Many people are interested in the question of whether it is harmful to do an MRI at a temperature
Magnetic resonance imaging is a diagnostic that is highly informative and safe (subject to compliance with the recommendations for use). The study is not routine. MRI is prescribed if it is necessary to clarify information obtained by other methods, with mixed symptoms, or in controversial situations.
During the use of magnetic resonance imaging in medicine, there were no cases of deterioration in the condition of the subject or aggravation of the disease in connection with the scanning. But patients often wonder whether it is possible to do an MRI with a temperature. Questions arise due to an incomplete understanding of the essence of the diagnostic procedure and the origin of contraindications.
What is MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a modern diagnostic method that provides deep visualization of internal organs and tissues. The method is based on the phenomenon of magnetic resonance of various electromagnetic fields in the body.
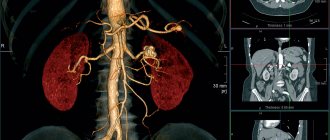
The source of resonance during the examination is the body of the subject. The tomograph records weak radio signals emanating from various structures in the area under study. The recorded signals are recorded by a special computer and converted into tomograms—images depicting the required area of the body.
MRI performs layer-by-layer scanning of organs and tissues in three dimensions. Amenable to examination:
- brain,
- abdomen,
- ligamentous apparatus of joints,
- muscles,
- spine,
- any organs and systems.
Magnetic resonance imaging scanners have different magnetic field strengths. Devices with parameters from 1.5 to 3 T (Tesla) are considered optimal. Devices with such indicators are called high-field. They provide high-quality images, allow you to carry out any examination and obtain the necessary information in a short period of time.
There are also medium- and low-field tomographs with a Tesla value of 1 and 0.23-0.35, respectively. Open devices have these parameters. In terms of the quality of clinical research performed, they are inferior to high-field devices. However, they will not lose their relevance due to the possibility of performing tomography in patients with claustrophobia, overweight and young children in the presence of parents without the use of medical sedation.
The study is directed by a specialist, or it can be carried out at your own request. Just don't abuse it. Although magnetic resonance imaging does not have irradiating properties, there are certain nuances for its implementation that a non-specialist may not be aware of. For example, CT or ultrasound is preferred to detect certain diseases. And in some cases, a standard x-ray may be sufficient. Therefore, you should initially contact a specialized specialist who will adequately assess the need for magnetic resonance imaging, and perhaps supplement it with contrast.
You need to know that MRI is less informative for organs and tissues containing large amounts of water. Thus, MRI is preferred over CT for examining the lungs and bones.
Group of relative contraindications to MRI
Relative contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging:
- claustrophobia (possible use of open-type equipment);
- the presence of non-ferromagnetic inner ear implants and other elements for medical purposes;
- the presence of tattoos containing metallic pigment (diagnosis is not excluded if the body pattern is localized outside the study area);
- mental disorders of the patient;
- first trimester of pregnancy and lactation;
- injuries accompanied by a serious human condition;
- the patient is overweight.
It’s worth taking a closer look at the four latest restrictions.
Mental disorders
The procedure itself does not pose a danger to persons with mental disorders, however, nervousness, aggressive behavior, panic attacks, alcohol and drug intoxication are reasons for refusing diagnosis.
The result of an MRI in this case may be a deterioration in the patient’s psycho-emotional behavior and poor-quality images. If the procedure cannot be canceled, the patient is asked to take sedatives.
Pregnancy and lactation period
Today, there is no direct evidence of the adverse effects of MRI diagnostics on the developing fetus. Therefore, a woman expecting a child, from a theoretical point of view, can be examined at any period of pregnancy, except for the 1st trimester.
Things are different if magnetic tomography is performed using a contrast agent. The components of the product can negatively affect the child and cause the development of severe pathological processes in the baby’s body after birth.
The same reason becomes a reason for refusing MRI diagnostics to a woman who is breastfeeding. You can resume lactation a couple of days after the procedure.
Trauma and serious condition of the patient
Certain injuries, such as open fractures, limit the use of MRI. During the diagnostic process, the patient will have to remain motionless for a long period - pain and discomfort will not allow the patient to remain calm.
The result of such a study can be not only a poor-quality image, but also a deterioration in the patient’s condition.
If it is not possible to refuse the procedure, it is permissible to use an open-type MRI scanner to alleviate the discomfort of the person being examined.
Open type (C-shaped)
When the pain is intense and does not allow the patient to remain in one position, it is worth considering replacing MRI with an alternative type of diagnosis.
Obesity
It is not easy to make a diagnosis using MRI for a person weighing more than 120 kg: the equipment table is not designed for such a weight, and the patient will not be able to fit into the magnetic tunnel.
An additional reason for refusing an MRI diagnosis to an obese person is the low information content of the technique in the case of people diagnosed with obesity.
A solution in such circumstances may be to conduct a study in an open-type tomograph. Some medical centers have specialized equipment designed for overweight people.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a diagnostic method that is characterized by an extensive list of limitations.
However, it is important to emphasize that all contraindications are objective and justified in order to preserve the health of the person being examined.
Before undergoing diagnostics, it is important to remain frank with the specialist and strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations when preparing for MRI diagnostics and during the scanning process.
MRI with contrast
Every fifth MRI is performed using contrast agents. They are essential for clearer, more targeted images. Depending on the area being examined, contrast may be administered intravenously or orally (by mouth). For example, for detailed diagnostics of the digestive system organs, oral contrast agents are used, which can be ordinary tea (blueberry, green) containing manganese.
Intravenous contrast is administered to examine the blood vessels in detail. It is worth noting that this type of MRI may be contraindicated in patients with chronic renal failure and allergy sufferers. Therefore, tomography should be carried out strictly according to the indications and prescription of the attending physician.
Does tomography have any disadvantages?
Against the backdrop of a huge range of positive aspects, including painlessness and the absence of x-ray radiation, a significant disadvantage of magnetic resonance imaging is its high cost, especially in private medical institutions. Diagnostics MRI is undoubtedly more informative than CT and radiography; for a number of indications it is used for precise localization and determination of the size of tumors. But the technique, which can be used repeatedly without harm to health, has some disadvantages:
- staying in a horizontal position for a long time, which is difficult for children, as well as people suffering from acute pain;
- For patients whose bodies contain metal devices (pacemakers, pumps, implants, etc.), examination is contraindicated;
- for mental disorders (epilepsy, claustrophobia), the MRI procedure is performed under the supervision of medical staff using an open apparatus;
- the fact of renal failure or an allergic reaction to contrast is a contraindication for MRI.
If, for certain indications, you have been prescribed a tomography session of any part of the body, do not worry. The scanning process does not require any special preparation. It is important to inform your doctor about all health problems, not forgetting about devices implanted in the body. During the procedure, you should lie still, not reacting to the noise and clicks of the tomograph.
Tags: Questions about MRI
Discussion: there is 1 comment
- Verka:
12/28/2019 at 15:10In addition, MRI helps to identify any vascular abnormalities and circulatory problems. Any infectious tissue lesions are also easily identified when studying the scan results.
How is an MRI scan performed?
MRI scans usually do not require any preparation. An exception is the study of blood vessels and abdominal organs. A few days before the test, you must adhere to a low-carbohydrate diet. During the day before the procedure, exclude gas-forming foods from the diet (carbonated drinks, fruits, vegetables, bread, tea, bread).
Immediately before the procedure, the subject must remove all metal objects from himself, as they negatively affect the action of the magnetic field. As a result, you may end up with a distorted image.
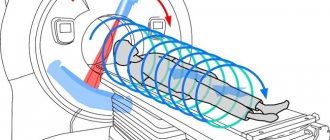
The patient is taken to a special room where the tomograph is located. Usually it is a horizontal pipe, inside of which you need to take a horizontal position. There are also devices with a vertical position, but they lag behind in image quality.
During the examination, the specialist has the opportunity to monitor the patient using special video equipment. An intercom is provided inside the tomograph, allowing the doctor and patient to communicate with each other.
To obtain a high-quality image, maximum patient immobility is required during the procedure. Its duration is on average about 20 minutes.
If necessary, contrast agents can be administered intravenously to allow a more detailed study of the area being examined.
For young children, this procedure is performed under general anesthesia, since a motionless body position is required.
Interpretation of the results is usually carried out within an hour after the MRI. The patient receives them the next day, or immediately if urgent.
Strengths
This concludes the description of the MRI procedure. It remains only to highlight its advantages over other examination methods and features:
- it is possible to identify abnormalities in the functioning and development of the brain that cannot be detected by other means;
- safety of contrast agent administration - the likelihood of a reaction is minimal, and it is always taken into account;
- identification of complex pathologies at the initial stages of their appearance;
- formations in the soft tissues of the brain and tumors are easily detected in the first stages of their formation;
- safety has been proven by scientific research, although the changes introduced by a strong magnetic field into the structure of irradiated tissues have not been studied, and science simply does not know what they might result in;
- absence of radiation harmful to living cells: X-ray or ionizing;
- the patient is affected only by a high-intensity magnetic field, and only for a short time;
- you can see brain tissue in transverse and longitudinal sections;
- the ability to study the state of cerebral vessels;
- determination of the real location of the appearance of pathologies, their exact shape and size in all planes.
Feelings during the examination
The procedure does not cause any painless sensations. Discomfort can only come from the patient remaining motionless on a hard surface for a certain period of time.
It should also be taken into account that when the device operates, the coils make noise, so you can use special headphones in advance.
Sometimes patients feel a feeling of warmth in the area being examined. This is due to a local increase in temperature during operation of the tomograph and should not cause concern unless it turns into a painful burning sensation.
How is an MRI done?
Before the start, the patient is instructed on how the MRI procedure is performed, and is asked about his readiness for it and his well-being.
You usually don't have to undress to get tested. It depends on the area of study. It is enough just to remove metal objects and clothing items containing them.
If magnetic resonance imaging with a contrast amplifier is planned, a dye is first injected intravenously. Likewise, children and those suffering from claustrophobia are given anesthesia before the scan begins.
The tomograph is a massive tube with a magnet, a scanner, radio frequency and gradient coils, as well as a conveyor table on which a person sits. When the equipment is started, the patient's body moves inside the tunnel. A magnetic field is formed that affects the examined area, and the scanner reads information about the concentration of relaxing energy. The obtained data is transformed into images, which can subsequently be presented in volumetric form. This is the principle of operation of an MRI scanner.
How long does an MRI take?
Depending on the scale of the examination, the technical parameters of the equipment, the experience and qualifications of the MRI technologist, an MRI takes from 30 to 60 minutes. When scanning multiple areas and requiring close attention to a specific area, the process can take up to two hours.
During the test, medical staff located in an adjacent room behind a glass viewing window maintain voice communication with the patient. If you experience pain or discomfort, you should press the signal button, which notifies you of the desire to immediately interrupt the procedure.
Since the tomograph makes quite a loud noise, the person being diagnosed is offered special soundproofing headphones.
At the patient's request, a relative is allowed to be present in the examination room.
Is it possible to do an MRI if you have a cold?
A cold is not a contraindication, so the question “Is it possible to do an MRI with a fever?” you can give a positive answer.
You should pay more attention to the accompanying signs of acute respiratory disease. It is usually accompanied by copious discharge from the nasopharynx, sore throat, and cough. Such symptoms interfere with obtaining complete information when undergoing an MRI of the head and brain. In addition, with a runny nose and cough, it is difficult to remain in a motionless position for a long time, and involuntary sudden movements will distort the final images.
The final decision on the advisability of the procedure during the cold period is made by the attending physician.
How often can an MRI be done?
When operating MRI equipment, no ionizing radiation is emitted. Over the many years of use of this diagnostic technology, there have been no recorded cases of deterioration of the patient’s condition or harm to his health. Based on this, doctors say that MRI can be done as often as necessary to establish or clarify the diagnosis.
For some diseases, the frequency of MRI is regulated. Thus, the monitoring interval for some benign neoplasms is 3 months, and patients with diabetes are recommended to undergo an MRI of the head once a year.
Generally accepted medical practice prescribes a series of examinations before and after surgery. This is carried out to monitor the condition of the operated organs or systems.
The following diseases are detected using MRI:
- Pathology of the brain and spinal cord.
- Neoplasms of benign and malignant nature.
- Pathology of the osteoarticular system.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Traumatic disorders.
- Inflammatory diseases of the urinary system.
- MRI can detect most brain pathologies. For frequent fainting, dizziness, traumatic brain injuries, and convulsions, tomography is indicated to clarify the diagnosis.
- In the vast majority of cases, magnetic resonance imaging is performed to assess the condition of the spinal cord and spine (protrusions, intervertebral hernias, osteochondrosis).
- In oncology, MRI is widely used for early diagnosis of tumors, detection of metastases, and for assessing the quality of treatment.
- Magnetic resonance imaging provides reliable and accurate data on the structure, size, and shape of certain structures, formations, and organs.
Why is MRI necessary?
Thanks to the use of a magnetic field, an effective method is indicated for diagnosing a wide range of pathological changes in the body. Unlike other examination methods, MRI does not pose the threat of ionized radiation, like computed tomography (CT). Magnetic tomography is relevant for studying the condition of tissues in the spinal region, as well as the brain, internal organs, all sections of the spine, articular and cartilaginous formations, and blood vessels.
Indications for head examination
MRI is prescribed to evaluate the structure and function of blood vessels located in the brain. The study allows you to obtain a series of images of any of the problem areas of the great vessels, to detect traces of traumatic changes in the bone structures of the skull and parts of the brain. In what cases is an MRI of the brain prescribed:
- impaired cerebral circulation, signs of stroke;
- suspicion of a tumor of the brain, its membranes, bone structures of the skull;
- the fact of abnormal development of the brain and cerebral vessels;
- after a traumatic brain injury to detect internal hematoma, bleeding;
- control of degenerative changes, consequences of dementia and sclerosis;
- to confirm the presence of an aneurysm;
- with inflammation affecting brain tissue;
- to assess the condition after surgery or treatment, including oncology.
Indications for prescribing an examination of the pituitary gland are a number of disorders, including disruptions of the endocrine system, metabolism (obesity), and vision problems of unknown etiology. Women are prescribed MRI of the pituitary gland for menstrual irregularities.
In addition to the ability to examine brain structures (cerebellum, pituitary gland, brainstem) and detect brain atrophy, indications for spectroscopy are the need to diagnose multiple sclerosis, cystic processes, and other diseases of the spinal cord. MRI scans of the head include the ability to record pathologies of organs located in the cranial area.
- Hearing aid. Detection of painful processes in the middle ear, anatomical anomalies, diseases of the inner ear. MRI of the head area is prescribed for complications in the ears after chronic inflammation in the upper respiratory tract.
- Visual apparatus. When a foreign body enters the eyeball or retrobulbar space. The orbits of the eyes are examined for tumors or injuries affecting the lacrimal glands, extraocular muscles, and optic nerve. Diagnosis of MRI is relevant for optic nerve atrophy, bleeding in the eye, visual impairment or loss of vision.
- Nasopharynx area. For migraines, frequent headaches of unknown cause, ear congestion, as well as allergic rhinitis and fungal sinusitis, MRI of the nasal sinuses and oropharynx is indicated. Tomography is prescribed if a tumor process is suspected in the paranasal sinuses area, in the thyroid tissues, or lymph nodes.
Since during the examination a person is placed in a closed capsule of a tomograph, which is a large magnet, the patient must remove all metal objects from himself. This is the key to obtaining high-quality images, as well as patient safety.
Indications for x-ray of internal organs
The most extensive area that is most often exposed to transillumination is considered to be the space of internal organs, an extensive network of vessels. After an ultrasound examination, MRI is used to clarify the diagnosis, especially for those patients for whom the procedure of computed tomography with contrast is contraindicated.
Chest area
- The pleural cavity, lungs if oncology is suspected (cancer search), and the mediastinal area are examined. MRI is used for differential diagnosis of tuberculosis, as well as inflammation and other pathologies.
- Thanks to scanning, it is possible to record the smallest changes in the vessels of the thoracic area during the formation of an aneurysm. Resonance imaging allows you to assess the condition of the heart muscle after a heart attack, confirm the fact of ischemia, heart disease, and the presence of blood clots.
- The indication for MRI is the need to detect emphysema, pneumonia, and monitor the condition of blood vessels by performing angiography if stenosis and aneurysm are suspected. The method is relevant for identifying pathological changes in the functioning of the heart chambers and valve system after heart surgery.
To obtain reliable results of heart scanning, it is necessary to use high-power tomographs, since the organ cannot be stationary.
The quality of MRI images is affected by respiratory function, therefore, to examine the cardiovascular system, devices that generate a magnetic field of 1.5 Tesla or more are used. A high-quality three-dimensional image allows you to see the beds of blood vessels and surrounding tissues from different angles, regardless of their depth, static or dynamic state.
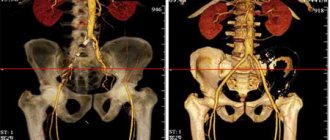
Abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space
When indicated for studying pathological changes in organs located in the abdominal cavity, CT is usually prescribed. The use of a CT scanner guarantees better visualization of the gallbladder and intestines. To examine the stomach, they use the fibrogastroscopy method, but to examine the vessels, bile ducts, liver, and adrenal glands, MRI is indispensable.
The method is indispensable for detecting and clarifying the extent of the disease process and its spread to neighboring organs. However, the expensive procedure is prescribed only in cases of extreme necessity. Diagnosis of the intestinal cavity, the condition of the kidneys and adrenal glands is justified if it is impossible to perform research using other methods.
Indications for checking the pelvic organs
- MRI is necessary for women to study anomalies and pathologies of the female genital organs, detect endometriosis, adhesions, and inflammatory processes. You cannot do without tomography when differentiating tumors in the uterus, cervical body, appendages, and detecting metastases. The indication for intestinal examination is suspicion of a tumor.
- For men, an MRI procedure is necessary for prostate diseases, abnormal development of the testicles or their inflammation, and diseases of the scrotum. Scanning is indicated for hernias (inguinal, femoral), tumor progression in the rectum, which affects nearby organs.
Tomography of the mammary glands has become one of the best methods for verifying dangerous processes (tumor and inflammatory). MRI provides visualization of details that are not subject to ultrasound diagnostics, allows you to monitor treatment after surgery, changes after injury.
Indications for spine scanning
Most often, patients are interested in indications and contraindications for examining the spinal column and articular-cartilaginous apparatus. The main prohibition on hardware diagnostics is the presence of metal objects in the human body, as well as the fear of closed spaces. Spectroscopy is not prescribed for pregnant women, and MRI is avoided for patients with inappropriate behavior.
The progressive method of non-invasive testing has become a real breakthrough in terms of studying the condition of the spine. At a completely new level of research, the surgeon has the opportunity to obtain three-dimensional sections of problem areas to detail the smallest details of the condition of the vertebrae and the space between them.
Thanks to the MRI technique, it is possible to detect the early stage of changes that are not yet recorded by the x-ray. Tomography is important for monitoring the dynamics of spinal disease, the effect of prescribed medications, in order to make timely changes to the treatment regimen. In what cases is the spine examined:
- for monitoring congenital and acquired pathologies;
- for injuries of the spinal column, pain of unknown cause;
- to identify inflamed foci, tumor processes, metastasis;
- to record manifestations of osteochondrosis and localize problem areas;
- for pinched nerves, intervertebral hernias, compression fractures of the vertebrae;
- if necessary, identify areas of narrowing of the spinal canal;
- to detect coccyx cysts and dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Based on the symptoms and localization of pain, the doctor has the opportunity to prescribe an MRI of any part of the spine or examine it completely. For certain indications, the cervical, thoracic, and lumbosacral regions, which are considered the most difficult to diagnose by other methods, can be examined. As a result of magnetic tomography, the specialist receives layer-by-layer images of each vertebra, visualization of discs, nerve endings, and from different angles.
Contraindications:
- Presence of electronic mechanisms (pacemaker).
- The presence of metal in the body (prostheses, clips, pins, bullets, fragments).
- Claustrophobia.
- Pregnancy (absolutely contraindicated up to 3 months).
- State of alcohol or drug intoxication.
- Heart failure.
- Availability of an insulin pump.
- Persons with mental disorders.
- Tattoos with metallic ink.
- High body weight (over 120 kg).
Contrary to popular belief, lactation, menstruation, and the presence of an intrauterine device are not contraindications to MRI.
Do not be upset if you find any of the above restrictions for conducting an examination at home. It is necessary to contact your doctor, perhaps he will find a way out of the situation or recommend alternative examination methods. For example, for mild claustrophobia, the doctor may prescribe sedatives; for high body weight or large waist circumference, suggest an open-type tomograph. Indications for examination of pregnant women of different stages are determined individually.
MRI Safety
At the moment, there is no information about side effects that occurred after undergoing an MRI examination. The technique does not involve exposure to ionizing radiation; repeated procedures can be performed in unlimited quantities.
Due to the lack of complete information about the effect of the magnetic field on the fetus, MR imaging is contraindicated in pregnant women up to 12 weeks. A theoretical risk for this group of patients cannot be excluded.
Since the procedure involves staying inside a cylinder for a long time, symptoms of claustrophobia are likely to develop. If the patient has previously manifested a fear of closed spaces, the doctor should be warned about this. Options for solving the problem: the presence of a relative in the examination room, prescribing sedatives, administering anesthesia.
Advantages:
- No special preparation required.
- Painless examination.
- There are no age restrictions.
- Can be used on any area of the body.
- A highly informative method for early diagnosis of tumor diseases.
- Full, detailed image of many organs and tissues.
- Magnetic resonance imaging has become widespread for identifying tumors in oncology, diseases of the nervous and osteoarticular systems.
- The ability to obtain images in three projections without changing the body position: axial, frontal and horizontal, which allows you to visualize the organ from all sides.
- No bone artifacts on the images.
- High differentiation of soft tissues.
- The possibility of using contrast agents in the study, which makes the equipment even more sensitive, and the resulting image more informative.
- It shows not only the structural parameters of the area under study, but also, in some cases, functional indicators (blood flow speed, brain activity).
Indications and contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging is a relatively safe method. It does not involve x-rays or ionizing radiation, so MRI can be done with virtually no restrictions.
Why is an MRI done? You can undergo the study either at your own request or on the recommendation of your doctor. An appointment is issued if a tumor is suspected in order to assess the consequences of the injury, in order to clarify the preliminary diagnosis, determine the nature of pain or discomfort.
Despite the conditional safety of the technology, a number of contraindications are still present, namely:
- the presence of non-removable metal objects (implants, prostheses, fragments, plates, etc.);
- the presence of non-removable electronic devices, for example, pacemakers;
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks;
- severe forms of claustrophobia and mental disorders;
- the presence of tattoos made from dyes containing metals;
- hematopoietic anemia (regarding contrast MRI).
When is an MRI prescribed?
MRI diagnostics is designed to analyze the condition of soft tissues of the entire human body. In what cases is MRI prescribed?
- For the purpose of examining organs and tissues to exclude or confirm a preliminary diagnosis.
- To monitor the dynamics of the disease and monitor the effectiveness of prescribed treatment.
- As preoperative preparation and postoperative control.
This method is indispensable when monitoring the tumor process. With its help, a primary diagnosis is made and the development of formations is monitored.
Tomography is effective in determining the causes of pain of unknown origin. It helps analyze the condition of the joints and can identify herniated discs and other changes in the spine, including those of traumatic origin.
During the scan, the condition of blood vessels and lymph nodes is clearly visualized.
Use in pediatrics
The electromagnetic waves emanating from the tomograph do not cause harm, therefore magnetic resonance imaging is actively used in pediatrics to diagnose a wide range of diseases. The procedure for performing an MRI on children is no different from how an adult procedure should be performed.
There is one important feature. The main condition put forward for the process is complete immobility of the patient. Violation of this rule leads to distortions in the images and, as a result, the provision of false information. Small children find it difficult to sit still, let alone lie still for half an hour. That is why young patients are put into a sleep state during the study.
At what age do children have an MRI without anesthesia? It all depends on the individual character traits of a particular child.
Flaws:
- The time required to obtain an image takes a few minus seconds. This time is sufficient for the occurrence of artifacts due to respiratory or cardiac activity.
- Inability to detect all bone changes and hard structures (stones, calcifications). In this respect, magnetic resonance imaging scanners are inferior to computer scanners. Therefore, MRI is used mainly for diagnosing soft tissue pathologies.
- Inaccessibility of research for low-income groups. The high cost of the examination is explained by the expensive operation of the equipment and the tomograph itself.
- Special conditions in the premises for operating the tomograph.
- Inability to use in patients with metal implants and artificial pacemakers. This is explained by the fact that the tomograph creates a powerful magnetic field that can heat and damage metal products.
For a comprehensive examination of the body, MRI occupies a leading position in terms of the degree of safety and information content of the method in comparison with ultrasound, X-ray, and CT. MRI scans all areas of the human body, and, if necessary, is supplemented with other more sensitive examination methods in each specific situation.
The MTP procedure does not in any way affect the state of health, so it can be repeated many times to assess the course of the disease or the dynamics of the treatment.
- CT and MRI - what's the difference?
- MRI of the lumbosacral spine
- Abdominal MRI
- MRI of the intestine, pros and cons of the method
- Computed tomography with contrast agent
Physics of the phenomenon
Magnetic resonance imaging operates on the principle of magnetic resonance, the basis of which is the saturation of the body's cells with hydrogen molecules. Depending on their environment, they have different properties and, as a result, emit electromagnetic waves in different spectra.
The hydrogen nucleus, as is known from chemistry and physics courses, contains a single proton with a certain spin (magnetic moment). It changes under the influence of artificial and strong natural fields, in particular magnetic fields, but with the condition that their frequency is in resonance with the proton vibration frequency.
Using the fact that the proton spin has only two opposite phases (vector directions of motion), tied to the magnetic moment of the elementary particle, it is possible to accurately determine the location of the dislocation of the hydrogen atom with certain frequency characteristics using electromagnetic waves of a high-intensity magnetic field. This concerns MRI technology. The operating principle is as follows:
- the spin (magnetic moment) of a proton placed in an external magnetic field is directed in the same direction (as the field) or in the opposite direction (in this case, its energy potential will be much higher than in the first case), there is no third option;
- under the influence of irradiation, a proton inverts its magnetic moment, and after the cessation of exposure to an external stimulus, it instantly returns it back;
- sensors detect a flash of energy during relaxation of an excited elementary particle;
- Based on the incoming data, the software analyzes it and builds an image.
The magnet used must be very strong. If the first devices were equipped with magnets with an induction of only 0.0005 Tesla, which gave a very low-quality and blurry low-resolution image, then modern tomographs use magnets with a strength of 1-3, and in some cases up to 9 Tesla. Elements that have a superconductivity effect, which manifests itself at low temperatures, are often used. They usually operate immersed in liquid helium.
The response to permanent magnets is much weaker than electromagnets, but the former have a clear advantage - they allow:
- conduct MRI studies while moving, standing or sitting;
- provide access to the patient to a doctor or x-ray technician.
To examine the spine and brain, low-field devices with field strengths below 1 Tesla are used.
To obtain accurate information about the localization of the hydrogen atom whose proton emits, a permanent magnet or electromagnet is often replaced by gradient coils. They add a magnetic disturbance in the form of a gradient to a uniform field. Thanks to it, high accuracy of data acquisition is ensured. It is the speed and power of the gradient that are one of the key characteristics of the tomograph. The resolution of the device and the quality of the signal (amount of noise) depend on them.
Types of MRI of the brain
- Standard - done without the introduction of contrasting solutions, but at the same time provides a sufficient amount of information.
- With contrast, before which drugs containing gadolinium salts are injected into the vein - gadopentetic and gadoteric acids, Omniscan, Magnevist, etc. These solutions penetrate into the bloodstream and, once in the rays of the MRI scanner, highlight the resulting “picture”. At the same time, the changed areas become better visible, which simplifies decoding. The technique is most often used to detect vascular abnormalities, multiple sclerosis and tumor formations. The dose of contrast agent is selected individually, taking into account weight.
- MR angiography – is performed to assess the condition of blood vessels in atherosclerosis, aneurysms, blood clots and pre-stroke conditions. It is done with gadolinium contrast to show blood flow problems in detail.
- MR imaging of the pituitary gland, an appendage that is an endocrine gland. The pituitary gland secretes hormones responsible for reproductive function, tissue metabolism and the regulation of human growth. An examination is prescribed if an adenoma is suspected - a benign tumor that causes migraine-like pain, hormonal imbalances, gigantism, infertility, obesity and sexual dysfunction. The same method is used to identify malignant pituitary formations that have similar symptoms and are accompanied by a pronounced deterioration in health.
MRI and CT
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are similar and sometimes even interchangeable types of diagnostics, but it would be a big mistake to consider them completely identical. Despite certain similarities, they also have huge differences, which allow the doctor to make a choice in favor of one of them. By the way, there is also a frequent question about whether it is possible to do an MRI without a doctor’s referral; for prevention, this is not a problem, but still a preliminary conversation with the doctor would be useful.
The essence of the MRI method is based on the ability of a magnetic field to cause resonance of the nuclei of hydrogen atoms in the body. The tomograph creates a field and radiofrequency pulses that capture images of facets and structures. This operating principle is completely harmless to the body. This method has found its greatest application in the diagnosis of soft tissues and the search for oncology.
CT works on a completely different principle, closer to conventional x-rays. Computed tomography uses ionizing radiation to penetrate body tissue. This makes the method not entirely safe: radiation tends to accumulate. The most common area of application of this method is the examination of the skeleton and hollow organs such as lungs, intestines, etc.
Thus, it turns out that sometimes it is indeed possible to replace one with the other. But you shouldn’t choose to do a CT instead of an MRI (or vice versa) on your own - usually the doctor who referred for the examination understands what his patient’s problem may be and which method will be better able to visualize it.
Mechanism of the procedure
The use of tomography takes place in a specially equipped place, where there will certainly be an MRI machine in the form of a tunnel, the so-called magnet, and a computer where the scanning results will be sent.
The patient must lie on a special movable table, his body is secured with belts and bolsters. Equipment capable of receiving and sending radio waves is attached to the examination site.
If necessary, the nurse injects a contrast agent into the vein through a catheter.
Next, the table with the patient is moved into the magnet, where the scanning itself begins. During the procedure, clicks and tapping are heard, so for a comfortable procedure, a person may be offered headphones or earplugs.
The study lasts on average from 15 to 45 minutes. Some discomfort can be caused by the need to not move all this time and sometimes hold your breath. This is especially difficult for children to cope with. Parents should prepare those who are older, for example, by comparing the procedure to a rocket flight into space, during which you cannot move. For children under 5 years of age, if there are compelling indications, this type of diagnosis is performed under general anesthesia.
It is important that inside the tomograph there is a communication system with which the child can communicate with his parents.
Relationship with other types of diagnostics
Another common worrying point is the numerous variations of the question “is it possible to do fluorography after MRI / x-ray after MRI” and the like, that is, combinations of MRI with other diagnostic methods. In order to answer them, you need to again turn to the principle of operation of the MRI scanner, which was described earlier.
Diagnosis using a computed tomography scanner, fluorography or x-ray has a cumulative “extreme limit”, after which these examinations will not be done unless absolutely necessary. All of these devices operate on a similar principle and use X-rays, which have, albeit a small, effect on the body.
An MRI is a completely different matter. Working on a completely different principle, the MRI scanner does not leave accumulated radiation doses in the patient’s body. Thanks to this, after a CT scan, you can do an MRI even on the same day. But it is clearly not worth combining CT with fluorography or x-rays in order to avoid too much radiation exposure.
This also answers the question of how long it will take to undergo a repeat MRI - the examination can be repeated at any time, here you should rely only on the possibilities and the need for repeat diagnostics. Is it possible to do it 2 times in a row - yes, but perhaps to save money and time it’s worth just going through one combined examination that includes all the necessary areas.
Benefits of the study
Indications for MRI take up more than one page and tend to expand the list, because doctors insist that this diagnostic method has a number of advantages compared to other types of studies.
- Tomography makes it possible not only to identify, but also to describe in detail pathological processes.
- This technology does not involve invasive intervention (incisions, punctures), but extremely accurately records any abnormal formations and disorders.
- The procedure can be performed on adults and children as many times as needed to make a diagnosis or monitor the results of treatment.
- The absence of ionizing radiation eliminates the risk of gene mutations and carcinogenesis.
- MRI readings take into account the reality of studying objects whose dimensions do not exceed a centimeter.
- Using the method, you can visualize tissue in longitudinal and transverse sections, as well as create a 3D image.