Increased hemoglobin during pregnancy poses a serious danger to the health of the woman and child. Fetal development may slow down. Therefore, indicators must be monitored and in case of deviations, indicators must be normalized.
High hemoglobin during pregnancy is uncommon. Usually there is a decrease. Therefore, the complex of examinations that a woman must undergo includes a general blood test. This is how hemoglobin is detected. This indicator is used to determine the woman’s health status.
What is hemoglobin and its norm
Most often, during gestation, patients experience a decrease in hemoglobin during pregnancy. This is a completely correctable condition, and with the right approach it can be easily corrected. Much more unusual is the clinical situation in which pregnant women have high hemoglobin.
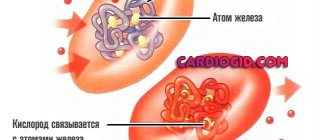
In fact, hemoglobin is a protein unit containing iron compounds and is necessary to provide tissues with oxygen. Hemoglobin transports oxygen supply to all cellular structures in the body, and also carries out the reverse transport of carbon dioxide. The calm course of gestational processes depends on the content of this protein in the bloodstream.
- At the stage of embryogenesis, a hemoglobin level of 112-160 g/l is considered normal;
- In the second trimester, protein is normally 100-140 g/l;
- In recent months, its level should be about 110-140 g/l.
Do not be afraid if the level of elevated hemoglobin in pregnant women exceeds the permissible norms by 20 units or more. This is how the mother’s body adapts to gestation. By the beginning of the second trimester, the indicators are normalized and remain within acceptable limits until the end of the prenatal period.
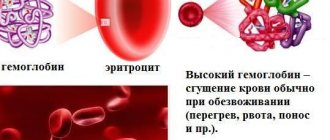
Initially, blood flow increases, blood thinning occurs, as a result of which there is a slight decrease in hemoglobin levels. Increased hemoglobin during pregnancy is much less common in gynecological practice. During the entire period of gestation, the hemoglobin content in the patient’s bloodstream is constantly changing, but this is not scary, the main thing is that it does not go beyond the permissible limits. Hemoglobin in pregnant women is determined by performing a general blood test. An increase in such a protein is usually of secondary origin, or occurs in the form of concomitant pathology.
Symptoms
How can you understand that you have high hemoglobin in your blood even before you take a blood test?
Symptoms of elevated hemoglobin appear as follows:
- Deterioration of visual function;
- Constant drowsiness and weakness in the body;
- Loss of appetite, problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- Pale skin;
- The pregnant woman's condition is not satisfactory.
Symptoms that relate to internal physiological processes
Regarding the internal symptoms that manifest themselves at the physiological level, it can be noted that with an increase in hemoglobin, the blood of a pregnant woman becomes so viscous that this leads to thrombosis.
During pregnancy, a sharp increase in hemoglobin leads to the fact that the fetus experiences an acute oxygen deficiency. The reason is poor, very slow blood circulation, which does not allow all beneficial substances to circulate in the body.
Why is it rising?
High hemoglobin in a pregnant woman is caused by various reasons, which can only be identified with proper diagnosis. Such an increase can be considered a normal phenomenon during early pregnancy. Experts explain that protein also begins to increase due to the restructuring of the mother’s body, its preparation for gestation. Therefore, in the first trimester, hemoglobin growth should not cause any concern.
Smoking causes irreparable damage to the baby's health
Another factor in blood changes is the pregnant woman living in high mountain regions where the air is thin. In such areas, even with a normal blood picture, the body does not receive enough oxygen. Due to hypoxia, forced stimulation of the secretion of additional blood cell structures occurs.
Short-term increases in hemoglobin levels by 10-20 g/l cannot be considered a deviation. Most often, such jumps are caused by changes in physical activity and overwork. Soon the natural restoration of hemoglobin occurs on its own. Factors such as hereditary predisposition, gastrointestinal pathologies, and disruptions in the absorption of B vitamins can increase the hemoglobin content.
Also, factors that increase hemoglobin protein include renal and cardiac pathologies, which cause an increase in red blood cells, and a lack of folic acid entering the body with food. Unhealthy habits have a negative impact on the chemical picture of the blood. Tobacco smoking has a negative impact on all patients, but especially on women carrying a child. In order not to cause irreparable harm to the baby, the pregnant woman needs to avoid smoking.
What symptoms suggest low hemoglobin in pregnant women?
The disease can manifest itself:
- asthenovegetative symptoms (constant weakness, frequent dizziness, drowsiness, tachycardia, shortness of breath, muscle weakness, decreased performance, fatigue);
- sideropenic symptoms (atrophic changes in the mucous membranes and skin, atrophy of the papillae on the tongue, blue sclera, yellowing of the skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle, a grayish tint to the face, alopecia, brittle hair, delamination of the nail plates, concavity of the nails), cheilitis, stomatitis, perversion of taste perception - patients feel the desire to eat raw meat products, chalk, sand, earth, etc. and a perverted sense of smell - patients like the smell of gasoline, solvents, etc.;
- neurological symptoms (urinary incontinence, irritability, tearfulness, nausea, impaired skin sensitivity, chilliness, cold extremities, swallowing disorders (discomfort when swallowing solid food)).
In isolated cases, swelling may occur.
Signs of elevated hemoglobin
If any factor increases the hemoglobin content, it will immediately affect the patient’s well-being. Pregnant women are especially sensitive in this condition, so any changes in well-being do not go unnoticed for them. The state of elevated hemoglobin protein is accompanied by the following symptoms in patients:
- Weakness and drowsiness;
- Impaired clarity of visual functions;
- Decreased performance;
- Lack of appetite;
- Pallor of the skin;
- Deviations in the functions of the excretory system;
- Increased blood flow viscosity.
If hemoglobin is high during pregnancy, then this may be due to a number of different factors, but regardless of the origin of the increased hemoglobin, the patient must understand the risks of such conditions.
What is included in prevention?
So, the first thing that absolutely any doctor will tell you regarding recommendations for preventing an increase in hemoglobin is:
- Proper balanced nutrition;
- An active lifestyle, which does not mean intense physical activity in the gym, but long walks in the fresh air.
- Drinking plenty of water.
If these measures do not have a positive effect on the well-being of a pregnant woman, then the doctor should prescribe certain drug therapy.
Why is elevated hemoglobin dangerous?
Any deviations in the blood flow pattern cause various kinds of disturbances. But for a developing fetus, even minor deviations can lead to critical conditions. Such a dangerous condition for the fetus as an increase in hemoglobin levels poses serious risks. For the full development of the baby, it is important to receive adequate nutrition. The baby receives all components through the maternal bloodstream. If the blood structure is too thick, then circulation through the vascular channels slows down significantly, which is why the baby does not receive the necessary nutrition.
There is no need to wait until the last minute, it is better to consult a doctor immediately
As a result of poor oxygen supply, very unfavorable consequences can develop, such as varicose veins or blood clots, cardiovascular problems, spontaneous abortion or premature birth. Also, an increased iron content in the pregnant body is fraught with fetal death, intrauterine growth retardation, and by the end of prenatal development, the baby often develops hypoxia against the background of increased hemoglobin. To avoid this, you need to bring the hemoglobin protein to normal.
It is important to prepare for pregnancy from the planning stage, at which the patient should be examined and bring the body’s condition back to normal. During the examination, blood and urine tests are carried out, sometimes an increase is required, and less often a decrease in hemoglobin is required. It is important to do this before conception so that deviations from the norm do not affect fetal development.
Experts evaluate not only the content of total hemoglobin protein, but also the level of its glycated form, which shows the numerical amount of sugar in the bloodstream over the past few months. If this hemoglobin form increases, the patient increases the risk of developing diabetes during pregnancy.
How to increase hemoglobin with nutrition
When the hemoglobin component decreases, specialists are in no hurry to prescribe medications to pregnant women; usually, if there is a slight deviation from the norm, they recommend radically reconsidering their lifestyle, regimen, and diet. In more complex cases, of course, they resort to therapy with iron-containing medications. Ideal products for normalizing protein during pregnancy are:
- Beef or veal liver, red meat;
- Oatmeal or vegetable puree;
- Baby juices for feeding babies;
- Heart, fish, kidneys, chicken;
- Buckwheat or lentils, beans or peas;
- Tomatoes and potatoes, pumpkin and onions, beets;
- Green or red apples, persimmons and plums, pomegranates;
- Black currant;
- Pomegranate and beet juice;
- Walnuts and caviar, seafood, dark chocolate.
It is recommended to eat these foods to normalize hemoglobin in pregnant women and to restore it even before conception, i.e., to prevent anemia in pregnant women. In order for iron to be absorbed better and more from foods, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of calcium products (kefir, cottage cheese, etc.) and increase protein foods in the diet. In addition, you should not drink coffee or tea with your food, because these drinks destroy protein, preventing it from being absorbed.
Diagnostics
Usually, an elevated hemoglobin level is detected by chance, because this condition is often asymptomatic for the mother. Pregnant women should pay attention if their health suddenly begins to deteriorate sharply and headaches appear. In such a case, tests should be taken to assess the condition of the pregnant woman. At the appointment, the doctor must examine the patient and examine the veins in the legs to rule out varicose veins.
- To determine the hemoglobin level, the patient undergoes a laboratory blood test.
- Tests include a general study and a coagulogram aimed at studying blood clotting.
- In a general blood test, hemoglobin and ESR, leukocytes and erythrocytes are determined.
- Normally, for women, hemoglobin should be 120-140 g/l.
- If a decrease in the level of less than 10% is detected, then physiological thickening is diagnosed.
- If the hemoglobin protein level is above 160 g/l, then the help of a qualified specialist is necessary.
It is important to conduct a general laboratory test of urine to exclude the possibility of renal damage. If a pronounced thickening of the blood flow is detected, then additional instrumental diagnostic studies are prescribed aimed at determining the degree of disturbance of the cardiac and venous circulation.
Patients are prescribed duplex ultrasound diagnostics, which determines the speed of blood flow in the main intraorganic structures. If the hemoglobin level is elevated, then these indicators will exceed the normative values. It may be necessary to conduct phlebography aimed at studying venous functions and clarifying prognoses. The technique involves introducing a contrast component into the veins.
Can pregnant women take iron supplements?
Dietary supplements containing iron should be used with great caution. In the 2nd trimester, a drop in hemoglobin levels is natural and quite natural. Recent studies claim that a decrease in hemoglobin to 90-70 g/l is not a sign of anemia. If it drops below this limit, you can use dietary supplements. The range of dietary supplements offered is quite large.
It is difficult to make a choice, but it is worth remembering such a dietary supplement as Hematogen, produced in the USSR. Currently, the domestic industry produces Ferrohematogen, which contains iron and vitamins A, D, K, E, B9. Today, this is the best and effective dietary supplement made from natural raw materials, which can quickly increase hemoglobin levels without the risk of adverse reactions.
Treatment methods
If hemoglobin increases for physiological reasons, then there is no need to reduce it. Therapy is necessary only in cases where there are severe clinical symptoms or there are obvious concomitant pathologies.
A specialist will help you create a suitable menu
Any deviations in blood flow should be considered not a pathology, but its symptom complex or characteristic symptoms of processes occurring in the body. The basis of therapy for patients expecting a baby is alternative medicine, lifestyle and daily diet adjustments.
Diet therapy
If you have elevated hemoglobin levels, it is important to follow certain dietary requirements. It is important to drink enough plain water per day, which will help maintain normal blood rheological properties. Red varieties of meat products should be excluded from the diet. This will help reduce exogenous sources of hemoglobin synthesis, which is already in increased quantities. When eating white meat, the hemoglobin level gradually decreases to generally accepted standards.
If the patient adheres to a certain regimen every day, her general condition will noticeably improve.
- Diversify your diet; it should always contain valuable microelements, but iron-containing foods should be completely excluded.
- Liquid is our everything. You need to drink one and a half liters a day. If the disease is advanced, then corrective measures must be taken urgently.
- Recommendations regarding the diet suggest some correction, requiring the avoidance of fatty and fried foods. You need to eat more fruit and berry dishes, do not consume fats;
- Fatty foods trigger cholesterol processes, as a result the blood becomes noticeably thicker and the vascular channels become clogged.
- You should prepare food for yourself by boiling or stewing; fried food is contraindicated.
It is quite possible to normalize hemoglobin content through dietary restrictions, you just need to follow the recommendations. If the clinical situation has become more serious, then the use of medications cannot be avoided.
Medicines
Drug treatment for elevated hemoglobin levels is used when the deviations are significant. As first aid, an infusion of glucose-saline solution (1:1) is performed to restore normal blood circulation. Such infusions allow you to restore a full blood picture in three days.
A blood test determines the overall clinical picture
There are no specialized medications to normalize hemoglobin levels, therefore therapy for increased blood iron-containing protein is symptomatic. The use of heparins is pointless, because these medications are contraindicated for pregnant women. Sometimes agents can be used whose action is aimed at improving rheological blood properties and normalizing capillary blood circulation, without serious interference with blood clotting functions.
Antispasmodics significantly improve peripheral blood supply and blood supply to intraorganic structures. Medicines do not have a negative effect on the fetus, so the medicine can be used during pregnancy. It is not recommended to take such medications on your own. Usually they are prescribed exclusively by a specialist. Such drugs do not cause blood flow or blood clotting disorders. To thin and normalize blood clotting, the doctor may recommend medications like Cardiomagnyl, Trental or Curantyl to the expectant mother. In addition to medications, the patient is recommended to take multivitamins.
Also, with elevated hemoglobin levels, pregnant women may be prescribed Pentoxifylline to relieve ischemic symptoms. Take these tablets with half a glass of water and swallow them whole. Frequency of administration: 2 pills three times a day. But if mommy has a tendency to bleeding or ulcerative lesions, taking such drugs is not recommended.
The use of other medications in the treatment of elevated hemoglobin levels is an unreasonably risky undertaking, since other medications can harm the baby or provoke certain complications of the prenatal period. Therefore, self-prescription of any medications, even vitamins, is unacceptable. Surgical measures for elevated hemoglobin protein, as a rule, are not used, but they cannot be completely excluded.
Folk remedies
Since mothers are prohibited from taking most medications, folk remedies are a priority. For non-traditional treatment of high hemoglobin, well-known recipes such as wheat germ, which have a pronounced blood-thinning effect, are used. You need to wash the grains and add water. The resulting sprouted wheat is usually used for internal use. This wheat should be washed down with boiled and cooled water.
Cinnamon and ginger are no less useful in such a situation. This mixture has special properties, which include increased penetration into blood vessels, normalization of hemoglobin levels, antioxidant and antitoxic qualities. Add 20 g of chopped ginger root and half a spoon of cinnamon powder to 1000 ml of water. The resulting tea is drunk while in position for a certain time until the blood picture is restored.
Decreased hemoglobin level
A general decrease in hemoglobin levels in a pregnant woman’s body is considered normal. However, if the indicator drops below 110 g/l in the first and third trimesters and below 105 g/l in the second trimester, the doctor may suspect anemia (popularly known as anemia). This disease is characterized by a significant decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood relative to normal, as well as a reduction in red blood cells and hematocrit.
Anemia is treated with medications
There are three stages of anemia:
- Light form (about 108–90 g/l).
- Medium form (about 89–70 g/l).
- Severe form (69 g/l and below).
Anemia is most often diagnosed in pregnant women:
- with chronic diseases of internal organs (gastrointestinal pathologies, hepatitis, kidney inflammation and others);
- those on a diet or deficient in vitamins and minerals;
- vegetarians;
- in case of blood clotting disorders;
- during multiple pregnancy;
- with an unfavorable obstetric history (miscarriages, abortions, missed pregnancies);
- with repeated pregnancy with a short interval (less than 2–3 years);
- with late toxicosis (gestosis).
The well-being of a pregnant woman can change momentarily, which is associated with hormonal and physiological processes occurring in the body. However, the symptoms of anemia are clearly expressed and can be observed constantly.
Signs and dangers of pathology
Signs of low hemoglobin levels are:
- excessive pallor and dryness of the skin, “cyanosis” of the skin and mucous membranes;
- peeling of lips, sticking in the corners of the mouth;
Seizures in the corners of the mouth may be a sign of anemia
- constant weakness and fatigue;
- low blood pressure;
- heavy breathing, shortness of breath, chest pain;
- rapid heartbeat, tachycardia;
- headache and insomnia;
- disturbance (perversion) of taste sensations.
Anemia is dangerous for the development of pregnancy. In the first trimester, due to anemia, the process of placenta formation may be disrupted; it may be underdeveloped or have a low presentation. In the future, this can lead to miscarriage, bleeding, or lack of oxygen to the fetus (hypoxia). In the second and third trimesters, anemia can cause late toxicosis, untimely rupture of amniotic fluid and premature birth, and low fetal weight. A baby born as a result of an anemic pregnancy may have health problems - weight loss, delayed intellectual and physical development, problems with the respiratory system.
Treatment methods
If there is a low level of hemoglobin in the blood, there are two methods for correcting this condition:
- Nutrition correction.
- Prescription of iron-containing drugs.
It is advisable to review the diet and increase the amount of foods rich in iron consumed to prevent anemia in case of minor deviations in the blood test. When anemia is established as a diagnosis, it is necessary to take iron medications as prescribed by a doctor in a strict dosage. Experts are of the opinion that treatment of iron deficiency conditions without taking such drugs is impossible, and the risk from using drugs during pregnancy is lower than the detrimental effect of this disorder on the woman’s well-being and fetal development.
It is not possible to correct iron deficiency using food alone, since this element is not completely absorbed from food. Tangible results even from taking pills occur only after a few weeks.
Patient reviews
during pregnancy, my hemoglobin “jumped” from 90 to 105. I drank an iron supplement and apples. And it’s okay, then everything fell into place, now, perhaps, in my son’s card they write pregnancy...complicated by ARVI and anemia
Anna_Ryzhenko
https://www.komarovskiy.net/forum/viewtopic.php?t=7561&start=75
I drank pomegranate juice (in glass bottles), ate buckwheat forcefully - I can’t stand it. And during pregnancy, the doctor prescribed special iron-containing drugs, because My hemoglobin has always been very low
Fly with gold teeth
https://www.woman.ru/health/woman-health/thread/4221742/
Hello everyone! I have the same problem. The first time I donated blood, hemoglobin was 94, they prescribed sorbifer, it rose to 112. Then they told me to drink it again, I started drinking it, and I started vomiting so much from it, I stopped doing it. And the other day again I donated blood, hemoglobin dropped to 84. Although I eat a lot of fruit... I don’t know what it is. I’m 33 weeks pregnant
Maria Ermilova
https://deti.mail.ru/forum/v_ozhidanii_chuda/beremennost/nizkij_gemoglobin_vo_vremja_beremennosti/
Short?! I carried my son at 65, gave birth and fed him... It’s hard, of course, but not fatal... With my daughter it was 119, but after giving birth the bleeding, intensive care and relatives were 65 in a couple of hours, so you’re quite normal...
Inessa Baroness
https://deti.mail.ru/forum/v_ozhidanii_chuda/beremennost/nizkij_gemoglobin_pri_beremenosti/
Prevention and prognosis
The main complications of the pathology develop against the background of the processes occurring with the patient. Prevention of increased hemoglobin levels in such patients is nonspecific. It is important for mom to monitor her own health, changes in well-being, appetite, etc. Such measures will help to timely assess the degree of risk of the disease and prevent the development of unfavorable concomitant conditions.
The prognosis for increased hemoglobin protein for pregnancy, if its level does not exceed acceptable values, is favorable. Therefore, there is no need for drug therapy, especially when there is no clear clinical picture. Treatment is usually carried out by normalizing blood clotting, rehydration and the use of alternative treatment.
What do the changes indicate?
Maintaining optimal hemoglobin levels during pregnancy is a very important goal that should be achieved. The change in concentration can be either up or down.
The deficiency state is registered in pregnant women much more often at this stage.
Low hemoglobin level
Reducing the concentration of this protein to 90-99 g/liter requires the mandatory preparation of individual recommendations. Usually in such a situation, the doctor will recommend that the expectant mother carefully monitor her daily diet.
Elevated level - causes and symptoms
Increased protein concentrations in pregnant women can lead to extremely negative consequences.
The reason for this may be:
- diabetes mellitus and other diseases with similar etiology and symptoms;
- presence of bad habits – smoking and excessive drinking;
- poor intestinal permeability;
- great physical activity;
- deficiency of vitamins B9 and B12;
- kidney and cardiovascular diseases;
- accommodation in mountainous areas.
It should be noted that if glycated hemoglobin is increased, this can lead to oxygen starvation in the baby, which can lead to disturbances in the development of the central nervous system and brain function.
With an increased concentration of such a protein in the body, the following clinical picture may develop:
- increased fatigue, constant feeling of weakness even with long and proper rest;
- drowsiness;
- decreased visual acuity;
- high blood pressure;
- pallor or cyanosis of the extremities;
- loss of appetite;
- frequent bouts of insomnia.
As mentioned above, an increased concentration of this protein in the blood of a pregnant woman can lead to negative consequences not only for the mother, but also for the child:
- increased risk of blood clots;
- oxygen starvation in the fetus, the consequence of which is a delay in mental and physical development.
It should be noted that elevated rates are diagnosed much less frequently than decreased ones, but are still no less dangerous for the mother and baby.
Iron requirements in pregnant women
The role of hemoglobin for the human body
Hemoglobin is a complex protein consisting of two elements:
- globin is a simple protein;
- heme is an element that contains iron.
The protein is found in red blood cells. The main function is to provide and transport oxygen to all tissues and organs. The iron needed for gems comes from certain foods. In addition, protein participates in the process of gas exchange with the external environment and stabilizes the acid-base balance of the body.
A dangerous feature of hemoglobin is that it has a strong attachment to carbon dioxide, much higher than to oxygen. This is precisely the danger of carbon monoxide for humans.
Blood testing is one of the important and simple methods to prevent many diseases.
Drugs to increase hemoglobin during pregnancy
As a rule, Fe (iron) preparations are used in tablet form, however, according to indications, the use of parenteral iron preparations may be recommended.
Indications for parenteral therapy are:
- significant decrease in hemoglobin levels;
- impaired absorption of Fe (iron) in the gastrointestinal tract;
- the patient has gastric or duodenal ulcers in the acute phase.
- For the treatment of patients with a slight decrease in Hb levels, it is recommended to prescribe Fe sulfate preparations in doses of sixty to one hundred milligrams per day.
- For moderate anemia, it is recommended to prescribe one hundred to one hundred twenty milligrams per day.
Exceeding the prescribed dosage and independently adjusting the prescribed treatment regimen is prohibited. This increases the risk of side effects.
For ferric iron preparations (polymaltose hydroxide), higher dosages can be used, since this form of the drug is better absorbed and tolerated, and, therefore, treatment is less likely to be complicated by undesirable effects from the therapy.
The administration of iron in combination with ascorbic acid preparations increases the degree of Fe absorption.
Also, according to indications, multivitamin preparations containing folic acid can be additionally prescribed (daily dose - four hundred milligrams).
Treatment lasts at least three months. All therapy is carried out under the control of a general blood test performed once a month. Normalization of laboratory parameters is observed in the fifth to eighth week of treatment.
To prevent the development of anemia during the first twelve weeks of pregnancy, it is recommended to take multivitamin preparations containing folic acid in a dose of four hundred to five hundred milligrams and ferrous sulfate in a dose of sixty milligrams.
Early prevention is performed to prevent the development of neural tube defects in the fetus.
For anemia in pregnant women, it is recommended to use, for example, Sorbifer Durules®, Ferronate®, Ferlatum®, Ferroplex®, Ferrum Leka®, Actiferrin®, Gyno-Tardiferon®, Tardiferon®, Fenyulsa®, Biofer®, etc.
The most common side effects from the therapy are constipation, nausea, loss of appetite, dizziness, and rarely allergic reactions.
Prices for some iron supplements:
- Fenulse® is the cost of an Indian drug produced by the pharmaceutical company Ranbaxy Libraries Limited® per package of 30 caps. is 300 rubles;
- Sorbifer Durules® - the cost of the Hungarian drug produced by the Egis® campaign is 550 rubles (pack of 30 tablets);
- Maltofer® - the cost of a Swiss drug produced by the Vifor® campaign is 340 rubles (pack of 30 tablets);
- Ferlatum® - the cost of the Italian drug produced by the pharmaceutical company Itapharmaco® is 940 rubles for twenty bottles;
- Ferrum Lek® - the cost of a Swiss drug produced by the Sandoz® campaign (pack of five ampoules) is 1,400 rubles;
- Tardiferon® is a French drug produced by the Pierre Fabre Medicine® campaign. The price for thirty tablets will cost the buyer 270 rubles;
- Biofer® - Indian tablets, produced by Micro Labs Ltd®. The price of the package (30 tablets) is 340 rubles.