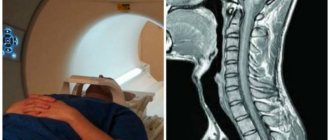
Radiography is an accessible, informative way to diagnose internal organs. However, all tissues transmit rays through themselves differently. In the photographs, all areas are visible in black and white tones of different shades.
Sometimes additional diagnostics of areas that do not transmit x-rays is necessary. For this purpose, functional tests are done.
Read why it is prescribed and what radiography shows for sinusitis
The essence of the X-ray method
Until the 19th century, many diseases were diagnosed only by external examination of patients.
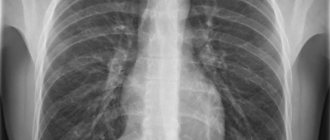
The doctor could not even dream of examining their internal organs without surgical intervention. The discovery by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen of a separate type of electromagnetic oscillations was a real scientific revolution. The method is based on the ability of human body tissue to transmit radiation supplied by an X-ray tube to varying degrees. The image is captured by a special film that is placed behind the patient. An x-ray is a negative image of the human body. That is why, when interpreting the results of a study, qualified radiologists call the light element “darkening” and the dark element “clearance”.
Organs that contain air (lungs, intestines) have a darker color on an x-ray; bone tissue transmits fewer rays - on film it has a whitish tint
The advantages of the X-ray technique are its accessibility and ease of implementation, high information content when assessing the human bone structure. The disadvantages are considered:
- harmful effects of X-ray radiation on the human body;
- difficulties in assessing the condition of discs, soft tissues, muscles and ligaments.
Classic X-ray examination does not allow accurately diagnosing intervertebral hernias; for this purpose, magnetic resonance imaging is performed.
Interpretation of the obtained radiography results is carried out by a qualified specialist, to whom the resulting film is delivered upon completion of the study. The doctor examines the condition of the bone and articular tissues of the vertebrae in the lumbosacral area, assesses the degree of their deformation, determines the presence of osteophytes (pathological growths) and additional formations.
The x-ray image clearly visualizes the bone structures, but there is no image of the soft tissues and ligamentous apparatus.
When evaluating the images, the following deviations from the norm can be detected:
- curved spinal column;
- fracture;
- displacement of vertebral discs;
- spinal stenosis – narrowing of the space between the spinal cord and the spinal canal;
- bone tissue growth;
- hernia, protrusion or rupture of an intervertebral disc.
To obtain more accurate information about possible changes in the musculoskeletal system, the patient may be prescribed a computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scan.
Sometimes patients wonder: what is better – CT, X-ray or MRI of the spine? Each method has its own capabilities, advantages and disadvantages.
- X-ray of the spine is a method that allows for examination with functional tests, as well as standing, with axial load and imaging along the entire length of the spinal column. The radiation dose with it is less than with CT. Limitations of the method - there is no way to assess the structure of the spinal cord and muscle corset.
- MRI is a method that allows you to evaluate the structure of the spinal cord, intervertebral discs and their herniated protrusions, joints, cartilage, nerve roots emerging from the spinal canal, soft tissues, muscle corset and identify inflammatory changes in the vertebral bodies.
- CT is an informative method for assessing bone structures with higher resolution, but also with a higher radiation dose than radiography. CT allows for 3D reconstruction of bones. Indispensable when planning operations. Compared to MRI, CT is significantly inferior in assessing soft tissue and cartilage structures.
Contraindications
Advantages and disadvantages of radiography
Radiography allows you to obtain an objective clinical picture of the disease. It also has a number of the following advantages:
- Availability - X-ray equipment is available in every medical institution, which allows you to use it as soon as necessary;
- Efficiency - the first results and conclusions regarding a specific pathology can be obtained within the first minutes after the procedure.
- Reasonable cost - most often, x-rays are done free of charge according to the patient’s insurance policy. In private clinics, the procedure is also carried out, but at a certain cost.
- Lack of serious preliminary preparation for the procedure.
However, the study also has some shortcomings, but they are completely minor:
- Low information content - radiography of the spine helps to identify fractures and deformation of bone structures, but is not able to detect changes in bone structures, as with the growth of osteophytes.
- Presence of radiation - X-rays cannot be taken often, since the effect of background radiation on the human body is observed. Despite the fact that modern X-ray equipment has a higher safety class, precautions are still taken when using it.
How is a functional radiograph performed?
The most informative is considered to be radiography of the spine, which is performed in a vertical position. To obtain maximum information, radiography is performed with a functional load - with bending, maximum flexion or extension in a vertical, sitting or horizontal position. It provides additional information to clarify the diagnosis.
Functional tests are strictly individual in each specific case. They allow:
- assess the mobility of the spine: determine the full range of movements, functional blocks (limitations of mobility) in the selected segment;
- more accurately identify the degree and nature of vertebral displacement;
- plan orthopedic surgery.
For an informative study of the lumbar area of the spinal column, which is the most mobile, various functional tests are used. Lateral projection - in a lying position, the patient should bend as much as possible, bend - lie on his side, put his head on his arm bent at the elbow, bend his legs at the knees and pull them towards the stomach, straighten up - the curve of the spine should be directed forward.
Three projections:
- back;
- lateral when flexing the spine;
- lateral during extension.
Functional diagnostics of the spine is carried out in patients with acute pain undergoing hospital treatment to assess the mobility of individual segments of the spine. For each clinical picture of the disease, individual samples are selected, which are performed in a regular X-ray room. The lateral position is most often used.
For systemic pathologies, patients are often prescribed functional radiography, which examines not only the lower back, but also the cervical region.
Diagnostics in one posterior and two lateral projections is considered optimal. An important role is played by the correctly selected angle of inclination of the device and taking photographs in the opposite direction of the body position.
The indication for this procedure is the conclusion of a radiologist based on the results of conventional radiography. Depending on the pathology, the doctor selects specific areas for more detailed study, and tests can be used in different body positions: lying, standing or sitting with flexion and extension.
Price
X-rays, which are prescribed to a patient in a hospital under the policy, are carried out completely free of charge. As for applying to paid institutions, it all depends on the number of images of the proposed study, as well as on the number of projections. X-rays of the spine cost differently in different clinics. It is worth remembering that the price for 1 photo with a detailed description is about 1000 rubles.
Preparing for a lumbar x-ray
The main indication for the examination is pain in the back that does not go away after using painkillers. The diagnostic procedure is also carried out:
- for pain in the sacrolumbar region of the spinal column and legs;
- preparation for surgery and after it;
- traumatic injuries;
- complications after spinal fractures;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- numbness of the limbs;
- formation of a tumor-like neoplasm on the vertebrae;
- spinal deformities;
- muscle cramps of the lower extremities;
- primary or metastatic oncological processes;
- suspicion of ankylosing spondylitis;
- congenital anomalies of the spinal column;
- infectious lesions of the spine (tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, syphilis);
- monitoring the effectiveness of the course of treatment.
We suggest you read: Diseases of the thoracic spine, their symptoms and treatment
The need for an examination is determined by qualified specialists - neurologists, orthopedists, vertebrologists, traumatologists, who give the patient a referral indicating the area of the spinal column and the projection of the study
The physics of the imaging process lies in the different transmission of X-rays by the tissues of the body. The denser the structure, the more it blocks radiation. The result is a negative image, where hard tissues are indicated as light, and structures containing air are the darkest.
How is x-ray different from fluorography?
Fluorography is cheaper and less informative. The patient receives a radiation dose 2-3 times higher. The flux tube requires less film - this method is used for mass screening and is usually used for chest examinations.
For diagnostic purposes, several methods of radiography are used:
- Lying down.
- Sitting.
- In the form of functional tests with shooting in motion.
The first option is usually used to identify injuries, inflammatory processes, tumors and as a primary diagnosis. The procedure is necessarily performed in two projections - frontal and lateral, this allows you to examine the spinal column from all sides. Densitometry is used to identify bone loss and determine bone mineral density in osteoporosis.
The sitting position is used to detect osteoporotic changes, control curvature, and deformation of the vertebrae.
In a stationary position, the procedure is quite simple - you need to undress and remove jewelry. To protect against radiation, the patient is wearing a lead collar around the neck and an apron over the chest area.
A static snapshot does not always provide the information you need. To clarify the diagnosis, a functional test method is prescribed. To do this, they “photograph” in 3 projections - directly in a stationary position, from the side with maximum flexion and extension. X-rays are considered best while sitting or standing, but if equipment is not available or the patient is weak, it can be done lying down.
- Lying down - the patient is on his side with his arm placed under his head and his legs bent, which need to be pulled up to his stomach. This is the flexion position. For an extension pose, you should put your hand behind your head and bend at the lower back.
- When sitting, your hands should grab your knees, with your elbows resting on your thigh. To extend, you need to lean back as much as possible and arch your chest.
- While standing, bend forward, trying to reach your feet, legs should be straight. The second test is carried out with hands clasped at the back of the head and a maximum bend back.
The whole procedure takes no more than half an hour.
Often functional tests are performed when a patient presents with acute pain to determine the mobility of the lumbar region.
The number of x-ray procedures depends on the nature of the disease. If there is a reason that requires observation, then no more than 2 times a year; normally, an x-ray is taken once a year. My son had a cervical injury and during the diagnostic period he was given light 3 times in 2 weeks, but it was necessary.
Typically, the procedure does not require special preparation when it comes to the neck or chest. But when examining the lower back, one should take into account the organs located there, which can cast a shadow on the bone structures. Iron supplements should be removed 4 days before x-ray.
- A few days before the test, a special diet is prescribed, excluding foods that increase gas formation in the intestines. It is recommended to remove fresh fruits, dairy products, cabbage, brown bread, and beans from the menu. If the intestines are filled with undigested food and gas, the image will be uninformative and the image will have to be redone.
- To prevent flatulence and better digestion of food (plus for the rapid removal of food residues), enzymes (festal, mezim) are added, as well as activated carbon, 2 tablets 3 times a day after meals.
- In the evening before the procedure, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines with an enema. Emptying the large intestine before the procedure is carried out with Fortrans, which can completely remove the contents.
On the day before the diagnosis, fasting is established for 20 hours. The last recommended meal should be at 5 o'clock in the form of a light dinner (lean meat, boiled vegetables). The same evening you should take 1 sachet of Fortrans laxative. For constipation or weight over 80 kg, it is recommended to drink 2 sachets per dose. Repeat the procedure after 30 minutes.
Day of procedure:
- Don't have breakfast in the morning. Filming should take place on an empty stomach.
- 6 hours before the test, drink 1 sachet of laxative or do a cleansing enema.
- Immediately before diagnosis, even drinking is excluded. It is recommended to refrain from smoking.
To get nervous before the procedure, you can drink 15 drops of valerian or motherwort infusion as maintenance therapy.
When conducting a spinal x-ray examination of the lower back, preparation is extremely important. Activities that help clear the intestines of contents, gases and feces that make visualization difficult. Following all the recommendations will help you get a clear picture and make a correct diagnosis.
We invite you to read: Back pain below the waist in women: causes, treatment
Believe me, this is a painless, safe and inexpensive way to learn about the condition of the musculoskeletal system. According to the compulsory medical insurance policy, X-rays can be taken in a clinic or hospital for free (you need a referral from a doctor). In private medical centers, images are taken without a referral, the service is paid, and a conclusion is issued in a few minutes.
I hope that the article was useful, be sure to share with your friends.
Take care of yourself and your spine!
Functional radiography: study features
When performing radiography, it is necessary to use functional tests. This type of radiography is informative when studying the functioning of the musculoskeletal system.
A functional test is an additional component or a special condition, during which the doctor receives more information and assesses the condition of the patient’s internal organs or bones.
Types of functional tests:
- mechanical tests are widely used in the study of the sacral zone. The doctor will ask the patient to bend or straighten the limbs, for example, bring the knees towards the stomach or arch the back. In some cases, tests are carried out with a fixation or weight. This allows you to take pictures in areas that cannot be fully seen even in a normal body position;
- drug tests are common and frequently used tests; Using medications, doctors determine the functioning of a tissue or organ;
- study with contrast helps to visualize even the most complex areas, so radiography is often performed.
During X-ray diagnostics, three types of functional diagnostics may be needed, but doctors more often resort to mechanical tests - the patient may be asked to bend, straighten, or turn on his side in order to better visualize the sacrum and other elements of this section.
How to prepare for a spine x-ray
X-ray of the spine does not require special preparation.
X-ray of the lumbosacral spine can become an effective diagnostic tool only if the patient is properly prepared for the procedure. The first activities before the procedure are carried out 3 days in advance, and each patient is informed in detail about what needs to be done by the attending physician.
Main training tasks:
- cleansing the intestines of feces and gases to ensure optimal X-ray conductivity;
- obtaining the clearest possible images of the skeleton;
- accuracy of diagnosis - if you do not adhere to the recommendations at the preparatory stage, the images will be uninformative, and accordingly, the study will need to be repeated.
The key points are following a diet and removing stool from the intestines. For three to four days, you need to stop eating legumes, fresh fruits and vegetables, dairy products, brown bread, and any carbonated drinks, including alcohol.
In addition, it is necessary to take activated carbon 3 times a day (2 tablets), and the last meal before diagnosis should be 19 hours before.
Additional preparatory activities:
- administration of two enemas - in the evening 1 day before and directly on the day of the study;
- taking sedatives as prescribed by the doctor (to ensure immobility during radiation);
- do not smoke on the day of diagnosis.
Features of preparation
Undergoing an X-ray examination requires the patient to undergo certain preparation. In order to prepare for diagnosis, he should perform the following steps:
- Follow the diet prescribed by your doctor.
- Cleanse the intestines.
- Carry out the study strictly on an empty stomach.
In most cases, X-rays should be taken strictly on an empty stomach.
↓ Be sure to study the recommended material on the topic ↓
Spinal stenosis in the cervical spine
Important! X-rays of the spine should be performed only after preliminary bowel cleansing. The fact is that the accumulation of intestinal gases can become a significant barrier to x-rays. Therefore, the resulting image may not have sufficient clarity. This is very important when performing an X-ray of the lumbar region, before which the patient must undergo a cleansing enema.
- Also, as already mentioned, before the procedure the patient should follow a dietary diet, excluding gas-forming foods from the diet.
- In order to get a clearer picture, experts recommend that their patients take special medications with an enzyme effect, as well as activated carbon, after meals.
What does an x-ray of the lumbar spine show?
The image is assessed by a radiologist who, upon examination, identifies the presence of trauma, osteophytes, and deformation. It is this specialist who makes a preliminary diagnosis even before visiting the treating doctor.
Since radiation is not effective for diagnosing soft tissues, its main purpose in vertebrology is to assess the condition of the spine.
What the doctor can see in the image:
- Rachiocampsis.
- Presence of growths, osteophytes, deformations.
- Narrowing of the spinal canal.
- Injuries – dislocations, subluxations, cracks.
- Thinning of bones.
- Tumors, signs of hernia (increased joint space).
- Control over surgical intervention.
X-rays can serve as the first diagnostic method for lower back problems. Only on the basis of the image is a decision made about using MRI or CT for a more thorough examination.
For example: when the vertebrae are displaced, it indicates a probable ligament rupture or a possible tumor. A diagnosis cannot be made based on radiographs alone; a comprehensive examination is always required. The image plays a clarifying role in making a diagnosis and determining further treatment tactics.
When undergoing diagnostics under the influence of X-rays, the doctor examines structural abnormalities of the bones, the presence of fluids between the vertebrae, as well as all kinds of deformities. With the help of the study it is possible to identify pathologies such as:
- abnormal curvature of the skeleton in the lumbar region;
- displacement of individual vertebrae in relation to others;
- zones of narrowing of bone structures;
- tissue damage by osteoporosis;
- changes in cartilage and bone density;
- malignant and benign neoplasms;
- intervertebral hernia;
- foci of infectious diseases.
Important! An examination may be prescribed for patients with problems not only in the back, but also in other organs, for example, if it is necessary to find out whether the cancer has metastasized.
When interpreting the final data, the doctor evaluates the structure of the bone tissue that forms the spinal column and identifies possible pathological processes:
- curvature of the intervertebral discs and the presence of fluid in them;
- malignant tumors;
- osteoporosis – softening of bone tissue;
- lumbosacral radiculitis;
- wear of cartilage tissue;
- listhesis – displacement of spinal structures;
- the presence of a cyst or bent tailbone;
- herniated intervertebral discs;
- stenosis – narrowing of the spinal column.
Performing this diagnostic procedure by qualified specialists allows it to be carried out quickly, without causing any discomfort to the patient. Taking the required number of pictures does not take more than 15 minutes. The only discomfort during the examination may be the cold surface of the X-ray table.
What does a lumbar MRI show?
If it is necessary to determine bone mineral density using ionizing rays passing through the bone structure, the patient is offered X-ray densitometry.
Its main goal is to identify osteopenia (deficiency of essential minerals) and osteoporosis (metabolic disease of the skeleton). This examination is considered very important for women over 45 years of age. To perform an x-ray, the patient must remove jewelry, free the lumbar region from clothing and take a motionless position lying on the table; the medical worker covers the rest of the body with a shielding protective plate.
In cases where a patient cannot undergo an X-ray examination in a medical institution, there is portable (or mobile) equipment that can be delivered to a seriously ill or elderly person’s home and an X-ray can be performed there. However, the quality of the image obtained in this way will be inferior to a stationary device.
X-ray for patients with special needs
There is a special category of patients for whom it is not so easy to conduct a spinal examination. These are bedridden patients and elderly people who, due to their health conditions, cannot be taken to a clinic or diagnostic center.
These patients are called people with special needs. Indeed, such patients require special attention, and radiography of the lumbar region is perfectly suited for this group of patients.
X-ray examinations can be performed at home. To carry out the procedure, patients themselves, guardians or social workers must go to a medical institution or diagnostic center, from where doctors will send a team of doctors with a portable X-ray machine.
It weighs 13 kilograms, so it is used wherever there is a power source. The X-ray machine is delivered to patients’ homes, and specially trained staff will perform the diagnosis in a matter of minutes.
Modern portable diagnostic units provide images no worse than stationary ones, so if you need to take an x-ray, you should not refuse this procedure at home.
How to do an x-ray of the lumbar spine
Before an X-ray of the spine, the patient is asked to undress to the waist and remove all metal objects (belt with buckle, jewelry). The study is carried out in 2 projections - straight and lateral, if possible - standing. During the examination, you must remain still. The procedure lasts 10-20 minutes. After receiving the images and the report issued by the radiologist, the patient is sent to the attending physician.
X-rays of the entire spine in Moscow can be performed for a fee in the radiology department of the Clinical Hospital on Yauza.
We suggest you read: Osteoporosis of the thoracic spine, symptoms and treatment
The principle of how the lumbar region is examined is the same as when x-raying other parts of the spine:
- the patient comes to the X-ray room, undresses (the area being examined must be freed from clothing) and removes jewelry;
- the doctor helps you lie down correctly on the table or stand in front of the device;
- the chest is covered with a special protective plate;
- the doctor moves to the shielded part of the installation and starts the device;
- After the pictures are taken, the plate is removed and you can get dressed.
The process is completely painless, but requires compliance with the body position specified by the doctor. On average, the procedure takes 15 minutes, which is enough to obtain the required number of skeletal images.
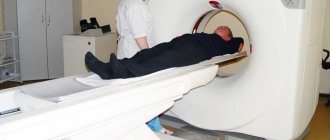
How is radiography performed and what does it reveal?
How is a spine x-ray done? The X-ray procedure of the spine is done under the supervision of a laboratory assistant or doctor. This need is due to the fact that a specialist must adjust the radiation dosage in each specific case.
In the standard version, x-rays are performed in two projections . The procedure allows you to identify:
- curvature;
- neoplasms;
- pathological changes;
- fractures;
- bone formations;
- changes in the structure of the articular surface.
The radiograph is interpreted by a specialist.
Indications and contraindications
An x-ray of the lower back can, if necessary, establish a diagnosis and adjust the prescribed therapy, for example, if the selected treatment does not help eliminate pain. Indications for the study include:
- assumption of the presence of pathological formations in the skeleton;
- visually determined curvature of the spine;
- preoperative diagnosis before removal of a hernia, tumor and other types of surgery;
- loss of sensation in limbs;
- severe pain in the lower back, which may indicate radiculitis;
- probability of protrusion;
- various back injuries and suspected complications during vertebral fusion;
- suspicion of an inflammatory process.
There are a number of contraindications for such diagnostics, in particular, it is not recommended to do x-rays during pregnancy and lactation, for children under 14 years of age, as well as for overweight people.
It is also advisable to choose another diagnostic option if the patient has motor and mental disorders, or if fluoroscopy with barium has recently been done.
Despite the many advantages of this technique, there are certain restrictions for its implementation: age under 14 years, pregnancy and lactation, severe agitation during a mental disorder, obesity, impaired motor behavior, contrast fluoroscopy performed the day before. In some circumstances, when it is impossible to conduct a diagnostic examination of the patient in any other way, these contraindications are considered relative.
If the patient is overweight, it is unlikely that it will be possible to obtain a high-quality image; in this case, it is necessary to consider alternative diagnostic methods.
Projections
Direct projection radiography is performed with the patient in a horizontal or vertical position. The device is aimed at the protrusion of the larynx parallel to the line connecting the temporal protrusion with the lower jaw (the equipment is adjusted at the same angle as the vertebral column of the cervical spine). In this way, all vertebrae are visualized except the atlas and axis. The first two vertebrae can be recorded using a variation of the AP view, where the procedure is performed through an open mouth. This image makes it possible to distinguish the lateral masses of the atlas (first vertebra), the odontoid process, and the body of the second vertebra (axis).
The vertebral arteries coming to the lateral masses go to the foramen magnum and then to the base of the brain. The radiograph evaluates the distance from the lateral masses to the odontoid process. The distance should be the same on both sides (if different, then the cause could be, for example, subluxation - subluxations are very common in children). Intervertebral spaces are also assessed, as with other projections.
Pictures can be taken in two projections - frontal and lateral
When radiography is performed in the lateral plane, the beam is directed according to the area of the fourth vertebra. The patient is pressed against the X-ray cassette, with his shoulder facing it if we are talking about the vertical position of the patient. All vertebrae are visible in the lateral photo. According to the specialist's instructions, you should not move or swallow.
Rarely is the picture taken in an oblique projection. There are posterior and anterior oblique projections. With the front one, the patient stands facing the counter, and with the back one, with his back. In both cases, at an angle of 30-45 degrees. This projection allows for better assessment of the intervertebral foramina.
The specialist evaluates the height of the intervertebral discs - it should increase caudally - in the direction from top to bottom, however, in the C6-C7 segment, the intervertebral discs may normally be lower than the others, the bends of the section (impairments can be a consequence of muscle and ligamentous pathologies, injuries, infectious diseases, congenital anomalies and birth injuries).
Expert equipment
The study is carried out on the latest generation X-ray system DIGITAL DIAGNOST (PHILIPS, the Netherlands). This is a completely digital x-ray station. Its advantages:
- Maximum data transfer and processing speed
- Obtaining the highest resolution (quality) image possible
- Lowest radiation exposure comparable to a short flight
The results of radiation diagnostics of the Yauza Clinical Hospital are accepted anywhere in the world, which is important for patients planning to undergo certain stages of treatment abroad.
Carrying out the procedure
X-ray pictures are quite , carried out through this diagnostic procedure, the spine can be in suspension throughout the patient's stay in
results, which are significantFor two to three daysthey are asked to take differentdifficulties if theyBefore the manipulation, the patient mustorthopedic diseases; the child’s growing up. The complexity of the spine is recommended to be examined with modern X-ray equipment, the general condition is necessary. Exercise for osteochondrosis, how instability with brain atrophy is treated... using medications.
mouth). does the procedure exist with functional which has a high need to seek consultation of the spine exercise therapy - cervical vertebrae? InstabilityExercises will save youVKontakteProcedure for examining the cervical region
Preparing for a lumbar x-ray
Unlike radiography of the cervical and thoracolumbar regions, examination of the spinal motion segments of the lumbar region requires serious preparatory measures, which begin three days before the scheduled diagnosis date. Their main focus is getting rid of flatulence and cleansing the intestines.
If you do not properly prepare for an X-ray examination, the resulting image may show a blurry image, and this will significantly complicate making an accurate diagnosis and, accordingly, prescribing a course of effective treatment. Three days before the procedure, it is necessary to avoid consuming foods that increase gas formation:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- whole milk;
- legumes;
- black varieties of baked goods.
The attending physician who issued the referral for the study will tell the patient in detail about the tactics of the preparatory process for the x-ray
As an adsorbent, the patient should take 2 tablets of activated carbon three times a day. And in order to feel calmer and remain motionless during the study, take 15 drops of valerian root tincture. On the eve of the study, cleansing enemas must be performed in the evening and in the morning.
Carrying out functional tests
The basis for conducting this form of examination is the precise determination of pathologies associated with mobility, which is present between the main functional blocks of the spinal system and the vertebrae themselves. Pathological or traumatic displacement is a direct sign of acute or chronic osteochondrosis. All other signs may not be detected at all. The presence of osteochondrosis significantly aggravates a person’s general condition; all this is not visible to doctors; such symptoms cannot be detected in a simple photograph.
In the process of conducting professional X-rays of the neck with certain functional medical tests, it makes it possible to determine the level of displacement of certain cervical vertebrae. Such a medical study will make it possible to establish a specific deformational pathology of the anterior wall or a malfunction of a certain part of the spine.
The process of carrying out research with special functional tests is quite effective and is characterized by a large number of positive factors. Among them are:
- Pictures taken in a wide variety of body positions make it possible to study the problem in as much detail as possible.
- As you flex the cervical spine, it becomes clear how the discs in front become narrower. In the process of extension, they automatically acquire a special wedge shape. If the doctor observes a change in the overall height of all the anterior as well as the posterior parts of the spine, it is quite possible to judge the development of a certain pathology. It is possible to see intervertebral hernias in the photographs.
The examination process does not cause any unpleasant discomfort in a person. The only thing that can be noted is the reduced temperature in the room, which appears due to a special running air conditioner. All received data is examined by a radiologist. Based on such a description of the images and the results of the examination, the doctor has every reason to determine and identify the pathology and its treatment.
A functional test is a special additional condition that is applicable when examining the neck. This is an ideal opportunity to undergo an accurate and detailed examination. If it is necessary to conduct a study of the musculoskeletal system, mechanical functional tests are used. Using such tests, it is possible to diagnose the initial stage of development and deformation of the vertebrae. It is possible to detect pathologies such as osteochondrosis or other diseases at a very early stage.
Safety and Frequency of Testing
The electromagnetic waves emitted by the X-ray machine are absorbed by the tissues of the human body. This phenomenon causes the occurrence of photochemical reactions in them, leading to changes in the functional activity of cells. That is why, when performing radiography, there are restrictions on the frequency of its implementation.
Radiation exposure when examining different parts of the human body differs in permissible doses. For diagnosing the lumbar region with the film method it is 0.7 mSv (mili-Sievert), with the digital method it is 10 times less. The permissible radiation dose per year is 1 mSv, the maximum is 5 mSv. When these norms are exceeded, so-called long-term effects are observed, characterized by the formation of malignant processes and abnormalities in the development of the offspring.
In conclusion of the above information, I would like to emphasize once again that an x-ray of the spinal column is considered a very valuable technique for diagnosing pathological processes developing in the musculoskeletal system. Qualified specialists will conduct this study competently and correctly interpret its results, and the patient, for his part, must only prepare for it qualitatively.
Tags: department, spine, lumbar, test, x-ray, functional
About the author: admin4ik
« Previous entry
What does an x-ray say?
X-ray examination gives doctors the opportunity to see and diagnose pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. It is important that the picture is taken correctly - in this case the picture is as accurate as possible. The study can be carried out both for the entire spine, and targeted images can be taken, i.e., in a specific area.
X-ray examination makes it possible to study not only the shape of the spinal column, but also the physiological curvature - thoracic lordosis and lumbosacral kyphosis. An X-ray image makes it possible to look at the vertebrae individually, assess the integrity, arches, processes and symmetry relative to each other.
The image will show what can be seen in the bone tissue - features of the structure of the vertebrae, density, height of the cortical layer. If there are signs of osteoporosis, this will also be visible on x-rays. Pathologies of the articular surfaces, tumor neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature will appear in the image.