Angiography with control of the resulting image using a computed tomograph is highly reliable and helps to identify disorders of the structure and patency of the arteries of the lower extremities. It is called multispiral because during the examination the tube rotates around a moving table on which the patient is located.
MSCT allows you to obtain three-dimensional images, which helps you choose the method of vascular surgery or evaluate its results.
What is MSCT
Multispiral computed tomography is the latest development in the field of diagnostics. The technique appeared on the basis of standard x-rays and combines the useful properties of several techniques: CT, ultrasound. It is more suitable for examining dense and hollow structures: glandular and bone tissue, blood vessels and lymphatic systems. Therefore, it is widely used in difficult situations.
MSCT is a computer scan of the body using x-rays. They illuminate specified areas and organs. The scanner generates and directs a beam of radiation onto the chest. Dozens of sensors with the highest degree of sensitivity capture the output signals, converting them into digital information. In the form of clear and three-dimensional images, all results remain in the memory of the tomograph and are used for diagnosis and study.
The unique technology allows the use of MSCT OGK in a number of medical situations:
- heart disease, coronary vessels;
- benign and malignant formations in different sectors of the mammary gland;
- rupture or inflammation of the esophagus, upper stomach;
- tissue injuries;
- changes in the structure of the ribs and spinal column;
- abnormalities or blockages of blood vessels.
When using MSCT, the specialist has the opportunity to fully examine the organs of the sternum. This allows you to see the problem in its entirety and determine the cause of shortness of breath or severe pain in just one session. Accuracy of up to 98% allows you to confirm controversial diagnoses made by doctors based on ultrasound or conventional x-rays.
What complications can there be after the procedure?
With increased sensitivity in the first days after the procedure, the following may occur:
- Itchy skin and rashes;
- Cough;
- Pressure surges;
- Nausea;
- Dizziness and headache.
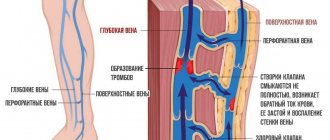
The examination reveals:
- Is there a narrowing or expansion of the lumen in the blood vessels;
- What condition are the walls of blood vessels in?
- Condition of surrounding tissues;
- Are there any obstructions to blood flow?
- The degree of vascular patency.
These indicators are the basis for drawing up a treatment plan: whether surgery is needed and what kind.
Indications and contraindications for MSCT
The multislice tomography procedure is not prescribed for simple diseases that can be more easily diagnosed:
- An enlarged group of lymph nodes in the presence of other symptoms of oncology.
- Severe chest injuries requiring emergency surgery.
- Rupture of an aneurysm or large vessels in the mediastinum.
- The need for a comprehensive study of tumors identified on radiography or bronchoscopy.
- Bleeding in the pleural cavity.
- Injuries to the pericardium or coronary arteries that supply the patient’s heart.
- Search for metastases.
- Establishing the stage and size of a tumor in oncology.
- Analysis of the condition of the cartilage tissue of the ribs in chronic inflammatory processes.
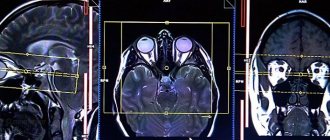
The main difference between MSCT and other methods of examining the chest organs is that the images are taken in ultra-thin layers of no more than 0.5–0.1 mm. This makes it possible to identify the smallest neoplasms, cracks and lesions that are inaccessible to the eye of doctors. Thanks to the compilation of a three-dimensional model, a specialist has the opportunity to promptly identify abnormalities in the development of blood vessels, the heart or the esophagus.
The MSCT method of the chest organs allows us to assess the condition of the human lungs and bronchial tree. There are many diseases and inflammations that require diagnostic accuracy:
- Oncological tumors and metastases, often occurring in cancer of the digestive organs and genitourinary system. The procedure is recommended to be performed during remission to control the remaining calcifications in the pleural cavity.
- Consequences of severe or advanced forms of tuberculosis, in which active destruction of lung tissue and the network of blood vessels occurs. Often the disease is accompanied by fluid accumulation, purulent abscesses and pleurisy.
For diseases of the respiratory system that provoke copious discharge with pus, blood, and severe shortness of breath. Using MSCT of the chest, you can diagnose rare pathologies: cystic fibrosis, fungal growths, foreign body intrusion.
Preparation for lung transplantation with virtual reconstruction of the entire course of the operation on the monitor. Doctors consider the following to be urgent indications requiring immediate MSCT of the chest organs:
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- pneumothorax;
- emphysema.
MSCT of the sternum is often used for cysts and fibrosis of the mammary gland. The rays easily penetrate glandular tissues, making it possible to detect neoplasms in the posterior lobes.
MSCT angiography of the arteries of the lower extremities
Patients with atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus often experience severe damage to the arteries of the lower extremities. Intermittent claudication, trophic changes in the skin, ulcers, secondary infections, impaired sensitivity and motor function, up to gangrene, with the need for limb amputation - this is an incomplete list of the suffering of these patients. The only possible radical treatment for such patients is open surgery or endovascular surgery to restore blood supply.
MSCT angiography allows a detailed assessment of the condition of the vascular bed and provides invaluable assistance in planning surgical treatment. The study is carried out in case of damage to the vessels of the lower extremities to identify aneurysms; hemodynamically significant narrowing (stenosis) and occlusion of the iliac, femoral arteries, and arteries of the leg. After surgery, MSCT angiography is necessary to monitor the patency of vascular stents or shunts; condition of vascular prostheses, as well as, if necessary, planning re-interventions.
Contraindications
With MSCT, the chest organs receive a certain dose of radiation, which is not dangerous to humans. But the procedure is not recommended for pregnant women: there is always a risk of abnormal development of cells and organs of the growing fetus. The second common restriction concerns patients weighing over 120 kg. This is due to standard scanning equipment designed for a similar mass. Some medical centers are purchasing more powerful scanners that can support a patient weighing up to 180 kg.
If it is necessary to identify pathologies of the circulatory system or blood vessels, a contrast agent is used with MSCT of the chest organs. In this case, the list of contraindications expands significantly:
- reaction to any drugs and products containing iodine compounds;
- asthma;
- hyperplasia of the thyroid or thymus gland;
- kidney dysfunction;
- diabetes.
Breastfeeding is not a contraindication to sternal scanning. If computer diagnostics is necessary, a woman is recommended to carefully express milk for 2 days.
Preparing for a CT scan
Before carrying out, it is necessary to set the indications for the study.
It should be remembered that this study involves x-ray radiation and its purpose must be strictly justified. In addition, during MSCT, a contrast agent is often administered, which is potentially harmful to the kidneys; the likelihood of adverse reactions when taking certain drugs increases. Therefore, only a doctor can give indications for a CT scan. When planning a study, you need to consider:
- Kidney function status;
- The patient is allergic to contrast media;
- The therapy the patient is receiving (for example, when treating diabetes with metmorphine, the contrast agent can cause complications);
- The patient has increased function or disease of the thyroid gland.
In patients with significant renal impairment or other relative contraindications to MSCT with intravenous contrast, the use of alternative research methods (ultrasound, MRI) should be considered.
How to prepare for MSCT
Multislice tomography is a simple procedure for the patient and takes place in a hospital setting. Preparation for MCT of the chest includes several recommendations:
- For one day, it is better to avoid foods and drinks with caffeine that increase blood pressure. This may show distorted results when examining the coronary vessels and heart.
- Prepare light clothes made from natural fabric in advance. The patient will have to lie on his back, so synthetic additives can cause irritation, tingling and discomfort.
- Before scanning your chest, you should remove all jewelry and clothing with metal fasteners.
- If it is necessary to use contrast, the patient is not recommended to drink water 4–6 hours before.
Before the scan, you should talk to your doctor and discuss taking regular medications. One-time discontinuation or dosage adjustment may be required.
MSCT of the chest is not prohibited when a pacemaker or metal implant is installed. But it is better to discuss their presence with doctors in advance: X-ray radiation does not interfere with the operation of such an implanted device, but it can cause distortion and obscure an important fragment in the image. The specialist will choose a different angle and control the scanning in several projections.
How is MSCT performed?
Before performing multislice MSCT of the chest, the doctor re-questions the patient about the presence of allergic reactions and contraindications. A person needs to change clothes and take a position lying on the tomograph table. The specialist selects the correct position, after which:
- the table automatically slides into the scanner;
- the patient must remain silent and calm;
- a specialist monitors the examination from a special room protected from x-rays.
If the condition worsens, tachycardia or blood pressure increases, the doctor must stop the examination and immediately provide assistance.
Applying Contrast
A contrast agent is a special drug that is injected orally and helps monitor blood flow in a specific organ. In MSCT of the chest, in most cases it is used in the form of a dropper. During the procedure, the images highlight areas with increased blood supply and abnormal lesions with small capillaries. This allows you to determine the type of tumor, narrow or completely blocked areas by blood clots.
Most patients tolerate chest tomography with contrast without complications. The drug is excreted from the body in the urine and rarely provokes allergies. In rare cases, nausea, discomfort or other unpleasant sensations may occur. Therefore, on the first day after MSCT with contrast, it is recommended to drink more clean water and reduce salt intake to normalize water metabolism.
How long does an MSCT study take?
A standard examination of the chest organs using MSCT takes no more than 15 minutes. Thanks to a large number of sensors, information is processed quickly and clearly. If it is necessary to use a contrast agent during the process, the total preparation time increases to 30 minutes.
Progress of the procedure
The patient is placed in a horizontal position on a special moving tomograph couch. Areas other than the one being examined are covered with a protective apron to reduce radiation exposure. A contrast agent is injected into a vein.
If necessary, the patient is given a sedative drug. The procedure lasts about half an hour. During this time, the patient should remain motionless. This will allow you to obtain an image of maximum accuracy.
After the diagnosis, the laboratory assistant helps the patient get up from the couch. The doctor interprets the results. The data is entered into the conclusion and recorded on electronic media.
The implementation and capabilities of MSCT are described in detail in the video:
What does it show
MSCT of the chest organs allows doctors to correctly diagnose in controversial or difficult situations, refutes or confirms the results of simpler studies. Images can provide the following information:
- the presence of a tumor ranging in size from 0.1–0.5 mm in the area of the pleura, lungs, and bronchial roots;
- inflammatory foci;
- metastases, hardening or thinning of bones;
- spinal injuries and hernias;
- consequences of osteoporosis;
- germination of tumors into the mediastinum, pericardium, aortic valve.
Using MSCT of the chest organs, doctors can monitor how effective the chosen treatment method, chemotherapy is, and assess the consequences of the operation.
Advantages and possible risks of MSCT
Advantages of computer MSCT of the chest for the patient:
- minimal number of contraindications;
- visualization accuracy up to 98%;
- painless scanning;
- the ability to visually search for formations without additional biopsy.
Surgeons use the results to build three-dimensional models before surgery and can conduct scientific research.
Radiation dose for MSCT
With multislice tomography, the patient receives a high dose of X-ray radiation. But the tomograph concentrates it at one point, eliminating the load on other organs. The procedure is quick, so risks are reduced to a minimum.
How often can MSCT be done?
Doctors recommend limiting scanning to once every 12 months. But the procedure is so informative that in case of urgent need it is repeated 2-3 times a year. If possible, it can be replaced with a safer MRI of the chest, additional ultrasound and angioscanning of the arteries can be performed.
Alternative Methods
For most patients, there is no difference between computer-based research methods. In fact, they visualize internal organs and systems in different ways, so their functions are different.
Which is better – MSCT or MRI?
Diagnosis of the chest organs MSCT allows you to examine hollow lungs filled with air, rib bones, and cartilage. Multislice tomography converts the data into a three-dimensional model, allowing you to see the lungs from several sides. MRI provides information in the form of standard photographs.