If a doctor suspects the presence of a genitourinary infection, then he prescribes various tests for his patients. One of these will be a urethral smear in women. Thanks to this analysis, you can see the presence of pathogenic flora and identify the number of red blood cells and leukocytes. Let's consider how the material is taken and how the result is interpreted.
A smear taken from the urethra is a scraping from the mucous surface. You need to prepare for the procedure. It will be prescribed by a gynecologist or urologist not only if there are complaints, but also as a preventive measure so as not to miss the onset of the disease.
From the history
The method of urethroscopy appeared in the last century. Before the urethroscope was invented, examinations were performed with a cytoscope, developed in the eighteenth century. If we compare a urethroscope and a cytoscope, the first one is smaller and has a better viewing angle. Over time, the urethroscope has been improved. Now you can observe all the changes in the body on the monitor screen.
Women have problems with the urinary system much more often than men. This is due to the structure of the urethra. In women it is shorter and wider. Because of this, inflammatory processes often occur in the urethra. For diagnostics, a device designed specifically for women is used. It is distinguished by its short length (about 15 centimeters) and wide probe.
There was a time when people did not go for this type of examination due to fear of pain. Previously, the procedure was painful, but now it is done with anesthesia. Most often, local anesthesia is used, less often - anesthesia.
Urethroscopy technique
The urethroscope contains a tube, a fiber-optic light source and a cystometer filled with carbon dioxide or water.
To avoid damaging the mucous membrane, the doctor carefully inserts the urethroscope through the external opening of the urethra, trying to maintain a lumen in the middle of the observed area.
First, the pressure required to open the urethra is measured. In normal condition, the opening pressure of the urethra is 70-90 cm of water column.
In people with stress urinary incontinence, the urethral opening pressure will be low, and in patients with an unstable bladder, it will be high.
At the very beginning of urethroscopy, the urethral mucosa is observed. The doctor notes the color of the mucous membrane, the presence of inflammation, and polyps.
Then the triangle of the bladder is examined, attention is paid to the color of the triangle, existing inflammation, and atrophic changes.
The functioning of the urethrovesical junction is also checked. Urethroscopy in men, like urethroscopy in women, is performed after the bladder is full. To do this, the patient is asked to hold urine, cough sharply, and try to push to record the response of the urethrovesical junction. Data are recorded from the time of the first urge to pass urine, the sensation of a full bladder, and the feeling of maximum bladder filling.
Differences in dynamic response parameters help separate patients with a healthy bladder from patients with stress urinary incontinence and an unstable bladder. Carbon dioxide, as a tensile medium, is not currently used due to its conversion to carbon dioxide, which can lead to measurement errors.
In dynamic urethroscopy , a urethroscope is used and a cystometer is attached to it, including a filling medium and light. Pressure measurement begins with a full bladder, when the urethroscope is inserted into one third of the urethra. The subject is asked to cough, strain and hold urine.
The data showed that in a healthy person, the urethrovesical junction closes when the bladder fills, the walls remain closed when straining and coughing, and open and quickly close when urine is suppressed.
In people with stress urinary incontinence, the urethrovesical junction opens slowly when the bladder is full, relaxes and opens when coughing and straining, and opens but slowly closes when urine is suppressed.
In a person who has an unstable bladder, the urethrovesival junction closes when the bladder fills, remains closed when coughing and straining, and opens and remains open even if the person tries to suppress urine.
At the end of the urethroscopy, the urethra is palpated and the bladder is checked for a diverticulum (a protrusion of the bladder wall) with pus draining.
Indications for use
Urethroscopy is indicated for the diagnosis of various urological pathologies
After an examination by a urologist or venereologist, urethroscopy is prescribed. Indications for manipulation are:
- urethritis;
- chronic pathologies of the urinary canal;
- suspicion of a cyst;
- suspected tumor;
- the presence of a foreign body in the urethra;
- urinary incontinence.
Indications for manipulation may include diverticula in the urethra and other pathological conditions.
What is it done for?
Urethroscopy is prescribed after some diagnostic methods have been carried out: a visual examination by a urologist and venereologist to begin with. Usually, an ultrasound is performed before such an examination. This is a very informative method, but if it does not give 100% results, urethroscopy is prescribed.
The most powerful means for penis enlargement
The guy went a little overboard with the product...
Gain weight
Find out details
dominator.ru
Examination with a urethroscope allows you to assess the condition of the urethral mucosa and, on this basis, clarify the diagnosis. Normally, the mucous membrane should be moist, shiny, and pink-yellow in color. There should be no protrusions or growths. Deviations indicate some kind of violation.
Indications for the study are:
- acute and chronic urethritis, or rather, suspicion of an illness - in this case the mucous membrane becomes swollen, red, loses its luster, uneven rough folds form on the inner surface of the urethra;
- granulation urethritis - the mucous membrane is loose, red, full-blooded. With this diagnosis, bleeding often occurs;
- colliculitis - usually accompanied by posterior urethritis. In this case, the seminal vesicle becomes bright red, increases in size and interferes with the normal outflow of urine and sperm;
- Littreitis – inflammation in the Littre iron ducts. The mucous membrane swells and purulent discharge appears;
- morganitis - inflammation in the area of Morganian lacunae, also accompanied by purulent secretion, swelling and redness;
- urethral strictures - narrowing of the canals in some area;
- erosions and ulcers are observed relatively rarely;
- neoplasms - as a rule, cysts and polyps are clearly visible on ultrasound, but there are exceptions;
- urolithiasis - urethroscopy is performed to determine whether stones can be removed through the urethra;
- the appearance of blood in the semen - to determine the cause of the symptom;
- venereal diseases;
- disturbances in ejaculation - the causes of this phenomenon are very diverse and among them urethritis is not the last place;
- disturbances in urination, especially stress urinary incontinence - the latter is perhaps the main indication for urethroscopy for women.
In addition, the procedure is periodically carried out in the treatment of chronic ailments of the urethra in order to observe the dynamics of development and the effectiveness of the course.
Complications
If any alarming symptoms are observed after urethroscopy, you should urgently contact a urologist
According to experts, urethrosopy is a safe procedure. With this type of examination, you can identify a variety of diseases and assess their complexity and stage. However, if you trust a non-professional, the procedure can lead to rupture of the urethra.
The procedure is done under general anesthesia.
Therefore, before going for an examination, it is necessary to inform the doctor about intolerance to anesthesia. Possible complications also include a feeling of discomfort after the procedure and pain during urination. Blood discharge from the canal may be observed. In a couple of days, all these manifestations will pass.
After diagnosis, changes may be noted such as:
- weakening of the jet;
- temperature increase;
- bleeding that continues for a long time;
- stabbing pains.
Pain when urinating after urethroscopy
All these symptoms indicate that you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. If this is not done on time, the consequences will be disastrous.
Types of research
There are the following types of ureteroscopy:
- Irrigation. In this case, the bladder is filled through a tube with an antiseptic colorless liquid. This leads to stretching of the bladder and canal walls, which facilitates diagnosis.
- Dry. Involves examining the urethra and bladder in an unstretched state. In this case, the bubble is filled with air using a tube.
In addition, there is another classification. This is due to the anatomical features of the male and female genital organs. In women, the urethra is the same along its entire length, while in men it is divided into an anterior and posterior urethra. Therefore, for men, urethroscopy is divided into 2 types:
- Front. Only the anterior part of the organ is studied.
- Rear. The entire length of the urethra is examined.
Reviews
Urethroscopy is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods. During the examination, the doctor receives enough information about the condition of the mucosa and can see the walls of the canal. Doctors believe that the procedure is very informative and allows you to obtain the most accurate information about the patient’s condition. Based on the results of the examination, you can track the dynamics of recovery.
According to reviews from those who have had urethroscopy, it is clear that it does not cause any consequences and has a positive effect on recovery (taking into account the administration of medications directly to the lesion). Of course, the procedure is not very pleasant, but due to anesthesia, there is no significant pain during it.
Important questions
Does it hurt
With the use of anesthesia, the process occurs without pain. Unpleasant sensations appear only at the time of administration of this anesthesia, which quickly pass. The main thing is not to be nervous; muscle tension complicates the task for the doctor and the patient himself. When entering the office, relax, tell the doctor about your concerns, the session will not begin until the patient is ready. Additionally, you can ask for a sedative.
How long does it last
Best materials of the month
- Why you can't go on a diet on your own
- 21 tips on how to avoid buying stale food
- How to keep vegetables and fruits fresh: simple tricks
- How to curb your sweet cravings: 7 unexpected products
- Scientists say youth can be extended
Depending on your goals, the process can take from 15 to 40 minutes. Diagnostic urethroscopy is quick, most of it takes preparation. If a biopsy or treatment is needed, it will take a little longer. In general, they try to carry out manipulations quickly and with maximum effectiveness.
Where to do
You can undergo examination or therapy using a urethroscope at a government institution, private clinic, or diagnostic center. When choosing between these options, it is better to give preference to specialized clinics. The progress of the operation depends on the quality and generation of the devices; for example, the new technology is distinguished by more flexible and thinner tubes and effective protection. It is also important to pay attention to the experience of the medical staff and the reputation of the clinic. It is better to look for reviews on hospital websites or forums.
How much does it cost
The cost of the service is influenced by the range of work, the quality of the equipment, and the reputation of the clinic. Diagnostic procedures cost around 20-40 dollars in a private clinic. The price of the treatment service will be 100-150 dollars. At the same time, in some institutions the price does not include anesthesia, so you will have to pay about 10-20 dollars more for it. In total, such a service will cost 200-250 dollars in the middle price segment.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons:
Preparing for diagnosis
To examine the female urethra, no special preparation is necessary. The only thing that is carried out is psychological preparation by the doctor, which consists of:
- suggest the most effective painkillers;
- talk about the progress of the research;
- voice possible complications.
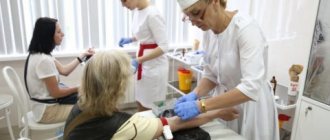
Before the procedure, you must undergo a series of tests. In each case, the doctor selects certain types of laboratory diagnostics that will help in performing urethroscopy. These include a smear, urine test and other types of tests.
Which doctor treats urethritis in women?
Symptoms indicating urethritis raise the question, which doctor should I go to? A highly specialized specialist involved in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system is a urologist.
Only timely and qualified consultation with this specialist guarantees quick relief from the disease and prevention of all possible relapses.
An experienced urologist, having adequately determined the diagnosis and identified the source of the disease, according to the developed algorithm of measures, prescribes an individual treatment course, which guides the patient until complete recovery.
Monitoring patients after surgery
After the procedure, patients do not need special care. If there is a stent, the surgeon indicates in the documents the timing of its removal and a study confirming the complete absence of stones and their fragments. It can identify the following types of diagnostics:
- Ultrasound;
- survey urography;
- computed tomography.
Most of the procedures performed are called “same day surgery.” The majority of patients return to normal life within one to two days after ureteroscopy.
List of infections
This simple test allows you to diagnose both nonspecific purulent diseases of the urogenital tract (urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis) and sexually transmitted diseases - gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, viral infections.
A general swab of the vagina or urethra can detect only certain types of bacteria. But basically it is an indicative method. The analysis does not allow many types of microorganisms to be distinguished from each other. The list of pathogens is limited to Trichomonas, Candida fungi, gonococci and other cocci. For an accurate picture of the vaginal microflora, it is necessary to conduct a bacteriological study.
A smear for latent genital infections in women is the most accurate method for diagnosing an infectious disease of the urogenital tract. It identifies all pathogenic microorganisms that are present in biological material:
- gonococci;
- Gardenerella and Trichomonas;
- chlamydia;
- Proteus bacillus and Klebsiella;
- mycoplasma and ureaplasma;
- herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, human papillomavirus (HPV);
- cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Epstein-Barr virus;
- other pathogenic streptococci and staphylococci (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and viridans, etc.)
The study can be carried out in several ways: inoculation on liquid or solid nutrient media, serodiagnosis or PCR analysis. Analysis for latent urological and sexually transmitted infections allows us to detect mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, HPV and CMV infection. In gynecological practice, a combination of several types of examination is often used for the most accurate diagnosis and subsequent diagnosis.
Consequences
What is urethroscopy is clear. Now it is important to study its possible consequences. After the study, you may still experience pain for a few days while emptying your bladder. In addition, light bleeding may occur.
It is necessary to contact a medical facility if the bleeding does not go away and becomes stronger, chills and fever develop. This can happen if an infection was introduced during the study.
It is extremely rare, but it still happens that a patient experiences a urethral rupture during diagnosis. This can cause severe pain during urination. In both cases, urgent medical attention is required.
It is important to understand that such complications can be avoided.
To do this, you need to choose clinics with a good reputation. Share:
How to detect urethritis using laboratory methods?
Laboratory methods help determine urethritis. They occupy the main place in the diagnosis of this pathology. The main methods that are used to identify urethritis are as follows:
- Bacterioscopic - examination of the taken material under a microscope.
- Bacteriological - sowing material on special media and studying the appearance of the grown colonies.
- Serological - determination of antibodies (immunoglobulins of different classes) to the most common and probable pathogens of urethritis. Immunoglobulins can be systemic (class G and M) and local (class A, they are synthesized locally in the mucous membrane).
- PCR diagnostics is the detection in the blood or other biological media (urine, urethral discharge, cervical canal) of certain genetic sequences characteristic of a particular pathogen.
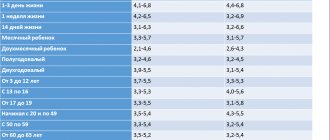
- General clinical – examination of urine and blood using standard methods to assess the presence and degree of the inflammatory process. These tests are prescribed to almost every person who seeks medical help.
To establish the correct diagnosis of urethritis (in the presence of suspicious clinical signs or inflammatory changes in a general clinical urine test), it is necessary to first examine the discharge from the urethra. But some factors can distort the reliability of this analysis, so doctors adhere to certain rules when collecting material.
How to prepare for urethral analysis and how it is performed
The rules for obtaining discharge from the urethra differ for women and men.
For women, these rules include:
- collection of material no earlier than 1 hour after urination;
- use a sterile cotton swab. If there is no discharge, then a special endobrush (a brush like a small brush), which is turned clockwise several times, is inserted into the urethra to a depth of 2-4 cm.
For men, the collection rules are as follows:
- 2 hours or more must have passed since the last urination;
- insert the endobrush into the urethra 2-4 cm and rotate 2-3 times clockwise.
In cases where urethritis occurs with unexpressed symptoms, and in chronic forms, taking the discharge using an endobrush is not always informative. Therefore, for such patients, doctors carefully scrape the mucous membrane using a Volkmann spoon. This procedure is well tolerated; minor discomfort may be felt during it.
The resulting material is either subjected to microscopy (bacterioscopic method) or sown on media (bacteriological method). Using a microscopic examination, it is possible to quickly and easily identify Trichomonas and gonococci (the method is less sensitive for other pathogens). But their absence in a smear does not mean that they are excluded as a cause of urethritis. In this case, if there are suspicious clinical symptoms, polymerase diagnostics is indicated. The detection of more than 5 leukocytes in one field of view in a smear is a reliable sign of an inflammatory process in the urethral zone, which is called urethritis.
Thus, using microscopy you can diagnose:
- fact of urethritis (presence of inflammation);
- its cause (a specific pathogen, especially if it is gonococcus or Trichomonas), which affects further tactics of patient management.
The advantage of bacteriological diagnosis of urethritis is the ability to determine the sensitivity of the causative microbes to antibiotics, so that the doctor can initially prescribe the one that will be most effective for a given patient.