Calcium is one of the most important elements in the human body. It is involved in metabolism, the formation of bone tissue and their healing during injury, maintains the level of metabolism, and contributes to the regulation of most important processes for life. A blood test for calcium helps to recognize the disease, identify an excess or lack of calcium, which also leads to various pathologies and disruptions in the functional functioning of the body's systems, and uncomfortable conditions.
Calcium is involved in the normalization of the endocrine glands, heart rate, functional activity of the heart and blood vessels, the central nervous system, transmitting impulses to organs and tissues, and helps muscles contract. The strength of teeth and bones, blood clotting, and the permeability of cell membranes depend on this element. Ca deficiency leads to disruption of enzyme activity and iron metabolism in the body.
Forms of calcium in the body
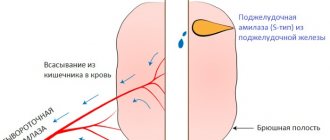
Total calcium (Ca) is divided into three forms, each of which has its own concentration in the blood. The share of ionized calcium accounts for 50%; the share of calcium bound to proteins, including albumin, is 40%; the anionic complexes contain 10% Ca, i.e. lactate, citrate, bicarbonate and phosphate are associated with it. Ionized calcium is considered the most important, since it contains no impurities and is actively involved in the calcium metabolism of cells.
It is important to know. Determination of ionized calcium in the blood is carried out in combination with pH and the level of total calcium in the blood. Indicators of ionized Ca increase by 1.5 - 2.5% with each decrease in pH by 0.1 unit. It is easier to find out the level of total calcium in the body than ionized calcium. Sometimes, with a normal concentration of total calcium in the blood, ionized calcium levels may be overestimated, then the high data is taken as a basis.
What does calcium metabolism depend on?
Most of it in the body is contained in bone tissue in the form of insoluble compounds - hydroxyapatites.
And only one percent of it in the form of compounds with phosphorus is soluble and can serve as a reserve in case of shortage. The other type is found in the blood plasma, where it comes from the intestines or as a result of leaching from the bones. In the blood, the element is contained in the form:
- compounds with albumin;
- salts: phosphates, sulfates, carbonates, etc.;
- free (ionized).
Of interest for the study is the total amount, as well as the level of free calcium in the blood; with the slightest fluctuations in it in the body, disturbances in the formation of bones and teeth can occur, the permeability of the vascular wall, the conductivity of nerve impulses, and muscle contractions can change.
This exchange is regulated by special hormones:
- calcitonin;
- parathyroid hormone;
- calcitriol.
Their production depends on the level of calcium; they activate its absorption in the intestines, the synthesis of vitamin D in the skin, decreased excretion by the kidneys or, conversely, leaching from the bones.
In a child’s body, calcium is not formed; all of it comes from food:
- in the prenatal period - thanks to the mother’s body;
- after birth - proper nutrition.
Vitamins A and D are of great importance in metabolism.
The latter comes from outside with food or is produced in the skin under the influence of sunlight. As a result of complex biochemical reactions, vitamin D absorbed in the intestines is converted into calcitriol, which regulates the level.
Despite the large amount of this mineral in food, it is not easy for the body to absorb calcium, since it is most often found in the form of poorly soluble compounds.
Acid gastric juice helps convert calcium into a form more convenient for absorption. Therefore, any foods or medications that reduce acidity may interfere with its absorption from food.
Dairy products (cream, cheeses, cottage cheese), in addition to a high concentration of the substance, contain a special enzyme - lactose, which helps lactobacilli produce lactic acid in the intestines, which breaks down calcium salts. Citric and tartaric acids, fats, and amino acids help improve absorption. But in cereals, spinach and sorrel, calcium is found in insoluble compounds that are poorly absorbed.
With insufficient intake and a decrease in the level of this substance, the body begins to destroy its own tissues, trying to restore balance, which leads to disturbances in the growth and development of the child, as well as various diseases.
See the following article on the site: adenohypophysis is the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, which is responsible for a number of the most important metabolic and hormonal processes in the human body. Read about the drug Cordarone, which is used in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmia, here.
For information on the levels of the hormone androstenedione in women, see here.
Normal levels of Ca in the blood
A biochemical blood test in which the Ca level reaches (in mmol/l) is considered normal:
- 1.75 – 2.6 – in newborn infants;
- 2.1 – 2.7 – in children under 1.5 years of age;
- 2.2 – 2.7 – in children 1.5 – 14 years old;
- 2.1 – 2.65 – in children over 14 years of age and adults under 60 years of age;
- 2.2 – 2.55 – in older people 60 – 90 years old;
- 2.05 - 2.4 - in old people after 90 years.
An adult needs 0.45 - 0.8 - 1.2 g (1000 - 1200 mg) of Ca per day, a child - 100 - 400 mg, pregnant and lactating women - 1500 - 2000 mg. During menopause – 1400 mg, for old people – 1200 mg and for newborn children – up to 600 mg. At puberty, boys - 280 mg, girls - 200 mg. The maximum daily norm of Ca is 2500 mg.
Replenishing the body with calcium should be discussed with your doctor, since medical sources indicate different daily doses of Ca for adults and children.
If a calcium test shows abnormalities, then the doctor will rely not only on the calcium level, but also on the symptoms of the disease to make the correct diagnosis.
Ca is outside the norm
Indications above normal indicate the following pathologies:
- malignant neoplasms;
- leukemia;
- acute renal failure;
- excess vitamin D;
- various forms of hypercalcemia, including physiological in infants and hereditary;
- pathologies of organs involved in the regulation of hormonal levels: thyroid gland, pituitary gland, adrenal glands;
- sarcoidosis
Pathologies such as:
- acute pancreatitis;
- liver dysfunction;
- improper kidney function;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- hypoparathyroidism.
In any deviation from the norm, in explaining the reasons for a decrease or increase in content, a number of factors are involved.
Rate this article:
Symptoms for analysis
The doctor records all the patient’s complaints and prescribes a general calcium test for the following symptoms:
- pain in joints and bones, in the heart and abdomen;
- paresthesia – a sensitivity disorder in muscle tissue: numbness, tingling, “crawling”;
- cramps and nervous tics in the muscles of the limbs, face, eyelids, around the eyes, etc.;
- nervous excitability and insomnia;
- arrhythmias, palpitations, shortness of breath, tinnitus;
- polyuria - excessive urination, especially at night.
A biochemical blood test is prescribed in the process of diagnosing the following diseases:
- osteoporosis and bone tuberculosis;
- cardiovascular and digestive systems;
- skin, muscles, tendons, connective tissue, etc.;
- conditions after injury, including burns;
- ulcers of internal organs;
- oncological tumors, including inside the body, in the brain, blood and skin;
- urolithiasis;
- pulmonary, cardiac and liver failure;
- hyperthyroidism or thyrotoxicosis against the background of a surge of hormones and an excess of T3 (thyroxine) and T4 (triiodothyronine);
- cachexia (severe exhaustion);
- sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease.
Blood biochemistry for calcium is prescribed during the period of preparation for surgical operations and before blood purification with an “artificial kidney” apparatus, which is called hemodialysis. Determination of the total level of Ca in the blood is mandatory during long-term treatment with calcium preparations: heparin, magnesia and others.
Free circulation of ionized Ca occurs in the blood, which makes it possible to activate all physiological processes. Calcium ionized blood shows the state of calcium metabolism, and the test is taken during resuscitation and treatment of extensive injuries, burns and conditions after surgical interventions and also before hemodialysis. The indications help diagnose cancer and thyroid hyperfunction. The level of both ionized Ca and total calcium should be monitored when taking bicarbonates and other drugs.
How to give calcium to your child
Calcium for children. Normal blood calcium levels in children. What foods contain calcium.
Calcium is necessary for a child from the first days of life. It is one of the most important minerals. Calcium takes part in the formation of bone tissue, teeth, and maintains muscle tone. It also underlies nervous excitability, reduces vascular permeability (therefore prescribed for skin diseases).
Cracks in teeth.
Brittle bones, frequent fractures.
Nails become brittle, dry skin.
Signs of calcium deficiency in infants:
Hair loss on the back of the head.
Poor restless sleep, as calcium is involved in nervous excitability.
Sometimes posture is disrupted and the shape of the legs changes.
All this may indicate a lack of calcium and the possible presence of rickets. If there is a suspicion of a lack of calcium in the body, you need to take a referral from a doctor for urine tests according to Sulkovich. This test shows the concentration of calcium in the urine. It is also better if a blood test is taken. Normal blood calcium is 2.15-2.5.
What does calcium metabolism depend on?
Calcium metabolism is influenced by many factors: the amount of vitamin D, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone and calcitonin. Both deficiency and excess of any factor leads to calcium metabolism disorders. Excessive intake of calcium also has a bad effect on the body. It prevents iron from being absorbed, is deposited in soft tissues, causing constipation and leg cramps.
This is why you cannot give your child calcium supplements on your own. It should be prescribed by a doctor and strictly according to indications.
Infants get enough calcium from breast milk. There is not much in quantity, but due to the ideal proportion with phosphorus, it is quickly and well absorbed. Cow's milk contains a lot of calcium, but the ratio with phosphorus does not allow it to be absorbed. And it turns out that phosphorus is excreted, since there is a lot of it, and with it calcium, as a result, little calcium is absorbed. And the load on children’s kidneys is very large, which is why in many countries around the world it is not recommended to drink cow’s milk before the age of 3.
After three years, the kidney regulates mineral metabolism well, and you can give cow's milk. For many parents, this will seem strange and it is quite difficult to convince them, so we recommend abstaining from cow's milk for up to a year, and then diluting it with water.
Formula-fed babies receive calcium from formula, but compared to breast milk, it is slightly less absorbed. With complementary foods, the child will receive additional calcium; it is also found in cereals, lactic acid products, fish, and eggs.
Older children should also receive foods high in calcium, which is essential during growth.
What foods contain calcium.
The leader in the amount of calcium is hard cheese, also cottage cheese, and milk. It is very useful to eat foods that contain calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D: seafood, egg yolk, beef liver.
Also useful are foods containing both calcium and phosphorus: beans, cabbage, apples. Many people mistakenly think that calcium is only found in dairy products and fish, but this is not true.
Here is a table of foods that contain calcium.
As you can see, it is also found in greens, vegetables and fruits.
What slows down calcium absorption: - chocolate, cocoa, spinach, caffeine, fatty foods.
Calcium supplements for children.
A calcium supplement must be prescribed by a doctor. For children, the best option is calcium gluconate; it is allowed even for infants. For children over 10 years of age, its dosage is 12-18 tablets, and for older children even more, so there is no point in prescribing this drug. It is better to use drugs with a higher dosage, for example calcium D 3 nycomed, Vitrum Calcium, Kalcemin.
If you are prescribed calcium, you must remember that the maximum time when calcium is absorbed is 9 pm, so you need to drink it after 6-7 pm, so it will be better absorbed. This information was obtained after multiple studies.
Preparatory period for the analysis
For diagnostic reliability and accuracy of test results, it is necessary to donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach from 8 to 11 o’clock. To do this you should:
- do not eat anything after an early dinner, you are allowed to drink still water;
- do not include heavy foods (fatty, fried, spicy) and alcohol in the diet during the day;
- do not eat foods high in calcium for a day: nuts, coffee, legumes, dairy products and cabbage;
- give up physical activity for a day;
- do not treat with drugs that affect the analysis parameters for a week.
Important. If the medications cannot be stopped, then the doctor needs to be informed about their use, duration and dosages, and indicate the names. Before donating blood, fluorography, radiography, ultrasound, rectal examination or physiotherapeutic procedures are not performed.
Deviations from the norm and causes
If the results deviate from the reference values of total and ionizing calcium, the first priority is to determine the cause of the violations. The patient needs to undergo additional tests, consult an endocrinologist, cardiologist, and also need hardware diagnostics (ultrasound).
Underestimated figures
Reduced levels of total calcium may be associated with hypoalbuminemia (low albumin protein), but this indicator does not affect active Ca alone. A decrease in the amount of bound and free macronutrients can be caused by chronic pathologies, acute conditions, and unhealthy eating behavior.
The main causes of hypocalcemia are:
- poor diet (lack of foods containing calcium and D vitamins in the menu, questionable diet, fasting);
- insufficient production of parathyroid hormone (primary hypoparathyroidism or pseudohypoparathyroidism);
- impaired resorption in the small intestine (malabsorption);
- chronic pathologies of the renal apparatus (nephritis, pyelonephritis, renal failure, nephropathy, etc.);
- acid-base imbalance with increased acidity (acidosis);
- disturbance of mineral metabolism and the process of bone tissue formation in infants (rickets);
- change in hormonal status in women during the postmenopausal period;
- previous operations on the parathyroid and thyroid glands;
- relapse of chronic pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas);
- benign proliferation of adrenal cortex tissue (hyperplasia);
- cancer tumors with metastases in the skeletal system.
Disturbances in calcium metabolism can be caused by incorrect use of medications (antitumor, diuretic, anticonvulsant, hormonal).
Inflated figures
Some causes of hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia have a common etiology (origin), but the body may respond differently to the resulting disorders. Factors that provoke an increase in calcium concentration include:
- excess synthesis of parathyroid hormone (hyperparathyroidism);
- malignant neoplasms, especially cancer of the blood (leukemia) and cancer of the lymph nodes (lymphoma);
- excessive activity of the thyroid gland in the production of certain types of hormones (hyperthyroidism);
- excess of vitamins D in the body;
- diseases of the kidneys, renal tubules, glomeruli, etc., of a chronic nature, as well as donor organ transplant surgery;
- a shift in the acid-base balance with the accumulation of alkali in the blood (alkalosis) and alkalization of the body due to the development of Burnett's syndrome;
- insufficient secretion of hormones from the adrenal cortex (hypocortisolism);
- increased production of growth hormone (samotropin), otherwise acromegaly;
- forced long-term immobilization (stationary state) in the postoperative period.
Medicines that distort test results
Calcium in the blood increases when treated with drugs containing calcium salts, parathyroid hormone and progesterone, androgens, as well as vitamins A and D, lithium, Tamoxifen, Testolactone, Tamoxifen, Isotretinoin, Ergocalciferol, Dihydrotahysterol , Danazol, Calusterone, diuretics in large quantities.
Ca decreases during treatment with sulfates, corticosteroids, Tetracycline, Methicillin, Insulin, Carboplatin, Plicamycin, Indapamide, Phenytonin, Carbenoxolone, Isoniazid, Calcitonin, Carbamazepine ", "Albuterol", "Alprostadil", as well as drugs with Mg salts, estrogens, glucose, glucagon, gastrin, ergocalciferol (a type of vitamin D) in large quantities, asparaginase, aminoglycosides, calcium oxalates, fluorite (D-Fluoretten 500 IE) .
Diseases associated with hypercalcemia
An excess of Ca is indicated by analysis in the following pathological conditions:
- iatrogenic hypercalcemia;
- hypervitaminosis D;
- sarcoidosis and other granulomatous diseases;
- acute renal and adrenal insufficiency;
- milk-alkali syndrome;
- hematological malignancies: multiple myeloma, lymphoma, leukemia;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- Williams syndrome (idiopathic hypercalcemia), which occurs in infants at birth;
- hypocalciuric hypercalcemia, inherited;
- primary hyperparathyroidism: adenoma, hyperplasia or carcinoma of the parathyroid glands;
- immobilization hypercalcemia when receiving calcium supplements in connection with the treatment of injuries, congenital hip dislocation, spinal tuberculosis, Paget's disease.
In case of an overdose of calcium drugs or the presence of hormonal disorders, tumors and other diseases, the symptoms of hypercalcemia are manifested by constipation, muscle spasms, lethargy and fatigue, extreme thirst, increased urge to urinate, and painful attacks in the kidney area.
Symptoms of calcium excess and deficiency
Hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia have characteristic manifestations, when they occur, it is necessary to examine the blood to determine the calcium level.
Symptoms of calcium imbalance
| Promoted | Demoted |
| limited physical capabilities, CFS (chronic fatigue syndrome) | cephalgic syndrome (headache) |
| dysania (sleep disorder) | psycho-emotional instability (unmotivated aggression or complete apathy to what is happening); |
| disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, manifested by nausea, constipation, difficult and painful digestion of food | aching joints, pain in the lumbar and cervical spine |
| polydipsia (permanent thirst) | violation of the structure of hair and nails (fragility, thinning, dryness) |
| pollakiuria (intensive emptying of the bladder) | dental problems |
| uncontrolled muscle contraction (convulsive syndrome) | failure of rhythmic heart function |
| tachycardia (increased heart rate) | hypocoagulation (decreased blood clotting rate) |
The first somatic signs of calcium balance instability are most often a decrease in tone and performance. Potential patients tend to associate this with fatigue from everyday stress and are in no hurry to seek medical help. The listed symptoms should not be ignored. If you feel unwell, you must undergo an examination, including a blood test for calcium levels.
Diseases associated with hypocalcemia
If there is not enough Ca in the blood, then a person may be sick:
- chronic renal and liver failure;
- acute pancreatitis with the presence of pancreatic necrosis;
- osteomalacia with malabsorption, malnutrition, decreased insolation (in adults);
- hypovitaminosis D with rickets (in children);
- hypoalbuminemia due to liver disease and nephrotic syndrome;
- hypoparathyroidism primary (hereditary) or secondary (autoimmune, after surgery);
- hereditary pseudohypoparathyroidism;
- hypomagnesemia.
With calcium deficiency, the body initially removes it from its own reserves, so characteristic symptoms do not appear. When the bones lose their mass, the patient’s eyelids and corners of the mouth, wings of the nose begin to twitch, fingers and toes begin to go numb, nails break and become covered with grooves, and teeth decay. Children's growth slows down.
When should calcium levels be closely monitored?
During a routine examination of the child, the pediatrician may notice some deviations from the norm, which will be associated with an increase in calcium metabolism. The doctor should immediately give a referral for a blood test and calcium level in it. Most often this occurs as a result of the following indications:
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system, as well as aches in the bones or they become very fragile.
- Before scheduled elective surgery.
- Cases of permanent fractures.
- Decrease in the albumin-globulin ratio.
- For stomach ulcers or diseases of the duodenum, as well as for dysbacteriosis.
- If the child does not digest lactose.
- When diagnosing various diseases.
- In case of disruption of the baby's muscles, which occurred as a result of improper functioning of the cell membrane.
- If the development of malignant tumors is diagnosed or suspected.
- Diseases in the kidneys or with the development of urolithiasis. And also in the presence of polyuria or urine output of more than two liters in one day.
- Failure of the heart and some changes or dysfunction in the vascular system of the body.
- Paresthesia.
- The appearance of permanent or temporary days.
- Screening for osteoporosis.
- Diseases such as hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia.
In newborns, as well as in infants, with calcium deficiency in the body, a disease such as rickets begins to develop. It causes symptoms such as hair loss on the back of the head, and the legs and posture begin to develop incorrectly. At the same time, a lack of calcium in a child’s body can affect the nervous system and its excitability.