One of the simplest and most accessible examination methods is ultrasound diagnostics, which allows you to identify a number of diseases. The complex of abdominal cavity examinations includes ultrasound.
But not everyone can decipher an ultrasound of the gallbladder normally. It is this organ that has a number of anatomical features that should be paid attention to.
Indications and contraindications for the study
Some conditions require an ultrasound of the bile ducts and bladder. These include:
- attack of hepatic colic,
- a history of gallstone disease,
- bursting pain in the right hypochondrium,
- yellowness of the skin and sclera of the eyes,
- traumatic injury to the abdominal cavity,
- dynamic observation of the patient during the prescribed course of treatment,
- suspicion of developmental abnormalities,
- monitoring the patient’s condition after surgery,
- the need to check the blood supply to the gallbladder before surgery.
The range of contraindications is extremely limited due to the high safety of the method and the ease of its implementation. You cannot do an ultrasound of internal organs if:
- inappropriate behavior of the patient, the presence of mental illnesses that prevent the manipulation,
- severe somatic condition of the patient, threat to his life,
- the patient is under artificial ventilation in the absence of a mobile ultrasound scanner,
- damage to the skin of the right hypochondrium (burn, abrasions, etc.).
Pathological changes
The anatomy of the liver and gallbladder is standard for all people. Normally, slight fluctuations in the size and location of the structures described above sometimes occur, which causes difficulties in the process of surgical interventions.
Before surgical treatment, a thorough diagnosis is carried out to determine the location of all abdominal organs.
Pathology of the common bile duct is accompanied by changes in its structure and size. Concretions (stones) can form inside the duct or worms can multiply, interfering with the normal passage of bile.
The corresponding processes cause local inflammation and swelling of the walls of the biliary tract with impaired digestive function. Pathology of the common bile duct in 85% of cases requires surgical intervention. The reason is a deterioration or complete cessation of the flow of bile into the duodenum with the progression of jaundice and digestive disorders.
Indications for diagnosis in children
An ultrasound examination of a child’s gallbladder can evaluate the shape, size, features of its structure and function. In addition, it is possible to visualize surrounding tissues, as well as determine the presence of various types of space-occupying formations.
Most often, pediatricians send children to an ultrasound diagnostic room if they have the following complaints:
- abdominal pain,
- stool discoloration,
- dark colored urine
- yellowing of the skin and white eyes,
- change in stool consistency
- other dyspeptic phenomena.
Since the diagnostic method is completely safe even for a child’s body, it is recommended for all newborns to undergo it. This allows us to exclude the presence of developmental anomalies and biliary dyskinesia in the infant.
How to do an ultrasound
The doctor examines the gallbladder transabdominally. That is, an ultrasound examination will be performed through the abdominal wall. The patient needs to lie on his back.
The doctor will apply a special gel to the sensor and begin the examination. The procedure is absolutely painless. An exception may be situations when a person has an exacerbation of any chronic disease of the gallbladder.
The study is deciphered immediately after the procedure.
What do doctors pay attention to?
The interpretation of the ultrasound of the gallbladder is carried out by a functional diagnostics doctor, taking into account the history of the disease, clinical picture, structural features of the body, and the presence of concomitant pathologies. Additional examinations and tests provide significant assistance in this regard. These include:
- general and biochemical blood status,
- urine microscopy,
- computer scan of the abdominal cavity,
- dynamic ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of organ function.
First of all, pay attention to the structure, anatomy of the gallbladder, and the features of its blood supply. It is usually determined in the right hypochondrium. If the bubble is not visible, one can suspect its congenital absence and severe developmental anomaly. Some diseases of the lungs and liver can lead to a downward displacement of the organ, which somewhat complicates an ultrasound scanning session.
It is important to remember that the results of ultrasound examinations will be reliable only if all the doctor’s recommendations for preparing for the procedure are followed.
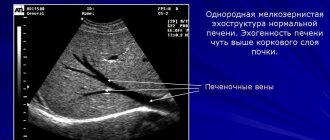
The contents of the gallbladder are normally determined by ultrasound as echo-negative and homogeneous . This means that with proper preparation for the study, the cavity contains liquid (bile) that does not have impurities. The contour (wall) around the contents is clear, hyperechoic, smooth, and thin. A vague outline may indicate the presence of inflammatory processes.
During diagnosis, other structures are also assessed, including the common bile duct of the biliary tract. This formation takes digestive enzymes to the duodenum, where the most important processes of food digestion occur. If the lumen of the common bile duct changes (narrowing or pathological expansion), the question of the presence of dyskinesia is raised.
Carrying out the procedure
When diagnosing a bladder, the best option is to simultaneously check all organs of the gastrointestinal tract. A typical examination begins with the patient lying on his back on a medical couch. Then the belly is exposed, the diagnostician applies a gel to it that improves the conductivity of ultrasound. If the bottom of the organ is covered by the intestines, then the person is asked to take a deep breath, and then hold his breath for a couple of seconds and turn over on his right side. To detect sand and stones, the patient must stand up and make several turns with his body.
Ultrasound with stress
Sometimes an ultrasound of the gallbladder with a load is required. This allows you to evaluate the contraction of the bubble. Initially, the procedure is also performed on an empty stomach. Then the patient is examined and eats a couple of eggs, 250 g of low-fat cottage cheese or sour cream. Instead of food, a sorbitol solution is used. After this, the scan is repeated three more times with an interval of five minutes.
Ultrasound after bladder removal
Ultrasound after resection of the bladder is called echo-choledochography. The examination is also initially performed on an empty stomach. The condition of the organ and all its ducts is assessed. Then food or sorbitol solution is taken. A repeat scan is done after 30-60 minutes.
Indicators are normal
To assess the condition of the biliary tract as completely as possible based on the results of ultrasound scanning, an algorithm for performing the procedure was created, during which the following indicators are noted:
- bladder shape: ovoid, round, decreasing towards the neck. In the same section, Hartmann's biliary pouch may be observed, which is formed as a result of pathological stretching of the walls due to cholelithiasis,
- Dimensions: length does not exceed 100 mm, diameter - 30 mm, wall thickness - up to 3 mm,
- diameter of the common bile duct (should normally be no more than 8 mm),
- organ contents: usually echo-negative, homogeneous, without foreign impurities,
- interlobar ducts (cross-sectional diameter no more than 3 mm).
In addition to these indicators, the condition of the surrounding tissues of the liver, lungs, diaphragm, pancreas, and spleen is always noted. This is necessary to exclude concomitant pathology and its effect on the biliary system.
Preparation
Preparation for determining the function of the gallbladder by ultrasound is a necessary condition for obtaining reliable results, if ignored, data distortion may occur. The preferred time to start preparation is at least 5-7 days.
- Taking alcoholic beverages and fatty foods is out of the question.
- All foods that cause gas formation are excluded from the diet: baked goods, legumes, raw vegetables and fruits, dairy products.
- It is recommended to take medications that speed up the digestion of food. The dosage and name of the product will be prescribed by the doctor; the most used are: Creon, Mezim.
- It is possible to prescribe carminatives for increased gas formation (Espumizan).
- The last meal on the eve of diagnosis is no later than 7 pm, breakfast is skipped. Provided that the procedure is scheduled for the afternoon, it is allowed to have a light breakfast.
For children over 8 years of age, preparation is the same as for adults. Preparing babies under one year of age who are breastfed is not required; the study is carried out before feeding.
Children from one to three years old need a 4-hour break from eating. Up to 8 years of age, fast for at least 6 hours.
Indicators for cholecystitis
Inflammatory processes in the biliary system are usually accompanied by characteristic changes in the ultrasound picture. The main signs of cholecystitis include:
- thickening of the walls of the gallbladder, changes in their echogenicity, contours,
- increase in the size of the gallbladder,
- the appearance of all kinds of small streak-like inclusions in the cavity, changes in the consistency of bile,
- infiltration of surrounding tissues, their swelling associated with secondary damage,
- disruption of interorgan interaction,
- increased blood flow in the cystic artery, detected during Doppler sonography.
The most vivid ultrasound picture is characteristic of acute cholecystitis. In this case, swelling of the wall can reach 25 mm. In this case, the patient complains of sharp pain in the right hypochondrium, dyspeptic symptoms in the form of nausea, vomiting. stool changes. These data enable the doctor to suspect an inflammatory process and pay closer attention to the problem area.
In severe cases, it is possible to identify a heterogeneous hyperechoic zone with unclear contours around the area of interest. This picture is typical for complications of cholecystitis in the form of gangrene, rupture or abscess formation of the inflammatory focus.
Cholelithiasis
The presence of stones in the biliary system allows a diagnosis of cholelithiasis to be made. The easiest way to identify them is ultrasound scanning. The following signs of pathology are noted:
- hyperechoic inclusions in the organ cavity with the effect of an acoustic shadow - this is the main symptom when writing a conclusion. Stones can be single or multiple. It is mandatory to measure their size, shape, as well as displacement when pressed with a sensor,
- During the examination, the doctor tries to determine the exact location of the stones. The entry of stones into the ducts changes the patient’s treatment tactics.
The presence of cholelithiasis does not exclude cholecystitis. On the contrary, during exacerbations these two conditions often accompany each other. Therefore, the conclusion may contain several identified pathologies at once.
Features of the picture with polyps
The ultrasound image of gallbladder polyps looks like solid formations located near the wall and associated with the organ. Polyps differ from stones in the following ways:
- no acoustic shadow effect,
- impossibility of displacement of formations,
- sizes usually do not exceed 10-12 mm,
- slow growth or lack thereof,
- the ability to visualize the stalk (attachment site) of the polyp,
- medium or hyperechoic structure,
- lack of blood flow and weak Doppler signal from the cystic artery.
Dynamic monitoring of the patient and additional examination methods are extremely important when interpreting data. This allows for differential diagnosis with cholelithiasis and malignant tumors of the biliary system. Re-appointment of ultrasound is necessary in case of attempts to dissolve cholesterol polyps to confirm the effectiveness of treatment.
Genetic deviations from the norm
The following types of developmental anomalies of the biliary system are distinguished:
- Pathologies of the gallbladder: congenital absence, reduction in size, change in shape, structure (diverticulosis, presence of septa), duplication, abnormal position (intrahepatic, on the opposite side of the body),
- Pathologies of the intrahepatic ducts: cysts and congenital displacement,
- Anomalies of the extrahepatic ducts: common bile duct cysts, its absence. In this case, differential diagnosis is carried out with pathological narrowing of the common bile duct.
Biliary strictures
Strictures are narrowings of the lumen of the ducts, due to which the outflow of bile into the duodenum is disrupted.
Experts divide the causes of such pathologies into three groups:
- traumatic - occur during surgery or mechanical damage, as well as as a result of obesity and radiation exposure;
- caused by inflammation (sclerosing cholangitis, opisthorchiasis, cholecystitis or chronic pancreatitis);
- tumor - occur when neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature appear.
Treatment of strictures of this duct, if necessary, is carried out surgically.