What is an anticoagulant plasma system?
The anticoagulant system in the blood plasma, in order to maintain the structure of the blood in liquid form, has mechanisms that combine perfectly with each other:
- Ideally smooth intima (inner wall) of arteries;
- The intima is covered with fibrin, which is applied in a thin layer;
- Rapid movement through the arteries of the blood circulation system;
- The blood contains endothelial charges - with a negative electrical charge, as well as formed components that prevent the walls of blood vessels from sticking together;
- The mechanism also includes blood composition coagulants.
Coagulants are divided into:
- Preceding primary coagulants are substances that are always present in blood plasma;
- Secondary substances - their production occurs as needed.
Inactive thrombin
The antithrombin protein is found in both the primary and second groups of coagulants of the hemostasis system.
Antithrombin also comes in several types:
- Antithrombin 2 is a heparin protein;
- Antithrombin 3 is heparin, which is found in plasma (plasma hemostasis factor);
- Antithrombin 4 is a macroglobulin molecule that is the primary type of antithrombin:
- Antithrombin factor 1 (fibrin) is a secondary factor that controls hemostasis in the blood arterial bed and resists severe thrombosis.
Secondary factors resist thrombosis in the arterial bed. Antithrombin 3 is part of the coagulogram.
The value of the antithrombin 3 indicator
The anticoagulant glycoprotein antithrombin 3 is a physiological primary anticoagulant that is constantly present in the blood plasma.
The synthesis of this protein occurs in liver cells and antithrombin 3, when working together with other physiological factors, inhibits thrombosis of the blood plasma, which prevents thrombosis inside the vessels.
Antithrombin 3 regulates the coagulation process by slowing down the active actions of thrombin, system factors Xa, as well as IXa and factor Xia.
Antithrombin functions as a major factor in the antithrombin activity of plasma cells.
This anticoagulant is helped by the primary elements of the hemostatic system:
- Macroglobulin molecules;
- Antitrypsin;
- Anticoagulant esterase.
Antithrombin 3, together with other anticoagulants, inhibits the activity of factors that clot blood:
- Urokinase factor;
- Factor VII;
- Factors IX and XII;
- Plasmin molecules;
- Kallikrein molecules.
At3 does not produce the required effect on its own; its abilities are enhanced by the formation of an antithrombotic complex with heparin.
Heparin occupies 80.0% of all molecules of the system, which acts against blood plasma coagulation.
Indications for clinical laboratory testing of blood composition
The study of blood composition using the coagulogram method is carried out in the following cases:
- Preventive testing of patients over 50 calendar years old, and who have previously had cases of thrombosis in blood vessels;
- To assess the quantitative composition of antithrombin and the quality of this protein;
- Thromboembolic diseases of the large arteries;
- Myocardial infarction;
- PE (pulmonary embolism);
- Ischemic stroke;
- Pathology thrombophlebitis;
- Complications during pregnancy - miscarriages;
- Fetal freezing in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- Detachment of the walls of the placenta;
- Pathology eclampsia;
- Preeclampsia disease;
- Preeclampsia disease;
- Testing blood composition for type C and type S proteins;
- Testing for lupus type anticoagulant;
- A long surgical operation that lasts more than 240 minutes;
- Severe intoxication of the body;
- Dehydration of the body due to intoxication, through prolonged diarrhea and large amounts of vomit;
- Pathology sepsis;
- State of shock;
- Control over the intake of heparins;
- For preventive purposes, arterial thrombosis in women during pregnancy and childbirth;
- Control over the state of the blood structure in patients with bed rest;
- Study after surgery to remove a blood clot.
Clinical blood test during pregnancy
How to properly prepare for analysis?
To study the blood composition for antithrombin using the coagulogram method, only venous blood is taken (find out what color it is). Biochemical analysis is not done without preliminary preparation of the body, especially indicators for proteins in the structure of the blood composition.
The material for study must be freshly taken.
In order to obtain the most correct coagulogram value in biochemistry, you need to prepare your body for the test:
- It is recommended to donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach;
- The last meal should be at least 10-12 hours before blood donation;
- For dinner, do not eat fried, salty, fatty foods;
- Do not drink alcohol before submitting material for analysis;
- Stop smoking at least 30-60 minutes before taking biological fluid;
- Two weeks before blood sampling, do not take medications that can affect the structure of the blood;
- If taking medications cannot be postponed, you must inform your doctor;
- Be calm before donating blood and at the time of collection.
AT to TPO is increased - reasons
A high level of antibodies exceeding the norm is usually observed in the following diseases:
- various viral diseases;
- chronic renal failure;
- thyroiditis;
- Graves' disease;
- thyroid injuries;
- autoimmune diseases of a hereditary nature;
- diabetes;
- rheumatism.
Also, elevated antibodies to TPO occur if, shortly before the tests, the patient underwent radiation therapy in the head and neck area. It should be said that the analysis for these antibodies is not used as part of the measure to monitor the therapy being carried out. The examination is necessary only to determine whether pathology is present or not.
Clinical laboratory test for antithrombin III
The Antithrombin 3 indicator is the basic index of the hemostasiogram technique.
Using this method, all components of the hemostatic system are determined:
- Prothrombin time;
- APTT index;
- Thrombin time index;
- Quantitative indicator of fibrinogen in plasma;
- Assessment of RKFM activity;
- The level of operation of the anticoagulant system is antithrombin index 3;
- D-dimer;
- Glu index in analysis;
- Indicators of proteins C and S.
Normf antithrombin 3
Biochemical analysis of blood plasma composition for antithrombin 3 is a marker index of the blood plasma coagulation process. This analysis is used in clinics to monitor thrombosis pathologies, as well as the destructive effect of blood clots on blood vessels.
The normative AT3 index changes from birth to old age.
Reference biochemistry indications for antithrombin 3 in this table:
| Age of the subject | Reference indicators |
| Less than 3 calendar days | 58,0 — 90,0 % |
| from 3 days of age to 30 days of age | 60,0 — 89,0 % |
| from 30 days of age to 12 calendar months | 72,0 — 134,0 % |
| from one year to the child’s 6th birthday | 101,0 — 131,0 % |
| from 6th birthday to 11 calendar years | 95,0 — 134,0 % |
| 11-16 years old | 96 — 126 % |
| More than 16 years | 66 — 124 % |
During pregnancy, the coefficients fluctuate depending on the period of intrauterine formation of the unborn baby.
Normal for women during pregnancy
| Weeks of pregnancy | Reference coefficients |
| from the 13th week of pregnancy to the 21st week | 74,0 — 115,0 % |
| from calendar week 21 to calendar week 29 | 73,0 — 114,0 % |
| from the 29th week to the 35th week of the baby’s intrauterine development | 76,0 — 112,0 % |
| from the 35th calendar week to the 42nd week | 70,0 — 116,0 % |
Analysis price
| Name of hemostasis test | Price in rubles |
| D-dimer indicator | 980 |
| Antithrombin coefficient 3 | 310 |
| APTT | 170 |
| Blood test for lupus anticoagulant | 680 |
| Prothrombin time | 220 |
| Protein S index | 1600 |
| Protein C index | 1580 |
| RFMK | 180 |
| Thrombin time study | 210 |
| Factor VIII testing | 880 |
| Von Willebrand factor test | 810 |
| Fibrinogen test | 200 |
conclusions
If a person has been tested for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase, and the required norm is exceeded, under no circumstances should you immediately panic. Small deviations in values are quite possible even among healthy people. If you still have some minor deviations, you can bring your tests back to normal without using additional medications. To do this, you will simply need to reconsider your diet and give up all sorts of bad habits, after first getting rid of excess weight. Most doctors advise completely avoiding regularly wearing necklaces and chains around the neck, as some metals can negatively affect the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Etiology of increased anticoagulant in blood plasma
Antithrombin 3 is increased, the causes are the following pathologies:
- Hepatitis in the acute stage of the onset of pathology;
- Cholestasis with acute signs of the disease;
- Pathology of liver cells;
- Kidney transplant;
- Insufficiency of vitamin K in the body;
- Acute inflammation in the body;
- Disorders in the endocrine system, malignant formations in the endocrine organs;
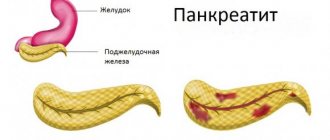
- Pathology of the pancreas - pancreatic disease in the acute stage;
- Temporary increase in women during menstrual flow;
- Long-term anticoagulant therapy with Warfarin.
Warfarin
Elevated levels of the Antithrombin 3 protein threaten dangerous bleeding.
Markers of autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases that develop due to excessive synthesis of antibodies can be recognized at the initial stage and their development into a chronic form can be prevented.
An increase in aggressive immunoglobulins in the circulatory system may remain a temporary autoimmune reaction if the cause of the endocrine system disorder is identified and eliminated in a timely manner.
One such marker is AT TG. It allows you to determine the presence of a malfunction and observe how the body reacts to the prescribed treatment.
The purpose of diagnosis is to prevent relapses and check the effectiveness of the therapeutic or surgical interventions used.
Markers of autoimmune diseases
Important! T3 and T4 - thyroglobulin derivatives affect cell development, tissue formation, metabolism of protein synthesis and oxidative processes.
Markers for a systemic examination of the endocrine system are also an analysis of the concentration of thyroglobulin, T3 triiodothyronine, T4 thyroxine, and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Antithrombin 3 deficiency
Deficiency of this coagulant can be congenital or acquired. Both types lead to thrombosis of the arteries.
Inherited genetic deficiency is divided into 2 types:
- Type 1 - the synthesis of this factor is reduced due to gene mutation;
- Type 2 - the synthesis of the anticoagulant is normal, only its activity is reduced.
Acquired anticoagulant deficiency also has 2 types:
- Type No. 1 - a small amount of anticoagulant produced;
- Type No. 2 - antithrombin is of poor quality and does not have an active function.
The following tests will help distinguish between congenital and acquired deficiency states by type:
- Protein activity testing;
- Test for a quantitative indicator of antithrombin - antigen.
Low anticoagulant index in blood plasma
Antithrombin 3 is reduced, which means that the following factors occur in the blood plasma:
- The tendency of the bloodstream system to thrombose arteries;
- Hereditary deficiency of antithrombin 3, which has a congenital etiology;
- Chiari-Budd syndrome;
- Cirrhosis of liver cells;
- Hepatitis of all types;
- Neoplasms in liver cells;
- Liver failure;
- Oncological neoplasms in kidney tissue;
- Kidney type failure;
- DIC syndrome in the acute stage of pathology;
- Thromboembolism is a pathology of blockage of large-diameter arteries;
- 3rd trimester of pregnancy in women;
- Mid-cycle of menstruation;
- Atherosclerosis - deposition of cholesterol plaques in large arteries, preventing the work of anticoagulants;
- Malignant neoplasms (cancer) with metastasis;
- Nephrotic syndrome (protein in urine);
- Pathology hypoproteinemia is a decrease in the protein index in the blood;
- Increased bleeding of the skin due to hemorrhagic rashes;
- Pathology malabsorption - the absorption of substances by parts of the intestine is impaired;
- Dystrophy in a severe stage;
- After surgery;
- Burns over a large area;
- Necrosis of tissue cells during myocardial infarction;
- Injuries due to heavy bleeding;
- Heparin therapy for a long period;
- Failure to comply with the dosage when taking oral contraceptives.
Why does the level change?
Antithrombin, like most blood components, can from time to time either increase or decrease relative to normal levels. If we are talking about an increase, then this is often due to the regular use of drugs that have a thinning effect on the blood. In addition, the following cannot be ruled out:
- acute lack of vitamin K;
- acute viral hepatitis;
- inflammatory processes;
- menstruation.
It is worth noting that if we are talking about an increase in the pathological nature, then a high risk of bleeding is created. This condition poses a danger to human health and life, and accordingly requires timely treatment.
Reduced antithrombin III levels may also occur. More often, it can be affected in this way by the launch of a coagulative cascade. This leads to a possible risk of developing thrombotic complications. This feature also appears in the last trimester of pregnancy. This feature is observed in girls in the middle of the menstrual cycle and when taking oral contraceptives or hormones. We are talking about estrogens.
We cannot exclude the option in which a reduced AT III level acts as a symptom of the development of a complex disease. Among this list, it is especially worth highlighting atherosclerosis, within which diseases of the cardiovascular system are present on a chronic basis. This leads to the deposition of cholesterol on the internal vascular walls.
Congenital antithrombin deficiency, liver diseases, and disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome cannot be excluded. This problem can occur with sepsis or thromboembolism.
As a rule, little is said about elevated antithrombin III. Sometimes patients themselves cannot figure out whether the indicator is low or high, because in relation to other laboratory tests the word “increased” is more often used, and people are accustomed to this. The fact is that with regard to antithrombin 3, indeed, more often we are talking about its reduced values, that is, about a deficiency, which, excluding the physiological drop in the level in newborns and during pregnancy (not lower than certain concentrations, however), is observed in the following cases:
- Long-term use of hormonal oral contraceptives;
- Conditions after surgical interventions, injuries;
- Prolonged bed rest (immobilization of limbs, for example);
- L-asparaginase therapy;
- The use of high doses of heparin, which markedly increases the destruction of antithrombin 3 in plasma;
- Delays in the ovulation process;
- Long-term use of corticosteroids;
- Massive blood loss;
- Genetically determined deficiency of this anticoagulant, including age-related hereditary thromboembolism;
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome (DIC syndrome), consumption coagulopathy;
- Damage to the liver parenchyma with impaired liver function providing protein synthesis (liver failure, cirrhosis, cancer);
- Malignant tumor processes;
- Thrombosis;
- Septic conditions;
- Shock;
- The use of high doses of blood products (fibrinogen, cryoprecipitate, fibrinostat) intended to stop bleeding;
- Nephrotic syndrome, when a large amount of AT III is lost in the urine.
There are significantly fewer cases when this natural anticoagulant is elevated:
- Acute hepatitis of viral origin;
- Treatment with indirect anticoagulants;
- Vitamin K deficiency;
- Cholestasis;
- Inflammatory processes (acute and chronic).
- Anabolic hormone therapy.
Treatment of anticoagulant imbalance
The lower value of the antithrombin index 3 is variable, and there are several physiological reasons for this - menstruation in women, pregnancy.
The level of this protein must be constantly monitored, because with a sharp decrease in it, more than 30.0% of patients die due to thrombosis of large-diameter arteries.
How to increase? The basis of drug therapy for low anticoagulant index is antithrombotic drugs.
In case of severe symptoms of thrombophilia pathology, drugs containing low molecular weight heparins are prescribed:
- The drug Enoxaparin sodium;
- The drug Dalteparin sodium.
Dalteparin sodium
If the level of the anticoagulant Sodium is too low, heparin is not used, as there is a risk of heparin-induced vein thrombosis.
During pregnancy, the drug Clexane is used, which contains low molecular weight heparins and exhibits the activity of factor Xa, as well as factor IIa.
The treating doctor prescribes the medication course and dosage individually and constantly monitors the anticoagulant index using the hemostasiogram method.
The dangerous period of pregnancy for a decrease in the antithrombin index is the 2nd and 3rd trimester. During this period, it is necessary to constantly monitor the hemostasiogram.
It is also recommended that non-pregnant women and men take drugs from the vitamin K antagonist group - the drug Warfarin.
With an increased antithrombin index 3, the drug course consists of drugs from the group - coagulants.
Medicines
Against the background of such treatment, therapy is carried out using the following means:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- glucocorticoids, for example, Prednisolone.
For some patients, surgery is necessary, and the indications for surgery may be as follows;
- Graves' disease;
- nodular toxic goiter;
- iodine-induced thyrotoxicosis.
In order to generally strengthen the entire body, patients are recommended to take vitamins and adaptogens. Subsequently, doctors prescribe medications that you will have to take throughout your life.
Traditional medicine will also be useful in treatment when the level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase begins to increase. As a rule, for three to four months the patient drinks tea, for example, from celandine, chamomile or licorice root, and at the end of the period it will be advisable for him to switch to other remedies.
If AT to TPO is elevated, treatment should be comprehensive and timely.
You can prepare herbal preparations yourself. An example is persimmon tincture, which will help normalize hormone levels. The procedure is as follows:
- squeeze the juice out of the fruit;
- mix two hundred milligrams of the resulting substance with a couple of drops of alcohol;
- leave the product for two days;
- drink one tablespoon of the resulting infusion before meals three times a day.
Complications and consequences of disturbances in the anticoagulant system
With an increased antithrombin index 3, there is a high risk of heavy bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth. Bleeding from injuries—internal and external—is the most common cause of death.
With a reduced index of this protein, there is a high probability of the occurrence of such dangerous pathologies, which often lead to death:
Acute coronary syndrome;- Ischemia of the cardiac organ;
- Myocardial infarction;
- TELA;
- Stroke;
- Thrombosis of the arteries of internal organs;
- Hypoxia of organs and tissues of the body.
Prevention
Systematic monitoring of plasma antithrombin 3 levels using a hemostasiogram, as well as using the coagulogram technique.
Promptly correct deviations of this protein in any direction.
For normal antithrombin 3 levels, take vitamin K for prevention.
Proper nutrition and adequate stress on the body.
As a preventative measure, take the drug Antithrombin III. This drug is used for congenital types of pathology, as well as acquired forms.
In case of congenital pathology, it is necessary to protect the vessels as much as possible from possible relapses of the disease. This suggests that unless absolutely necessary, do not use methods of intravenous drug administration and unnecessary blood sampling.
Antithrombin in pregnant women: deviation from the norm
If the value has not increased by much, the doctor simply observes the situation and may need to repeat the study. And only if the level goes off scale, medications are used.
A serious deviation cannot be ignored. Changes can lead to deep vein thrombosis in the legs, intrauterine fetal death, and miscarriages.
The level of antithrombin in pregnant women is monitored to prevent it from reaching a critically low level, which is dangerous for the life of the mother and fetus. Although a slight decrease, especially by the third trimester, is normal.
Life forecast
A high antithrombin index 3, as well as its low coefficient, are dangerous for humans, since in a complicated form they carry a mortal danger. With timely diagnosis and competent, adequate treatment, this protein can be kept within standard values.
With constant therapy and monitoring of the hemostatic system, the prognosis is favorable.
If treatment is not timely, irreversible processes in the hematopoietic system and disturbances in the blood flow can occur in the body, which can be fatal. In the complicated form of low antithrombin index 3, the prognosis is unfavorable.
AT TG is very elevated - what does this mean for hormonal balance?
Thyroglobulin (TG) is a simple protein synthesized by the thyroid gland. It is an amino acid structure of molecules necessary for the production of the main thyroid hormones - triiodothyronine T3 and thyroxine T4. These hormones are involved in the body's metabolism.
Before its breakdown, unused thyroglobulin accumulates in the spaces between the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. It enters the circulatory system only after conversion in the form of hormones.
In a healthy body, the presence of this protein in the bloodstream is minimal or absent.
Changes in TG levels within normal limits are influenced by:
- thyroid gland volume, size and number of nodules;
- human activity, need for hormones;
- physiological characteristics;
- regeneration after illnesses;
- drug or chemical exposure.
If the level rises to an undesirable level due to metabolic disorders, the body tries to defend itself and begins to produce antibodies (AT) or immunoglobulins (IG).
Attention! Antibodies are synthesized to protect against foreign agents and substances undesirable for normal biochemical metabolism. Their insufficient or excessive quantity is a characteristic of disorders of the immune system.
Understanding what AT TG is in a blood test makes it possible to assess the need for examination. A blood test is a test for the state of the body during hormonal imbalance, malfunction of the thyroid gland, development or suppression of oncological processes.
Indications for analysis may include deterioration in well-being in the form of manifestations:
- fatigue, constant fatigue;
- sleep disturbances, insomnia;
- apathy, lethargy, depression;
- nervousness, causeless mood swings;
- sudden fever or chills, hot flashes;
- sensation of a “lump” in the throat, change in voice;
- an increase in the size of the thyroid gland;
- dermatitis, deterioration of the nail plates and hair.
Timely diagnosis makes it possible to timely diagnose a developing disease and take preventive measures to treat it at an early stage.