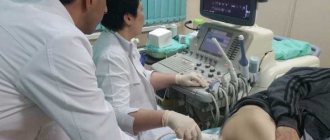
Ultrasound diagnostics is an effective, safe method for identifying abnormalities of the thyroid gland and associated regional tissues and organs. The procedure is easy to perform, low price for the service and easy to prepare.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland allows you to detect tiny formations in the tissue of the gland that produces specific hormones. An important organ responsible for the condition of bone and muscle tissue. The functioning of the heart, brain, and the quality of the body’s metabolic reactions depend on the proper functioning of the endocrine gland.
What does an ultrasound of the thyroid gland show?
The gland is located shallow, so an ultrasound examination makes it possible to examine it completely, determine the general condition of the organ and compare its indicators with standard ones. An ultrasound will not show those parts that are located behind the trachea or chest, but this does not interfere with identifying changes in the thyroid gland and determining the diagnosis.
Clinical manifestations of thyroid diseases are usually mild, so identifying the occurrence of pathologies without ultrasound diagnostics is problematic.
Dimensions, volumes
Ultrasound can determine the size of the thyroid gland very accurately by measuring the thickness of the isthmus connecting the lobes of the “thyroid gland”.
Organ volumes may differ from standard templates, depending on the patient’s body weight. When measuring organ volumes in children, it is necessary to take into account gender and age.
Organ structure
Normally, the structure of the organ is homogeneous and is characterized by granularity.
Loss of homogeneity of the thyroid gland may indicate the following problems:
- inflammatory process;
- diffuse toxic goiter;
- autoimmune thyroiditis.
Echogenicity
Echogenicity is the tone, shade of the tissue of the gland being examined on the monitor. Ultrasound is reflected from the tissues of the organ, and this process is displayed on the screen in the form of color shades.
Echo signs of a healthy thyroid gland are visualized in gray. With low echogenicity, less often with increased echogenicity, there are inflammatory processes in the organ. In this case, the “thyroid gland” becomes darker than the muscles located next to it.
Normally, on the screen of ultrasound equipment, the thyroid gland is lighter than the nearby muscles.
Extra options
When diagnosing the thyroid gland, the following parameters can be additionally examined:
- Organ structure. Normally, the gland consists of 2 lobes and an isthmus. A pyramidal lobe or tissue projections may be present.
- Location of the gland. It can be low, sometimes it can be located just below the trachea.
- Focal formations are assessed if there are nodules, cysts or calcifications.
- Presence, structure, size, structure of visible lymph nodes. They can be used to diagnose signs of tumor formation (the appearance of microcalcifications, cystic transformation, increased blood flow in the tissues of the lymph node). Normally, areas are visualized in red.
- The structure and degree of response to ultrasound of the salivary gland located in the parotid region.
- The structure and size of the larynx and soft tissues of the neck - areas located next to the thyroid gland are visible.
- Condition of the follicles. Normally there are about 30 million.
This video talks about the structure of the thyroid gland and the norms of the organ's indicators. Author: Zelimkhan Magomedov.
How is ultrasound performed?
Long preparation is not required before the study, but there are several rules:
- It is recommended not to eat a few hours before
- If you plan to do Doppler ultrasound, you must take an iodine-containing drug 3-4 hours before
- Before lying on the couch, you need to remove all jewelry from your neck and free yourself from your collar, scarf and any other element of clothing or decor.
Doppler ultrasound is a type of analysis that allows you to combine a black and white image of the thyroid gland with a color display of blood flow. It allows you to determine:
- Patency of blood vessels
- Violations of their walls (thinning/thickening)
- Direction and speed
- Resistance index
The procedure itself goes like this:
- The patient lies down on the couch
- A special cream is applied to his neck
- The sonologist moves the device over the thyroid gland, and at this time the data is transmitted to the screen and recorded on the computer hard drive
The total research time is about 15 minutes.
Norms of ultrasound of the thyroid gland
Normally, the thyroid examination protocol should be deciphered as follows:
- the shape of the gland is standard;
- contours are clear and even;
- structure – homogeneous;
- density – standard;
- nodules and cysts – absent;
- lymph nodes are not enlarged.
For men, women and children, the norms for thyroid ultrasound indicators are different.
Normal organ volume for men and women
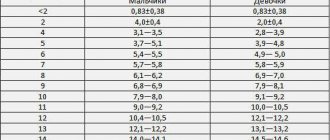
Table of normal sizes of the thyroid gland in adults:
| Patient weight, kg | Normal volume, cubic meters cm | Normal volume, cubic meters cm |
| In men | Among women | |
| 50 | 18 | 15 |
| 60 | 20 | 18 |
| 70 | 23 | 21 |
| 80 | 28 | 25 |
| 90 | 30 | 28 |
| Over 100 kg | 34 | 32 |
Normal sizes of the thyroid gland in children:
| Age, years | Floor | 0-2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| Volume, cubic cm | Girls | 0,84-1,22 | 2-2,4 | 1,3-1,7 | 1,-2,2 | 2,1-2,9 | 2,4-3,4 | 3,1-4,3 | 4,0-5,6 | 4,2-5,8 | 4,4-6 | 6,3-8,7 | 7-9,6 | 7,2-10 | 9-12,4 |
| Boys | 0,84-1,22 | 2-2,4 | 1,4-2 | 1,8-2,6 | 2,1-2,9 | 2,8-3,8 | 3,1-4,3 | 3,4-4,6 | 3,6-5 | 4,2-5,8 | 5-7 | 6,3-8,7 | 6,9-9,5 | 8,1-11,1 |
Left and right lobe, isthmus
Normally, the thyroid gland has two lobes and an isthmus that connects them. Its length should not be more than 5 mm.
The normal sizes of shares are:
- height 4 cm;
- width 2 cm;
- thickness 2 cm.
Individually, a deviation in the size of the thyroid lobes is possible from 1 to 5 mm, and the patient should not have any complaints.
Outlines of the thyroid gland
This is the outline of an organ on the monitor during an ultrasound. Normally, the “thyroid gland” has clear and continuous contours of the entire set of tissues. In the picture this is reflected by the heterogeneous color of the fabrics, which indicates their different densities.
Regional lymph nodes
In a normal state, the lymph nodes are not enlarged and have an even and clear contour. The length is usually half the width. There should be no increased blood flow in the tissues of the lymph nodes, and especially cysts, since both of these signs are a symptom of the presence of a malignant lesion.
Thyroid nodules
These are homogeneous black formations, which are also called follicles. If neoplasms no larger than 4 mm are visible on ultrasound, this is not a deviation from the norm. Pathology can be considered the presence of formations larger than four millimeters.
4 types of echogenicity
The echogenicity of the “thyroid gland” on the monitor has a gradation from dark gray tones to light gray. If black is present, this indicates the presence of a malignant tumor.
The interpretation of the results of ultrasound of the thyroid gland contains the following descriptions of the echogenicity parameter:
- Isoechogenicity. This indicates that the tissue is normal.
- Hyperechogenicity. This is a light area with no diffuse tissue.
- Hypoechogenicity. There may be dark areas with an inflammatory process.
- Anechoicity. The black zone of the organ is interpreted as cysts or tumors.
This video explains what symptoms you should pay attention to first when self-examining your thyroid gland. Provided by the Boris Uvaidov Health channel.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparing for a thyroid ultrasound does not require much time, but there are certain requirements. When the sensor presses on the neck, nausea and vomiting sometimes occur. This point should be taken into account and, if necessary, not eat before the procedure itself. When conducting diagnostics in women, the most reliable results are revealed 6 - 7 days after the end of menstruation.
For the examination, clothing that does not restrict movement is required. During the examination, the patient lies on his back. The doctor must have free access to the neck area. Clothes that can be loosened are best. If the neck is covered, the doctor will ask you to undress to the waist. You must have a towel with you to remove the lubricating gel after the examination.
You must first remove all jewelry from the neck area that interferes with the full-fledged work of the specialist. To reduce discomfort, the patient needs to relax and distract from the doctor’s actions. If necessary, you can take mild sedatives. The day before the procedure, completely abstain from alcohol.
During the examination, you must remain completely still. This will shorten the procedure time. In some cases, it will be necessary to stop taking iodine-containing medications several days before the examination. The doctor who referred you for the ultrasound should warn you about this.
Degree of pathological changes
In medicine, there are 5 degrees of pathological changes:
- The first degree means that an increase in size or deviation of parameters from the norm when palpating the “thyroid gland” can be determined visually.
- Second degree. Organ and tissue nodes are easily identified during anterior examination and during swallowing.
- The third degree determines pronounced thickening of the neck and excess size of the thyroid gland.
- The fourth degree indicates that the pathological process is already affecting the functions of other organs. There are signs of thyroid dysfunction.
- The fifth degree is characteristic of an increase in the size of the thyroid gland. At the same time, it is difficult for a person to swallow, shortness of breath and coughing begin.
Indications for analysis for an adult patient
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland is prescribed in the following cases:
- The patient is pale and does not feel well
- He experiences a sore throat/neck and does not have colds
- Hormone tests show abnormalities
- Arrhythmia
- Drowsiness, apathy and lethargy
- Sudden obesity or exhaustion
- Too frequent mood swings
When planning pregnancy, such a study should also be carried out.
Common pathologies detected on ultrasound
An ultrasound of the thyroid gland can show pathologies that can be divided into two types: an increase in the size of the organ and abnormal production of hormones.
The state of the thyroid gland is normal, with hypo- and hyperthyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a disease associated with a reaction to low levels of thyroid hormones. A symptom may be reduced organ size. There are several degrees of this disease.
Primary hypothyroidism is caused by the following factors:
- hypoplasia or hyperplasia of the thyroid gland;
- congenital disorder of thyroid hormone synthesis;
- thyroiditis;
- nutritional characteristics (iodine deficiency, excess thiocyanates present in cabbage, rutabaga, turnips, turnips and cassava, excess calcium and lithium ions that block iodine uptake);
- medical actions (gland removal, radiation therapy, taking medications).
Secondary hypothyroidism is associated with hypopituitarism or a defect in the synthesis and transport of thyroliberin from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland.
Tertiary is associated with inactivation of circulating in the blood:
- T3 and T4 autoantibodies;
- TSH autoantibodies;
- proteases in sepsis.
There may be a connection with a decrease in the sensitivity of target cell receptors to hormones.
Hyperthyroidism
Unlike hypothyroidism, this syndrome is associated with an increased level of thyroid hormones in the blood. Its degree depends on their number. One of the symptoms of this disease is a severe enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Euthyroidism
According to external manifestations, this is the normal functioning of the thyroid gland, the absence of symptoms of hypo- and hyperthyroidism. Euthyroidism does not mean that the thyroid gland is healthy. Most often, this diagnosis is made in conjunction with goiter - euthyroid goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland with normal organ function). This condition is usually associated with iodine deficiency.
Nodular goiter
Tissue proliferation syndrome, or nodular goiter, occurs:
- uniform (diffuse);
- uneven;
- focal with the appearance of formations (colloid).
In this case, the pituitary hormone does not cope with the complete elimination of iodine deficiency, which leads to the appearance of nodes.
Diffuse toxic goiter
This disease is associated with hereditary autoimmune abnormalities. It is characterized by a symptom such as exophthalmos - a forward displacement of the eyeball (bulging of the eyes).
Since thyroid hormones have different physiological functions, this disease can manifest itself in the following pathologies:
- Various heart disorders. Symptoms may include arrhythmia, tachycardia, high blood pressure, and chronic heart failure.
- Disruptions in the endocrine system, namely weight loss regardless of diet, heat intolerance, menopause or cycle disruptions in women.
- Dermatological problems such as increased sweating, changes in the shape and structure of nails, erythema, swelling of the extremities.
- Neurological problems. They may manifest themselves in the form of tremors, weakness, headaches, myopathy, anxiety and restlessness, and insomnia.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms, which manifest as diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
Cyst
On ultrasound, the cyst looks like a formation filled with fluid.
If there is an inflammatory process in the patient, the following may be detected:
- pain in the front of the neck;
- temperature increase;
- hoarseness of voice.
If a cyst is suspected, the puncture method is used together with ultrasound. It is used to analyze for the presence of cancer cells to exclude the presence of cancer.
The disease is accompanied by inflammatory viral or bacterial processes. In patients suffering from this disease, the volume of the “thyroid gland” increases, and the cyst can grow into the surrounding tissues and merge with them.
Thyroiditis
This is an inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can combine several diseases. The most common is autoimmune thyroiditis (AIT). This is a chronic inflammation of the thyroid tissue, which has an autoimmune genesis and is associated with damage and destruction of the follicles and follicular cells of the gland. Typically, AIT occurs without symptoms, and is occasionally accompanied by an enlargement of the thyroid gland.
To diagnose autoimmune thyroiditis, in addition to ultrasound, you need:
- conducting clinical tests;
- histological examination of the material obtained after a fine-needle biopsy.
Neoplasms
They look like high-density formations that have uneven contours on ultrasound. Most often they are small, called nodes. In some cases, enlarged lymph nodes indicate the development of a tumor of the endocrine organ.
This video explains how thyroid diseases are diagnosed using ultrasound. Presented by the Pharmamed channel. RF St. Petersburg".
What to do next
After any deviations are identified, additional examinations are carried out. A CT scan, MRI, scintigraphy, or aspiration biopsy may be prescribed. Without them, an accurate diagnosis cannot be made. Additional studies are necessary to confirm or refute the suspicion of a particular disease.
You can get an ultrasound for free in clinics. Once the diagnosis is made, drug therapy may be prescribed. In case of iodine deficiency, its optimal amount is restored. Next, an ultrasound is done as a check and prevention. After 60 years, the procedure should be performed annually.
What should be in conclusion
At the end of the thyroid examination, the doctor gives the patient a form with the ultrasound results. This is a document that is drawn up in the form of a protocol. You can decrypt it yourself.
The conclusion must include the following information:
- the condition of the cervical lymph nodes, is there inflammation;
- the condition of the parathyroid glands, size and volume, as easily visible on ultrasound;
- echo signs;
- shape, size and volume of the thyroid gland;
- organ location;
- description of contours;
- presence of formations and their characteristics;
- state of blood flow.
Frequency of examination
A little preparation for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland is carried out each time before diagnosis. The frequency of examination depends on the reason for which the doctor prescribes.
Women under the age of 50 are examined every 5 years. If annual preventive examinations require this, then the woman undergoes it every year. At some enterprises with a certain hazard class, people are not allowed to work without such medical examinations.
If a woman is over 50 years old, then the frequency of examinations reaches 2-3 times a year for the timely detection of thyroid diseases. When diagnosing a disease or having complaints from the patient, diagnostics are prescribed every 4 to 6 months.
In case of doubt about the diagnosis or to clarify it, the frequency of studies can be up to 3 times a week. The doctor prescribes diagnostics at the slightest suspicion of a malfunction of the thyroid gland. Particular attention is paid to women over 50 years of age, as well as those planning pregnancy. Persons who receive large doses of ultraviolet radiation in their professional activities undergo an ultrasound scan twice a year.
Photo gallery
Photo of chronic thyroiditis on ultrasound of the thyroid gland
Sample ultrasound protocol for the thyroid gland
Photo of thyroid cancer on ultrasound
Take care of your health - contact MEDSI
MEDSI specialists
– candidates and doctors of medical sciences, endocrinologists of the highest qualification categories – use the latest equipment for performing ultrasound of the thyroid gland:
Pro Focus 2202 Philips iU22.
Here each patient receives:
- Comfort and respectful treatment
- Diagnostics and support of qualified personnel
- Urgent consultations and ultrasound – appointments can be made by calling 8
- Modern examination equipment from Philips
Video
This video describes in detail how an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland is performed. Presented by the Mortenenko channel.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the HROMOSOMA website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes (100.00%)
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the benefit of the article: Rate the author ( 1 vote(s), average: 5.00 out of 5)
Discuss the article:
Diagnosis of women
Women need more preparation than men. The latter will only need to not be late for the procedure. In women, the effectiveness of the procedure depends on the menstrual cycle. The most optimal time would be between 7-9 days after the discharge ends.
Testing should not be done during menstruation
During pregnancy
In pregnant women, impaired thyroid function is most common. Because her body is being rebuilt to meet the needs of the baby. The hormones produced by this organ not only affect the development and growth of the fetus, but also the course of pregnancy. Impaired activity of the thyroid gland can lead to miscarriage.
If the doctor suspects organ dysfunction, the woman is prescribed an ultrasound. This diagnosis is completely safe for the unborn baby. It can be carried out without any fear for the baby’s health. Any violation of an organ negatively affects its health, causing deviations in growth, development, and decreased intelligence.