Introduction
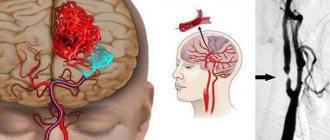
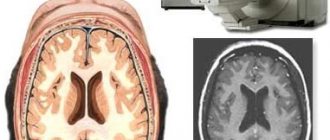
The veins of the brain
are divided into superficial and deep. The superficial veins mostly collect blood from the cerebral cortex and flow partly into the sinus sagitalis superior (superior veins), partly (below the vein) into the sinus transversus and the sinuses of the base of the skull. The veins lack valves and are distinguished by their numerous anastomoses. The deep veins collect blood from the central gray nuclei and ventricles of the brain and merge into one large vein.
| Anatomical diagram of the location of the veins of the brain | MR angiography of cerebral veins |
What does MRI of cerebral veins show?
MRI is a highly accurate method that allows you to obtain a three-dimensional picture of the venous network of the brain in three projections.
MRI screening helps identify a range of potentially life-threatening diseases and conditions:
Venous stagnation
It occurs due to a violation of the ability of blood vessels to perform their function of draining blood from the brain. Stagnation of venous blood contributes to headaches, dizziness, and fatigue. But its main danger lies in the gradual development of oxygen starvation of the brain and swelling, which can lead to serious impairment of well-being.
Neoplasms
Benign and malignant neoplasms can compress the venous bed, complicating the outflow of blood and leading to a rapid deterioration in overall health
Thrombosis of veins and sinuses
Blockage of the venous bed by a thrombus can lead to disruption of the outflow of blood in the brain area. Symptoms appear gradually and often include headache, dizziness, vomiting and confusion. Venous thrombosis rarely develops acutely, often occurring with moderately severe symptoms.
Thrombophlebitis of the cerebral veins
Inflammation that occurs due to blockage of the lumen of a vessel by a thrombus. The disease is accompanied by fever, headaches and vomiting.
Stroke
Cerebral vein stroke is not that common. 98% of cerebral strokes occur due to bleeding from the arteries. The remaining 2% are hemorrhages caused by damage to the veins. Symptoms of the disease develop gradually and may not be taken into account by patients for a long time, which makes diagnosis difficult using conservative methods.
Aneurysm
A protrusion of the vessel wall, which over time can lead to hemorrhage into the medulla.
Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy is the name given to dystrophic changes in brain tissue due to insufficient nutrition and oxygen supply. Encephalopathy can occur, among other things, as a result of disturbances in venous outflow in a local area of the brain or chronic pulmonary and heart failure.
MR venography can detect almost any pathology of the cerebral veins, even at the initial stage of their occurrence.
Classification of tomographs
For MRI of neck vessels, two types of devices are used: closed and open tomograph. They differ not only in design features, but also in diagnostic capabilities.
Open tomograph
– a classic tunnel apparatus consists of a scanning capsule up to two meters long and 65-70 cm in diameter, a retractable table, and an operating control system.
The weaknesses of the equipment include:
- Discomfort in a confined space.
- Restrictions on weight and body dimensions.
Strengths of closed tomographs:
- Generate high voltage magnetic field.
- They create projections with high resolution and wide detail.
- The early stages of the disease are diagnosed.
Open tomograph
– consists of an upper module with a magnet located above the pull-out couch, and a lower module with a magnet installed under the couch. The absence of closed circuits allows examination of patients of any psychological state, age and body type.
Disadvantages of open type devices:
- Poor resolution and low detail of images.
- Longer study time.
| Open MR tomograph | Closed-type MR tomograph |
Considering the ability of the equipment to generate a magnetic field of a certain strength, tomographs are divided into 4 categories:
- Low-field with a voltage of 0.5 Tesla.
- Mid-field ones with an intensity of 1 Tesla are effective in diagnosing pathologies at later stages.
- High-field devices with a voltage of 1.5 Tesla determine the early stages of diseases.
- Ultra-high-field tomographs with a magnetic field strength of 3 Tesla visualize neurophysiological processes, the slightest defects and disorders in real time.
For an effective study of the vessels of the neck, a closed tomograph with a magnetic field voltage of 1.5 Tesla is sufficient.
| Image quality depending on equipment power |
Limitations in tomography
Absolute contraindications:
- The patient has a pacemaker. However, there are currently new models of stimulants, the presence of which is not a contraindication for such a study. It is necessary to consult with a specialist and find out what type of pacemaker the patient has.
- The presence of a hemostatic clip. Under the influence of a magnetic field, the clip may become unusable and bleeding will begin.
- The presence of metal implants inside the body.
There are also relative restrictions. If there are absolute contraindications, it will not be possible to do a vascular MRI, because scanning can be fatal. With relative contraindications, this is acceptable provided that the benefits of the procedure outweigh the possible risks.
Relative contraindications:
- Heart and kidney failure.
- Pregnancy, 1st trimester. The procedure is allowed, but only without the use of a contrast agent.
- Age up to 5 years. The study is carried out, but only under general anesthesia.
- Claustrophobia. In this case, MRI of the head and vessels (veins, arteries) of the brain is allowed only if an open type tomograph is used.
- Excess body weight. For obese people, the procedure is indicated on an open tomograph.
- People with diabetes and wearing an insulin pump. The magnetic field may cause the device to malfunction.
- Allergy to contrast agent. In this case, MRI of the arteries and veins of the brain without contrast is allowed.
- Tattoos on the body made with a pigment that contains metal compounds.
MRI of cerebral vessels is one of the most accurate research methods, allowing one to determine pathology in the early stages of its development, when x-rays cannot help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis. An oncologist, neurosurgeon, or neurologist can prescribe a study. Despite the safety and high degree of information content, this diagnostic method has contraindications. Therefore, before conducting the study, it is necessary to inform the doctor about all existing problems, and also prepare yourself mentally so that the tomography goes smoothly and clear images are obtained.
Indications
Any pathological changes in the structure of the veins lead to disruption of brain activity.
You should pay close attention to the following symptoms and perform an MRI of the area:
- Frequent dizziness.
- Migraine.
- Noise in ears.
- Bleeding from the nose of unknown origin.
- Fainting conditions.
- Impaired concentration.
- Memory loss.
- Mental disorders.
- EPI syndrome without obvious signs of epilepsy.
- Weak sensation in the arms and legs.
A neurologist or neurosurgeon may refer you for an MRI examination in the following situations:
- Congenital anomalies of the cerebral veins.
- Malformations of the vascular bed.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Suspicion of an aneurysm.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Suspicions of neoplasms in the brain affecting the venous bed.
- Search for metastases.
- Determining the need for surgery.
- Checking the effectiveness of treatment of pathologies that adversely affect the structure of the veins.
- Quality control of surgical intervention.
Value of the study
Venography is valuable because it helps doctors identify difficult-to-diagnose diseases.
Several years ago, experts did not even suspect that using instrumental methods it would be possible to diagnose diseases without characteristic symptoms in the early stages of development.
Venography allows you to assess the condition of individual structures and the venous bed. The procedure is necessary to make a diagnosis and check the effectiveness of early treatment. The method is also used to draw up a surgical procedure for certain pathologies.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging has certain limitations and contraindications. They are divided into absolute and relative.
Relative contraindications
are of a temporary nature; the study becomes possible when the patient’s condition or scanning conditions change.
The list of restrictions includes:
- The patient's weight is more than 12-130 kg.
- Anxiety disorders and pathological fear of closed spaces.
- Neurological syndromes in the acute stage, provoking convulsive muscle contractions or uncontrolled movements.
- First trimester of pregnancy.
- Decoration of the face and body with permanent makeup and color tattoos using metal particles based on coloring pigments.
- Inappropriate behavior caused by alcohol intoxication or high levels of psychotropic drugs in the blood.
Absolute contraindications
– high-risk factors for the patient’s health that reduce the effectiveness of the examination to zero.
MRI may cause harm to health in the following conditions:
- Implantation of an insulin pump.
- Presence of a cardiac pacemaker (defibrillator, pacemaker).
- The presence of metal clamping clips on veins and arteries.
- Vascular stands made of ferromagnetic materials.
- Installation of a cochlear hearing implant.
- Help of the Ilizarov apparatus in healing complex fractures.
- The presence of bullets, metal fragments near vital organs.
Contraindications to contrast to improve MRI performance are collected in a separate category. A patient can undergo an MRI scan without harm, but have limitations on the use of contrast agents.
The most common contraindications:
- A persistent allergic reaction to gadolinium derivatives included in the enhancement solutions.
- Liver and kidney failure in acute or chronic form.
- Six-month recovery period after transplantation of an excretory system organ (kidneys, liver).
- Infant age up to 4 weeks.
- Lactation.
- Pregnancy.
There may be other individual contraindications, so before the procedure it is necessary to undergo laboratory blood tests and consult with a specialist.
Contrast for head venography
MRI of brain veins is performed only with contrast: dyes are used to enhance the clarity of the images. In magnetic resonance diagnostics, drugs containing gadolinium are used as indicators. Compared to iodine-containing agents that are used for computed tomography of veins and arteries with contrast, they extremely rarely cause complications.
This diagnostic method helps:
- assess the severity of circulatory disorders in the brain (with ischemic diseases, after TBI, etc.);
- analyze pathologies that arise due to differences in hydrostatic pressure in brain tissues and blood vessels (for example, with neoplasms);
- determine the state of blood flow when planning surgery;
- examine tumors and their blood supply before surgery or after radiation and chemotherapy.
MRI of the vessels of the head - volumetric reconstruction (arteries are indicated in yellow, veins in blue)
How does the procedure work?
MR angiography of neck vessels is performed by appointment. Conventionally, the procedure is divided into three stages: preparation, scanning, obtaining results.
Preparation is divided into the following steps:
- The patient must arrive at the clinic in advance to fill out documents and enter into an agreement to receive paid medical services.
- Then a special questionnaire is filled out so that the specialist can establish possible restrictions and contraindications in advance.
- To study the vessels of the neck with contrast enhancement, it is necessary to determine the patient’s body weight so that the doctor can calculate the correct dosage of the drug.
- Then the doctor selects the optimal type of contrast agent and determines the maximum allowable dose.
- It is best to undergo an MRI in light, loose clothing, devoid of metal rivets, fasteners, or decorative ornaments, which is why in some clinics the patient is given a disposable medical kit.
- It is necessary to remove jewelry, glasses, hairpins, leave your phone, watch and cards with personal belongings.
- The nurse explains the rules of conduct during an MRI of the neck vessels.
- The patient is escorted to the office to the machine.
The scanning procedure is as follows:
- The patient is placed on the retractable platform of the tomograph in such a way that he is comfortable throughout the examination.
- The nurse secures the body with special fixations to ensure complete immobility during the scan. For convenience, the nurse can place special cushions under the head.
- The conveyor moves the patient into the field of action of the magnetic scanner.
- A laboratory technician is paid to perform an MRI through a special window.
- Contrast involves performing a procedure in two stages: a native MRI examination and a repeat scan after the administration of a contrast solution.
The results are obtained as follows:
A radiologist interprets the received images. If the doctor has a high workload, results may be scheduled for the next day. In a normal situation, the conclusion will be ready within 1 hour.
The patient receives a recording of images on electronic media and/or images printed on film, as well as a conclusion based on the diagnostic results.
In some MRI centers, a special employee is responsible for sending results by email to patients so that they do not have to return to the clinic. Other medical institutions practice uploading study data to the patient’s personal account.
How to do an MRI of cerebral vessels
After the patient enters the radiologist's office, the doctor asks several questions about bothersome symptoms and contraindications for the procedure. The patient is asked to remove all metal objects and lie down on the tomograph bed. Normal operation of the tomograph is accompanied by noise, knocking and other loud sounds; this should not be alarmed. In our medical center, each patient is given headphones that play pleasant, calm music during the examination.
Preparation for MRI of the head and blood vessels
The patient is given a special button in his hand, which can be pressed during the procedure to inform the doctor about a sudden deterioration in health.
Duration of the procedure
MR angiography of blood vessels is performed in 20-30 minutes using an open-type device that generates a magnetic field of 1.5 Tesla.
An ultra-high-field tomograph with a voltage of 3 Tesla allows you to increase the speed of diagnostics. The study will take about 5-7 minutes.
A comfortable open-type tomograph generates a low level of magnetic field voltage up to 1 Tesla, therefore, the duration of the diagnosis will increase from 40 minutes to an hour.
Contrast doubles the examination time.
What does it show
With normal functioning of the venous outflow of the brain, the MR image will demonstrate the absence of signs of mechanical and organic damage, hemorrhages, or abnormal structure of the vascular bed.
If pathologies are hidden in the structure of the cerebral veins, the specialist will find:
- Location and extent of vascular damage.
- The extent of the hemorrhage.
- Signs of inflammatory processes.
- Impaired cerebral circulation (narrowing of the venous lumen, thrombosis).
- Deformations and disturbances in the structure of the vein (aneurysm, thickening of the walls, atherosclerosis).
- Violation of the location of the jugular vein bulb.
- The presence of hematomas compressing the veins.
- Neoplasms affecting the condition and functioning of veins.
- Penetration of metastases.
- Disturbances in the restoration of brain structures after neurosurgical intervention.
Vascular malformations
The pathology is associated with a congenital disorder of the structure of the circulatory system. The vessels and arteries of the brain intertwine with each other, forming glomeruli. Malformations cause compression of certain parts of the brain.
Pathology is classified into several types:
- arterial;
- arteriovenous (racemotic, fistulous, cavernous, micromalformation);
- venous.
Patients with malformation can live for a long time, unaware of the circulatory disorders they have. The disease does not manifest clinical signs until the pathological plexus grows in size.
Pressure placed on the brain leads to the following symptoms:
- impaired coordination and motor skills;
- rapid fatigue even in the absence of physical activity;
- visual and auditory dysfunctions;
- headaches.
Malformation can be determined using MRI and CT. The fight against pathology is carried out surgically and is aimed at removing the overgrown part of the vessels. After a computed tomography scan, images are obtained in a three-dimensional projection. They show hemorrhages in the brain, which indicate the presence of an arteriovenous malformation.
Using an MRI scanner, you can obtain both flat and volumetric images of the vascular system. Angiography helps to study in detail the structure of each vessel. It is performed painlessly for the patient and is considered a non-invasive way to examine the brain. Using the procedure, you can determine the exact number of draining structures and create a competent treatment regimen.
Venous malformation is shown in the figure below. The image identifies small dilated vessels shaped like a jellyfish. They drain into a large transcortical vein. On T1 VI, dilated veins are shown in white, draining into the main vein.
What's the difference with and without contrast?
In some situations, native MRI of neck vessels is not informative enough. The doctor uses contrast enhancement to more clearly visualize thin capillaries and tumors.
Contrasting
- this is the introduction of a special solution based on drugs containing the metal gadolinium.
The MRI sequence with contrast includes the following steps:
- A basic native scan is performed.
- After which a special contrast solution is injected into the vein.
- Re-scan is started.
Contrast allows you to identify pathological areas on MRI images with more contrast. The substance seems to illuminate the tumor from the inside, allowing the radiologist to determine the most accurate size, location, shape, nature and degree of development of the disease.
Even a patient who does not have medical knowledge in this field can see the qualitative difference between MRI projections without contrast and with contrast enhancement:
| On the left is an MRI performed with contrast; on the right without contrast solution | ||
CT or MRI, which is better?
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are two completely different diagnostic methods. Each of them has characteristic advantages and weaknesses. In order for the comparison to be objective, it is necessary to evaluate the following indicators:
Image acquisition technology.
MRI relies on the effect of magnetic resonance and visualizes the vessels of the neck thanks to a burst of activity of hydrogen atoms. A CT scan performs a step-by-step scan using X-rays.
Device capabilities.
The neck consists primarily of soft tissue structures, which are visualized with maximum accuracy by MRI. CT has advantages in imaging bone tissue. This method is used to identify problems with the vertebrae that impair the conductivity of the vessels of the neck.
Security and restrictions.
MRI is a safe research method, but has limitations in the form of implanted ferromagnetic devices. In this case, patients are referred to a CT scan. Computed tomography has limitations on the number of procedures per year, as it exposes the body to dangerous ionizing radiation. CT scans are performed no more than 1-2 times a year. Magnetic resonance imaging allows for the freedom to carry out the required number of procedures.
Duration of the procedure.
CT is an operational research method; scanning takes 1-2 minutes. In this regard, MRI is inferior, since the patient has to spend 15 to 30 minutes in the tomograph.
| CT | MRI of cerebral veins |
CT allows you to build 3D models:
| 3D model |
When is a magnetic resonance examination prescribed?
For the study of vascular abnormalities of the brain and the diagnosis of diseases, today there is one of the most accurate methods - magnetic resonance imaging. This is a study using a powerful magnetic field, as a result of which the doctor receives an online image of brain tissue on a computer screen. The same image is then transferred to film, where it is most convenient to examine the smallest details and see inflammatory areas of tissue, if any.
There are human diseases and conditions in which pure tomography will not be enough, then the doctor has the right to prescribe an MRI of the brain in vascular modes. In this case, the gray matter itself is not visualized, but the entire circulatory and vascular system of the brain tissue is clearly visible, this allows you to see veins, vessels and their thin sections, arteries, and determine whether there are pathologies or the development of tumors.
MRI of cerebral vessels is prescribed for migraines, injuries, fainting and suspected tumors
What might lead a doctor to make this prescription? Patient complaints or a good indicator of the general MRI picture against the background of a general deterioration of the condition.
The patient may experience:
- throbbing pain on one side of the head;
- decreased vision, loss of clarity;
- sudden dizziness due to vascular lesions;
- a sharp increase in pain or, conversely, its sharp decrease;
- loss of consciousness during increased physical activity;
- numb face, impaired swallowing function.
Timely diagnosis of MRI of the brain with a vascular program helps not only to identify the disease, but also to assess the degree of its severity, draw up a treatment plan and prevent the development of the disease already at the initial stages of development. A study in this mode can show the condition of the arteries, venous sinuses, and liquor spaces. A huge advantage is that the method is non-invasive, that is, the contrast agent does not pose a danger to humans, and there is no radiation exposure during the procedure. MRI in vascular mode is absolutely safe and is fully controlled by a doctor.
X-ray or MRI, which is better?
Radiography of the vessels of the cervical spine and magnetic resonance imaging of this area have different technological bases. Consequently, each of them has its own category of advantages and disadvantages. Comparing them to each other is not entirely correct. In order for the assessment to be objective, it is necessary to analyze the following aspects:
Image acquisition technology.
MRI technologies are based on the capabilities of magnetic resonance. The vibrational pulses of hydrogen atoms are formed into an image after processing. X-ray scans the body using ionizing radiation.
Device capabilities.
X-rays show the bone structure; angiography will require contrast. And even in this case, the image will only show the location of the vascular network and the location of thrombosis. MRI is used to diagnose tumors, vessel wall dissection and other soft tissue pathologies. This method is ideal for studying soft tissue structures.
Safety.
X-ray studies have an unfavorable radiation exposure on the body, so they are carried out no more than 2 times a year. MRI can be performed an unlimited number of times not only per year, but also per month.
Availability and cost of procedures
.
X-ray, as a diagnostic method, is widely available. The test can be done at your local clinic. The compulsory medical insurance program provides the opportunity to receive the service free of charge. MRI of neck vessels, despite its high effectiveness, is used much less frequently. The devices are available only in inpatient departments, large regional medical institutions, and specialized commercial clinics. Free diagnostics can only be performed in a hospital; in other cases, the service is paid. The cost of an MRI is almost 4 times higher than the price of an x-ray. Image quality.
The result of an MRI is a high-resolution image with a lot of detail. This image makes it possible to recognize even minor degenerative changes. X-ray photography is of lower quality and can detect pronounced changes.
| X-ray | MRI of cerebral veins |
The need to use contrast
Venography is performed with or without radiopaque agents. The substances used are excreted by the kidneys after 24 hours and are not dangerous to the body of the test subject.
The method of administering contrast agents is intravascular. After the procedure, the body is scanned using a computer or magnetic resonance imaging scanner.
The use of contrast is necessary only in cases where there are difficulties in making a diagnosis using vascular ultrasound or functional tests.
Indications for conducting studies with radiopaque agents:
- deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities;
- varicose pathology of the legs;
- congenital pathologies of vascular structure;
- performing coronary artery bypass surgery.
Venography of the brain is often performed without the use of contrast agents. This is due to the fact that computer and magnetic resonance tomographs produce a series of layer-by-layer images. They provide specialists with the necessary information without the use of special drugs.
Ultrasound or MRI, which is better?
Ultrasound and MRI of neck vessels are technologically different research methods. Each of them has strengths and weaknesses. To make an objective assessment, it is necessary to take into account the following parameters:
Method of obtaining an image.
Ultrasound diagnostics relies on the ability of waves to pass through tissue and be reflected at a certain speed. Vascular MRI analyzes the burst of hydrogen atoms in tissue cells caused by an increase in magnetic field voltage.
Device capabilities.
Ultrasound research techniques are suitable for express diagnostics and preliminary diagnosis. MRI allows you to expand the clinical picture of vascular pathology - a violation of the structure of the walls of blood vessels or soft tissues that can provoke a violation of vascular conductivity.
Duration of the procedure.
An ultrasound scan takes a short period of time – 5 minutes. Magnetic resonance imaging can take up to 30 minutes on average.
Availability and cost of procedures.
Thanks to the current compulsory medical insurance program, patients can undergo an ultrasound scan free of charge by appointment in their clinic. MRI is an expensive diagnostic method, therefore it is a paid service. A certain number of social quotas are allocated for MRI diagnostics, but their number is hundreds of times less than the number of patients who need the procedure. Patients in inpatient departments can undergo MRI free of charge. For magnetic resonance imaging on an outpatient basis, you must obtain a referral to a regional diagnostic center or contact a specialized commercial medical institution. If we compare the cost of diagnostic procedures in commercial clinics, the price tag for MRI is 2 to 4 times higher than the price for ultrasound.
| Ultrasound | MRI of cerebral veins |
Venography of the brain - possible complications
The procedure “MRI venography of the brain” is completely safe and completely painless. The only inconvenience associated with this examination is the need to lie for a long time without moving. Since there are usually no side effects when using contrast agents, magnetic resonance analysis of the vascular system is recommended for people with allergies to iodine-containing substances. But, like any medical intervention, the examination requires the mandatory completion of a questionnaire in which existing diseases are indicated.
When performing venography of the head, the following are possible:
- the appearance of various sensations (tingling sensation, warmth, etc.) under the influence of radio frequencies and magnetic fields - they disappear immediately after the end of the procedure;
- discomfort from the specific sounds that the device makes - to muffle the noise before scanning, patients are offered headphones (in some clinics with music) or earplugs;
- panic attacks in people with a fear of small enclosed spaces - in such cases, sedatives can help.
A rehabilitation period is needed only for patients for whom the procedure was performed in a hospital under anesthesia. Due to the absence of X-ray radiation, repeated MRI examinations are possible without quantitative restrictions.
Cerebral vessels on an MRI scan
To kid
Magnetic resonance imaging of the vascular bed of the neck has no age restrictions. If necessary, the study is carried out on babies from the first days of life.
To obtain high-quality projections, you must remain still during scanning. This is an impossible task for small children, so the study is carried out using superficial anesthesia. Commercial MRI centers are not always licensed to carry out such activities. In such medical institutions, the lower age limit is set at seven years. At this age, children are more patient, assiduous and able to follow the instructions of a specialist.
Children of primary school age are often frightened by unpleasant sounds inside the tomograph, the absence of parents nearby and limited space in the tunnel. To solve this problem, the doctor may refer you for examination in an open tomograph. Low noise levels, more comfortable conditions and the opportunity for parents to be nearby during the scan help the child to endure the procedure calmly.
Children have the same indications and/or contraindications for MRI as adult patients.
Photo
| Arteriovenous malformation |
| Venous thrombosis |
| Venous sinus thrombosis |
| Thrombosis of the vein of Galen |
| Cerebral vein thrombosis |
Price
On our website, many clinics list prices for MRI, including MRI of cerebral veins.
To see prices, you need to go to the list of clinics in your city. To do this, select your city on the “Addresses” page.
On the page for the list of city clinics, in the form for selecting a clinic based on parameters, in the “Research area” field, select “MRI of cerebral veins.”
The list will be filtered and the clinics will be sorted by ascending price, which will allow you to find out where to get an MRI of the veins of the brain cheaper.
| List of clinics filtered by MRI of the brain using the example of the city of Moscow |
If prices are not indicated on the website, then you need to call all the clinics and find the best price for you yourself.
When talking with the operator, be sure to ask if there are any promotions or discounts. For example, some 24-hour clinics offer discounts on MRIs at night.
You can get an MRI with compulsory medical insurance or VHI insurance. To do this, you need to find out which clinic does MRI under insurance, using the information on the website or calling the clinics yourself if there is no information on the website. In the form for selecting a clinic by parameters, there is a field “MRI under insurance”. Next, you need to find out the list of documents that the clinic operator will tell you, collect them and you will be able to undergo an MRI with insurance, which will allow you to save a lot.
Prescriptions and contraindications
An MRI of the brain is done if there are internal injuries or external injuries to the skull (fractures, internal deformities). Vessels must be examined in case of high intracranial pressure, severe vegetative vascular dystonia. An MRI technique is required after a mini-stroke, to determine the presence of blood clots, or with constant causeless pain in the head. Tomography is indicated for:
- suspected neoplasms in the tissues of the brain or the organ itself;
- examination of nerve tissue;
- to assess the extent of brain disease after heart attacks and strokes;
- examination for the likelihood of various forms of vascular anomalies;
- suspected multiple sclerosis or cerebral hemorrhage;
- monitoring the patient after surgery to identify complications or abnormalities.
People with congenital heart defects and vasculitis must be examined. MRI of the brain is done for athletes and people with bad habits, as they increase the risk of diseases of the vascular system.
On a note!
The research method is used to monitor the course of pathologies and determine the effectiveness of treatment.
For children, MRI examinations are performed, in addition to the main indications, for fainting, muscle cramps, partial loss of hearing or vision. If children are lagging behind in development, there is a sharp change in mood. The MRI technique is indicated for epilepsy.
Contraindications
Contraindications for the study include insulin pumps, all implants and stimulators. MRI is not recommended for patients with heart failure, claustrophobia, or an existing allergy to the contrast agent. It is not advisable to perform diagnostics on people who have tattoos with metal particles on their bodies. The MRI technique is not used when hemostatic clips are in the brain. Relative research prohibitions include pregnancy.
Reviews
On our website, people leave reviews for clinics about their MRI experience.
To read patient reviews, you need to go to the list of clinics in your city. To do this, select your city on the “Addresses” page.
The list in the block of each clinic will show a button to go to the list of reviews, if there are reviews, or a button to go to write a review, if there are no reviews yet.
| This is what review buttons look like, using the example of the city of Moscow |
You can also leave a review about your MRI experience so that other people can choose the most suitable clinic.
To leave a review, you need to click the “Your review” button and you will be taken to the review writing form. Or if there are already reviews, then you need to go to the end of the list of reviews and there will be a form for writing a review.
To open the review writing form, click the “Leave a review” button.
Fill out the form and send it for moderation.