessed as severe, an intrauterine blood transfusion is performed. This procedure saves the baby's life and gives time to fully develop. If the concentration of antibodies in the blood is high, delivery is carried out ahead of schedule by cesarean section. In the early stages of pregnancy, a woman is sewn into a fragment of the baby's father's skin. This measure helps reduce the risk of developing blood group conflicts.
Plasmapheresis is considered one of the methods for treating blood group conflict. The procedure has virtually no contraindications. Pregnant women need to undergo about 20 sessions - 3 liters of plasma are cleansed in one procedure. Along with the donor plasma, the woman’s body receives protein medications necessary for the normal development of the fetus in the womb.
Rh factor and pregnancy
Compatibility of Rh factors during pregnancy is one of the tests that is carried out in the antenatal clinic. When a woman registers with a gynecologist, she will need to donate blood to determine her group and Rh factor. It can significantly affect the course of the next nine months. If the baby inherits the positive Rh of the father, and the mother has a negative Rh, then the protein in the child’s blood is unfamiliar to the mother’s body. The mother's body "considers" the baby's blood a foreign substance and begins to produce antibodies, attacking the baby's blood cells. If there is a Rhesus conflict during pregnancy, the fetus may experience anemia, jaundice, reticulocytosis, erythroblastosis, hydrops fetalis and edematous syndrome of the newborn (in the latter two cases there is a high probability of death of the child).
Causes of the conflict
A woman with negative Rh and a man with positive Rh are able to conceive. If the mother’s Rh factor is positive and the father’s is negative, then the risk of developing a conflict is 50%. The parent's blood type during pregnancy affects the degree and speed of formation of possible pathologies. During the first pregnancy, if a blood transfusion was not performed, the chances of avoiding a conflict increase sharply. This means that if the mother’s Rh is negative, the child may be born with Rp (+).
It happens that the female body is not able to produce a sufficient amount of antibodies. The main reasons for the development of incompatibility are fertilization of the egg after abortion or miscarriage. In this case, the risk of developing a conflict increases several times. In a woman, the factor does not change during pregnancy and for the rest of her life, only the amount of antibodies produced by the body in the blood may increase.
A conflict can develop in a woman whose first pregnancy ended in a caesarean section. If during childbirth doctors separated the placenta manually, and the patient has a history of uterine bleeding, then the risk of Rp incompatibility is 50-60%. Women with a negative Rp factor should be especially attentive to their own health - mothers who have suffered the following pathologies while pregnant are at risk:
- acute respiratory viral infections;
- gestosis;
- cold.
Antibodies produced by the body do not disappear anywhere. Their number increases with each subsequent pregnancy. If the structural structure of the chorionic villi is disrupted, the mother’s immunity begins to produce antibodies at an accelerated rate.
Blood type and Rh factor: compatibility
The cause of incompatibility may be not only Rh blood type, but also blood type.
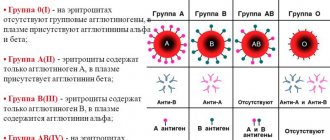
What are the different blood types? They are distinguished by the presence of specific proteins.
Four groups:
- the first (occurs most often) - O - there are no specific proteins in it;
- the second - A - contains protein A;
- the third - B - contains protein B;
- the fourth (the rarest of all) - AB - contains both type A and type B proteins.
First
(Rh negative) can provoke a conflict in the mother:
- for protein of the second group (A);
- for protein of the third group (B);
- for Rh protein (positive).
Second
(Rh negative) can provoke a conflict in the mother:
- for protein of the third group (B);
- for protein of the fourth group (B);
- for Rh protein (positive).
Third
(Rh factor is negative) the mother can provoke a conflict:
- for protein of the second group (A);
- for protein of the fourth group (A);
- for Rh protein (positive).
Fourth
does not conflict with any other group. The only case when an immune reaction is possible is if the mother has group IV and is Rh negative, and the father is positive.
Table 1. Statistics
| Blood groups parents | Possible blood type of the child (probability, %) | |||
| I+I | I (100%) | — | — | — |
| I+II | I (50%) | II (50%) | — | — |
| I+III | I (50%) | — | III (50%) | — |
| I+IV | — | II (50%) | III (50%) | — |
| II+II | I (25%) | II (75%) | — | — |
| II + III | I (25%) | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| II + IV | — | II (50%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| III+III | I (25%) | — | III (75%) | — |
| III + IV | — | II (25%) | III (50%) | IV (25%) |
| IV + IV | — | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (50%) |
Who is at risk?
Blood type conflict becomes likely when the pregnant woman and the unborn child have different groups (Table 1):
- The mother has I or III – the child has II;
- The mother has I or II; the child has III;
- The mother has I, II or III - the child has IV.
Women with type I blood who are carrying babies of groups II or III are at greatest risk. This combination most often provokes a conflict regarding the blood type of the mother and her baby, which can cause hemolytic disease of the newborn. Doctors also pay special attention to the following combinations of blood groups in partners (Table 2):
- Women of blood group I – men II, III or IV;
- Women of group II – men III or IV;
- Women of group III - men of groups II or IV.
Rh positive during pregnancy
If you are Rh positive, then your husband’s Rh negative will not affect the course of your pregnancy. In the case when a child inherits a negative Rh factor, there is no protein in his blood that is “unfamiliar” to the mother’s immune system, and a conflict will not arise.
- Rh-positive mother + Rh-positive father = Rh-positive fetus
The child has inherited the positive Rh factor of the parents, and the pregnancy will pass without complications. - Rh-positive mother + Rh-positive father = Rh-negative fetus
Even if the parents' Rh factor is positive, the baby can be negative. In this case, we can still talk about the compatibility of Rh factors during pregnancy: the mother’s body is “familiar” with all the proteins in the child’s blood. - Rh-positive mother + Rh-negative father = Rh-positive fetus
Both the mother and the fetus are positive, and there is no conflict during pregnancy. - Rh-positive mother + Rh-negative father = Rh-negative fetus
Although mother and fetus have different Rh blood factors (mother and child have positive and negative, respectively), there is no conflict.
As already mentioned, Rh blood is a protein. And since the mother’s body already has this protein, the fetal blood does not contain components unfamiliar to the mother’s immune system.
Probability tables
Geneticists claim that when analyzing the likely hereditary characteristics of a child’s blood, the blood type during pregnancy of people of both sexes (husband and wife) is assessed according to the same criteria. (50%/50%). Experts have compiled several tables that allow a preliminary assessment of the degree of risk.
Probability tables share:
- by Rp (+) or (-) ;
- 1 of 4 groups.
Material taken simultaneously from mom and dad reveals the presence of special marker proteins in her. They are found on the surface of red blood cells. The immunological property of blood does not affect health in any way; husbands and wives often have different Rhesus values. A conflict arises at conception if people have different Rp ((+) red blood cells merge with (-)). Rhesus - conflict during pregnancy (table) allows doctors to minimize the risk of developing pathology in the fetus.
By Rh factor
The concepts of “Rh factor and pregnancy” are closely interrelated with each other. A conflict is possible if the mother is Rh positive and the father is Rh negative. Such people have children with different factors. If the factor is negative for a woman and a man, then with 100% probability the child will be born with Rp (-). Cases where the parents are positive and the child is Rh negative have not been registered.
Rhesus - conflict (table):
| Rp (father) | Rp (mother) | Rp (child) | Conflict forecasting (in %) |
| floor. (+) | floor. (+) | floor. (+) | 0% |
| floor. (+) | neg. (-) | 50% (+) or 50% (-) | 50% |
| neg. (-) | floor. (+) | 50% (+) or 50% (-) | 50% |
| neg. (-) | neg. (-) | neg. (-) | 0% |
The likelihood of Rh conflict increases with the fusion of marker proteins found in red blood cells. The parent's Rp (factor) may be different, but the child's factor may be different.
By blood type
Blood type during pregnancy determines the likelihood of incompatibility. Letter designation of groups:
- I - 0;
- II - A;
- III - B;
- IV - AB.
Compatibility table for blood groups:
| Father's blood | Mother's blood | Blood of a child | Forecasting conflict |
| excluded | |||
| A | 0 or A | excluded | |
| IN | 0 or B | excluded | |
| AB | A or B | excluded | |
| A | 0 or A | 50% | |
| A | A | A or 0 | excluded |
| A | IN | any group | 25% |
| A | AB | A, 0 or AB | excluded |
| IN | 0 or B | 50% | |
| IN | A | any group | 50% |
| IN | IN | B or 0 | excluded |
| IN | AB | AB, B or 0 | excluded |
| AB | A or B | 100% | |
| AB | A | A, AB or 0 | 66% |
| AB | IN | AB, B or 0 | 66% |
| AB | AB | AB, B or A | excluded |
Important information: How is a person’s Rh factor inherited (passed on) and what should the child’s parents have?
The fusion of red blood cells occurs as the fetus forms.
Rh factor negative during pregnancy
Rh negative during pregnancy is not always a death sentence for the baby. The main thing is that it is the same for both the baby and the mother.
- Rh-negative mother + Rh-negative father = Rh-negative fetus
The baby inherited the Rh factor of his parents. And since both the mother and the fetus have no protein (Rhesus) in their blood and their blood is similar, then a conflict does not arise. - Rh-negative mother + Rh-positive father = Rh-negative fetus
This is one of the cases when the Rh factor is very important: the compatibility of the blood of the mother and the fetus affects the next nine months of intrauterine life. Although a woman is Rh negative during pregnancy, it is good that the fetus is also Rh negative. There is no Rh in either the mother's blood or the fetus's blood.
When does it start?
When pregnancy begins, the woman's Rh factor does not change. During the first pregnancy, conflict may not arise. As the fetus develops and forms, antibodies produced by the mother's body enter the child's bloodstream. The first 2-3 weeks, during gestation, the blood of the mother and child mixes. Antibodies are not dangerous for a woman’s body, but they can cause harm to a child’s body.
According to statistics, Rhesus occurs - incompatibility in the second and subsequent pregnancies. Test results show possible deviations. In rare cases, a mother, father or child may become a carrier of chimerism. From the point of view of genetics, this phenomenon is poorly studied; chimera people have information about two groups simultaneously written in their genetic code.
When does Rh-conflict pregnancy occur?
Rh negative mother + Rh positive father = Rh positive fetus
Please note: no matter what group the mother has, negative Rh during pregnancy becomes a cause of conflict. In this case, the embryo inherits it from the father and brings the “new protein” into the body of the Rh-negative mother. Her blood “does not recognize” this substance: there is no such protein in the body. Accordingly, the body begins to defend itself and produce antibodies. They penetrate the placenta into the baby's blood and attack his red blood cells. The fetus tries to defend itself: the spleen and liver begin to work hard, and they increase significantly in size. If a child has few red blood cells left, he develops anemia, or anemia.
Features of the antigen
Rh factor is an antigen that is found on the surface of red blood cells. 85% of people have a positive Rh factor. In the rest of the group of people it is negative. The Rh factor has absolutely no effect on a person's life.
The exception is pregnant women who have a negative Rh factor. If the test is positive, the father of the child may have a conflict antigen.
During pregnancy, the Rh factor of the fetus overcomes the mother's placental barrier. In turn, the mother’s body begins to recognize the child as foreign. This leads to the production of protective antibodies. When protecting a woman, there is a threat to her child. If the conflict antigen is severe, it can lead to the death of the baby. A miscarriage in a representative of the fairer sex can occur at different stages of pregnancy.
Antibodies from the mother penetrate the placenta and destroy the red blood cells of the fetus. As a result, large quantities of bilirubin appear in the blood. It turns the baby's skin yellow. As a result of the conflicting antigen, rapid destruction of red blood cells is observed. The liver and spleen produce them intensively, which leads to the appearance of a conflict antigen.
The Rh factor is a fairly important aspect in bearing a child, which must be taken into account when planning a pregnancy.
Rh negative during pregnancy
There is a vaccine - anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin, which prevents Rh-conflict during pregnancy. It binds the antibodies that the mother’s body produces and brings them out. Vaccination can be carried out during pregnancy. If you are Rh negative and your husband is positive, this is not a reason to give up motherhood. Over the course of 40 weeks, you will have to donate blood from a vein several times:
- up to 32 weeks - once a month;
- from the 32nd to the 35th week - 2 times a month;
- from the 35th to the 40th week - once a week.
If Rh antibodies appear in your blood, your doctor can detect the onset of a Rh conflict in time. In case of conflict pregnancy, immediately after birth, the newborn is given a blood transfusion: the group and Rh factor must be the same as that of the mother. This is especially important in the first 36 hours of the baby’s life - the mother’s antibodies that enter the child’s body are neutralized when they “meet” familiar blood.
How to resist Rhesus conflict
Knowing that the next pregnancy may turn out to be Rh-conflicting, the first-time mother is given drugs with anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin in the first 72 hours after the baby is born. This eliminates the red blood cells of the fetus that have entered the maternal bloodstream, and thus eliminates the need to build an immune defense from antibodies.
For prevention, immunoglobulin is also indicated at 28 and 34 weeks; an anti-Rhesus drug is also administered for bleeding or after invasive medical interventions. During the next pregnancy, in the absence of antibodies, the procedure with immunoglobulin is repeated.
The medicine does not penetrate the placental protection and does not affect the development of the fetus.
Rezonativ is one of the trade names of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin
If the opportunity to prevent Rh conflict is missed, and the fetus develops hemolytic disease, the only way out is intrauterine blood transfusion by cordocentesis (through the umbilical vein). The procedure is unsafe and is sometimes accompanied by:
- infection of the fetus;
- leakage of amniotic fluid;
- bleeding;
- premature placental abruption.
At the same time, blood transfusion reduces the risk of premature birth and alleviates the baby's condition.
Some married couples resort to IVF to avoid Rh conflict. Among the resulting embryos, those that have inherited negative blood are implanted into the uterus of a Rh-negative woman - then intrauterine “war” is excluded.
Video: if there is a “blood feud” in the womb
When can immunoglobulin prophylaxis be carried out?
To prevent conflict in subsequent pregnancies, women with a negative Rh factor should undergo prophylaxis. This is done after:
- childbirth (within three days);
- abortion;
- analysis of amniotic fluid;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- placental abruption;
- transfusion.
Remember: if you and your baby’s group and Rh are different, this is not an indication that there will definitely be problems. Group and Rh are just the presence or absence of specific proteins in the blood. The reaction of the body and the development of pathologies in our time can be successfully controlled with the help of medications. Your attentiveness to your body, as well as an experienced doctor, will help you bear a healthy baby.
How should the treatment be carried out?
The main thing is to promptly find a good and qualified doctor who will professionally approach this issue.
Treatment at the perinatal center
If the husband has a negative Rh factor, and his wife is diagnosed with a positive one, then there is absolutely no need to worry. This is important to remember. Only women with Rh- are at risk. Treatment primarily consists of:
- Complete examination of the woman;
- Redirecting her to a specialized perinatal center, where they will monitor the health of both mother and child;
- Administration of anti-Rhesus serum during pregnancy for preventive purposes;
- Stimulation of labor in order to quickly conduct a blood transfusion to the fetus.
- Administration of immunoglobulin within 72 hours after birth.
When the doctor sees in the test table that the woman’s blood is negative and the father’s is positive, then this is no longer as dangerous as it was before. Modern medicine has advanced so much that even such couples now have a high chance of giving birth to a healthy baby, like everyone else.
How do your chances of conceiving depend on your blood type?
Quite a lot is already known about the influence of blood groups, for example, on the likelihood of developing Alzheimer's disease, cancer, blood clots, etc. However, virtually nothing was known about the effect on fertility. And finally, thanks to the efforts of Turkish doctors, research has appeared in this area.
A study published last week found that men with type O are four times less likely to develop impotence compared to guys with other blood types. Experts from Ordu University in Turkey noted that blood type is as important a risk factor as smoking, excess weight, and high blood pressure. The reason is not clear, but scientists have said that in people with type A blood, the penis has a large number of veins, the lining of which can become damaged, leading to erectile dysfunction.
Blood type also affects female fertility. Girls with the second group are more likely to bear a healthy child for a long time than with the first. Studies have shown that women in the first group quickly deplete their egg reserves early in life. But at the same time, women with type 0 have a lower risk of developing preeclampsia - high blood pressure during pregnancy, which can be dangerous for mother and baby.
Naturally, representatives of the rest of humanity (which, by the way, are a little more than half, because people of the 1st group account for a little more than 40%) should not panic either - a higher probability does not mean a 100% chance. Likewise, representatives of the “happy” group should not relax ahead of time - reduced risk does not mean zero.
Rh factor, blood group, blood protein, antibody production, anemia, immune reaction, Rh compatibility, anemia, hydrops, fetal edema, immunoglobulin
How to avoid negative consequences
As we can see, compatibility by blood group, as well as by Rh factor, is a necessary condition for a successful pregnancy. Future parents, when starting a relationship, are unlikely to consider the blood type of their significant other as an important factor. But genetics can play a cruel joke and you won’t be able to get pregnant if you mix separate blood types.
In rare cases, this is due to the appearance of specific antisperm antibodies in relation to antigens of the male seed in their carrier or in the fallopian tubes of a woman. They appear when interacting with red blood cells through the uterine mucosa. The starting point in the formation of antisperm immunoglobulins is the presence of inflammation in the endometrium. Other possible causes of the occurrence of reactive components include:
- excess leukocytes in the semen;
- penetration of sperm into the gastrointestinal tract;
- coagulation of erosion in the cervix;
- pathological changes in sperm;
- incorrect implementation of artificial insemination.
You should be prepared for trouble in the event of a union between a “negative” woman and a “positive” man. Rhesus conflict is dangerous due to the following complications:
- the most common is the development of hemolytic disease of the fetus in various forms;
- the mother had previously received incompatible blood transfusions;
- pregnancy loss;
- rare - intrauterine hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the fetus;
- immune hydrops fetalis.
People with a positive Rh factor represent an advantage of the population of the entire Earth, while a negative Rh factor is found in only fifteen percent out of a hundred. Rh conflict occurs in women with negative Rh and positive in men.
So what actually happens in the body of a pregnant woman during such conflicts? Antibodies in the blood of the expectant mother try to harm the baby’s red blood cells, and the small body tries to produce red blood cells again. It is necessary to urgently take measures and carry out the necessary treatment so that the mother’s body does not have time to cope with the small, fragile body of the child and cause him dangerous diseases or improper formation of internal organs.
If there is an obvious conflict, doctors recommend terminating the pregnancy, but the final word remains with the parents. Those women who register with the consultation in the early stages, in most cases, give birth to healthy, full-term children. The most important thing is to follow all the recommendations, and love and faith can do a lot.
What is the danger of developing Rh conflict?
As a result of Rh conflict, hemolysis occurs - the destruction of red blood cells of the fetus's erythrocytes, and he develops hemolytic disease. Its essence is that due to hypoxia (lack of oxygen), the function of all organs and systems is disrupted. In addition, the breakdown of hemoglobin in destroyed red blood cells produces the pigment bilirubin, a substance toxic to the body.
The severity and consequences of the conflict depend on the antibody titer in the mother’s blood; it can have varying degrees:
- mild, when there is no massive breakdown of red blood cells, anemia is not expressed, but only increased bilirubin in the blood, the child is born with hemolytic jaundice;
- moderate, manifested by anemia (anemia) of the fetus with impaired organ function, enlargement of the liver, spleen, it is not always possible to save it, and newborns require intensive care;
- severe, when hypoxia and intoxication are pronounced, swelling of the brain and other organs develops, the so-called “nuclear” jaundice, such a fetus often dies and a miscarriage occurs.
Why is blood compatibility important for conception?
The genetic parameters of the parents' blood form a set of genes for inheritance by the fetus that is formed during conception.
The group and Rh factor are constant throughout life, so a preliminary study before pregnancy allows you to identify possible conflicts in advance.
When planning a pregnancy, parents have the opportunity to calculate their blood compatibility options. If the percentage of absence of any blood conflict is high, then for future parents, conception and the pregnancy period will proceed as normal.
The classification of blood groups into first, second, third and fourth is based on the content of agglutinins in plasma and agglutinogens in erythrocytes. The Rh factor is the presence (positive) or absence (negative) of a protein antigen on the membrane of red blood cells, the most common of which is type D antigen.
When it happens
This conflict appears in two categories of cases:
- when the mother’s blood group does not match that of the fetus
- in the situation of an Rh-negative mother pregnant with an Rh-positive child.
The use of immunoglobulin is prescribed by a doctor according to an individual regimen and implies:
- monthly check-ups up to 30 weeks
- once every two weeks from 30 to 36 weeks
- once a week from 36 weeks until delivery.
Also, prophylactic administration of anti-rhesus is carried out immediately after childbirth, which helps prevent conflict in possible future pregnancies.
Modern medical technologies make it possible to maintain pregnancy in any conflict.
Conception planning is the greatest help, since the attending physician is aware in advance of the risks of incompatibility, which allows him to select a pre-treatment regimen and subsequent pregnancy management. During the gestation period, the problem of incompatibility is concentrated on measures that prevent the mother's immune system from reacting to the fetus.
Dangerous moments
If mother and fetus are incompatible, the most dangerous development option is hemolytic disease of the embryo, which leads to an abnormal increase in the size of the child’s liver, jaundice, and developmental delays due to insufficient blood supply to the brain.
Determining the compatibility of Rh factors is one of the first tests that is carried out in the antenatal clinic. Blood characteristics can seriously affect the mother's health during pregnancy.
Pregnancy proceeds normally only if the mother's body produces antibodies that do not mistake fetal cells for foreign elements. Thus, women with type 1 blood always give birth without complications. In most cases, they have healthy and strong children, even from men with inappropriate blood type and Rh factor.
If the mother has a positive Rh factor and the father has a negative Rh factor, the chances of having a baby with a positive Rh factor are higher. However, at the moment of conception, blood incompatibility occurs: during gestation, the woman’s body produces antibodies that attack the baby’s cells. The fight against fetal cells is carried out because the woman’s body recognizes them as foreign due to their protein content.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Cytomegalovirus infection in pregnant women
Constant attacks put the child in serious danger. Often the struggle ends in the death of the fetus. If the baby survives, this effect on the mother’s immunity does not go away without a trace. Pregnancy with blood incompatibility is fraught with such complications (toxicosis, fatigue, weakness, etc.).
If there is a conflict of Rhesus in mother and child, it is necessary to avoid infections and colds in every possible way, and be less nervous and worried. The combination of Rh factors is shown in the table.