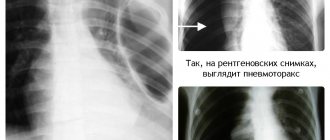
Enlarged heart on fluorography: reasons
An enlarged heart can be diagnosed at any age. An enlarged organ on fluorography does not always mean the presence of heart disease. In healthy people, this size is individual. This depends on many factors: from the structure of the chest to the power of physical activity. For a person with a large build and short stature, an enlarged heart to the left will be the norm, as well as its vertical expansion for a thin person with tall stature.
Department of Propaedeutics of Internal Diseases and Therapy Cardiac Percussion
Department of Propaedeutics of Internal Medicine and Therapy Cardiac Percussion Lecture for 2nd year students in specialty 060101 – “General Medicine” Associate Professor Balashova N. A.
Lecture plan • Rules of percussion • Boundaries of relative cardiac dullness • Boundaries of absolute cardiac dullness • Determination of vascular bundle, configuration, diameter heart • Reasons for changes in the boundaries of the heart
Purposes of cardiac percussion: Determination of the size of the heart, its configuration, the size of the vascular bundle. The principle of percussion is based on the difference between the environments of the lung tissue and the heart.
There are: relative cardiac dullness - an area corresponding to the true size of the heart covered by the lungs (dull percussion sound) absolute cardiac dullness - an area of the heart adjacent to the chest, not covered by the lungs (an absolutely dull sound is heard)
Rules of percussion • The patient’s position should be comfortable: for seriously ill patients lying down, in other cases standing with arms down along the body • The doctor’s position should be comfortable for examining the patient; as a rule, finger-finger percussion is used • The finger-pessimeter is pressed tightly to the chest, located parallel to the expected border. They go from the lungs to the heart, the border is marked in relation to a clear percussion sound
Rules of percussion • When determining the boundaries of relative dullness of the heart, quiet percussion is used, when determining the boundaries of absolute dullness - the quietest • Percussion is carried out in the following order: right, left, upper borders of the ATC, configuration of the heart, boundaries of the ATC, dimensions of the vascular bundle
Boundaries of the OST • The boundaries of relative cardiac dullness are the true boundaries of the heart. • Covered by the lungs • Upon percussion, a dull percussion sound is determined
Boundaries of relative cardiac dullness • Right • Left • Upper
Right border of the OST • Determine the lower border of the right lung along the midclavicular line • Rise 1 rib higher (IV intercostal space) • Expand the plessimeter finger parallel to the sternum (the desired border) • Percuss along the intercostal space until the percussion sound becomes dull • Normally, the right border of the relative dullness of the heart is located along the right edge of the sternum or 1 cm outward from it. • Formed by the right atrium (RA)
Left border of the OST • Determine the apical impulse • Percussion in the 5th intercostal space, moving from the anterior axillary line towards the heart until the percussion sound becomes dull. • The left border is located 1 -1.5 cm medially from the left midclavicular line and coincides with the apical impulse. • Formed by the left ventricle (LV)
• The upper border of the OST is percussed from top to bottom, 1 cm outward from the left sternal line until the percussion sound becomes dull. • The upper border is normally located at the level of the third rib. • Formed by the left atrial appendage
• Determination of the heart configuration. • To determine the configuration of the heart, the boundaries of the right and left contours of the relative dullness of the heart are additionally identified, percussing on the right in the II, IV intercostal spaces, and on the left in the II, IV, V intercostal spaces
The right contour of the heart is formed by • II m/r – aorta • III m/r – superior vena cava • IV m/r – right atrium
The left contour of the heart is formed by • • II m/r – trunk of the pulmonary artery III m/r – left atrial appendage IV m/r – left ventricle
Normal configuration of the heart • Observed when the cardiac waist is represented by an obtuse angle 1 - contours of relative dullness; 2 - absolute stupidity; 3 - waist of the heart. • Cardiac waist is the angle between the vascular bundle and the left ventricle
Mitral configuration of the heart The mitral configuration is characterized by a flattening of the waist of the heart due to dilatation of the left atrium (with mitral heart defects)
Aortic configuration of the heart With an aortic configuration of the heart, an emphasized waist of the heart is observed due to dilatation of the left ventricle (with aortic heart defects)
Boundaries of the AST • The area of the heart not covered by the lungs • Upon percussion above it, a dull percussion sound is determined
Determination of the boundaries of absolute dullness of the heart • Percussion is performed from the previously found boundaries of relative dullness of the heart towards the area of absolute dullness. • The right, left and upper boundaries are marked along the edge of the pessimeter finger facing the louder percussion sound.
NB! • The right border of absolute cardiac dullness is normally located along the left edge of the sternum. • Left 1 – 2 cm medially from the left border of relative dullness of the heart, • Upper at the level of the IV rib. • The boundaries of the AST are formed by the right ventricle
Determination of the boundaries of the vascular bundle. 1 – midclavicular line. • Percussion is performed with quiet percussion, moving a vertically positioned finger plessimeter along the 2nd intercostal space on the right and left towards the sternum. • Formed by the aorta, superior vena cava, pulmonary artery • Normally, the boundaries of the vascular bundle coincide with the right and left edges of the sternum, its width does not exceed 5 – 6 cm.
Measuring the diameter of the heart • To measure the diameter of the heart, determine the distance from the right and left borders of the relative dullness of the heart to the anterior midline Determination of the diameter of the heart: 1 – right border of the heart; 2 – left border of the heart; 3 – anterior midline. • Normally, they are 3-4 cm and 8-9 cm, respectively, and the diameter of the heart is 11-13 cm.
Interpretation of cardiac percussion data Changes in the boundaries of the heart 1. Mitral stenosis; 2. Pulmonary heart.
Tricuspid valve insufficiency Stenosis of the right atrioventricular orifice (a very rare disease) Displacement of the mediastinum to the right to the left Dilatation of the right ventricle Dilatation of the right atrium Displacement of the right border of the ostium Diseases and syndromes Dilatation of the right ventricle and right atrium. Right Reasons 1.
Left-sided hydrothorax; 2. Left-sided pneumothorax; 3. Right-sided obstructive atelectasis; “Dangling” (“drip”) heart Asthenic body type Displacement of the mediastinum to the left 1. Left-sided obstructive atelectasis; 2. Right-sided hydrothorax or
Interpretation of cardiac percussion data (continued) Shift of the left border of the OST to the left Dilatation of the left ventricle 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Aortic insufficiency; Mitral insufficiency Aortic stenosis (stage of decompensation); Arterial hypertension; Acute myocardial injury; Chronic left ventricular heart failure (myogenic dilatation) Displacement of the mediastinum to the left “Recumbent” heart To the right 1. 2. 3.
High position of the diaphragm (ascites, flatulence, obesity) Shift of the mediastinum to the right 1. 2. Right-sided hydrothorax; Right-sided pneumothorax; Left-sided obstructive atelectasis; Right-sided obstructive atelectasis; Left-sided hydrothorax or pneumothorax (the left border is often not detected)
Interpretation of cardiac percussion data (continued) Displacement of the upper border of the OST Heart configuration 1. 2. Mitral stenosis; Mitral insufficiency; Mitral Dilatation of the left 1. atrium and smoothing 2.
waist heart Mitral stenosis; Mitral insufficiency; Dilatation of the left ventricle and emphasized waist of the heart 1. 2. Aortic insufficiency; Aortic stenosis (in the stage of decompensation); Right Dilatation or aneurysm of the ascending aorta 1. 2.
Arterial hypertension; Atherosclerosis of the aorta; To the left Dilation of the pulmonary artery High pressure in the pulmonary artery Dilation of the descending aorta 1. 2. Arterial hypertension; Atherosclerosis of the aorta; Expansion, lengthening and reversal of the aortic arch 1. 2.
Arterial hypertension; Atherosclerosis of the aorta; Up Aortic Dilatation of the vascular bundle Right and left Dilatation of the left atrium
Interpretation of cardiac percussion data (end) Dilatation of the right ventricle 1. 2. 3. Mitral stenosis; Pulmonary heart; Tricuspid valve insufficiency; Extracardiac causes Extension of absolute cardiac dullness 1. 2.
High aperture; Wrinkling of the pulmonary edges; Tumor of the posterior mediastinum, bringing the heart closer to the anterior chest wall; 3. Reduction of absolute dullness of the heart Extracardiac causes 1. 2. 3.
Emphysema; Left- or right-sided pneumothorax; Low position of the diaphragm (“hanging” heart in patients with asthenic physique)
Thank you for your attention!
Source: //present5.com/kafedra-propedevtiki-vnutrennix-boleznej-i-terapii-perkussiya-serdca/
Enlargement of the heart to the left
Hypertrophy of the ventricular walls means an increase in the heart muscle. The following reasons can lead to pathology:
- vices;
- diabetes mellitus and high blood pressure;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- pregnancy period;
- anemia;
- alcohol consumption;
- renal failure;
- irregular training with enlarged heart muscle in athletes;
- rheumatism;
- myocardial infarction.
People who are constantly forced to do hard work, these include professional athletes, their main vital organ is forced to work more actively. Regular increased exercise leads to the proliferation of muscle cells. Fluorography will definitely show that their heart is enlarged to the left in the picture. Reducing the load to moderate will bring the enlarged organ back to normal. If the amount and strength of the load is not changed for a long time, complications and death may occur.
Changes begin to appear when the load increases regularly. The pathology has no clear signs, but it can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath and fatigue;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- feeling of heaviness on the right side under the ribs;
- headache and tinnitus;
- high blood pressure;
- cough for no reason.
Enlargement of the organ to the left is more common, which may indicate diseases such as hypertension, stagnation of blood in the systemic circulation, and various defects. This condition is sometimes called "bull's heart."
What does an enlarged heart mean on the left side of fluorography?
X-ray diagnostic methods make it possible to identify various pathologies of internal organs. So, it is possible to notice that the heart is enlarged to the left in the fluorography image. Experts advise not to ignore this symptom, but to contact a cardiologist who could correctly identify the disease and prescribe treatment.
What does expansion of the heart to the left mean?
The average weight of this cone-shaped hollow muscular organ in an adult man is approximately 300 grams, in a woman - 250 grams. Its dimensional characteristics are comparable to the size of a clenched fist: longitudinal size - 12 centimeters, transverse - 8-9 centimeters, anteroposterior - 6 centimeters.
An expansion or increase in the volume of an organ is called cardiomegaly. If it is expanded on the left, this is a symptom of transformation of the left ventricle, which means hypertrophy of the heart muscle. This sign means that it has become larger in diameter.
As a rule, the increase in volume occurs on the left side. This may be a manifestation of hypertension (hypertension), blood stagnation in the systemic circulation, and other pathologies. Sometimes this phenomenon is called “bull’s heart”.
Causes of pathology in adults
Provoking factors for cardiomegaly can be:
- diabetes;
- hypertension;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- the onset of pregnancy;
- anemia (anemia) – a decrease in the level of hemoglobin protein in the blood, which is responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood;
- renal failure;
- alcohol abuse;
- rheumatism – inflammation of the connective tissue structures of the cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems;
- ischemia – impaired blood supply to the myocardium;
- Myocardial infarction – damage to the heart muscle. It develops with an acute lack of oxygen. Occurs due to blockage of a blood artery by a blood clot. Subsequently, the damaged areas die off. The process of their death is called necrosis;
- athletes with enlarged heart muscle undergoing irregular training;
- genetic predisposition;
- cardiomyopathy - thickening of the walls of the ventricles, stretching of the cavities of the heart.
The described pathology does not manifest itself in any way at first, but over time, with increasing loads, the following symptoms may appear:
- a condition characterized by shortness of breath, fatigue;
- swelling in the lower extremities;
- the appearance of a feeling of heaviness on the right under the ribs;
- cephalalgia, tinnitus;
- causeless cough.
Enlarged heart in children
An increased volume of an organ in children can be a congenital pathology, which will subsequently cause serious health problems. It is important to identify such deviations from the norm immediately - from the first days of a child’s life to six months.
Cardiomegaly in children can occur due to the presence of an inflammatory process of connective tissue in the body - rheumatism. This disease, in turn, can appear as a complication after a sore throat, exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, or with some types of caries. It is acquired and develops regardless of the child’s age.
Signs of the described pathology in children may be:
- weakness;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the sternum area;
- fever 1-2 weeks after recovery from tonsillitis;
- sweating;
- increased fatigue;
- pain in muscles, joints.
The reasons for the appearance of signs of an enlarged heart on a fluorography image may also be:
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy - manifests itself in thickening of the wall of the ventricle, most often the septum between the ventricles;
- myocarditis is an inflammatory process in the heart muscle. It can be of viral, fungal, bacteriological origin, or may appear due to autoimmune problems or improper use of medications;
- endocarditis – inflammation of the endocardium (inner lining);
- pericarditis is an inflammatory process in the serous membrane.
The last two pathologies in minor patients are quite rare.
If the described symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor; it is highly undesirable to leave this situation without proper attention.
Is it possible to detect on fluorography that the heart is enlarged? How does this manifest itself?
An enlarged heart is almost always noticeable in a fluorography image. The condition manifests itself in the fact that the shadow of this internal organ increases in size and changes shape. It is also visualized that its boundaries have been increased.
Is it possible to make an accurate diagnosis based on a fluorographic image?
An enlarged heart in a fluorography image can only indicate the presence of diseases or pathologies of this internal organ, but this is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis.
The diagnosis is made by a combination of signs, which include cardiomegaly. Moreover, treatment is prescribed not for the symptom itself, but for the disease that caused it.
After proper therapy, the size of the organ returns to its previous parameters.
What additional diagnostic measures are taken?
To make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment, the following types of examinations are required.
- X-ray of the sternum area. You can notice an expanded shadow of the heart group and determine congestion in the circulatory system.
- Electrocardiography (ECG).
- Echocardiography (EchoCG). Allows you to determine the parameters of the heart muscle, the size of the chambers, identify necrosis (death of cells/tissue areas) or ischemic disease (impaired blood supply to the myocardium due to damage to the arteries).
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the heart muscle.
- Computed tomography (CT).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Immunological and biochemical blood tests. They determine the levels of hemoglobin, bilirubin, protein, hormones and urea.
The doctor will be able to prescribe adequate treatment only after making a diagnosis. And to determine the disease, the doctor carefully examines not only the data of hardware examinations, but also the results of clinical tests, as well as the clinical picture.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
Such drugs dilate blood vessels and lower blood pressure, reducing the workload on the cardiovascular system. The drugs have the following names: Enalapril, Captopril, Lisinopril. A side effect is often a dry cough.
Angiotensin receptor blockers
Being analogous to ACE inhibitors in terms of pharmacological effect, these drugs do not cause a dry cough as a side effect.
Beta blockers
The use of beta blockers helps reduce heart rate and normalize blood pressure. However, such drugs are only auxiliary in treatment.
Diuretics
Diuretics (diuretics) can improve blood flow to the heart and help lower blood pressure. The names of these drugs: Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide.
It is not recommended to resort to self-medication; only a doctor can make a diagnosis and determine an effective drug therapy regimen.
Surgery may also be required. It consists of restoring or completely replacing the arterial valve. In severe cases, a whole organ transplant is necessary.
Prevention
Prevention of cardiomegaly can be a change in lifestyle. One of the main factors in the occurrence of heart pathologies is obesity. It is recommended to maintain a normal body mass index. Losing weight if you are overweight, against the background of an already enlarged heart, helps stabilize the condition.
A special diet is recommended to prevent cardiovascular diseases. It is advisable to consume fish, soybean, flaxseed, corn or olive oil at least twice a week.
To strengthen the heart muscle, you need to eat cranberries, cabbage, viburnum, eggplants, peaches, dried apricots, apples, pomegranates, walnuts, melon. To normalize blood pressure, you need to avoid excessive consumption of salt and salt-containing foods.
In addition, it is advisable to reduce the consumption of alcoholic beverages or completely abandon them.
Although an increase in heart volume may be caused by intense physical activity, in moderate doses, sports activities can only benefit the patient. Thus, yoga, Pilates, and walking will help strengthen the heart.
If hypertrophy has already been identified, it is better to consult a physiotherapist. He will help you choose a set of therapeutic exercises, designed for about half an hour. Regularly performing this set of physical activities will reduce the volume of the heart muscle.
Eight hours of sleep and avoidance of excessive physical and emotional stress are helpful. In addition, regular walks outside are recommended.
Thus, a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition will help minimize the risk of complications with an enlarged left ventricle.
Risks and possible complications
There are various prognoses that are directly dependent on the diagnosis made when the heart expands to the left.
- For arterial hypertension (hypertension, high blood pressure), the prognosis is considered favorable. After taking the medications prescribed by the doctor, the patient’s condition returns to normal, the heart returns to its normal parameters and does not enlarge again.
- If a ventricular septal defect is observed, surgery is necessary. Otherwise, the pathology will lead to aortic valve insufficiency, serious rhythm disturbances will occur, and left ventricular dysfunction is possible. All of the above can cause death. After the operation, the patient’s condition returns to normal, and he no longer faces such heart problems.
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (stretching of the heart cavities) is characterized by a poor prognosis. Full recovery becomes possible only after a heart transplant.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (thickening of the walls of the ventricles) - the prognosis is relatively unfavorable, the disease may be asymptomatic. Without proper and timely treatment, there is a risk of death. When undergoing treatment procedures, the likelihood of death becomes lower.
- Metabolic cardiomyopathy is a non-inflammatory myocardial lesion of various etiologies. It can cause insufficiency of cardiac functions, in particular contractile function. The prognosis is favorable. If you establish proper metabolism, complete recovery will occur.
- Myocarditis. Characterized by a favorable prognosis. Complete recovery is possible within 1-2 months in nine out of ten cases, after 1 year in the remaining patients.
- Aortic stenosis (the mouth of the aorta becomes narrow, as a result of which blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta is impaired) - without treatment, the life expectancy will be from 1 to 4 years from the time the disease is detected. With proper treatment, the prognosis is relatively favorable.
- Exudative pericarditis (inflammation of the serous membrane of the heart) has a favorable prognosis, all patients recover.
Source: https://iDiagnost.ru/issledovaniya/fluorografiya/chto-znachit-rashirnnoe-serdtse-v-levoj-chasti-flyuorografii
Fluorography
To avoid complications, it is necessary to undergo fluorography regularly (2 times a year). The specialist will pay attention to the shadow in the space between the lungs. Expansion occurs due to an increase in the main organ in one direction or another. An enlarged heart on fluorography is not a diagnosis. It is impossible to assess the condition of an organ based on the results of a fluorography image. The image description may contain the following terms: “mediastinal expansion to the left,” “cardiac expansion to the left,” or simply “expansion.” This will be one of the auxiliary studies and does not play a major role for the cardiologist in determining the exact diagnosis.
Fluorography of the heart has a certain degree of error, but with regular examination it is possible to notice any deviations in time. In this case, it is recommended to consult a cardiologist as soon as possible.
Mechanism of development of cardiomegaly
The pathogenesis of cardiomegaly depends on the cause. Most often, left ventricular hypertrophy occurs in people with metabolic syndrome, coronary artery disease, or arterial hypertension. When oxygen supply is low, the heart muscle contracts more strongly than usual and gradually increases in size. Roughly the same thing happens with hypertension. In this case, the heart does not have time to pump blood quickly enough due to its high pressure, so the organ requires more effort. The mechanism of development of cardiomegaly differs in stenosis and valve insufficiency. In the case of these pathologies, the blood does not completely flow into the adjacent chamber or vessel (aorta, pulmonary artery) and causes stretching of one of the parts of the heart. With long-standing defects, both the ventricle and the atrium enlarge. In some cases, hypertrophy of the entire organ may occur. Right ventricular failure occurs with pulmonary pathologies and liver diseases.
What does expansion of the heart to the left mean?
Enlargement of the heart to the left and an increase in its mass are called cardiomegaly in medicine. This may concern both the entire organ and one of the chambers. To recognize the disease, it is necessary to carry out a number of diagnostic procedures. The detection of an enlarged heart on fluorography does not mean that the organ is susceptible to disease. This is due to the individuality of the human body.
The article will touch on the causes of heart enlargement, which affects the occurrence of the disease, as well as how cardiopulmonary resuscitation is performed and treatment methods.
For additional information, you can directly contact the portal specialists.
Consultations are conducted free of charge online.
Symptoms
Some people have no signs of an enlarged heart. Others, on the contrary, complain of the following symptoms:
- changes in heart rhythm (often arrhythmia);
- shortness of breath unrelated to physical activity;
- swelling of the limbs;
- chest pain;
- increased fatigue;
- noise in ears;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- fainting (rare);
- cough (with pulmonary pathology);
- sleep disturbance.
Clinical manifestations are more pronounced with left ventricular hypertrophy.
Features of the disease
Often, the mechanism for the development of an increase in cardiac volume is associated with ventricular dysfunction. In this case, either one or both at the same time can increase. The enlargement also affects the atria. Factors influencing changes in the size of the ventricles include a decrease in their plasticity and the accumulation of decay products in the organ after metabolism.
Cardiomegaly is often diagnosed in people involved in professional sports. It is possible to identify the true cause of the expansion of the shadow boundaries only by instrumental examination. Enlargement of the right side of the heart is considered a false disease, which often occurs against the background of systematic physical activity. This is also diagnosed during pregnancy.
What are the features and causes of heart enlargement?
When the heart becomes enlarged, or otherwise referred to as cardiomegaly, there is an enlargement of one or all four chambers of the heart - the right ventricle and right atrium, the left ventricle and the left atrium. Depending on the severity of organ hypertrophy, the degree of damage and loss of functional features are distinguished, which can lead to the development of various complications.
Cardiomegaly or enlarged heart?
Every year, hundreds of thousands of citizens die from cardiovascular pathologies around the world. In most cases, the reason for this is untimely consultation with a doctor and deterioration of cardiac function.
Enlargement of the organ is associated with the development of ventricular hypertrophy, accumulation of metabolic products and neoplastic processes. Cardiomegaly often occurs in healthy people, this includes athletes and pregnant women.
The volume of the heart varies within different limits for each person. If we talk about gender differences, then in men this organ is larger than in women. So for the age category from 20 to 30 years, the approximate heart volume will be the following values:
- women – 580 cm3;
- men - 760 cm3.
This figure also depends on body weight. A diagnosis of cardiomegaly should be made only after a thorough examination, because in some cases a slightly enlarged heart is the norm, which is strictly individual for each person.
Dilatation of the right or left ventricle: causes
Enlargement of the walls of the right or left ventricle is called hypertrophy. In this case, the functioning of the myocardium is disrupted and, as a result, their functional activity worsens. Depending on the location of the depletion of the heart muscle, different etiologies are distinguished.
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Enlargement of the walls of the right ventricle is most often observed in children with congenital defects of intrauterine development. Also, one of the main reasons is associated with an increase in pressure in the pulmonary circulation and the discharge of blood into the right ventricle. In this case, the load on the right ventricle increases.
In adults, the cause of right ventricular hypertrophy is often diseases that interfere with normal breathing. These include the following pathologies:
- rachiocampsis;
- pulmonary vascular diseases (compression, embolism, thrombosis, etc.);
- bronchial asthma;
- tuberculosis;
- bronchiectasis;
- Chronical bronchitis;
- polio, etc.
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Left ventricular hypertrophy is dangerous due to sudden cardiac arrest, causing myocardial infarction and death. Thickening of the walls of the left ventricle can result from the following cardiac pathologies:
- developing atherosclerosis of the aorta;
- hypertonic disease;
- congenital or acquired heart defects;
- obesity.
To prevent the development of such serious diseases, you need to follow preventive measures, which means sticking to a healthy lifestyle and seeing a doctor in order to diagnose all disorders in a timely manner.
Causes of cardiomegaly
Most often, an enlarged heart in diameter is diagnosed in adults. Predisposing factors that contribute to the expansion of the boundaries of the shadow of the ventricles and atria are quite diverse, in most cases this is associated with cardiovascular pathologies. So, the etiology of the appearance of cardiomegaly includes the following reasons:
- excessive exercise;
- pregnancy;
- idiopathic cardiomyopathy;
- heart defects;
- anemia in severe forms;
- infectious diseases where the target organ is the heart muscle;
- complications after viral diseases;
- myocardial ischemia or infarction;
- inflammatory processes in the heart;
- severe stress loads;
- excessive alcohol consumption, drug addiction, smoking;
- kidney disease and renal failure;
- rheumatic carditis and endocarditis;
- hypertension, etc.
If an enlargement of the heart muscle is detected, the doctor prescribes the necessary diagnostics and treatment.
Clinical manifestations
When the heart expands across the diameter or in other parts, the patient may experience unpleasant symptoms. This includes the following clinical severity:
- increased fatigue;
- shortness of breath at rest or with minor physical exertion;
- increased blood pressure;
- the appearance of pain in the heart area;
- formation of edema in the lower extremities;
- headaches and dizziness;
- short-term loss of consciousness.
Other signs characteristic of a particular cardiac pathology, if present, may also be added.
Treatment
During treatment, it is important to identify the focus, which means to determine the disease or disorder that triggered the occurrence of heart enlargement. As soon as this is diagnosed, treatment is prescribed aimed at eliminating this pathology.
As an auxiliary therapy, medications are prescribed, the purpose of which is to reduce the obstacle to normal blood outflow while simultaneously unloading the increased work of the ventricles. This will prevent the risk of complications such as myocardial infarction, angina, shortness of breath and arrhythmia.
If therapeutic actions are ineffective, the doctor may prescribe surgery to improve blood flow. However, they resort to it only in extreme cases.
General recommendations
In addition to treatment recommendations, it is imperative to follow preventive measures. For heart problems, it is very useful to follow these tips:
- You should avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, which have a toxic effect on the myocardium (heart muscle).
- In order to prevent the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels, foods high in cholesterol should be excluded from the daily diet. It is advisable to consume fish, olive, flaxseed, corn and soybean oil at least 2 times a week.
- To strengthen and maintain the heart muscle in normal working condition, it is useful to include viburnum, cranberries, cabbage, eggplants, peaches, dried apricots, apples, pomegranates, walnuts, melons, etc. in the daily diet.
- It is necessary to reduce salt intake to at least 2 grams. per day, especially for patients with increased swelling.
- If obesity is recorded, it is necessary to create a proper balanced diet aimed at eliminating extra pounds.
- Sleep at least 8 hours, do not become physically and emotionally overtired.
- Walk outdoors more often.
Enlargement of the heart is not a diagnosis, but only a temporary condition of the heart muscle. With correct and timely actions, you can get rid of this disorder and significantly alleviate your condition.
(2 5,00 of 5) Loading...
Source: https://SosudInfo.com/heart/prichiny-rashirniya-serdtsa.html
Conditions for the development of the disease
The condition when the heart is enlarged in diameter is most often diagnosed in adults. Factors that increase the boundaries of the shadow of the atria and ventricles are varied and are often associated with pathology of the heart and blood vessels.
Common reasons include:
- high physical activity;
- pregnancy;
- Chagas syndrome;
- genetic predisposition;
- high pressure in the aorta and blood vessels;
- severe form of vascular anemia;
- various heart diseases;
- kidney dysfunction;
- ischemia, heart attack;
- the heart is enlarged to the left due to lung diseases.
Of course, there are factors that may not always lead to expansion. For example, viral infections, parasitic diseases, immune system diseases, and more.
Signs of growth of the organ shadow within the ventricles and atria are similar to other diseases of the cardiovascular system.
The following symptoms are observed:
- chest pain;
- dyspnea;
- swelling of the legs and arms;
- high fatigue;
- fainting;
- pale skin.
You can find out that the heart has expanded its boundaries during examination using ultrasound, radiography, echocardiography or MRI. For example, Figure No. 1 is presented in the form of a fluorography image. The shadow marked in the image indicates the expansion of the organ's shadow.
Figure No. 2 allows you to visually compare the normal state of the atria and ventricles, and the moment when the organ expanded its boundaries.
The course of treatment with medications depends on the severity of the disease:
- Diuretic medications reduce pressure in blood vessels.
- To avoid the risk of blood clots in the vessels, anticoagulants are prescribed.
- To restore the functioning of the cardiac system, angiotensin prescription blockers are prescribed. The drugs Warfarin and Heparin are effective in treating atrial and ventricular dysfunction.
- Medications of the beta blocker group are designed to normalize the pulse.
The expansion of the organ's shadow leads to various consequences - blood clots, cardiac arrest, rhythm disturbances, and death.
The greatest danger is the enlargement of the boundaries of the ventricle of the left chamber. This pathology most often leads to death.
If conservative treatment methods have no effect and the patient’s condition worsens, then doctors advise surgery. The type of intervention is considered on an individual basis. For example, they may prescribe inserting a defibrillator under the skin to adjust the rhythm.
Symptoms of the disease
Manifestations of cardiomegaly are purely individual. In some cases, symptoms do not occur at all, and a person learns about the expansion of the organ’s boundaries by chance, for example, during fluorography or a doctor’s examination. If the pathology makes itself felt, its manifestations are not much different from the symptoms of diseases of the cardiovascular system. But there are cases when the pathological process develops so rapidly that a “bull’s heart” quickly forms.
Signs include:
- Pain behind the sternum.
- Dizziness, loss of consciousness for no reason.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Shortness of breath with slight exertion.
- Arrhythmia (change in rhythm).
- The appearance of edema (especially in the lower extremities in the evening).
- Cough not associated with respiratory diseases.
Expanding the size of such an important organ of the cardiovascular system entails very dangerous consequences. If the heart rhythm is disturbed, there is a risk of cardiac arrest. The occurrence of noise should be monitored by a doctor, because it indicates a change in the structure of the valves. An enlarged heart affects the quality of the entire cardiovascular system. Over time, there will come a point when the organ cannot pump the required amount of blood, so the risk of developing heart failure increases over the years. If the problem is ignored, then you can get a serious complication - “bull heart” (an increase in the size of the organ to critical).
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
In medicine there is such a concept as “the border between life and death,” which means that death can occur at the moment between heartbeats. During this period, irreversible consequences can occur throughout the body if help is not provided.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, carried out in a timely manner and according to the rules, allows you to neutralize the pathological process. The sequence of actions is distinguished by time:
- Two minutes - resuscitation without preparation with a defibrillator.
- From 2 to 10 minutes – closed massage and electric charge.
- More than 10 minutes - defibrillator and all means of cardiac stimulation.
Risk factors
You may be at higher risk of developing an enlarged heart if you have one of the following risk factors:
- High blood pressure. Measuring your blood pressure above 140/90 millimeters of mercury puts you at increased risk of developing an enlarged heart.
- Family history of enlarged hearts or cardiomyopathy. If an immediate family member, such as a parent or sibling, has an enlarged heart, you may be more susceptible to developing this condition.
- Blocked arteries in your heart (coronary artery disease). In this condition, fatty plaques in the arteries of the heart obstruct blood flow through the heart vessels, which can lead to a heart attack. When part of the heart muscle dies, your heart must pump harder to get enough blood for the rest of your body, causing it to enlarge.
- Congenital heart defect. If you are born with a condition that affects the structure of your heart, you may be at risk of developing an enlarged heart.
- Heart valve disease. The heart has four valves—aortic, mitral, pulmonary, and tricuspid—that open and are close to direct blood flow through your heart. Conditions that can damage the valves can cause your heart rate to increase.
- Heart attack. Having a heart attack increases your risk of developing an enlarged heart.
Fluorography of the heart shadow extended to the left
How can you determine which chamber of the heart is dilated?
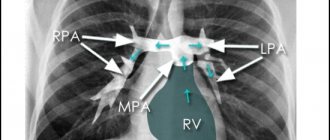
- Dilatation of the ventricles. In this case, a displacement of the lower part of the heart contour to the left and posteriorly is usually observed. RV dilatation can be distinguished from LV dilatation by assessing the condition of their outflow tracts. When the pancreas is dilated, dilation of the pulmonary arteries is often observed, while the aorta appears reduced. LV enlargement is usually accompanied by enlargement of the aorta, while the pulmonary arteries remain normal. — LA expansion. The image taken in the frontal projection shows a bulging of the arch between the left pulmonary artery and the LV. In addition, a shadow of double density can be observed downward from carina tracheae. In the lateral projection, LA expansion is accompanied by a posterior displacement of the descending left lower lobe bronchus. — The expansion of the RA is accompanied by a displacement of the lower part of the right contour of the heart to the right.
Which of the most common pathological conditions accompanied by chest pain can be detected using radiography?
— Aortic dissection — Pneumonia — Pneumothorax — Subcutaneous emphysema — PE — Pericarditis (if X-rays suggest the presence of a large amount of fluid in the pericardial cavity) — Esophageal rupture — Hiatal hernia
X-ray of the chest organs
should be performed in all patients complaining of chest pain, even if the most likely cause of the pain is myocardial ischemia.
What are the reasons for the widening of the mediastinal shadow on a chest x-ray?
There are many potential causes of mediastinal
. It can be observed with aortic dissection/rupture, as well as in the presence of a mediastinal hematoma that has developed as a result of chest trauma or improper placement of a central venous catheter. In obese patients, widening of the mediastinal shadow may be due to lipomatosis. Another reason for this phenomenon may be an oncological process, especially germ cell tumors, lymphomas and thymomas.
Finally, the mediastinum may appear dilated on radiographs
performed using a portable X-ray unit (compared to those made using a stationary unit in a standard anteroposterior projection).
Causes
In the case of physiological arguments that provoke an increase in heart volume, the growth of muscle fibers of the myocardial walls occurs due to an increase in the contractile force of the organ.
The result is a change in its size, and compaction affects not only muscle tissue, but also the structures of the chambers. If the progress of cardiomegaly leads to the spread of the process throughout all cardiac structures, the disease ends with extensive myocardial hypertrophy.
Causes of the congenital form
The birth of a baby with congenital heart pathology, recorded on an x-ray, is considered a very serious anomaly. About 35% of newborns die due to sclerosis of areas of the heart muscle, blockage of valves and organ chambers by blood clots.
Congenital syndrome is often diagnosed in the fetus at the stage of intrauterine development. The causes of heart problems are not only due to congenital abnormalities, but also due to the behavior and health status of the mother.
Among the main prerequisites for cardiomegaly is the reaction of the mother’s body to the following provoking moments:
- previous viral infection, taking medications contraindicated for pregnant women;
- exposure to adverse environmental factors (mainly radiation);
- the presence of congenital heart diseases (cardiomyopathy), genetic abnormalities;
- mother’s adherence to bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking, drugs);
- poor quality nutrition of the pregnant woman, as well as injury during pregnancy.
Signs of the congenital form of the disease appear from the first weeks of a child’s life. In a newborn, shortness of breath, tachycardia, blue discoloration of the skin are recorded, and cardiomegaly is accompanied by a number of other equally dangerous pathologies. The syndrome can appear suddenly after the birth of a child; hypertrophy can be triggered by birth trauma or a severe form of asphyxia during childbirth.
Reasons for the acquired form
Cardiomegaly, if not congenital, is often an independent problem that accompanies other heart diseases.
Initially, an enlargement of one of the chambers is detected on a chest x-ray; the severity of the process depends on the duration and severity of the disease that provoked it. Usually these are pathologies of organic or inorganic type, most of which occur with impaired cardiohemodynamics.
| Type of disease | Explanation |
| Hypertension | The increase in mass occurs gradually, creating problems with blood flow due to the resistance of the vessel walls. The pathology starts from the left ventricle, develops over a long period of time, and spreads through the left atrium. |
| Defects (congenital) | Valve defects are accompanied by additional stress on the heart. At first, cardiomegaly occurs in a latent form; as the underlying disease progresses, the syndrome develops quickly. |
| Ischemia | Ventricular hypertrophy is always present in extensive types of myocardial infarction. Frequent complications are ventricular (left) aneurysm, cardiosclerosis, heart failure (HF). |
| Cardio-sclerosis | The sclerotic process contributes to the enlargement and expansion of the left ventricle, asymmetric hypertrophy of the interchamber septum. Typical consequences are arrhythmia and heart failure. |
| Myocarditis | The disease of viral etiology occurs with moderate enlargement of the heart. Increased inflammation leads to intoxication of the muscle tissue of the organ, which is noticeable on the x-ray. |
| Cardiomyopathy | Taking into account the type of pathology, the symptoms of cardiomegaly cover all parts of the myocardium or its individual parts. The reason is mainly related to endocrine disorders (hormonal imbalance). |
| Aneurysms | After myocardial infarction, 15% of patients suffer from an aneurysm. Localization area: the anterior or posterior wall of the left ventricle, the apex of the heart. |
| Tumors | The type of compaction (benign or malignant), as well as the location of its localization, affects the severity of cardiomegaly. |
| Pericarditis | The cause of muscle tissue proliferation is effusion. The entry of fluid into the pericardial cavity impedes the functioning of the heart muscle, which leads to enlargement of the organ. |
| "Pulmonary" heart | The anomaly develops with increased blood pressure in the pulmonary circulation, which leads to dysfunction of the respiratory system. The right sections suffer not only from hypertrophy, but also from dilatation. |
Cardiomegaly is clearly visible on an x-ray only when the enlargement of the heart walls exceeds 2 mm. While listening to the heart rhythm, characteristic noises are recorded, and while palpating the cardiac zone, the doctor discovers a protrusion of an important organ.
In addition to the listed reasons, the formation of the syndrome is provoked by endocrine pathologies (thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus), their consequences are reflected in the condition of the myocardium. The result is thickening of the chamber walls, which over time leads to a diagnosis of cardiomegaly.
Causes of an enlarged heart
The weight of an average man’s heart is 332 grams, a woman’s – 253. It is considered normal if the weight of the organ varies within these limits.
As for the sizes, they are usually correlated with a person’s fist. For an organ to function normally, it is very important that all its parts (atria, ventricles) are normal, or more precisely, the thickness of their walls, length and width as a whole.
What to do if fluorography (x-ray, ultrasound) showed that the heart is enlarged and dilated?
How dangerous is it to literally have a big heart? And as a result of what can the organ become larger? Let's figure it out in order.
The most important reasons why the heart is larger than normal in a fluorography image include:
- great physical activity;
- diseases.
In people who engage in heavy physical labor every day, as well as in professional athletes, the heart also works harder: it is forced to beat more often and pump blood faster.
This leads to the fact that there are often more heart muscle cells and they grow. As a result, the weight of the organ and its size increase.
If physical activity in the future is moderate, an enlarged heart for this reason does not pose a health risk.
If a person subjects his body to excessive stress for a long time, then it is possible to develop a pathology such as a hypertrophied heart, which is already fraught with serious complications and even life-threatening.
The reason that the heart is enlarged in size can be diseases of the cardiovascular system (coronary diseases: for example, hypertension, coronary disease) and the heart itself (viral, inflammatory diseases), as well as heart defects.
So, if there is a defect and the organ is unable to function normally in order to properly supply the entire body with blood, the organ can enlarge.
Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment for cardiomegaly
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day.
The heart is one of the most important organs of the human body. One of the most dangerous symptoms of diseases that affect not only the cardiovascular system, but also other organs, is an enlarged heart (cardiomegaly). This can manifest itself in different ways: in one case, the patient has symptoms characteristic of diseases of the heart muscle, in another, he lives for a long time and does not even suspect the presence of pathology.
Coronary diseases
Hypertension is the most common cause of heart enlargement.
This is explained by the fact that due to increased blood pressure, the organ is forced to pump large volumes of it and work in enhanced mode.
This causes the heart muscles to enlarge and the organ itself to expand.
If a person has ischemia, the heart muscle cells constantly do not receive enough nutrients, as a result of which they degenerate, and connective tissue appears in their place.
The latter, unlike muscle tissue, is not capable of contraction; as a result, the organ cavities become deformed and increase in size.
What to do if an x-ray showed that the organ is enlarged, and the cause of this phenomenon is a disease of the cardiovascular system?
The answer to this question is simple and obvious - treat the root cause and return the organ to normal limits.
If a patient is diagnosed with hypertension, he is usually prescribed pharmaceuticals that lower blood pressure. The latter helps restore the normal size of the organ.
A patient with hypertension or coronary artery disease who has been diagnosed with an enlarged heart must take medications.
The fact is that despite the increased size of the organ, a large heart performs its most important function - pumping blood - much worse, which means that human organs and systems do not receive the nutrients they need - heart failure develops, and the whole body suffers.
Treatment of bovine heart with various methods
Only when doctors have established the reason why a particular person’s heart is enlarged do they decide how to treat it. Treatment of the disease is carried out with medications, physiotherapy and traditional methods. In severe cases, when it turns out to be ineffective, surgical intervention is prescribed, including a heart transplant. Cardiomegaly syndrome, which appears against the background of the underlying disease, requires its mandatory correction.
Medicines
When treating bovine heart disease using drugs, patients are prescribed drugs from the following groups according to clinical recommendations:
- diuretics (diuretics) – help remove excess water from the body and reduce blood pressure, which reduces the load on the heart muscle,
- ACE inhibitors - prescribed to lower blood pressure and increase the pumping function of the organ,
- angiotensin receptor blockers - prescribed to people who cannot take ACEs due to individual health conditions,
- digoxin – helps stabilize the pumping activity of the heart and reduce the patient’s need to stay in the hospital,
- anticoagulants – help reduce the risk of blood clots, which cause heart attacks, strokes and heart attacks,
- drugs to eliminate arrhythmia - help maintain the correct heart rhythm and reduce the risk of developing attacks of arrhythmia src=»https://osostavekrovi.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02d/kardiomegaliya-prichiny-simptomy-10.jpg» class=» aligncenter" width="540″ height="300″[/img]
Medicines are prescribed first. In the initial stage of the disease, they are usually the main method of therapy. For grades 2 and 3 of pathology, medications are combined with other types of treatment.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Treatment using physiotherapy is carried out during exacerbation and remission of the disease, but only with 1st degree of the disease. Contraindications for this method of exposure are grades 2 and 3 pathology, severe arrhythmia, heart and circulatory failure.
The most common procedures prescribed for bovine heart disease are:
- electrophoresis using drugs that relieve inflammation,
- ultra high frequency therapy,
- magnetotherapy,
Magnetotherapy
- inhalations using steroid hormonal drugs,
- decimeter therapy,
- hypoxic therapy,
- radon baths,
- carbon dioxide baths.
Specific procedures for each patient will be selected individually depending on their overall health.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is required when treatment of cardiomegaly with medications is ineffective or the patient’s condition is severe. Invasive methods can be used:
- installation of pacemakers for coordinated operation of both ventricles of the heart,
- ICD stimulator - required to control the heart rhythm and, if it is disturbed, gives a weak electrical impulse to restore correct muscle contractions,
ICD stimulator
- replacement of a damaged heart valve, in which an artificial or donor one is placed in its place (re-replacement of the valve is periodically required),
- coronary bypass surgery - indicated in cases where bovine heart disease is caused by coronary artery disease due to disturbances in blood flow in the heart muscle,
- installation of a mechanical left-hand pump,
- Heart muscle transplantation is a last resort measure, which is indicated in particularly serious patient conditions when other treatment methods are ineffective.
In older people, radical surgery such as a heart transplant is rarely performed due to the severity of the procedure. Their main invasive treatment is the installation of pacemakers and coronary bypass surgery.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine can be used as an additional treatment in consultation with the attending physician. Their action is aimed at strengthening the heart and cleaning blood vessels. Use:
- A tincture made from rosemary and red wine. To obtain the drug, 100 g of plant material is poured with 2 liters of wine. Infuse the composition for a month in the dark. Drink the product 3 times a day, 20 ml for 9 months.
- Red beet juice with a teaspoon of honey. Useful for congenital heart diseases.
- Garlic juice. It is useful to drink it to strengthen the heart every morning on an empty stomach, 7 drops with a teaspoon of olive oil.
- Cranberries with sugar. Helps with heart problems and is taken a tablespoon 4 times a day.
Relying only on folk remedies for bull's heart is unacceptable. This will not only be ineffective, but also deadly.
Non-coronary diseases
Another fairly common cause of an enlarged heart is inflammatory processes affecting muscle tissue (carditis), primarily rheumatic carditis.
So, if a person has suffered a serious infection such as tonsillitis or scarlet fever, complications (rheumatism) can also affect the most important organ that transports blood.
In this case, the muscle loses its elasticity, and the ventricles are overstretched, as a result of which the size of the organ can increase several times, and its functionality, accordingly, will decrease several times.
In this regard, timely treatment of rheumatic carditis is very important. To date, drugs have been developed to completely eliminate streptococcal infections and prevent overstretching of the heart.
If therapy is not followed, the person may die. In addition, being a carrier of streptococcus, the patient infects others.
Endocarditis is an inflammatory disease that affects the internal cavity of the heart and its valves.
Endocarditis in an advanced stage causes expansion of the organ, loss of muscle elasticity and ability to contract. The disease requires immediate treatment.
Myocarditis is a consequence of viral infections, accompanied by arrhythmia and shortness of breath, and heart failure may occur. Video:
In this regard, a patient with myocarditis needs immediate medical attention and supportive care.
Chronic alcohol consumption can cause cardiomyopathy and cardiac dystrophy, as a result of which the heart cavities expand and the heartbeat rhythm changes significantly.
Also, patients with alcoholism, as a rule, have high blood pressure - another factor that contributes to the modification of the heart muscle.
If a person recovers from alcoholism and stops drinking alcohol, and if he has hypertension, takes blood pressure-lowering medications, after some time the organ will restore its normal size.
Thus, if a fluorography image reveals an increase in the size of the heart, you should immediately contact a specialist, find out the cause of the pathological changes and, if necessary, begin therapy: the problem is solvable in most cases.
Diagnosis of cardiomegaly
A cardiologist can usually assume the presence of cardiomegaly already during the initial examination of the patient based on the existing symptoms and the results of listening to the work of the heart. To determine an accurate diagnosis, a complete examination is performed on the patient, which uses a number of differential diagnostic methods:
- ECG. A classic test that allows you to determine the correct heart rhythm.
- X-ray of the heart area. Cardiomegaly on an x-ray is accurately determined if the pictures are taken in two projections. In this case, a more intense contour of the left ventricle and an increased position of the left bronchus in direct projection are visible. Changes in the size of the right atrium are quite difficult to detect on x-ray. Sometimes only smoothing of the curvature of the silhouette of the heart muscle on the right side is recorded. The method relates to the primary diagnosis of cardiomegaly, since it is available in all medical institutions and is quite informative for the doctor.
X-ray picture of cardiomegaly
- Echocardiography. The study reveals dilation of both the left and right ventricles and a deterioration in the contractility of the organ. The presence of hypertrophy of the cardiac septum and a direct increase in myocardial thickness are also diagnosed. If the information content of the study is insufficient, the procedure is performed through the esophagus.
- MRI. A modern method that most accurately determines all changes in the heart muscle, its weight and wall thickness.
- Complete blood test. The patient undergoes biochemistry, serological blood tests and immunological tests.
- Catheterization of cardiac cavities. Indicated for identifying and assessing the possibility of eruptions of their cardiac ventricles into the aorta.
During the examination, it is important to identify the disorder at an early stage, then therapy can achieve a pronounced effect.
prevention
Tell your doctor if you have a family history of conditions that may cause an enlarged heart, such as cardiomyopathy. If cardiomyopathy or other heart diseases are diagnosed early, treatment can prevent the disease from getting worse.
Controlling risk factors for coronary heart disease—tobacco use, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes—helps reduce the risk of increased heart disease and heart failure, reducing the risk of a heart attack.
You can help reduce your chance of developing heart failure by eating a healthy diet and not drinking too much alcohol or using illicit drugs. Controlling high blood pressure through diet, exercise and possibly medication also prevents many people with enlarged hearts from developing heart failure.
If you have symptoms of a heart problem, your doctor will do a physical exam and run tests to determine if your heart is enlarged and to find the cause of your condition. These tests may include:
- Chest X-ray. X-rays help your doctor see the condition of your lungs and heart. If your heart is enlarged on X-ray, other tests will usually be needed to find the cause.
- ECG. This test records the electrical activity of your heart using electrodes attached to your skin. The impulses are recorded as waves and displayed on a monitor or printed on paper. This test helps your doctor diagnose heart rhythm problems and heart damage from a heart attack.
- EchoCG. This test to diagnose and monitor an enlarged heart uses sound waves to create a video image of your heart.
This test can evaluate the four chambers of the heart. Your doctor can use the results to see how efficiently your heart pumps, determine which chambers of your heart are enlarged, look for evidence of previous heart attacks, and determine whether you have congenital heart disease. - Stress test. A stress test, also called an exercise test, provides information about how well your heart works during physical activity. Exercise stress usually involves walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike while your heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing controlled.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In a cardiac CT scan, you lie on a donut-shaped table called a trestle. An X-ray tube inside the machine rotates around your body and collects images of your heart and chest. In a cardiac MRI, you lie on a table inside a long tubular machine that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to receive signals that create images of your heart.
- Blood analysis. Your doctor may order blood tests to check the levels of certain substances in your blood that may indicate a heart problem. A blood test can also help your doctor rule out other conditions that may be causing your symptoms.
- Cardiac catheterization and biopsy. In this procedure, a thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the groin and threaded through the blood vessels in your heart, where a small sample (biopsy) of your heart, if indicated, can be removed for laboratory analysis. The pressure in the chambers of your heart can be measured to see the blood enter your heart. Photos of your heart's arteries may be taken during the procedure (coronary angiogram) to make sure you don't have a blockage.