Cancer is the second most common cause of death in developed countries, after diseases of the cardiovascular system. Increased life expectancy and the influence of harmful environmental factors contribute to the steady growth of cancer. In developed countries of Europe and the USA, the incidence of cancer and other malignant tumors is higher than in Ukraine, but the mortality rate as a percentage is much lower. This imbalance arises primarily from insufficiently effective early diagnosis of cancer. The lack of mandatory medical supervision and certain peculiarities of the thinking and way of life of our fellow citizens lead to the detection of cancer only when the chances of being cured are minimal. Recently, medicine has achieved good results in the treatment of many malignant tumors. Some of them, if diagnosed early, can be cured completely.
Symptoms of cancer
Cancer, like other malignant tumors of most organs, does not have any obvious symptoms. The development of cancer begins with the transformation of a tissue area where cells appear that carry an altered division and differentiation apparatus. Sometimes cancer occurs against the background of so-called precancerous processes. Precancerous lesions may have a high or low probability of developing into cancer. For example, a precancerous condition is cervical dysplasia or a gall bladder polyp.
Stages of cancer
The stage of cancer can be simplified in this way: precancerous condition - so in situ (microscopic changes), when the tumor does not extend beyond the site of its formation - local lesion (the tumor extends beyond the boundaries of its organ, but does not affect adjacent tissues) - regional spread (affects adjacent organs and regional lymph nodes) – distant spread (the appearance of metastases in distant organs). An important prognostic factor is the ability of the tumor to invade. Invasiveness is the ability to penetrate adjacent tissues. Tumors with high invasiveness develop quickly and become widespread in a short time. The most striking example is malignant melanoma. Tumors with low invasiveness can remain in the first stage for years in the organ in which they originated, for example, this happens with thyroid cancer or prostate cancer (although not always).
If cancer occurs against the background of a previous disease, the patient can be considered “lucky”. A precancerous condition can, in principle, be detected before cancer develops and radically cured. For example, with a stomach ulcer, a person experiences obvious symptoms, primarily pain, which force them to see a doctor. Of course, there are people who are in no hurry to seek help, which sometimes causes irreparable damage to themselves.
There are no specific symptoms of early stages of cancer. As the tumor progresses, so-called nonspecific symptoms begin to appear: weakness, fatigue, slight increase in body temperature, sweating. Such symptoms can be alarming, and the first test that is prescribed to the patient in this case will be a general blood test. When performing a general blood test, mild anemia (decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and/or red blood cells) and an increase in ESR can be detected. However, such nonspecific symptoms develop already in the later stages of cancer.
Rectal cancer - what is it?
This malignant cancer originates from the epithelium of the rectum. This tumor has the characteristic features of any malignant formation - rapid growth, invasion of neighboring tissues, metastasis.
Men and women are equally susceptible to the disease. An increase in the number of cases is observed from the age of 45, and the peak incidence occurs among 75-year-olds.
Cancer diagnostic methods
The most common methods for diagnosing cancer can be divided into imaging methods and laboratory methods. Imaging methods include radiography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography, radioisotope scanning, and ultrasound. Laboratory techniques include identifying cancer markers in the blood and histological examination of tissue samples. In our article we will describe the role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of cancer and other malignant neoplasms.
Ultrasound diagnosis of cancer
Ultrasound is the simplest and fastest method for early diagnosis of cancer. Although a diagnosis of cancer cannot be made without confirmation by other imaging techniques and biopsy, ultrasound is a very accurate tool. The role of ultrasound is screening, that is, a quick assessment of suspicious changes, sometimes with 100% accuracy. Recently, experience has been accumulated that expands the boundaries of ultrasound capabilities, for example, in the diagnosis of intestinal and stomach cancer. Many modern ultrasound scanners are equipped with a function such as elastography. Elastography allows you to evaluate the structure of the suspicious area and makes the study more accurate.
Traditionally, the most accessible organ for ultrasound diagnostics is the thyroid gland. Diagnosis of thyroid cancer is complicated by the fact that the criteria for malignancy, although described, are still not pathognomonic, that is, uniquely inherent in one disease. An assessment of the vessels of a suspicious node, both geometric and hemodynamic (the spectral characteristics of intranodal blood flow are studied), comes to the rescue. The data obtained from elastography are very encouraging. If the node is large or has other signs of malignancy, a biopsy of the node is prescribed. It is also mandatory to study regional lymph nodes, into which cancer cells can theoretically penetrate.
Ultrasound of cerebral vessels is not very informative for diagnosing cancer, but when performing a duplex scan of cerebral vessels, one can notice displacement of blood vessels or an abnormally developed vascular network, which will give rise to prescribing a clarifying method of examination - MRI.
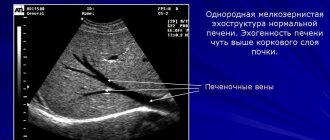
Diagnosis of cancer using abdominal ultrasound can be very accurate. With liver ultrasound, both primary tumors are available for diagnosis - for example, hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, and metastatic lesions. Ultrasound of the gallbladder often reveals polyps that have the potential for malignancy and require observation. Sometimes, with extensive operator experience, tumors of the papilla of Vater can be diagnosed. Diagnosing cancer with pancreatic ultrasound is often difficult due to poor imaging conditions. As a rule, they occur in obese patients and the role of ultrasound diagnostics in the search for pancreatic cancer is lower than CT. However, due to its simplicity and low cost, ultrasound of the pancreas is used very widely. The spleen is clearly visible during ultrasound, but fortunately, malignant neoplasms and metastases are almost never found in this organ. When examining the pancreas, attention is also paid to the nearby retroperitoneal lymph nodes and the lymph nodes of the hilum of the liver. Often, their increase serves as an indirect sign calling for the patient to be prescribed an additional CT scan to look for a possible malignant tumor. Recently, ultrasound of the intestines and stomach is often used. Despite the fact that the sensitivity of the method is limited and it is possible to diagnose a tumor that has already reached a large size, the method is very useful, since it is often the first study that allows one to suspect cancer. Kidney ultrasound is very informative for diagnosing renal cell carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma, Wilms tumor and metastatic lesions. Ultrasound of the bladder makes it quite easy to detect cancer and polyps. True, the diagnosis is confirmed by cystoscopy. Breast ultrasound for diagnosing cancer in combination with elastography is very informative, regardless of the age of the woman being studied. Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages allows one to suspect endometrial cancer and ovarian cancer. Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate gland is performed using elastography and Doppler examination of blood vessels. Many soft tissue tumors can be diagnosed using ultrasound. In this case, elastography is also used. Malignant soft tissue tumors have quite characteristic features, which allows the use of this method with a high degree of confidence.
At what stage can cancer be detected?
Currently, if cancer is detected early, it is more likely to be curable. Therefore, it is very important to identify it at the very beginning of development. For this examination, it is necessary to undergo at least once a year, especially if signs characteristic of malignant neoplasms are observed.
The table provides recommendations on how often it is necessary to examine certain organs in order to identify their diseases, including using ultrasound.
| Organ | Provoking factors | Regularity |
| Breast gland in women | Hormonal imbalance, alcohol, smoking, nutrition | Once a year |
| Stomach, pancreas | Little greenery, small amounts of vegetables and fruits, fried and smoked foods, alcohol abuse | Once a year |
| Intestines | Frequent consumption of fatty and meat dishes, few plant foods | Once every two years |
| Lungs | Smoking, frequent inhalation of harmful substances, polluted areas, especially near factories and other air-polluting enterprises | Once a year |
| Prostate | Inactive lifestyle, diet, sexually transmitted infections. | Once a year |
What does an abdominal ultrasound show?
Thanks to the study, it is possible to establish the cause of the pathology in the following situations:
- abdominal pain or discomfort;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- feeling of a full stomach;
- excessive gas formation;
- intolerance to fatty foods;
- frequent attacks of hiccups;
- feeling of heaviness in the left or right hypochondrium;
- high blood pressure;
- jaundice;
- pain in the lower back;
- weight loss that is not related to diets;
- high temperature without the presence of colds;
- increase in abdominal size;
- as a control over the effectiveness of therapy for pathological changes affecting the organs of the digestive system;
- as a form of routine examination, including also cholelithiasis and organ structure abnormalities.
An abdominal examination can also be prescribed to pregnant women in order to monitor the normal development and location of the fetus.
Abdominal ultrasound showing intestines?
Etiology
The causes of the malignant process have not been precisely established. The connection between colon cancer and adenoma, a benign tumor of epithelial origin, has been reliably established.
There is an increased incidence of cancer in patients who refused surgical treatment of adenoma, and a decreased incidence in people who underwent surgery. People with familial intestinal polyposis who do not receive treatment are more likely to get sick.
Also, the presence of the original tumor process explains the fact that no intestinal cancer measuring less than 3 mm was recorded.
Risk factors for bowel cancer
The presence of benign tumor-like diseases - intestinal polyposis. These diseases are caused by a genetic predisposition, and the risk of malignancy of such polyps is 90-100%.
- Diffuse familial polyposis - it can be suspected in the presence of chronic diarrhea, periodically appearing blood in the stool, and abdominal pain of varying intensity.
- Villous polyposis is accompanied by a large secretion of mucus during bowel movements.
- Turcot's syndrome is diagnosed if, in addition to polyps in the intestine, a tumor is found in the brain.
- Peutz-Jeghers-Touraine syndrome is manifested by a combination of polyps and nevi on the skin of the face.
Polyps in the intestines
Chronic inflammatory diseases of the intestinal tract:
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis is a disease of unknown etiology, characterized by the development of chronic inflammation and necrosis of the intestinal mucosa. Catarrhal colitis is accompanied by chronic diarrhea with bowel movements up to 20 times a day, blood and pus in the stool, and bloating.
- Crohn's disease is a chronic disease that affects different parts of the digestive tract, mainly the ileum and colon. In this case, granulomatous inflammation develops in the wall of the organs. It is also manifested by frequent bowel movements and abdominal pain, which complicates the differential diagnosis.
- Diverticulosis of the large intestine is a pathology of the organ wall, leading to the formation of intestinal protrusions. These pockets can trap feces, undigested debris, and intestinal parasites. They are susceptible to the development of inflammation.
- Chronic colitis - of any etiology.
- Chronic intestinal obstruction - adhesive, occurring after surgery, as a result of spontaneously developed adhesive disease, or dynamic, caused by disturbances in the innervation of the organ wall.
- Dysbacteriosis - caused by taking antibiotics or errors in choosing a diet. The risk of cancer increases if the disease lasts longer than 8-10 years.
External factors:
- Errors in nutrition. There are separate studies showing an increased risk of colon cancer when consuming large amounts of thermally and chemically processed red meat. Lack of fiber, causing impaired peristalsis.
- Exposure to physical and chemical carcinogens - radiation exposure, aniline dyes and other less common substances.
Preparing for an abdominal ultrasound
To get the most accurate result, you need to properly prepare for the study. Gases accumulating in the intestines may interfere with a clear scan. To minimize their number, experts recommend switching to a more gentle diet at least two to three days before the test.
It is advisable not to consume all types of baked goods and not to eat fatty meat. Nuts, legumes, fruits, raw vegetables, various sodas, and fresh milk also cause excessive gas formation, and you should not drink or eat them before scanning. Drinking alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited. When scheduling a test in the morning, it is better to do it on an empty stomach, and you should even refuse plain water.
During the afternoon study, the last meal should be no later than 4-5 hours. It is also not recommended to drink water or any drinks. What an abdominal ultrasound shows can also be clarified by your doctor.
Before the study, for prevention, the specialist may prescribe the use of laxatives that reduce the formation of gases or improve the digestion of medications. On the day of the ultrasound scan, it is imperative to relieve the intestines. If a laxative does not help you go to the toilet, then you can use a cleansing enema in the morning and evening. Patients should bring their own sheets and tissues to the examination.
Will an abdominal ultrasound show pathologies in the liver?
Is ultrasound used in oncology?
Currently, ultrasound is being used more and more in oncology. For example, it can be used to determine whether there is cancer in the stomach or intestines, at what stage, and whether metastases have appeared. This became possible thanks to elastography. Using this method in modern medicine, tissue density is determined. A specialist examining a particular organ uses this method to identify a tumor (the tumor and the healthy part of the organ will have different densities). In addition, the image shows other tissue deformations: enlargement, thickening, curvature, reduction, etc.
Today, treating specialists often choose between traditional biopsy and dynamic observation using ultrasound. A very strong argument in favor of the latter is the fact that it allows one to minimize the number of painful procedures for collecting suspicious organ tissue for examination. Therefore, it is already possible to say with a high degree of probability that ultrasound will soon be the main method for detecting malignant tumors.
The most accessible organ for ultrasound testing is the thyroid gland. Using echolocation (elastography), a suspicious node is examined. If the node is enlarged, darkened, or other changes are visible, the patient is referred for further examination, which will confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Liver examination
An organ such as the liver is the most important not only in the abdominal cavity, but in principle in the entire human body. It is she who is responsible for the synthesis of necessary substances, as well as the neutralization of accumulated harmful toxins. When is liver ultrasound recommended:
- If there is a suspicion of neoplasms, abscesses, injuries.
- When examining a patient whose tests reflect abnormalities in liver function.
- During the treatment of AIDS, hepatitis, cancer or infectious diseases.
- For the selection of contraceptives or treatment of gynecological diseases.
- With a comprehensive analysis of the state of organs.
- As a preventive examination, which is carried out every year.
Using an ultrasound of the liver, a specialist can identify many defects in its condition or functioning. Most often, ultrasound is used to diagnose:
- hepatitis of various origins;
- liver cirrhosis;
- various tumors;
- the presence of abscesses and cystic formations;
- liver obesity (fatty infiltration or steatosis).
By examining the liver, other diseases that are less common can also be seen. Will an abdominal ultrasound show gallbladder disease?
Is cancer visible during the procedure?
Although ultrasound examination of gastric cancer is performed routinely, the informative value of this examination (especially not in specialized oncology clinics) remains low. Whether cancer can be seen on an ultrasound depends on the following factors:
- Sensitivity of information content to the quality of training. In addition, it is not always possible to completely get rid of the presence of gases in the lumen of the stomach (even when using medications).
- Lower quality of visualization of hollow organs. This is the main disadvantage of ultrasound research methods. Therefore, clinical guidelines recommend the use of contrast-enhanced computed tomography if gastric cancer is suspected.
- Depends on the qualifications of the specialist. In most general clinics, gastric examination is carried out by doctors who do not always pay attention to nonspecific signs of the oncological process.
- Use of outdated equipment. In small regional centers, ultrasound is usually performed on devices that are more than 5-7 years old, which reduces its information content.
Whether an ultrasound will show stomach cancer depends on the qualifications of the doctor. A stomach problem can be detected in large oncology clinics, where such patients are diagnosed every day.
Please note: It is impossible to make a diagnosis of stomach cancer based on ultrasound. It is imperative to supplement the diagnostic program with gastroscopy, biopsy with cytological examination and computed tomography with contrast.
Gallbladder examination
A scan is prescribed to determine the motor functions of the gallbladder, which is located in the abdominal cavity. To determine its motility, the number of contractions of the organ over a certain time interval is measured. Ultrasound makes it possible to determine:
- dyskinesia of any type (hypo- and hypertonicity, sphincter insufficiency, spasms);
- inflammatory pathologies: cholangitis, cholecystitis, cholecystocholangitis. Ultrasound also makes it possible to determine the specific course of these diseases, their phase, features of inflammation, and localization.
It is worth noting that on the day of the examination it is not advisable to drink or eat until the end of the ultrasound.
What an ultrasound of the abdominal organs shows is of interest to many.
Study of vessels located in the abdominal cavity
The study is based on the fact that it allows penetration into blood vessels due to the reflection of sound waves from red blood cells. These waves, after certain transformations, appear on the monitor in the form of a color image, which allows you to determine the presence or absence of pathologies. Ultrasound, or Doppler Doppler, of blood vessels makes it possible to analyze:
- venous portal system;
- mesenteric superior artery;
- iliac arteries;
- celiac trunk;
- vena cava and other vessels.
What pathologies will the study show?
Using ultrasound, the following pathological conditions can be determined:
anatomical abnormalities of the stomach;
- gastritis with hypersecretory state;
- benign and malignant neoplasms of the stomach;
- peptic ulcer;
- metastases of tumors from other localizations;
- intragastric bleeding;
- enlargement of the lower esophageal veins (with increased pressure in the portal vein system of the liver);
- narrowing of the antrum of the stomach;
- the presence of third-party bodies;
- enlargement and inflammation of nearby lymph nodes.
What does an abdominal ultrasound show in women?
The patient is sent for an urgent examination (ultrasound) and in case of suspicion of the following pathologies:
- liver abnormalities;
- gallstone disease;
- cholecystitis;
- abnormalities of organ development;
- pancreatitis of any form (acute, chronic);
- aortic (abdominal) aneurysm;
- tumors;
- to assess the prevalence of neoplasms (if any);
- hepatitis.
The presence of menstruation does not affect the procedure at all. With menstruation, as well as without it, this technique shows the same result. During the examination, at the doctor’s request, you will need to briefly hold your breath several times. Diagnostics is carried out in real time, which ensures the most reliable result at the end of the study. Thus, in 20-30 minutes spent in the ultrasound room, you can get complete information about the functioning of all the patient’s internal organs.
How to determine it yourself?
If a person suspects the development of cancer, then before visiting the hospital, you can conduct a rapid test for the presence of hidden blood inclusions in the stool. The rapid test is sold at any pharmacy, and when using it you must follow the instructions. To do this, you will need a fragment of feces, which is diluted with a special solution and placed in the test indicator window. Next, according to the instructions, you need to check the outcome indicators and understand whether there is a risk of developing cancer. This home method of stool analysis has several advantages:
- accurate diagnostic performance;
- no preparatory procedures are needed;
- quick results;
- no contraindications or dangers in use.
Ultrasound of the pancreas and stomach
Most often, a stomach examination is prescribed if the patient has an ulcer or gastritis. However, it is advisable to undergo an ultrasound in case of systematically manifested heartburn, constant belching, diarrhea and vomiting.
During research, tumors of a malignant and benign nature, disorders in the gastric walls, catarrhal inflammations, ulcers, various types of oncological diseases, stenoses that can develop in the initial stages with virtually no symptoms may be discovered. Thanks to the examination of the pancreas, pancreatitis can be detected in a timely manner. What else will an abdominal ultrasound show in adults?
General information
Currently, even in the conditions of modern medicine, experts find it difficult to answer unequivocally what is the true cause of the occurrence of tumors in the kidneys. Doctors identify only a number of different provoking factors, including: hereditary predisposition, inflammation, the presence of stones, radiation, bad habits, chronic infections, disorders of the immune system.
Angiomyolipoma is a benign kidney tumor. Source: urologia.expert
Doctors also note that on ultrasound, a kidney tumor can have a different appearance. If we consider benign formations, the list is as follows:
- Cysts are capsules containing a liquid component inside. If there are many of them, then polycystic organ disease is diagnosed.
- Adenomas - these neoplasms grow over a long period of time, but they do not provoke the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms.
- Lipomas are formed from fat cells, and if they rapidly increase in size, the work of the filtration organ becomes difficult.
- Angiomyolipoma - often detected on ultrasound in the fairer sex, is considered a benign tumor and is diagnosed extremely rarely.
As for tumors of a malignant nature, which, in the absence of proper treatment, can transform into an oncological process. They are often accompanied by severe symptoms: weakness, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, urinary retention, high blood pressure.
Spleen examination
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of the spleen in the human body. This organ is located in the abdominal cavity and destroys those blood cells that have been used up, transforms hemoglobin into hemosiderin and bilirubin, acts as a source of red blood cells and lymphocytes, produces the necessary antibodies, and also serves as an excellent barrier to various foreign particles or bacteria.
The spleen is a rather “delicate” organ, because it senses any changes affecting all organs located in the abdominal cavity and immediately suffers from them. That is why it is advisable to perform liver ultrasound in the following cases:
- if congenital defects are suspected;
- with damage to the peritoneum;
- for cancer and chronic diseases;
- for leukemia;
- for infectious diseases: hepatitis, typhus, mononucleosis, etc.;
- if the formation of neoplasms is suspected.
Examination of the spleen can be performed during routine examinations. Ultrasound makes it possible to detect the presence of a spleen in a patient (sometimes people can be born without it), to determine how “correct” its structure, location, stability of fixation is, whether the size is optimal, whether there is a heart attack or other lesions. Some of these indicators help determine the development of other diseases. For example, an enlarged spleen, that is, splenomegaly, may be a sign of:
- jaundice;
- leukopenia;
- infections;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
This is what an abdominal ultrasound shows in a child.
In some cases, the disease can develop almost unnoticed by a person. The patient may experience only minor negative symptoms, which are often not given any significance. But even minimal deviations in any organ can become a source of serious illness.
“We take cars for technical inspection - we need ourselves too”
— What diseases does ultrasound help diagnose most often?
- Mostly tumors and neoplasms - benign, malignant. Only a biopsy can give a 100% diagnosis: this is when a piece of tissue is taken and examined under a microscope. But we can detect and suspect that the formation is malignant, and quickly refer the patient further.
Sometimes we can determine with a high probability that the formation is benign, and invite the person for a follow-up ultrasound examination in three to six months. This applies to any neoplasm in any organ - be it the mammary glands, prostate gland, abdominal cavity, and so on.
— Are there signals in the body that say it’s time for an ultrasound?
— Ultrasound should not be neglected under any circumstances. For example, abdominal pain. We tell all patients: if the situation is acute, call an ambulance. But you may not even reach that level. Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen in women and men, some formations that a person has felt in himself - in these cases, you definitely need to come for an ultrasound to understand which doctor to go to.
— Should the result be taken as a recommendation?
— Now patients are quite literate, they read a lot of information on the Internet, which is often good - they more or less know where to go and what diseases ultrasound can help with. But, unfortunately, many people think that he can do everything. They come and say: “Something is wrong with me, I need to do an ultrasound.” Ultrasound of what? This method is not a panacea.
Lymphatic structures visualized by ultrasound
Lymph nodes located behind the peritoneum should not normally be visualized. This means that their size is normal and ultrasound cannot detect them. An increase in these organs indicates either the presence of an infectious disease in the abdominal cavity, or that there are cancer cells of the hematopoietic system. In addition, this may mean metastases of a tumor of any organ located nearby.
Survival prognosis
After radical surgery, survival rate for 5 years ranges from 34-68%. The outcome of treatment is influenced by the stage at which the tumor was diagnosed, the condition of the patient himself, his age, and concomitant diseases.
Depending on the stage of the tumor process, five-year survival rate is determined by the following figures:
- Stage 1 – up to 77%;
- Stage 2 – up to 73%;
- stage 3 – 46%;
- Stage 3b – 43%.
Stage 4 is not considered in these statistics. Radical operations are often impossible to carry out, because tumor metastases are disseminated throughout the body. The lethal outcome depends on the general condition of the patient.
When should an ultrasound scan of organs located in the abdominal cavity be performed?
Experts recommend not waiting for the disease to reach its climax, but doing an ultrasound at the first appearance of the following symptoms:
- not too strong, but constant discomfort after eating or prolonged fasting;
- unpleasant odor in the mouth or bitterness;
- sharp or stabbing pain;
- burning and heaviness in the hypochondrium;
- suspicion of an increase in the size of any organ located in the peritoneum;
- increased formation of gases in the intestines;
- abdominal injuries or bruises;
- diagnosed diseases: pathologies of the digestive system, diabetes;
- before preparing for surgical interventions.
How often can you do an ultrasound for cancer?
It is recommended that men after 40, and women after 45, be examined annually by ultrasound. If there is a risk of cancer, for example, breast cancer, the recommendations are different: - from 20 to 30 years - once every 3 years; from 30 to 40 years - every year. When examining the breast on an ultrasound, a fibroadenoma (benign tumor) is also detected, which in very rare cases turns into cancer. But there are risks. Therefore, if you undergo an ultrasound once a year, you have an almost 100% guarantee of defeating this disease.
From this video you will learn more about diagnosing cancer using ultrasound:
Ultrasound of internal organs
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs is a rather long procedure, lasting about half an hour. During this time, the sonologist examines and evaluates the condition of the patient’s internal organs as a whole, their size, location, structure and general condition of the abdominal cavity. An ultrasound will show inflammation in the abdomen, the size of the organs, as well as the presence of fluid and tumors. In the conclusion, both normal data and those that were obtained are described. Do not be alarmed if the actual sizes of the organs differ slightly from the “standard” - the location and size of the organs depend on the age, physique and characteristics of the patient’s body. Interpretation of an ultrasound may take longer and will be performed by the attending physician rather than a sonologist.
Digestive system
It includes the liver and gall bladder, intestines, stomach and pancreas.
The liver is responsible for breaking down fats and ridding the body of accumulated harmful substances. Therefore, for example, when taking potent drugs, doctors recommend taking hepatoprotectors, that is, drugs that protect the organ, improve its functioning and remove poison.
Normal liver values should be approximately as follows:
- The dimensions of the right lobe are up to 12 cm, the left lobe is up to 7 cm;
- The diameter of the portal vein is up to 13 mm, the vena cava is up to 15 mm;
- The diameter of the bile duct is up to 8 mm;
- The angle of the right lobe should be no more than 75 degrees, the angle of the left lobe should be no more than 45.
The edges should be smooth and clear. The liver should be equally dense in structure, without compactions and neoplasms. The ultrasound should show blood vessels and ligaments.
As a rule, the condition of the gallbladder is described together with data on the liver, since these organs are not only located nearby in the abdominal cavity, but also perform the same function: bile, necessary for the breakdown of fats that occurs in the liver, is produced and stored in gallbladder. Diseases such as cholecystitis and the formation of gallstones are associated with improper functioning of the gallbladder.
Normally, this organ should have the following parameters:
- Length – from 6 to 9 cm;
- Width – from 3 to 5 cm;
- The thickness of the organ walls is up to 4 mm;
- The lower edge of the bladder may protrude from the lower edge of the liver by 1 cm.
Ultrasound also shows the size of the gallbladder ducts, through which fluid enters the duodenum and liver. The diameter of the bile duct should be no more than 6 mm, the diameter of the hepatic duct should be no more than 5.
The pancreas produces digestive enzymes, as well as insulin and glucagon. Improper functioning of this organ is fraught not only with pancreatitis and stomach problems, but also with the appearance of diabetes.
A normal pancreas test result should be something like this:
- Head – no more than 32 mm;
- Body – no more than 21 mm;
- Tail – no more than 35 mm;
- Pancreatic duct – no more than 2 mm.
The structure of the pancreas should be homogeneous, and the density should correspond to the density of the liver or be slightly higher. The contours of the organ must be clear. As in other cases, blurred contours and increased sizes indicate tissue inflammation and swelling. Cysts, tumors and stones in the ducts will also be noticeable during an ultrasound examination.
Ultrasound of the intestines and stomach is rarely done, since these are hollow organs through which ultrasound passes poorly, making it impossible to detect mucosal lesions. But the test shows the presence of fluid or foreign bodies in the cavities, which can be useful in making a diagnosis.
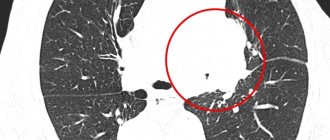
Will ultrasound help detect metastases?
With cancer, metastases very often appear - new foci of malignant neoplasms. Most often they are found in the lymph nodes, liver, and lungs. With various cancerous lesions of organs, metastases appear in certain places. For example, with stomach cancer, metastases usually appear in the lungs, liver, and peritoneum. For lung cancer - in the adrenal glands, another lung, liver, etc.
Ultrasound can also detect metastases
Therefore, first of all, in case of cancer, it is necessary to check the relevant organs. The stages of diagnosing metastases are conventionally divided into two stages:
- initial examination (immediately after cancer diagnosis);
- secondary, observation by a doctor after treatment.
In modern medicine, metastases are detected not only using radiography, tomography, but also ultrasound.
Spleen and lymph nodes
The spleen, along with the kidneys and liver, is involved in blood purification. This organ produces antibodies, filters the blood from bacteria and protozoa, and destroys spent blood cells.
Disturbances in the functioning of this organ are less common and do not lead to such fatal consequences as disturbances in the functioning of the liver or pancreas. In its normal state, the organ will be approximately 12 cm in length and 8 cm in width. With inflammation and the appearance of neoplasms, the dimensions of the organ will increase, and the echostructure will be heterogeneous. If the transcript of the ultrasound results indicates that the spleen is enlarged, you should take a closer look at your health: often inflammation of this organ indicates an infectious disease or problems with blood circulation. If an ultrasound shows a heterogeneous echostructure, this may indicate the death of spleen tissue.
The conclusion describes the number of examined and pathologically changed lymph nodes, their location, shape, size and internal structure. As with the spleen, pathologies in the lymph nodes often indicate diseases of other organs.
Kidneys and ureters
Ultrasound of the kidneys is often prescribed separately from ultrasound of other organs. This study helps to identify organ dysfunction, tumors, the presence of stones and other unpleasant diseases. Normal kidney parameters should be something like this:
- Size – 5*6*12 cm, thickness of the parenchyma, that is, the outer shell – up to 25 mm. One kidney may be slightly larger than the other, but not more than 2 cm;
- The structure is smooth, the contours are clear, echogenicity is at the level of the liver or slightly lower;
- Mobility during breathing – no more than 3 cm.
Along with the kidneys, the doctor may examine the ureters and adrenal glands. They should be free of new growths, stones and sand.
Other types
Sigmoidoscopy is a method of examining the rectum through a sigmoidoscope.
Irrigoscopy is based on the use of X-ray irradiation of a person using a contrast agent. The image will show the size of the tumor, the condition of the intestinal mucosa, and other pathologies. During irrigoscopy, the patient does not experience pain or discomfort. The method of sigmoidoscopy is also used, showing changes in the mucous membrane at a distance of 30 cm from the anus. An endoscope is used for this.