Mycoplasma hominis is a small bacterium that lacks the typical bacterial peptidoglycan cell wall. Because of this property, the microorganism is difficult to visualize using simple laboratory methods.
Mycoplasma belongs to the genus Mollicutes, which represents a group of opportunistic bacteria. They can coexist with normal human microflora without provoking pathological processes. But, at the same time, the absence of a cell membrane makes the microorganism resistant to many antibiotics, in particular to tetracyclines.
Today, it is customary to divide mycoplasma into six groups, depending on the pathologies that it provokes. The most common are two types - M. hominis and U. urealiticum (genitalium), affecting the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system.
Mycoplasma is a fairly common infection among STIs. It is often combined with other pathogenic bacteria - Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea), Chlamydia (chlamydia) trachomatis, Treponema pallidum (syphilis). Mycoplasma often causes the development of urethritis, cystitis, and inflammation of the prostate gland.
When is a mycoplasma test prescribed?
According to some microbiological studies, the level of Mollicutes colonization in the urogenital tract (in the presence of signs of disease) ranged from 21% to 54% in women, and from 4% to 13% in men. In the upper respiratory tract, the rate ranged from 1% to 3% among healthy adults.
Among patients with chronic respiratory diseases, 7-8% (in particular, in the presence of pneumonia).
In children with chronic tonsillitis, bacterial colonization ranged from 20% to 30%.
Doctors recommend diagnosing mycoplasma when identifying the following pathological processes:
- Inflammation of the urinary tract. Diagnosed as urethritis, with mycoplasma it is difficult to treat, and is prone to relapses.
- Bacterial vaginosis. A condition caused by changes in the vaginal bacterial flora.
- Inflammation of the fallopian tubes. Salpingitis, often developing against the background of an STD, can lead to the formation of adhesions and subsequent infertility.
- Inflammation of the cervix. The medical term is cervicitis. It often occurs asymptomatically, becoming chronic and accompanied by the formation of erosions on the uterine mucosa.
- Infertility of unknown etiology.
A test for mycoplasma and ureaplasma is mandatory if the following clinical manifestations are present:
- pathological discharge from the vagina and urethral canal;
- burning, soreness, itching sensation during urination;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- rashes, redness on the skin of the external genitalia.
With a long-term mycoplasma infection, a number of complications may develop. For example, menstrual irregularities, the appearance of acyclic bleeding, pain in the rectum.
In more severe cases, male infertility and disruption of the ovulatory cycle develop, which is accompanied by the inability to conceive.
Types of pathogens of mycoplasmosis
The pathogens that cause the disease are microscopic organisms that can initiate infectious and inflammatory processes in the body of men, women and even children. Mycoplasmosis analysis can identify different types of mycoplasmas:
- Pneumonia (Mycoplasma pneumoniae);
- Hominis (Mycoplasma hominis);
- Mycoplasma genitalium;
- Ureaplasma urealyticum.
Of the listed microorganisms, only the first can cause respiratory diseases, while the rest cause genitourinary tract diseases.
How to prepare for a mycoplasma test?
Diagnostics does not require special preparation from the patient.
But to obtain the most accurate results, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- Biological material is taken from women a few days before or after menstruation.
- Two to three days before the test, it is necessary to exclude sexual contact, taking antibiotics and alcoholic beverages.
- Men are not recommended to urinate for 2 hours before taking biomaterial from the urethral canal.
Read also: How is an examination by a urologist performed?
To determine the opportunistic agent Mycoplasma, three types of laboratory tests are used:
- bacteriological culture (bacteriological culture);
- enzyme immunoassay (ELISA);
- polymerase reaction (PCR).
Concomitant treatment (according to symptoms)
A child infected with mycoplasma is given non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs at high temperatures to alleviate the patient’s condition. Children are prescribed ibuprofen or paracetamol in the form of an oral suspension or rectal suppositories. You can use a vasoconstrictor nasal spray, take antihistamine drops or oral syrup (Zirtec or similar Zodak, Loratadine, Fenistil for the youngest patients).
Concomitant treatment reduces irritation and sore throat, but does not affect the causative agent of the disease.
Anti-cough medications, for example Sinekod, are recommended to be given only in the first days. Then the child will be able to rest from attacks of painful coughing. In the future, the doctor prescribes expectorants to thin and facilitate the discharge of sputum. The use of pharmaceutical drugs and folk remedies that strengthen the immune system for the treatment of mycoplasma is justified.
Mycoplasmas in children after the acute period of the disease remain in the body, although in small quantities. Full recovery does not occur, immunity to the pathogen is not developed. Against this background, laryngitis, pharyngitis, and bronchitis periodically occur. Often respiratory and urogenital mycoplasmosis become chronic.
Bacteriological culture
The most common and cost-effective option for diagnosing a pathogen. Based on the cultivation of bacteria from a test section of material on nutrient media, in laboratory conditions.
The analysis allows you to detect the presence of bacteria and clarify its exact quantity. Diagnostics takes quite a long time; it takes at least two weeks to get results. However, the accuracy of the study is almost 100%.
Currently, experts rarely recommend bacterial culture; more modern methods of detecting mycoplasma - PCR, ELISA - are increasingly being prescribed. This is due to certain disadvantages of bacteriological culture. These are the duration of execution, the need to transport the biomaterial in a special environment, and the increased demands of mycoplasma on nutrient fluid.
For laboratory testing, material is taken from the urethral canal or a portion of urine. It is often recommended to study both types of biological material to obtain more informative results.
To minimize the risk of obtaining a false positive/false negative result, material is collected according to the following principle:
- 4-6 weeks after the end of antibacterial therapy;
- in male patients - three hours after the last urination;
- in women - a few days after the end of menstruation.
Treatment of bacterial infection
If you are only worried about a runny nose or low-grade fever, then antibacterial drugs will not be required. Antibiotic treatment is a specific therapy for mycoplasmosis. Macrolides, fluoroquinolones, and tetracyclines are considered the drugs of choice. Other medications are given depending on the symptoms.
Oral antibiotics:
- Erythromycin - 20–50 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day for 5–7 days. The daily dose is divided into three doses.
- Clarithromycin - 15 mg per 1 kg of body weight. Give in the morning and evening, with an interval of 12 hours between doses.
- Azithromycin - 10 mg per 1 kg of body weight on the first day. In the next 3-4 days - 5-10 mg per kg of body weight per day.
- Clindamycin - 20 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day, 2 times a day.
Mycoplasmas grow more slowly than other bacteria. Therefore, the duration of treatment is not 5–12 days, but 2–3 weeks.
Clindamycin belongs to the lincosamide antibiotics. Clarithromycin, erythromycin and azithromycin belong to the group of macrolides. Tetracycline antibiotics are used less and less due to the spread of resistant bacterial strains. There is a practice of combining antimicrobial drugs that differ in their mechanism of action. For example, doctors may prescribe a combination of erythromycin and tetracycline. Another option is to change the antibiotic during a long course of treatment. The choice of remedy is influenced by the child’s allergies to substances belonging to certain groups of antibacterial drugs.
Tablet forms of antibiotics are more difficult to give to children, especially if it is necessary to calculate the dose and divide one capsule into several doses. Doctors recommend treating children under 8–12 years of age with suspensions, which are prepared from an antibacterial substance in the form of powder and water. Such products are produced in glass bottles and equipped with a dosage pipette, a convenient measuring cup or spoon. The drug in pediatric dosage usually tastes sweet.
PCR study
It is considered the most informative method for studying infections caused by pathogenic microorganisms.
The polymerase reaction has ultra-high sensitivity, therefore, the accuracy of the results reaches 99%. In addition, PCR analysis can detect the presence of pathogenic microflora at the preclinical stage, when there are no obvious signs of the disease. Today it is generally accepted that PCR is the only accurate method for detecting mycoplasma.
Several diagnostic methods are used - qualitative and quantitative.
The first technique allows you to identify a specific type of bacteria and indicate the time when the patient was infected.
The second technique (quantitative method) is aimed at determining the exact amount of the pathogen and the effectiveness of the therapeutic effect. Quantitative PCR is usually prescribed for patients with previously diagnosed mycoplasmosis and for those who have undergone antibacterial treatment.
PCR is one of the expensive ways to detect an infectious process. However, it allows you to detect the causative agent of the disease in just a few hours. In this case, the material can be almost any type of biological fluid. This is urine, pathological discharge from the vagina, secretion from the mucous membrane of the urethral canal.
Blood and ejaculate are also collected for research. The speed and accuracy of the analysis allows us to identify the earliest stages of the infectious process, thereby increasing the effectiveness of therapy tenfold.
Features of treatment of mycoplasmosis
Diagnosing mycoplasma is an indicator that there is an active infectious-inflammatory process in the human body, which requires mandatory treatment. The main method of treatment in this situation is to take antibacterial drugs, the action of which is aimed at suppressing the growth of the pathogen.
The prescription of a particular drug is carried out taking into account the symptoms of the disease and the characteristics of its course. It is important to understand that only antibiotics can help cure mycoplasmosis, so you should not rely too much on traditional treatment. The use of infusions of chamomile, calendula and St. John's wort helps relieve muscle tension and eliminate initial symptoms, however, they are unable to completely eliminate the pathology.
It is important to begin treatment immediately after diagnosing mycoplasmosis and complete recovery can only be confirmed by a negative test result for the presence of the pathogen in the human body.
Mycoplasmosis is a dangerous pathology that can provoke the development of many complications. It is for this reason that it should definitely be treated, and not hope that everything will go away on its own.
Mycoplasmosis is a disease that, when developed, can cause serious complications in the body. Therefore, the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease should serve as a reason to conduct research for the presence of the pathogen in the body. To identify and promptly begin treatment of mycoplasma, tests should be performed as early as possible. The causative agent of the disease is quite dangerous, especially during pregnancy, so contacting a doctor if its signs are detected is mandatory.
ELISA testing
Immunoassays are antibody-based analytical methods for pathogen detection using quantitative/qualitative methods to identify them.
The principle of immunoassays is based on a specific antigen-antibody reaction. Therefore, ELISA is used all over the world for the diagnosis of infectious and viral diseases. Also in pharmacology to detect certain types of drugs in the body.
Read also Where to get tested for sexually transmitted diseases
Antibodies are produced in response to infection, and therefore ELISA can indicate with 98% probability that a past infection has occurred.
ELISA is highly sensitive and relatively inexpensive, which makes it useful as a preliminary diagnostic procedure.
The analysis is widely used in testing HIV and a number of other pathologies of the urogenital tract.
Regarding mycoplasma, ELISA indicates whether the patient has been previously infected and whether the immune system has been able to cope with the infection.
As a standard, when antibodies to mycoplasma are detected, qualitative or real-time PCR is prescribed.
Mycoplasmosis of the kidneys and other organs
Children can become infected from adults through direct contact - sleeping in a shared bed, sharing a toilet seat, or sharing a towel. It happens that the source of mycoplasma becomes kindergarten staff. In the respiratory and urogenital forms of mycoplasmosis, epithelial cells are mainly affected. Dystrophic changes in the tissue and its necrosis begin.
Infection of the genitourinary system in adolescents leads to cystitis, pyelonephritis, and vaginitis. Mycoplasmas initiate pathological processes in the liver, small intestine, and various parts of the brain and spinal cord. Mycoplasmosis in teenage girls manifests itself in the form of vulvovaginitis and mild lesions of the urogenital tract. The course of the disease is most often asymptomatic; in severe forms, pain occurs in the lower abdomen and mucous discharge appears.
Mycoplasma in the blood of a child can cause the development of a generalized form, which is characterized by damage to the respiratory system and a number of internal organs. The liver increases in size and jaundice begins. Possible development of meningitis, brain abscess, meningoencephalitis. A pink rash appears on the body, and the eyes become watery and red (conjunctivitis).
Analysis results: transcript
The interpretation of the results obtained is carried out by the attending physician.
The doctor will explain in detail what the analysis shows and, if necessary, prescribe appropriate treatment.
Bacteriological culture
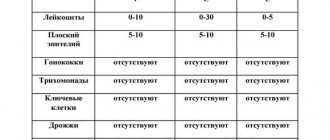
This type of analysis determines the concentration of pathogenic microorganisms; at the end of the analysis, the results are indicated in the form of titers.
It is quite easy to decipher the diagnosis; if there is a value of 10^3 CFU/ml, there is no infection; if the value is higher, treatment is required. If necessary, a polymerase reaction is performed to more accurately determine the bacteria.
ELISA
When diagnosing using the ELISA method, it is possible to obtain three variants of results: “doubtful”, “positive”, “negative”.
A negative result can only be said when there are less than 8 immunoglobulin M antibodies and less than 5 IgG. However, such results do not always indicate that mycoplasma infection is absent.
If you were infected less than two weeks ago, laboratory testing will show a negative result in 90% of cases.
If a questionable result is obtained, a repeat study is performed or another type of diagnostic measure is prescribed. It is recommended to carry out the analysis after a few weeks.
If the laboratory report is positive, the patient is infected.
In this case, an increased number of immunoglobulin M antibodies is observed - more than 9.
If the test is positive, the patient is given a diagnostic test to determine individual antibodies. These are immunoglobulins A and G, which allow identifying a specific type of mycoplasma (hominis or urealyticum).
To determine these types of infection, their DNA is isolated from biological material. Next, the replication process is started, which allows you to obtain complete information about the disease.