Indications
An X-ray of the thoracic spine is done if the following pathological conditions are suspected:
- spinal injuries;
- scoliosis, kyphosis;
- osteochondrosis;
- infection of the vertebrae;
- congenital developmental pathologies;
- tumors in the chest area;
- intervertebral hernia;
- vertebral displacement.
The indication for X-ray of the thoracic spine is the presence of the following symptoms in the patient:
- chest pain;
- abdominal pain not related to pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- increased pain in the sternum when coughing, taking a deep breath, or sudden movements;
- discomfort, unpleasant sensations in the limbs;
- back stiffness;
- loss of sensitivity, numbness;
- paresthesia of fingers;
- chronic tachycardia of an idiopathic nature;
- difficulty breathing;
- poor posture;
- coughing up blood.
X-ray examination of the thoracic region is also prescribed to identify pathologies of the cardiovascular or bronchopulmonary system, inflammatory processes, and microtraumas.
How is the X-ray procedure performed?
X-rays are performed in a special room with a stationary device or at the patient’s home using a portable X-ray machine. To examine the thoracic region, you must undress to the waist and remove all metal jewelry.
To prevent the possibility of shading of the vertebrae by internal organs, photographs are taken in 2 projections : frontal and lateral. The examination lasts several minutes. During this procedure, the patient must lie still.
Any change in body position leads to deterioration in the quality of the images. As a result, an incorrect diagnosis may be made.
For an AP photograph, the patient is placed on a special couch on his back. The pillow cannot be used. Legs should be straight, arms extended along the body. For a lateral projection radiograph, the patient is placed on his side, the supporting hand must be placed under the head, and the other hand must be clasped around the knees.
In some cases, x-rays are taken while standing . The patient is placed directly in front of the emitter, with his back pressed tightly against the sensor or film cassette. Lateral X-rays can also be performed in a standing position.
The patient turns sideways and raises his arms up behind his head. Some vertebrae can be seen if examined in an oblique projection.
In some situations, it is recommended to take x-rays with contrast agents. After all, radiography reflects only the bone base of the spine. To visualize the spinal cord or intervertebral discs, they must be stained with a contrast agent.
The doctor may prescribe:
- myelography;
- pneumomyelography;
- discography;
- epidurography;
- venospondylography.
The technique is selected depending on the complaints and the expected diagnosis.
Myelography is necessary to identify tumors and areas where the spinal cord is being compressed. Liquid radiopaque contrast agents are injected into the spinal space.
Pneumomyelography is one type of procedure. To carry it out, radiopaque gas is injected instead of liquid.
To perform discography, a contrast agent is injected into the core of the problem disc. It detects diseases of the intervertebral discs.
Epidurography is intended to visualize narrowing of the spinal canal, inflammation of the spinal cord, and hernias. Contrast is injected between the bone walls and the membrane of the spinal cord.
Venospondylography is necessary to examine the venous blood flow of the spine. Contrast is injected into the cancellous bone located in the spinous process of the vertebra.
Only an experienced specialist should carry out the procedure for introducing contrast agents into the spine. If it is possible to do a CT or MRI instead of an x-ray contrast examination, then it is better to give preference to these procedures. Before contrast is administered, a spinal puncture is sometimes performed, and the resulting fluid is sent for examination. .
Contraindications
X-ray of the spine is a relatively safe procedure, but not everyone is allowed to have it. The main contraindication to this research method is pregnancy. This is explained by the fact that radioactive radiation can seriously harm the embryo, causing deviations in its development or even miscarriage. It is also not recommended to take x-rays during breastfeeding, since radiation changes the structure of milk. You can breastfeed only 14 days after the study.
Other contraindications to the procedure include:
- the patient’s inability to remain still;
- psychical deviations;
- severe pathologies;
- the presence of a large fat layer;
- the presence of postoperative scars in the chest area.
If a study was carried out using a barium suspension, then X-rays of the spine are allowed only after a day, when the body has cleared itself of the harmful substance. Otherwise, the research results will be distorted.
Contraindications to X-rays
There are a number of situations in which spondylography cannot be done.
Contraindications include:
- serious condition of the patient;
- internal bleeding;
- pregnancy (especially 1st trimester);
- pneumothorax (air in the pleural area).
But if necessary, during pregnancy, X-ray diagnostics are performed . The radiation dose to the fetus for any 2 consecutive months should not exceed 1 mSv. During the study, shielding or diaphragm is performed.
Shielding involves protecting parts of the body that are not being examined with a lead apron that reflects X-rays. Using aperture, the width of the beam of rays is changed, and a more concentrated flow is directed to the area being examined.
The information content of the procedure is reduced if the patient is obese. It will not be possible to obtain clear images if the person being examined, due to certain diseases, cannot maintain a stationary position.
What does it show?
X-rays of the thoracic spine are performed in several projections, so that at the end of the procedure, the specialist receives an average image of the area under study. An X-ray allows you to assess in detail the condition of the spinal segments, as well as nearby internal organs.
Using this diagnostic method, you can study in detail the structure and shape of the thoracic vertebrae, intervertebral discs, and cartilage tissue. An image of the thoracic spine shows various pathological changes, damage, inflammation and tumors. But with the help of an X-ray examination, it is impossible to examine the condition of soft tissues, see damage to the musculo-ligamentous apparatus, blood vessels or nerves.
X-ray of the thoracic spine - what it shows
The spine is a complex biological mechanism that performs many functions and is responsible for the functioning of all organs. Only a professional can correctly evaluate an x-ray and identify pathologies in the thoracic spine.
During the examination, the doctor analyzes the configuration of the department, the shape, structure and position of individual vertebrae, the condition of the intervertebral discs, joints, the shape and size of the spinal canal.
Normal indicators
Normally, the thoracic spine is in a state of slight flexion - physiological kyphosis, while the vertebrae form a regular arch. The vertebral bodies in the photographs have the shape of rectangles with clear, smooth contours, their structure is homogeneous and the same in all segments.
The distance between the vertebral bodies corresponds to the thickness of the intervertebral discs; normally, these distances are almost equal and depend on the size of the vertebrae. The larger the vertebrae, the greater the distance between them should be.
The vertebrae are connected to form the spinal column using intervertebral joints, which provide mobility to the spine; normally, these joints are clearly visible on x-rays. The diagnostician can judge the condition of the spinal canal by the configuration of the section as a whole, by the shape and position of the thoracic vertebrae, their arches and processes.
During functional tests, a healthy spine is mobile; during movements, the vertebrae can evenly shift relative to each other up to 1-2 mm, but the shape of the vertebral arch remains correct.
What pathologies can be identified
An X-ray of the thoracic spine can reveal the following abnormalities.
- Malformations of the vertebrae and postural disorders (kyphosis, scoliosis, kyphoscoliosis). Early detection of this pathology in children and adolescents allows for the necessary correction to be carried out in time and to avoid serious complications in the future.
- Spinal injuries. With fractures or dislocations, the shape of the section is disrupted, the vertebrae are displaced, and characteristic changes in the shape and structure of the broken vertebrae may be visible.
- Neoplasms. Malignant tumors and metastases lead to the replacement of normal bone tissue with pathological cells, so in the picture you can see a vertebral fracture caused by cancer. Benign tumors are less likely to cause fractures; they can be diagnosed by changes in structure, compaction or thinning of bone tissue, and changes in the shape of the vertebra.
- Inflammatory diseases of the vertebrae (spondylitis) are manifested by deformation of one or more vertebrae, blurring of their contours, decreased density and gradual destruction. Common causes of spondylitis are tuberculosis and osteomyelitis.
- Inflammatory diseases of the intervertebral joints - spondyloarthritis, due to which the spine loses mobility and can take on a characteristic appearance. For example, with ankylosing spondylitis, the spinal column becomes like a bamboo stick.
- Osteochondrosis is considered one of the most common diseases. In the photographs, the doctor can see kyphosis, signs of flattening and compaction of the intervertebral discs, the growth of bone tissue around them, characteristic deformation of the vertebral bodies, and arthrosis in the intervertebral joints.
- Osteoporosis is a metabolic disorder in which bone tissue loses calcium. In this case, the vertebrae look “transparent” on x-rays, and the disease itself causes pain in the bones, spine and often leads to fractures even with light loads.
How to prepare?
There is no need to carry out any special preparatory measures before an X-ray examination of the thoracic spine. It is enough just before the procedure to expose the upper part of the body and remove any existing jewelry or objects made of metal from the body.
During the examination, the specialist may give the command to turn around, hold your breath, or do some other action. You must listen to the doctor and do everything he says. No other preparation is needed for an x-ray of the thoracic spine. Sometimes it is necessary to stop eating 8 hours before diagnosis and stop eating foods that increase flatulence.
Functional testing study
Osteochondrosis of the vertebral discs can only be determined during examination of the thoracic region in functional tests. It is preferable to perform fluoroscopy, which monitors dynamic changes.
For the examination, the patient is asked to straighten up as much as possible and then bend over. Sometimes additional weights or fixation in the thoracic area or changes in the position of the arms are required. This helps to identify functional disorders of the spine. Sometimes it takes 5-6 pictures for a reliable and complete picture.
This diagnosis determines vertebral instability, which indicates disorders in the intervertebral joints and osteochondrosis changes.
How do they do it?
After the patient has rid the upper body of clothing and jewelry, the x-ray procedure begins, which occurs in several stages:
- The patient wears a special lead apron that protects the body from radiation exposure.
- The patient is placed in a device, which comes in two types: horizontal or vertical. Depending on the type of device, the patient is placed standing or lying on his back (side).
- Pictures are taken in 2(3) projections. A second x-ray is often taken while tilting. Most often, during diagnosis, a person is asked to lie on his side, pull his legs to his chest with one hand, and put the other hand behind his head. During diagnosis, the doctor may ask you to change position and hold your breath.
- To determine the displacement of the vertebrae under load, radiography can be performed with functional tests. To do this, the patient must perform a number of movements prescribed by the doctor during the study. Most often you need to bend or extend the body.
- X-rays scan the thoracic spine, impulses are transmitted to a computer, where a layer-by-layer image of the area under study is built. The image remains on digital media, and the photo is also printed.
- Upon completion of the procedure, the patient gets up, gets dressed and waits for the results of the study.
The duration of the procedure is 10-20 minutes. During this entire time, the patient must remain motionless and follow all the doctor’s commands.
Characteristics of radiography
The main feature of radiography is to take pictures of the required organs from different angles: back, chest and side section.
Using X-rays of the thoracic region, the position of the spine and each individual vertebra can be determined:
- X-ray films clearly show the transverse and spinous processes, the location of the arches and the degree of damage to the intervertebral cartilages.
- Using this technique, the costal and vertebral joints are assessed: tubercles of costal tissue, transverse processes, heads of ribs and vertebrae. By conditionally limiting and marking the arches with the inner edges, the visibility of the spinal canal increases.
- Lateral projections allow you to see the lower and middle vertebral sections of the skeleton: endplates, cavities and intervertebral cartilages.
https://www.youtube.com/watch{q}v=NJVO95zSnlY
Correct positioning of the patient in the device during the procedure is of great importance when taking x-ray images. For a front projection x-ray, the x-ray beam must be positioned at the level of the nipples, so the patient's position must be perpendicular to the x-ray stand. For lateral projection, the patient's image is turned with his back to the X-ray beam.
Decoding the results
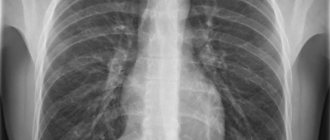
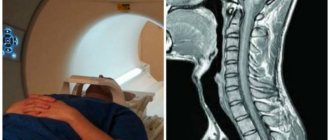
Upon completion of the procedure, the radiologist writes a description of the resulting x-ray image, which is then transferred to the attending vertebrologist for interpretation. Along with the image, the subject receives a report indicating the dose of radiation received. An X-ray of the thoracic spine in two projections looks like a negative photograph, in which soft tissues are indicated in a dark color and hard structures in a light color.
In a normal condition, an x-ray of the thoracic spine should show 12 vertebrae of the correct shape and size, without any damage or pathological changes. The spine should be slightly curved forward, there should be no tissue swelling or inflammation nearby. Curvature of the spine, misalignment of the vertebrae, fissures or stenosis are abnormalities that require treatment.
How to do an X-ray of the thoracic spine
The study is carried out in the treatment room of the X-ray department of the medical institution. The position of the patient and the number of necessary images depend on the tasks that the attending physician sets for the diagnostician, as well as on the condition of the patient himself.
- To identify spinal deformities and calculate the degree of curvature during functional tests, patients are examined in a standing position at the screen (vertical radiography).
- To assess the condition of the vertebrae, intervertebral discs and joints in severe, weakened, elderly patients, radiography is performed in a lying position on a special work table.
In two projections
Traditionally, X-rays of the thoracic spine are performed in two projections: direct, when the patient lies on his back or stands with his back to the screen, and lateral, in which the patient is placed on his side or placed with his right or left side to the screen. Such a study allows you to evaluate the shape of the entire department, see different parts of the vertebrae, their displacement relative to each other (listhesis), and analyze the significance of changes in the intervertebral discs.
Sometimes one projection (direct or lateral) is enough to determine the degree of scoliosis or kyphosis. And in case of severe combined deformities of the spine, kyphoscoliosis of the 3rd and 4th degrees, a polypositional study with additional images in oblique projections can be performed. There may be 4 such pictures, sometimes more.
Radiography with functional tests
Functional testing is carried out in a standing position. Usually two lateral photographs are taken.
- First, the subject is asked to bend at the thoracic region, rounding his back as much as possible - to assume the position of maximum flexion.
- Then the patient should bend back - take the position of maximum extension.
This study is intended to assess the interaction of the vertebrae during movements, determine the mobility of the thoracic region as a whole, its segments, and identify abnormal vertebral displacements (instability).
What are the side effects?
During the study, the patient is exposed to radiation. In small doses, such X-ray radiation does not pose any danger to human health and life. But in large quantities this leads to mutation of cells and their malignancy. However, you should not be afraid of radiation, since a one-time procedure does not in any way affect the human radiation background. It is allowed to carry out X-ray examinations no more than 5 times a year. To reduce the risk of side effects, the dose of radiation received should be recorded after each procedure. This will allow you to control the level of exposure.
Advantages of fluoroscopy
The latest X-ray machines allow you to take high-resolution images and immediately download them to any digital media. This allows the patient to contact several doctors with the results in order to obtain an objective and informative assessment of his condition.
Digital imaging, as we see in the photo, allows diagnosticians to study the image down to the smallest detail. That is why modern medical centers refuse to use outdated X-ray equipment.
Actions after the procedure
At the end of the procedure, the patient is given an x-ray, which is then examined by the attending physician. The information obtained is entered into the patient’s outpatient card, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed. Immediately after this, the person can go home. X-rays do not affect the person’s condition in any way, so there is no rehabilitation period; the person can immediately eat, drink, smoke or drive. There are no restrictions after the procedure.
To quickly remove radioactive substances from the body, it is recommended to consume more fermented milk products, nuts, carrots and seafood. Radiography allows detailed examination of bone segments, but does not provide any information about soft structures. Therefore, often after this study, additional more informative diagnostic methods are prescribed - CT or MRI.
Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
The advantage of the method is its accessibility, low radiation exposure (within 1 mSv), and the absence of contraindications. It is designed to identify pathology and select the optimal method for further diagnosis, for example, CT or MRI.
The disadvantages include not very high information content. Due to the complex structure of the spine, some important details cannot be seen on x-rays. Intervertebral discs, spinal cord, and nerve roots are soft tissues, so they are not visible on x-rays at all; a diagnostician can judge their condition only by indirect signs.
What is the price?
X-ray of the thoracic spine is an informative non-invasive diagnostic method that can be done in many medical institutions in Moscow and St. Petersburg. The main advantage of this procedure is its availability and low cost. The price of the study depends on the complexity of the study, the location of the clinic, the quality of the equipment and the professionalism of the specialists, and is in the range of 200-3000 rubles. In many cases, an X-ray examination can be done for free if you contact a government medical institution.
Preparing for the study
No special preparation is required for diagnosis. Often performed as a rapid test and identifies acute conditions that require urgent correction.
You can prepare for the examination in the X-ray room by undressing to the waist and removing jewelry that may distort the result. Taking a cross into your mouth or hanging a chain on your ears will not work during this study, since the diagnosis also includes the last cervical vertebrae, which may be covered with metal.
Where to do it?
You can get an x-ray of the thoracic spine at the following addresses.
| Clinic name | Address | Price |
| Multidisciplinary clinic "Miracle Doctor" | Moscow, st. Shkolnaya, 49 | 1400 rub. |
| Consultative and diagnostic department of City Hospital No. 15 | St. Petersburg, st. Avangardnaya, 4 (Veteranov Avenue) | from 1100 rub. |
| City Clinical Hospital No. 19 (GKB19) | Moscow, Bolshoi Predtechensky Lane, 15 | from 500 rub., free under compulsory medical insurance |
| Medical center Doctor nearby in Strogino | Moscow, st. Kulakova, 20/1L | from 1200 rub. |
| Clinic "Family Doctor" | St. Petersburg, st. Academician Pavlova, 5E | from 700 rub. |
The principle of operation of the X-ray machine
The method of operation of the X-ray machine is based on displaying the signal as it penetrates tissue and recording the indicators on an X-ray sensitive medium.
As a result of penetration through objects with different density indexes, X-ray radiation spreads around the perimeter and generates data with different degrees of saturation. As a result, a summarized shadow image of the organs appears. Therefore, x-rays are performed only to diagnose heterogeneous formations.
If previously X-ray images could only be reproduced on film media, now the incoming signal can be recorded on an electronic disk. Equipment with electronic media is much more expensive than film counterparts. The diagnostic display from digital scanners is displayed directly on the device screen and remains in the system along with the patient’s medical indicators.
Diagnostic radiography is always performed with image projection in at least two projections. The radiographic picture is a plane with a three-dimensional volume, therefore, several images are required for a detailed analysis of the location of pathological foci.
The qualitative diagnostic result is determined by three parameters:
- The voltage that is applied to the X-ray tube.
- Current strength.
- Time period of tube operation.
The parameters may vary depending on the anatomical characteristics (weight category, presence of scars) of the patient and the individual characteristics of the X-ray apparatus.
What is a spinal x-ray?
Radiography is considered an informative diagnostic method. It allows you to accurately identify all problem areas of the thoracic region. Experts call this examination of the spine spondylography.
X-rays are taken using a special fluoroscope apparatus. Inside it there is a beam tube, into which the process of particle acceleration occurs. They flow through the human body in a directed flow, lingering in areas with a high calcium content.
After this, the rays are projected onto a special screen, leaving an imprint. Subsequently, the specified print is reproduced on paper.
The nature of X-rays is similar to sunlight. The rays are electromagnetic waves. There is no need to be afraid of excessive radiation when taking x-rays. For conventional film radiography of the thoracic region, the radiation dose is 0.5 mSv.
For example, with computed tomography this figure is 10 times higher. The permitted radiation dose is 1 mSv per year annually for 5 consecutive years or 5 mSv once a year.
X-rays are a common way to determine the condition of the thoracic spine.
The advantages of this method include:
- speed of implementation;
- high information content;
- low cost;
- the ability to take a picture in any hospital or at home using mobile fluoroscopes.
The examination is considered safe if carried out no more than 2 times a year. If necessary, the images are repeated more often.
Video: “How does X-ray work?”
When X-rays are contraindicated
Because the imaging process relies on radiation exposure, not every patient can undergo this procedure. Although the dose of X-ray or gamma radiation is small and does not cause harm when used correctly, such a study is carried out only when there are no contraindications.
When carrying a child, you should also not go for an x-ray of the thoracic spine. Radiation exposure can cause functional impairment in fetal development. This procedure is avoided even in later stages, replacing it with alternative methods.
If there are large scars in the area being examined after surgery or injury, diagnosis is contraindicated for you. Scars distort the image, making diagnosis more difficult. The same applies to grade 3 obesity - a large amount of adipose tissue also interferes with radiography, the photos are less informative. The doctor may still order such a test if there are no alternatives.
If the patient suffers from a mental disorder, he will not be taken for an x-ray. To obtain clear data, the subject must remain still for some time and follow the radiologist’s commands, for example, hold his breath. With severe mental disabilities and mental changes, a person cannot fulfill this requirement.
A barium examination is considered a temporary contraindication. X-rays can be taken after such a procedure only after 4 hours.
In most cases, the session is postponed to the next day. For people for whom this technique is contraindicated, other examination methods are recommended - MRI, CT, angiography, etc. In extreme cases, doctors are forced to examine the problem area only during surgery.
Preparatory stage
Having understood what the x-ray of the thoracic spine shows, you can proceed to performing manipulations to prepare for the x-ray.
During preparation, several rules are followed:
- Two days before the procedure, it is recommended to follow a special diet. This diet involves avoiding baked goods, dairy products, milk, fresh cabbage, potatoes, and beans. It is forbidden to eat foods that increase flatulence.
- If you have problems with flatulence, doctors advise using activated charcoal, one tablet three times a day, a couple of days before taking an x-ray.
- The last meal consumed on the eve of the study should occur no later than 19:00.
- An enema can be used to cleanse the intestines on the day of the procedure. This is required because the large amount of gases prevents the free passage of the X-ray beams. As a result, the photo of the chest x-ray is unclear, and it is quite difficult to determine the diagnosis.