Ultrasound – what is it and why is it needed?
Ultrasound examination of the endocrine gland is a simple and safe procedure for the patient
. It is necessary to determine the presence (or absence) of pathologies, inflammation, neoplasms or other problems in this organ.
The study helps to identify:
- Enlargement or reduction of an organ
- Presence of nodes, cysts and tumors
- General inflammation or tissue damage
- Obstruction of blood flow
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes
- Impossibility of pregnancy
The examination mechanism is quite simple and painless:
- The patient is placed on a chair or couch in such a way as to provide access to the neck
- The doctor applies a special composition to the patient's throat
- Then the doctor picks up the sensor and moves it from different sides over the part of the body being examined.
- During the process, signals about the state of this endocrine organ are transmitted to the monitor and are also recorded on magnetic media
- The result is an image and data on the condition of the organ, which the doctor compares with normal
If any signs of abnormalities are found in the tissues or structure of the thyroid gland, the doctor prescribes other tests to clarify, confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Ultrasound capabilities
Since the thyroid gland is not located deep under the skin, modern ultrasound equipment allows us to study its entire structure in detail, in addition to the areas that are hidden by the sternum or trachea.
During an ultrasound scan of an organ, the following characteristics of the organ are revealed:
- Outlines;
- Structure;
- Structure;
- Echogenicity;
- Location.
Below, each of these points is discussed in more detail.
Normal thyroid gland on ultrasound
Outlines
In a normal state, the boundaries of the gland are clear, but with pathological changes, such as inflammation or neoplasms, they become, on the contrary, unclear.
Structure
A healthy glandula thyreoidea includes two lobes connected by an isthmus. Quite often there is an additional structural unit in the form of a pyramidal lobe, the location of which is the midline of the body of the organ upward from the isthmus.
Sometimes there are small outgrowths of tissue, not exceeding 10 mm in length. They stretch in the direction of the lower poles of the lobes - the horns of the thymus gland. Endocrinologists call these outgrowths “anti-pyramids”.
In some cases, intrauterine developmental disorders of the organ occur, in which the thyroid gland may not divide into two, but completely move to one side (agenesis or aplasia of one of the lobes). If glandula thyreoidea does not develop at all, then this condition is called complete aplasia.
Structure
A normal organ has a homogeneous structure with a characteristic granularity. Its heterogeneity indicates the presence of inflammation.
Features of calculating the linear dimensions of various structural elements of the gland are given in the following table:
| Anatomical zone of the gland | Available sizes for ultrasound measurements |
| Right lobe | All three linear dimensions perpendicular to each other |
| Left lobe | -//- |
| Isthmus | Antero-posterior thickness |
Evaluation of focal formations is carried out in the presence of cysts, nodes and calcifications.
Different types of thyroid calcifications
Echogenicity
This characteristic implies the tone or shade in which a certain area of tissue will be visible on the display of the ultrasound machine. With its help, you can characterize lymph nodes, determining their presence, size, structure, structure.
Also, based on this criterion, signs of various types of neoplasms are diagnosed (microcalcifications, cystic transformation, increased blood flow in the lymph nodes).
Location
The thyroid gland may be located:
- low;
- typically;
- aberrant (pathological).
In addition, during an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, you can study some organs and tissues located in close proximity to it:
- trachea;
- larynx;
- esophagus;
- nerve trunks;
- salivary glands;
- The lymph nodes;
- parathyroid glands;
- large blood trunks.
The thyroid gland contains many important anatomical structures.
In some cases, ectopic (displaced) fragments are located near the main body of the thyroid gland, for example, to a level below the trachea.
Education
Normally, there should be no pathological inclusions in the structure of the thyroid tissue. What does an ultrasound of the thyroid gland show in the presence of pathological formations?
This diagnostic method allows you to evaluate:
- type of formation (nodule, cyst or calcification);
- their number;
- size;
- echogenicity and structure.
A small nodule in the thyroid lobe was detected by ultrasound
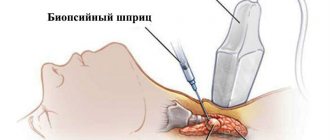
Important! All large thyroid nodules, whose diameter exceeds 10-15 mm, are subject to puncture biopsy followed by histological examination. This diagnostic test is performed to exclude malignant neoplasms of the organ.
Condition of the lymph nodes
Normally, regional thyroid nodes are not enlarged and painless.
Their various changes may indicate:
- development of inflammation:
- increase in l/nodes in size;
- signs of lymphadenitis;
- formation of a malignant neoplasm:
- presence of microcalcifications;
- increased blood flow in regional lymph nodes;
- cystic transformation.
The picture shows the regional lymph nodes of the neck
Important! Even if nothing worries you, it is important to undergo regular preventive examinations. Medical instructions recommend checking your thyroid function once a year. This is especially true for women over 35, whose risk of developing endocrine pathology is much higher than for men.
The average price for thyroid ultrasound in diagnostic centers is 900 rubles.
When should you get tested?
The frequency of ultrasound examination of the endocrine gland depends on individual characteristics such as age, medical indications, and the presence or absence of ailments. Individual parameters:
- Age up to 50 years: preventive examination every five years
- For older people over 50: prophylaxis every two to three years
- During pregnancy and its planning: to eliminate negative effects on the fetus
For some medical indications and ailments, you need to be examined as soon as possible:
- In the presence of already established endocrine problems
- To monitor treatment or its results
- If there is a risk of recurrence of endocrine gland dysfunction
- With a noticeable enlargement of the thyroid organ, palpable seals and nodes
- Sudden weight loss or weight gain
- In case of unstable emotional state – apathy, nervousness
Frequent pathologies encountered during ultrasound interpretation
The pathologies listed below account for 90% of diagnosed thyroid diseases.
- Hypothyroidism is a pathology caused by insufficient production of thyroid hormones and is characterized by a decrease in the size of the gland. The condition is characterized by a reduced level of thyroid hormones in the blood. Clinical manifestations depend on age and severity of the disease.
- Thyroiditis causes an enlargement of the thyroid gland due to swelling. There is pain in the neck, radiating into the ear, pain when swallowing, fever and headaches. Inflammation is caused by bacteria or viruses. Ultrasound shows thyroiditis with a heterogeneous structure and increased echogenicity.
- Diffuse toxic goiter causes an enlargement of the gland. The pathology is characterized by increased excitability, irritability, rapid heartbeat and weight loss. A distinctive feature of the disease is rare blinking and an increase in the volume of the muscles of the eyeball.
- Nodular goiter is diagnosed by a dense lesion with clear boundaries. On palpation, pathology can be detected by pronounced tissue compaction.
- The cyst in the picture looks like a rounded cavity with clearly defined contours containing fluid inside. With a purulent lesion, the patient feels pain in the neck and the temperature rises.
- Tumors of a benign and malignant nature are compactions in tissues with clear (with a benign process) or blurred boundaries (with cancer).
Preparing for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland
For this test - ultrasound of the thyroid gland - no special preparation is required. There are no restrictions on foods that can be eaten on the eve of the study.
But there are a number of recommendations:
- Elderly people should not eat before the procedure, as they may feel nauseous. This is due to age-related changes in the body
- Preparation for ultrasound of the thyroid gland in women is due to the fact that they are recommended to undergo this examination on days 7-9 of the menstrual cycle in order to avoid possible distortion of the result
- Before the procedure, it is necessary to free the neck from various interfering elements: collars, jewelry, etc.
- Preparation for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland for children does not differ from that for adults. But so that the child does not get scared, parents need to tell him about exactly how the procedure will take place, what the doctor will do and why
Indications for the study
In most cases, the endocrinologist refers the patient to an ultrasound scan if, upon palpation, he finds a compaction in the thyroid gland, a bumpy surface, or an increase in size. Indications also include:
- patient complaints of difficulty swallowing, sensation of a lump in the throat, coughing, hoarseness;
- weight loss, tachycardia, hand tremors, nervousness and increased excitability, heat intolerance;
- swelling of tissues, weight gain, constipation, chilliness, slowness of movements and thinking;
- detection of an increase or decrease in hormones of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, hypothalamus.
Ultrasound is also prescribed in the absence of clinical manifestations:
- patients whose professional activities come into contact with harmful chemical compounds and radiation;
- with a hereditary predisposition to thyroid diseases;
- living in areas with iodine deficiency;
- taking any hormones for a long time;
- after 45 years;
- when planning pregnancy (congenital hypothyroidism can cause mental retardation in the child);
- women with menstrual irregularities;
- living in unfavorable regions with iodine deficiency.
Can ultrasound be performed on pregnant women and children?
Since the procedure is safe and painless, it is also suitable for children and pregnant women.
Small child
can be examined while sitting on the parents' lap. If your baby has been exposed to any stress, it is recommended to consult a doctor, as this condition can affect the functioning of the glands.
Women
It is recommended to do an ultrasound of the endocrine gland both at the planning stage of pregnancy and when it has already occurred. Since the developing fetus takes resources from the mother’s body, it is necessary that all her organs work correctly. Disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland can lead to hypothyroidism and negatively affect the health of the developing child.
For those who are trying to get pregnant but cannot
, you also need to contact an endocrinologist for diagnosis, since the problem may be in this gland of the body.
Decoding the results
Ultrasound diagnostics is a highly informative examination method. An endocrinologist has the right to decipher its results.
During the procedure, the doctor pays attention to several parameters
- Location: The thyroid gland in proper condition should be located in the front of the neck, in the center or at the bottom. Normally, the location is considered typical; in case of deviation, it is considered aberrant (for example, the placement of an organ at the root of the tongue).
- Structure: a healthy gland resembles a butterfly - it has 2 flat sections that are connected by a small isthmus. A common pathology is the formation of additional lobes or outgrowths. If there are no deviations, the structure is considered classic.
- Size: each age group has its own norm for the size of the gland. The normal dimensions of the thyroid gland in an adult are: length - 2.5-4 cm, width - 1.5-2 cm, thickness - 1-1.5 cm.
- Volume: the parameter is calculated by the sum of the volumes of both lobes of the thyroid gland. Each lobe has its length, width and thickness measured. Normally, the volume of the right and left parts of the thyroid gland should be approximately the same.
Standard indicators of thyroid volume:
- for females - less than 18 cm³;
- for men – less than 25 cm³.
However, the indicators are relative and may vary depending on the patient’s weight. During the examination, the doctor adjusts the norm and enters the data into the report.
The normal volume of the thyroid gland is presented in the table below.
| Weight, kg | Thyroid volume/cm³, men | Thyroid volume/cm³, women |
| Less than 40 | 12,5 | 12,1 |
| 41-50 | 15,5 | 14 |
| 51-55 | 17 | 15,5 |
| 56-65 | 20 | 19 |
| 66-75 | 25 | 22 |
| 76-85 | 28 | 25 |
| 86-95 | 30 | 28,5 |
| More than 96 | 34 | 32 |
Other organ parameters are also assessed.
- Contours: the indicator characterizes the visibility of the boundaries of the organ. It can be clear or fuzzy. Blurred contours indicate inflammation or neoplasms.
- Echogenicity: the parameter determines the ability of an organ to transmit ultrasonic waves through itself. Healthy tissues on the screen are an even gray color. If echogenicity is reduced, the shade becomes darker; if echogenicity is increased, it becomes lighter. The changes are caused by inflammation, benign and malignant tumors. When interpreting ultrasound, echogenicity is indicated “without features.” A heterogeneous echostructure can be local (with individual areas of heterogeneous color), diffuse (with heterogeneity of the entire organ), mixed.
- Nodes: in the normal state of the organ there are no neoplasms. When identified, they are classified depending on their size. Follicles are formations with a diameter of up to 4 mm (permissible deviation, does not require treatment). Focal - formations with a diameter of 4 to 10 mm (do not require treatment, the patient is advised to have regular ultrasound scans every six months). True nodes or tumors are formations with a diameter of more than 1 cm. Cysts are hollow formations with fluid inside. Neoplasms larger than 1 cm can be benign (adenoma) or malignant (cancer). A clear sign of oncology is blurred boundaries and black color of the organ.
- Regional lymph nodes: in a healthy state, they have a smooth, clear contour. The length is 2 times the width. They do not contain nodes or other neoplasms.
Contraindications
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland is suitable for all people, regardless of gender and age.
The only limitation
there is the presence on the patient’s neck, in the place where the gel should be applied and through which the study is carried out, of any skin disorders. It could be:
- Extensive painful rash
- Eczema
- Streptoderma is an inflammation caused by streptococcus
- Burn
Only in these cases, ultrasound of this endocrine gland is contraindicated.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland in men
Ultrasound diagnosis of the thyroid gland in men does not have any special requirements. It can be noted that representatives of the stronger sex are much less likely to suffer from diseases of this organ, however, the following pathologies can be identified in them:
- thyrotoxicosis;
- cyst;
- organ cancer;
- endemic goiter;
- autoimmune thyroiditis.
Often, thyroid ultrasound for men is prescribed by related specialists to establish a diagnosis (general practitioners, cardiologists, oncologists, gastroenterologists).
Take care of your health - contact MEDSI
MEDSI specialists
– candidates and doctors of medical sciences, endocrinologists of the highest qualification categories – use the latest equipment for performing ultrasound of the thyroid gland:
Pro Focus 2202 Philips iU22.
Here each patient receives:
- Comfort and respectful treatment
- Diagnostics and support of qualified personnel
- Urgent consultations and ultrasound – appointments can be made by calling 8
- Modern examination equipment from Philips
What you need to know about the procedure
Patients are often interested in what needs to be done and how to prepare before undergoing ultrasound diagnosis of the thyroid gland. The procedure does not cause any difficulties; the doctor carefully examines the organ using a sensor. The examination includes:
- assessment of structure density;
- comparison of organ size with the norm;
- search for formations and nodes;
- analysis of the location of large blood vessels near the thyroid gland;
- scanning of lymph nodes in the adjacent area, etc.
After the procedure, the doctor makes a conclusion and makes a diagnosis. It is better to do a preventive examination no more than once every 6 months. You can receive a referral for the procedure after an examination, when deviations in the functioning of the body have been noted. Hormonal imbalances and an increase in organ size are good reasons to conduct an ultrasound examination.
How to prepare for the study:
- It is better not to eat before the procedure to prevent a gag reflex;
- during the preparation period, you can do a blood test for hormones, which will establish the necessary indicators: T3, TSH, AT, TPO;
- do not wear tight clothes, do not cover the neck area with jewelry;
- remain calm and do not move during the examination;
- do not allow children to be active in their movements, as this interferes with a full examination.
How is the research going?
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is always performed in an office equipped for this purpose, equipped with a special apparatus.
If the patient has not chosen suitable clothing before the procedure and access to the neck is difficult, the doctor may ask to undress to the waist. The thyroid gland is examined in the supine position.
To facilitate access to the organ, the doctor can place a special cushion or pad under the patient’s neck, which can highlight it.
A pad is placed on the back of the neck: it may cause some inconvenience, such as difficulty breathing and swallowing, but this is not something to be afraid of - this element simply allows the doctor to make the examination more accurate.
In addition, ultrasound of the thyroid gland is often performed without such additional elements.
After the patient has taken the desired position, the doctor applies a special gel to the neck area where the thyroid gland is located, which conducts rays and illuminates the organ, making the examination possible.
The diagnosis takes only a few minutes: the doctor can move the sensor several times to record the dimensions, as well as possible deviations and abnormalities in the condition of the organ - all this is displayed on the screen of the ultrasound machine.
After the diagnosis is completed, the patient is given a napkin to remove any remaining gel, or he can do this with a towel that he brought with him.
The results of the study are not released immediately: first, the data obtained is sent for decoding to the doctor who is treating the patient, after which the patient will be able to find out the results of the study at a follow-up appointment.
In some cases, if the data obtained using ultrasound is insufficient, other thyroid tests may be prescribed: hormone tests, blood tests, etc.
Considering that problems associated with the thyroid gland are among the most difficult to diagnose, and preparation for an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland is very simple, we can conclude: today ultrasound is the safest and easiest way to monitor this organ, so avoid or There is no need to be afraid of this procedure.
Ultrasound can be performed on absolutely everyone, regardless of age and gender; moreover, even fairly frequent procedures (once every six months or more often) will not cause any harm to health, but will help to identify developing problems in a timely manner and find optimal ways to solve them.
Our article explained why and why an ultrasound of the thyroid gland is performed, as well as how to properly prepare for this procedure. We hope you find the material useful.
Relatively recently, when ultrasound examination was unavailable, doctors diagnosed thyroid pathologies purely visually and by touch. Modern medicine widely uses diagnostic techniques such as ultrasound. With its help, studies of many organs are carried out, including the thyroid gland. And timely diagnosis can sometimes save a patient’s life. This procedure is one of the very important diagnostic methods now, because with the help of ultrasound you can “see” what is happening in the organ.
This procedure is one of the simplest and most accessible, even when it is performed in a paid clinic. Ultrasound is inexpensive. A question often arises for those who are going for such a study for the first time: how to prepare so that everything goes well? In this case, there is no need to prepare for an ultrasound examination. The only condition: this procedure is usually done on an empty stomach. It is not recommended to eat or drink before the procedure.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the parathyroid glands
Ultrasound diagnostics of the parathyroid glands is aimed at identifying any pathological changes in this area of the body. Using this procedure, you can identify tumors and other formations (benign, malignant), determine the increase or decrease in their size and any other negative processes.
Ultrasound as a diagnostic method in this case is indicated in the presence of the following symptoms:
- a decrease in bone strength, which is manifested by frequent fractures and the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- cramps in the limbs;
- joint pain or discomfort;
- fatigue, decreased performance;
- development of eye diseases, including cataracts;
- If the child has any disorders, then he will experience a delay in mental and physical development.
How is the procedure carried out?
The procedure is quite simple.
The patient lies down on a special couch with his head thrown back, a soft pillow or cushion is placed at the level of the shoulder girdle. A gel that conducts ultrasound well is applied to the neck in the area of the thyroid gland. An ultrasound transducer is applied to the neck and ultrasonic waves are emitted. The sensor is a transceiver that emits and receives a reflected echo signal. This information is processed by a computer and the result is displayed on the monitor. During the procedure, the patient does not experience any discomfort; sometimes there may be slight discomfort due to incorrect body position.
When is it necessary to perform an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland?
How often can a thyroid examination be done using ultrasound? This technique is indicated in the amount necessary to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe the effectiveness of treatment. If, in the presence of certain symptoms during ultrasound, the thyroid gland is somehow changed, it will be re-examined after taking medications or other therapeutic procedures. Also, this diagnosis is used to clarify the diagnosis after examination by an endocrinologist, when an enlargement of this organ in the neck area was detected. You can find out how much an ultrasound of the thyroid gland costs at the specific medical center where the procedure is planned (for example, on average in Moscow it is about 1,500 rubles).
The interpretation of the results and, if necessary, treatment is prescribed exclusively by an endocrinologist, who should be contacted after diagnosis.
For preventive purposes, you can do an ultrasound once a year. This is enough to promptly identify any pathologies. Ultrasound of the thyroid gland with such frequency in the absence of characteristic symptoms is indicated for the following group of patients:
- pregnant women and women over 35 years old;
- people living in areas with iodine deficiency among the population;
- in the presence of type 1 diabetes mellitus, rheumatism, autoimmune diseases;
- with bad heredity;
- after treatment of cancer;
- workers in hazardous industries;
- residents of regions with excess background radiation standards.