Every woman carrying a child must undergo many laboratory and instrumental examinations that will help assess the state of health and minimize risks for the expectant mother and the fetus itself. One of the most important tests is blood testing for antibodies during pregnancy.
Testing allows you to identify foreign microorganisms in the blood serum, as well as assess the compatibility of the fetus with the mother’s body. Also, such an analysis is carried out if an infectious disease is suspected and allows you to determine whether the body can independently resist the disease or whether it will require taking medications.
What are antibodies? And how to decipher the results of the analysis?
Antibodies are proteins that the immune system produces in response to infection. In laboratory diagnostics, it is antibodies that serve as markers of infection. The general rule for preparing for an antibody test is to donate blood from a vein on an empty stomach (at least four hours must pass after eating). In a modern laboratory, blood serum is examined on an automatic analyzer using appropriate reagents. Sometimes a serological test for antibodies is the only way to diagnose infectious diseases.
Tests for infections can be qualitative (they answer whether there is an infection in the blood) or quantitative (they show the level of antibodies in the blood). The level of antibodies for each infection is different (for some there should be none at all). Reference values (normal values) of antibodies can be obtained with the test result. In the online laboratory Lab4U you can take a set of tests for all TORCH infections at one time and with a 50% discount!
Why analysis is important
The analysis should not be neglected even if you have experienced your first successful pregnancy.
Sensitivity, or maternal sensitization, to foreign antigens increases with each subsequent pregnancy. Under appropriate conditions, maternal antibodies destroy the fetal blood cells and lead to anemia and hemolytic disease of the newborn.
The baby may die due to cardiovascular pathologies caused by anemia.
Hemolytic disease is fraught with serious complications:
- encephalopathy;
- death of a newborn;
- liver failure;
- developmental delay;
- enlarged liver and spleen.
Various classes of antibodies IgG, IgM, IgA
Enzyme immunoassay determines infectious antibodies belonging to various Ig classes (G, A, M). Antibodies to the virus, in the presence of infection, are detected at a very early stage, which ensures effective diagnosis and control of the disease. The most common methods for diagnosing infections are tests for IgM class antibodies (acute phase of infection) and IgG class antibodies (sustained immunity to infection). These antibodies are detected for most infections.
However, one of the most common tests - hospital screening (tests for HIV, syphilis and hepatitis B and C) does not differentiate the type of antibodies, since the presence of antibodies to the viruses of these infections automatically assumes a chronic course of the disease and is a contraindication, for example, for serious surgical interventions. Therefore, it is important to refute or confirm the diagnosis.
A detailed diagnosis of the type and amount of antibodies for a diagnosed disease can be done by taking an analysis for each specific infection and type of antibodies. Primary infection is detected when a diagnostically significant level of IgM antibodies is detected in a blood sample or a significant increase in the number of IgA or IgG antibodies in paired sera taken at an interval of 1-4 weeks.
Reinfection, or repeated infection, is detected by a rapid rise in the level of IgA or IgG antibodies. IgA antibodies have higher concentrations in older patients and are more accurate in diagnosing ongoing infection in adults.
A past infection in the blood is defined as elevated IgG antibodies without an increase in their concentration in paired samples taken at an interval of 2 weeks. In this case, there are no antibodies of classes IgM and A.
Useful video about Rh conflict during pregnancy
We recommend reading: D-dimer during pregnancy: what should be the normal level
Author
Yulia Prokofieva
Obstetrician-gynecologist
She received a higher medical education with a degree in obstetrician-gynecologist. Married, raising a child. All articles by the author
I like!
IgM antibodies
Their concentration increases soon after the disease. IgM antibodies are detected as early as 5 days after onset and reach a peak between one and four weeks, then decline to diagnostically insignificant levels over several months, even without treatment. However, for a complete diagnosis, determining only class M antibodies is not enough: the absence of this class of antibodies does not indicate the absence of the disease. There is no acute form of the disease, but it may be chronic.
IgM antibodies are of great importance in the diagnosis of hepatitis A and childhood infections (rubella, whooping cough, chickenpox), easily transmitted by airborne droplets, since it is important to identify the disease as early as possible and isolate the sick person.
Antibodies as an indicator of the state of the immune system
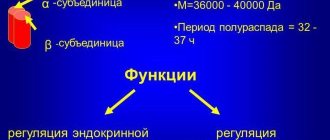
Antibodies (or immunoglobulins) are special protein molecules. They are produced by B lymphocytes (plasma cells). Immunoglobulins can either be free in the blood or attached to the surface of “defective” cells.
Antibodies were discovered in 1890 by E. Behring and S. Kisato while studying the effect of diphtheria toxin on rabbits. This was the name given to substances that formed in the blood of rabbits and could not only neutralize the toxin, but also destroy diphtheria infection.
Having recognized a foreign substance - an antigen, the antibody attaches to it using the so-called protein tail. The latter serves as a kind of signal flag for specialized immune cells that neutralize the “intruders.”
There are five classes of immunoglobulins in the human body: IgA, IgD, IgG, IgE, IgM. They differ in mass, composition, and, most importantly, properties.
IgE and IgD are contained in blood serum in small quantities and have no diagnostic value. The most significant for analyzing the state of the immune system and making a diagnosis are IgM, IgA and IgG.
IgM is the first immunoglobulin that the body begins to produce in response to infection. It is highly active and stimulates various parts of the immune system. Makes up 10% of all immunoglobulin fractions.
About five days after the antigen enters the body, IgG begins to be produced (70–75% of all immunoglobulins). It provides the main immune response. More than half of all immunoglobulins released during illness belong to this class.
Class G antibodies are so small that they can cross the placenta. It is the antibodies transferred to the child from the mother during pregnancy that protect the newborn in the first months of his life.
IgA is mainly localized in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, stomach, intestines and genitourinary system. That is, where pathogens most often enter our body. This class of immunoglobulins binds foreign substances and prevents them from attaching to the surface of the mucous membranes. The share of IgA is 15–20% of the total number of immunoglobulins present in the body.
IgG antibodies
The main role of IgG antibodies is the long-term protection of the body from most bacteria and viruses - although their production occurs more slowly, the response to an antigenic stimulus remains more stable than that of IgM class antibodies.
Levels of IgG antibodies rise more slowly (15-20 days after the onset of illness) than IgM antibodies, but remain elevated longer, so they may indicate a long-standing infection in the absence of IgM antibodies. IgG may remain at low levels for many years, but upon repeated exposure to the same antigen, IgG antibody levels rise rapidly.
For a complete diagnostic picture, it is necessary to determine IgA and IgG antibodies simultaneously. If the IgA result is unclear, confirmation is carried out by determining IgM. In case of a positive result and for an accurate diagnosis, a second test, done 8-14 days after the first, should be checked in parallel to determine the increase in IgG concentration. The results of the analysis must be interpreted in conjunction with information obtained in other diagnostic procedures.
IgG antibodies, in particular, are used to diagnose Helicobacter pylori, one of the causes of ulcers and gastritis.
Serological and immunological studies
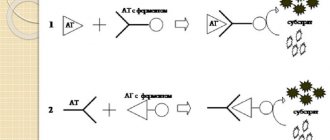
Using serological analysis, the interaction of antigens with antibodies in blood serum is studied. As a result of this diagnosis, specific antibodies formed during the immune response are determined. Serological reactions are widely used to determine microbial antigens. For example, the agglutination test is sensitive for detecting IgM antibodies and less sensitive for detecting IgG.
The basis of immunological analysis is the specific reaction of antibodies and antigens. With their help, pathologies of bacterial, viral and parasitic etiology are identified, and titers to them are determined.
Antibody analysis in the diagnosis of TORCH infections
The abbreviation TORCH appeared in the 70s of the last century, and consists of capital letters of the Latin names of a group of infections, the distinctive feature of which is that, while relatively safe for children and adults, TORCH infections during pregnancy pose an extreme danger.
The blood test for TORCH infection is a comprehensive study, it includes 8 tests:
— Determination of antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1,2 IgM and IgG
— Determination of antibodies to cytomegalovirus IgM and IgG
— Determination of antibodies to the rubella virus IgM and IgG
— Determination of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii IgM and IgG
Often, infection of a woman with TORCH complex infections during pregnancy (the presence of only IgM antibodies in the blood) is an indication for termination.
Interpretation of results: normal indicators
The concentration of certain antibodies in the blood has its own norms:
- IgA level - 0.35-3.55 g/l
- IgG level – 7.8-18.5 g/l
- IgM level - 0.8-2.9 g/l
If, as a result of the study, IgG and IgG antibodies are not detected, i.e. are negative, this indicates that the body has not encountered infections and infection can occur at any time. In this case, the study is carried out every month.
If the result is positive, i.e. the presence of antibodies in the blood indicates that the woman has recently had an infection, before or during pregnancy. The doctor will prescribe an additional examination, since this condition can be dangerous for the fetus.
Positive lgG and negative lgM indicate a past infection and this will not affect the development of the fetus.
If the tests show IgG negative and IgG positive, then the infection occurred during pregnancy. When testing for antibodies to TORCH infections, there should normally be no IgM in the blood. In medical practice, AT-IgG is considered a normal variant.
If there is no IgG to the rubella virus or an insufficient level, it is necessary to get vaccinated. It can only be done with a negative IgM level. Antibodies to rubella will be present in the blood. After vaccination, you can become pregnant 2-3 months later. Antibodies to phospholipids should normally be less than 10 U/ml.
Deviations from the norm: consequences for the fetus
Abnormal antibodies may affect normal fetal development
When the woman has negative Rh blood and positive blood in the fetus, a Rh conflict develops when antibodies enter the baby’s bloodstream. As a result, the child may develop jaundice, hemolytic disease, and anemia.
Rh conflict between mother and fetus can lead to disturbances in the functioning of the brain and heart due to a lack of oxygen supply during gestation.
Hemolytic disease can cause organ dysfunction in the fetus. At birth, a child may experience an increase in the size of the liver and spleen. In case of hemolytic disease, a blood transfusion is performed in the baby.
If antibodies are detected in the blood, the cause of their appearance should be determined.
To determine the degree of risk to the fetus, the antibody titer is determined throughout the entire period of pregnancy. In this way, their concentration can be detected in 1 mm of solution.
Consequences for the fetus:
- If the antibody titer is 1:4, then this indicates an Rh-conflict pregnancy. If the antibody titer is significantly increased (1:16), then in this case amniocentesis is indicated. With such a titer, the likelihood of intrauterine fetal death. Amniocentesis is performed no earlier than 26 weeks of pregnancy.
- If the titer is 1:64, then they resort to early delivery by cesarean section.
- Detection of antibodies to toxoplasmosis in the blood in the early stages can lead to infection of the fetus with this infection. As a result, the child’s liver, spleen, and nervous system are affected. The woman is offered an artificial termination of pregnancy. In the later stages, the probability of transmitting the infection to the baby is 70%, but the risk of complications is reduced.
- The presence of antibodies to rubella in the blood of a pregnant woman is dangerous for the fetus, since the nervous tissue, heart, and eye tissue are affected. If the infection occurred at the beginning of pregnancy, then this is an indication for termination of pregnancy. In the second and third trimester, antibodies do not cause serious consequences. The child may be developmentally delayed, some organs may not function properly, etc.
- If the mother has antibodies to cytomegalovirus infection, this can lead to the death of the fetus. In other cases, it is possible to give birth to a child with congenital pathology in the form of dropsy of the brain, enlarged liver, pneumonia, heart disease, etc.
- With an increase in antiphospholipid antibodies, immune aggression develops. Immune cells destroy phospholipids, resulting in antiphospholipid syndrome. This condition is very dangerous during pregnancy and can cause miscarriage, oxygen starvation, placental abruption and the development of intrauterine pathologies. All this is associated with impaired blood circulation in the placenta.
Rh antibodies during pregnancy
In the middle of the first trimester, antibodies are intensively synthesized, which is the cause of Rh conflict. The protein concentration in people with a positive Rh factor is 85%. When the indicator does not correspond and there are no such proteins, we are talking about negative Rh.
The danger is that a pregnant woman with a negative Rh factor can carry a baby who has inherited the father's Rh factor - positive. In the second trimester, the mother's antibodies penetrate the placenta and act aggressively on red blood cells, which subsequently has a detrimental effect on the development of the baby. As a result, liver dysfunction occurs, heart muscle dysfunction occurs, and the brain suffers. The outcome of this development is sad, since the fetus freezes.
Negative factors for bearing a baby during conflict:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- blood transfusion (hemotransfusion);
- termination of pregnancy for various reasons;
- placental abruption;
- C-section;
- separation of the placenta by hand;
- puncture of the amniotic membrane (amniocentesis);
- lack of prevention.
For women, Rh negative usually sounds like a death sentence, and they deny themselves the happiness of being a mother. It is necessary to understand that the antibody titer during gestation increases if the fetal red blood cells are introduced into the mother’s bloodstream.
By donating blood for antibody titers during pregnancy, their function in a particular case is determined. If they are fighting TORCH infections, there is no reason to show concern. Antibodies can also identify the fetus as a foreign agent and concentrate aggressive activity against it, which can pose a threat to the baby. The antibody titer during pregnancy with a negative Rh factor increases. This contributes to the development of Rh conflict.