Almost every person on Earth is a carrier of some kind of viral infection. This is due to the fact that every minute we come into contact with many harmful microorganisms: viruses, fungi, bacteria. Viruses that parasitize the body for a long time have a destructive effect on it. Moreover, the consequences may be such that the harm caused to the body cannot be eliminated.
Viruses
Viruses are parasitic microorganisms (particles of nucleic acids RNA, DNA). Parasitism is their way of existence. They live and feed at the expense of the organism within which they exist. Outside the body, viruses (outside) die; they simply have nothing to feed on.
When a person has a strong immune system, he resists the proliferation of viruses. But with weakened immunity, viruses become more active. Once settled in a favorable environment, viruses multiply rapidly, quickly and without limit.
Even when viruses “dormant” in the human body, this also causes harm to physical health. Inflammation of the mucous membranes, gynecological, urological, constant colds - this is not a complete list of the harmful effects of viruses, that is, the process of destroying human health is underway.
In women, viruses affect the genitourinary system, which causes erosion, inflammation of the mucous membranes, urinary tract, and then infertility.
Viruses are extremely dangerous for pregnant women. They affect the fetus, causing miscarriage or a stillborn baby.
What are viral diseases
It should be understood that a cold is not a specific disease, it is a condition that is a consequence of severe hypothermia. This led to a weakening of the immune system, an increase in temperature and created favorable conditions for human viral diseases to develop further after the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. They penetrate the cells of the human body, begin to actively multiply there, parasitizing different parts of the body systems and using them as a nutrient substrate. This leads to cell death and the manifestation of disease symptoms.
Immunity is the enemy of viruses
Once in the body, viruses are attacked by the human immune system. Viruses come in many varieties, and our immune defenses are unable to fight some of them. Therefore, certain types of pathogens settle in the human body and live there, hidden. They awaken to action when the immune system weakens. That is, a person lives and does not suspect that he is infected with a viral infection, but a blood test for viruses reveals it. If the result is the presence of viruses, immediate and competent treatment will completely heal the body. It’s better not to take risks and monitor your physical condition; virus tests help a person with this. You should never forget that a person who has a viral infection, even if not in the acute stage, is its carrier, that is, he poses a danger to others.
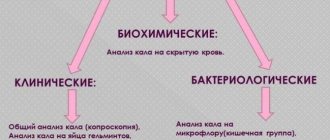
Difference between viral and bacterial infectious diseases
The problem of differentiating viral and bacterial infections is extremely relevant today. And it is extremely difficult for a doctor in a clinic, who is allotted only 12 minutes to communicate with a patient, to do this in the allotted time. For this, various diagnostic methods are used:
- Bacterial diseases are accompanied by high fever and the presence of purulent discharge (from the nose, on the surface of the tonsils, with sputum).
- Bacterial diseases are characterized by the absence of positive dynamics on days 5-7 (which most often occurs with viral infections) and a second wave of deterioration after a period of improvement (with the exception of adenoviruses).
- Blood test: viral infections are characterized by an increase in the number of lymphocytes, and bacterial infections - neutrophils. In both cases, the level of leukocytes and ESR increases.
- Express test for streptococcus and influenza virus (not carried out everywhere).
- Microscopic examination of nasal discharge, throat swab, sputum analysis.
- Other tests: procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, study of protein fractions. They are expensive and are used as a last resort.
The difference between infections caused by bacteria and viral infections is that the main aspect of their treatment is antibiotics. Western experts give a certain percentage of patients (20-30%) for whom self-healing from bacterial diseases is possible, because the human immune system is very strong and can even fight them. However, the lack of antimicrobial treatment in this case is fraught with serious complications, including such serious illnesses as pneumonia, meningitis, endocarditis and sepsis. Therefore, if effective antibiotics are available, the risk caused by not treating (hoping to hit that 20-30% of people) is not justifiably high.
Timely consultation with a doctor in case of a cold infection significantly reduces the risk of complications. You should not self-medicate, even with a banal ARVI.
There are several ways of transmitting viral and bacterial infections, some of them are similar (for example, contact), but there are also differences. The most important thing is why viral and bacterial diseases should not be confused - these are different methods of treatment. If antibiotic therapy is prescribed for bacterial infections, then treating viral infections with antibiotics is useless.
Methods for detecting viral infections
The materials for analysis for viruses are: blood, urine, feces, saliva, scraping of the mucous membrane, smear.
The presence of viruses can be detected using various medical diagnostic methods. To do this, they do a blood test for viruses using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method and the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. ELISA and PCR research methods are highly accurate modern methods for testing blood for viruses. Even a general blood test will not give such an accurate result.
ELISA is a test for antibodies to viruses. The study reveals whether there are specific antibodies in the blood, the etiology and stage of the disease.
PCR is a molecular genetic diagnostic method that detects whether there are viruses in a person. The analysis shows the presence and nature of the virus even before the onset of the disease. PCR never gives false results. If there are no viruses, then the virus test will be negative.
An old way to detect viruses is microbiological culture (BAC culture). The method, although ancient, is quite accurate. The material for the study is scrapings from the urethra and vagina. The scrapings are left in the nutrient substance and observed whether (and how quickly) microorganisms grow.
Only a qualified doctor, after examining the patient and listening to his complaints, can decide what tests for viruses need to be taken.
What are the symptoms of a bacterial infection?
It also happens that an untreated viral infection can turn into a bacterial one. After viruses attack the human body, this leads to a weakening of the immune system, as a result of which bacterial flora more easily develops in the body. The bacteria that most often cause respiratory tract infections are streptococci.
A bacterial infection usually begins abruptly and suddenly. Patients complain of a sore throat, high temperature (higher than in the case of a viral infection). A distinctive feature of bacterial infections is a fever above 38°C.
In addition, during a medical examination, you can observe enlargement and soreness of the cervical lymph nodes and tonsils, on which plaque is present, white or gray.
The throat is very hyperemic, sometimes even crimson in color. Catarrhal discharge due to a bacterial infection is thick, serous-purulent, and may have a greenish tint. There are complaints of nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain.
The cough occurs less frequently, and if it does appear, it is wet. The course of the infection is more intense than with a viral infection. A bacterial infection can develop in the mouth. For example, if dentures are poorly cared for, stomatitis may develop.
Data confirming the presence of viruses
A general blood test shows the development of a disease in the body if lymphocytes, monocytes, and ESR are above normal, and neutrophils and leukocytes are below normal.
The human immune system produces immunoglobulins (IGM, IGA, IGG) in response to the introduction of foreign microorganisms (that is, viruses). Their presence in the blood is detected by the ELISA method. If immunoglobulins have formed, then viruses are definitely present. This virus test determines the stage of the disease and the form of infection (acute, chronic, asymptomatic), and the degree of effectiveness of the prescribed treatment. The disadvantage of this type of research is that it is not the virus itself that is being studied, but the body’s response to it.
Each virus has unique DNA. It can be used to determine what kind of foreign microorganism it is. This study is carried out by the PCR method. The research methodology is based on molecular biology. If the analysis shows the presence of genetic material belonging to a virus, it means that a person is infected with this virus. In addition to the type of virus, such an analysis for viruses gives an idea of their number and vulnerability to certain medications. This makes it possible to select effective methods and methods of treatment. The PCR method absolutely accurately detects all types of viruses.
What is a virus and how is it different from bacteria?
The name “virus” comes from the Latin word virus and translates as “poison”. In fact, these are the smallest intracellular parasitic microbes, because they live and reproduce only inside the host - in almost all living organisms (bacteria, fungi, plants, animals and humans). Despite their “cunning”, all viruses have a primitive structure: one nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by one or more shells. There are simple viruses (non-enveloped) and complex viruses (enveloped). Simple viruses include: polio viruses, hepatitis A viruses, adenoviruses. Examples of complex viruses: hepatitis B, influenza, parainfluenza, measles, HIV, herpes. Viruses also differ in form:
- rod-shaped (tobacco mosaic virus)
- bullet (rabies virus)
- spherical (poliomyelitis viruses, HIV)
- filamentous (filoviruses)
- in the form of sperm (many bacteriophages).
The sizes of viruses are so small (18-400 nm) that they can only be seen using an electron microscope. The units of measurement are nanometers, as opposed to bacteria (micrometers, microns). By the way, viruses are approximately 100 times smaller than bacteria. The smallest viruses are polio virus (20 nm), hepatitis A (30 nm), hepatitis C (50 nm), rabies virus (170 nm), the largest is variola virus (350 nm).
Viruses differ from bacteria not only in size, but also in the number of genes (the minimum for viruses is from 4 to a hundred, for bacteria - from 3000); nucleic acids (viruses contain only one - DNA or RNA, and bacteria - both); the number of enzymes and, of course, the form of life itself: viruses reproduce only inside living beings, and bacteria are free-living.
Interesting fact: the discoverer of viruses and the founder of virology is the Russian scientist D.I. Ivanovsky. In 1892, he described the unusual properties of tobacco pathogens (tobacco mosaic) that passed through bacterial filters and were called “filterable particles.”
How to get tested?
In any clinic, the patient will be explained what tests are taken for viruses. It is possible to donate blood for testing in any hospital where there is a laboratory. Currently, there are paid medical diagnostic institutions where they also do tests. The results will also be given here, but doctors must decipher the results. To confirm the diagnosis, sometimes you need not only test results, but also other diagnostic methods.
It is important to properly prepare for donating blood for testing. Otherwise, a false positive or false negative result may result.
Basic rules on how to prepare and get tested for viruses:
- Blood sampling is carried out in the morning (from 7 to 10 hours).
- Blood sampling is carried out only on an empty stomach. Before the procedure, you cannot eat anything, you can only drink water (tea, coffee, juices, drinks are excluded).
- Do not take medications for a week before donating blood for testing. If it is necessary to take medications, then you must tell your doctor about this, who will give you a referral for testing.
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages, alcohol-containing balms, or tinctures a week before donating blood.
- Before the tests (for about a week), stick to a diet, do not eat fatty, pickled, smoked, or fried foods.
- Ideally, you should not smoke for several days before the procedure, but since passionate smokers will not adhere to this, at least do not smoke for 2 hours before taking blood.
- A month before the test, stop using oral contraceptives, suppositories and ointments.
It is very good for the patient to be in a calm physical and emotional state before donating blood. Increased excitability or physical activity affects the structure of the blood.
The technique of collecting blood for analysis is simple; it is taken from a person’s ulnar vein.
Treatment of viral diseases
The course of therapy depends on the type of pathogen. For example, if it is necessary to treat ARVI, childhood viral pathologies (mumps, rubella, measles, etc.), then all medications are used to eliminate the symptoms. If you follow bed rest and diet, the body itself copes with the disease. Treatment of viruses is carried out in cases where they cause significant discomfort to a person. Apply for example:
- antipyretics if the temperature is above 37.5 degrees;
- vasoconstrictor drops are used to relieve nasal swelling;
- in rare cases, antibiotics (if a bacterial infection has occurred);
- NSAIDs that relieve pain and lower fever, for example, aspirin, paracetamol, ibuprofen.
During treatment, doctors recommend drinking more fluids to combat intoxication of the body, moderate nutrition, bed rest and room humidity of at least 50% where the patient is. Treatment for influenza is no different, but the doctor must monitor the patient, because this disease can cause serious consequences. One of them is pneumonia, which can lead to pulmonary edema and death.
If such complications begin, treatment must be carried out in a hospital using special medications (Zanamivir, Oseltamivir). When diagnosing the human papillomavirus, therapy consists of keeping the immune system in good shape, surgical removal of warts and condylomas. In cases of severe viral pathologies. For example, HIV requires a course of antiretroviral drugs. It cannot be completely eliminated, but it can be kept under control and prevent the spread of the disease.
If the genital organs are infected with herpes, it is necessary to take special medications; their maximum effectiveness has been confirmed in the first 48 hours. If you use the products later, their medicinal effect is significantly reduced and the course of treatment can last from several weeks to several months. Herpes on the lips needs to be treated with local remedies (ointments, gels), but even without them, the wound heals within a week.
Antiviral drugs
In medicine, there is a certain number of medications in this group that have proven their effectiveness and are used constantly. The entire list of drugs is divided into two types:
- Medicines that stimulate human immunity.
- Drugs that attack the detected virus are direct-acting drugs.
The first group refers to broad-spectrum drugs, but their use leads to serious complications. One example of such drugs is interferons, and the most popular of them is interferon alfa-2b. It is prescribed for the treatment of chronic forms of Hepatitis B, and was previously prescribed for hepatitis C. Patients had a hard time tolerating such therapy, which led to side effects from the central nervous system and the cardiovascular system. In some cases, pyrogenic properties appear and cause fever.
The second type of PPD medications is more effective and is easier to tolerate by patients. Among the popular medications, the following treatment options are distinguished:
- Herpes - acyclovir. Helps overcome the symptoms of the disease, but does not kill it completely.
- Influenza – influenza neuraminidase inhibitors (Zanamivir, Oseltamivir). Modern influenza strains have developed resistance to previous medications (adamantanes), and they are not effective. Name of drugs: Relenza, Ingavirin, Tamiflu.
- Hepatitis . For the treatment of group B viruses, interferons are used together with Ribavirin. For hepatitis C, a new generation of drugs is used - Simeprevir. Its effectiveness reaches 80-91% of sustained virological response.
- HIV . It cannot be completely cured; antiretroviral drugs provide a lasting effect, cause remission, and the person cannot infect others. Therapy continues throughout life.
Main indications for prescribing tests
The appearance of a reddish rash of unknown origin on the body, irritation, itching, burning of the mucous membrane, soreness, discomfort in the lower abdomen and groin, unhealthy discharge from the genitals, poor appetite, constant fatigue, weight loss, regularly recurring colds - these are all indications for carrying out analyses.
If there are a lot of papillomas on the body, then it is necessary to do tests for viruses and to determine the type of virus. In some cases, everything can end in cancer.
Where can I get tested for coronavirus?
All laboratories and clinics performing coronavirus testing by city.
Moscow and Moscow region
St. Petersburg and Leningrad region
Astrakhan
Barnaul
Belgorod
Bryansk
Vladivostok
Vladikavkaz
Vladimir
Voronezh
Volgograd
Grozny
Ekaterinburg
Kazan
Kaluga
Kaliningrad
Krasnoyarsk
Krasnodar
Kemerovo
Kirov
Kursk
Lipetsk
Makhachkala
Ivanovo
Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Tagil
Novosibirsk
Novokuznetsk
Irkutsk
Izhevsk
Omsk
Orenburg
Penza
Ryazan
Rostov-on-Don
Saratov
Samara
Sevastopol
Stavropol
Sochi
Surgut
Tolyatti
Tomsk
Tula
Tyumen
Tver
Permian
Yaroslavl
Chita
Chelyabinsk
Cheboksary
Ufa
Ulan-Ude
Ulyanovsk
Khabarovsk
Decoding the results obtained
The ELISA research method is based on identifying antigens to different viruses. A new microorganism that settles in a person receives a response from his immune system. Each type of virus has its own antigen. The presence of the LGG antigen to the virus indicates that immunity to it has already been developed, since the person has had this viral infection before. If there is an LGM antigen, then the virus has entered the body for the first time, and the process of developing immunity to this virus is underway. During the acute phase of infection, both antigens are present in the blood.
It is not even a doctor who can decipher the result of a PCR study; if there is DNA of a virus, then there is a virus. In some cases there are also errors. The method itself is very accurate; errors can occur due to the fault of the health workers who took the blood.
How to treat: drugs
The best drugs against viral infections are those whose clinical effectiveness has been proven and meets international GCP rules. There are only a few such drugs today.
Antiviral drugs are divided into several groups:
- having a direct effect on the virus,
- stimulating the production of interferon and interferons directly (effectiveness has been proven by in vitro studies, but do not have evidence of effectiveness recognized by the medical community),
- homeopathic (not recognized as effective by scientific medicine).
Oscillococcinum or Aflubin can be prescribed as homeopathic support. They are suitable even for very young children. However, the decision whether to give an antiviral drug to a baby remains at the discretion of the parents, since their effectiveness has not been proven.
Typically, the basis of treatment offered by doctors is antiviral drugs:
- Viferon,
- Isoprinosine,
- Citrosept,
- Remantadine.
All these drugs are suitable for children from one year old.
“Spot-on” antiviral medications exist for several diseases, such as influenza and mononucleosis. Anti-influenza drugs officially registered today are oseltamivir and zanamivir (neurominidase inhibitors). Their appointment is preceded by a test for the presence of the virus - a throat swab.
The baby may also be prescribed immunomodulatory drugs (for example, Kipferon (its analogues) or Cycloferon) or immunostimulating drugs (for example, Glutoxim or Poludan).
Their purpose is to activate internal defense mechanisms. They are strong biologically active agents and are not completely harmless (no standardized clinical trials have been conducted on these drugs).
Important! They are used only when indicated and as prescribed by a doctor (for example, if a child gets sick more than 5 times a year or there is no fever, which is one of the signs of a “lazy” immune system).
Additional signs of the need to prescribe such drugs may include the following:
- dull split hair,
- brittle, constantly peeling nails,
- flaky skin.
You should definitely inform your doctor about the presence of such manifestations in your child. The dosage regimen is determined by the doctor depending on the goals and age. For example, pediatricians may prescribe Cycloferon for prevention once a day, half an hour before meals:
- 4-6 years old take one tablet per dose (150 mg/day),
- 7-11 years old take 2 tablets per dose (up to 450 mg/day),
- from 12 years and adults, 4 tablets per dose (up to 600 mg/day).
Antihistamines are also prescribed:
- Suprastin,
- Zyrtec,
- Zodak,
- Ghismanal (the last three are newer).
This is done in order to relieve swelling of the nose, which often occurs with viral infections. Suitable for children up to one year old. Since a single cure for ARVI has not been synthesized, a complex of drugs that relieve its symptoms is usually offered for the treatment of children.
On a note! If the prescribed drugs have a form of release such as suppositories, then in agreement with the pediatrician you can use it (this is especially true for young children who, due to their age, cannot swallow a pill).
What to take additionally
Some doctors prescribe the drug "Polysorb". This remedy has a special therapeutic effect; it removes toxins of various origins from the body. Suitable for children up to one year and older.
The list of drugs may also include:
- Umlakor is a new generation antimicrobial drug. Suitable for children from one year old;
- "Miramistin" - a local antiseptic can be prescribed both for the treatment and prevention of acute respiratory viral infections (it is recommended to give it to children from three years old);
- "Polyoxidonium" is another drug that is used to prevent diseases. This drug can be used in children over 6 months of age;
- “Acyclovir” is prescribed to children over 2 years of age when a Herpes simplex type virus is detected as an infectious agent. The tablets are also active against Varicella zoster and Epstein-Barr viruses;
- "Bronchomunal" - has an immunomodulatory effect and is prescribed for relapses of bronchitis, otitis, tonsillitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis and laryngitis;
- "Aminocaproic acid" orally (intravenously) is prescribed for hospital treatment of a child. Indications for use are bleeding and organ diseases with hemorrhagic syndrome. It is used as a prophylactic agent during blood transfusions.
What diseases do tests detect?
The research results allow us to detect: hepatitis B, C; herpes; Epstein-Barr virus; papillomavirus; immunodeficiency virus; adenovirus; rotavirus; sexually transmitted infections (including syphilis).
A patient with a viral infection should never self-medicate. Treatment should be prescribed by a qualified doctor, a specialist in viral infections. Treatment should be carried out under the supervision of this doctor.
The patient must limit his contacts with people and follow all procedures prescribed by the doctor.
Ebola
One of the deadliest viruses known to the world today. It can take different forms (there are 5 types of Ebola fever) and be transmitted in different ways. This microorganism causes hemorrhagic fever in humans and primates. The disease most often manifests itself as vascular damage, which leads to the development of thrombohemorrhagic syndrome (THS).
Historical reference
The Ebola virus was first discovered in October 1976 in the Democratic Republic of Congo near the Ebola River.
The largest outbreak of the fever occurred in West Africa in 2014–2016. The infection has spread beyond the continent: cases of infection have been recorded in Europe and the USA. The number of people infected during the entire epidemic amounted to 29,000 people, 11,000 of them were fatal.
It all started when on August 22, 1976, a missionary school teacher, returning home, bought dried monkey and antelope meat from a hunter on the road. The teacher had dinner with the antelope with his family, and a little later he ate monkey meat alone. On August 26, he went to a local hospital complaining of high fever, sore throat and abdominal pain. Doctors diagnosed him with malaria and gave him an injection of chloroquine. The symptoms went away, and 4 days later the man began to have stomach bleeding. On September 8, the teacher bled to death and died. His disease was transmitted to 9 other patients who were in the same room with him. They all later died from severe bleeding.
Over the next two months, the number of infected people grew, and medical staff were also among the sick. Having gone through all possible options from dysentery to typhoid fever, the doctors agreed that they were dealing with a previously unknown virus.
Source of disease
Ebola is still being monitored by scientists. The fever and its new variants occur in animals, but it is not yet known how new forms of the virus may affect humans. In 2020, Novosibirsk scientists presented a vaccine against the Ebola virus. Now it is successfully used among doctors who work with pathogens at the epicenter of infection.
The Ebola virus is transmitted through contact with biological fluids, skin, secretions, personal belongings of patients and materials contaminated by them. It is recommended to avoid any contact with infected animals and not to eat their meat. We are talking about animals such as antelopes, monkeys, porcupines, bats.
Symptoms
- sudden increase in temperature;
- severe weakness;
- headache;
- muscle pain;
- a sore throat;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- bleeding during bowel movements;
- skin rashes;
- impairment of kidney and liver function;
- internal and external hemorrhage.
Prevention
When staying in African countries, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- use protective masks;
- when in contact with patients, use protective gloves;
- refrain from visiting crowded places;
- do not buy food from local markets;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene, use antiseptics;
- regularly ventilate the living space and carry out wet cleaning;
- If symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Rotavirus (stomach flu)
Due to the 40% fatality rate, the disease caused by rotavirus is considered life-threatening. Children under five years of age are at particular risk of infection. The causative agent of the disease is the Reoviridae virus, isolated in 1943. Once in the body, it causes severe dehydration followed by intoxication. The occurrence and development of the disease is seasonal – the virus becomes active in the winter. Focal cases of the disease are most often recorded in nursing homes and preschool institutions. The most famous outbreak of rotavirus infection was recorded in 2005 (Nicaragua - 30% mortality). According to research, it is assumed that the outbreak of rotavirus arose due to a mutation of the virus. Another outbreak of focal infection was previously known in Brazil (1977). The origins of the virus are unknown. A person can become infected by drinking dirty water, through household appliances, or through close contact with an infected person. The period of development of symptoms of malaise is up to five days.
Symptoms of rotavirus infection
1. Primary – against the background of weakness and loss of strength, an increase in temperature to 40 degrees, vomiting, and the appearance of light yellow clay-like stools. 2. Secondary – signs of dehydration (loss of fluid) worsen; against the background of vomiting and frequent loose bowel movements, there is no appetite, a runny nose and sore throat, dark urine. Treatment is carried out comprehensively - simultaneous relief of dehydration symptoms, reduction of body intoxication, intravenous fluid administration. Vaccination of the population in countries with an insufficient level of medical care and severe signs of unsanitary conditions is used as a preventive measure against rotavirus infection.
The ranking of the top 10 dangerous viruses on the planet is not final. Which of them is the most dangerous is also impossible to predict. Every day, scientists discover new types of viruses, study their origin and nature, and try to understand how safe they are for human existence. However, despite high scientific achievements, the problem of human resistance to viruses remains relevant to this day. To preserve our population, constant active opposition to destructive viral diseases is necessary. Therefore, it is very important to know the etiology of the most aggressive, but already familiar to humanity, biological microorganisms.
Features of taking tests by a child
The first blood test in children is carried out in the maternity hospital. This allows the doctor to form an opinion about the baby’s health in the first days of life and to identify hereditary diseases such as phenylketonuria (metabolic disorder) or hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function).
If no signs of pathologies or disorders are observed in the baby, then after three months a general blood test is performed, which is necessary in preparation for vaccination.
In addition, if necessary, children under one year of age may be prescribed a biochemical blood test. This allows you to evaluate the functioning of internal organs, detect infection, and diagnose a number of diseases at an early stage.
Also, a general blood test and a general urine test are necessary for children to enter kindergarten and school. Research is also carried out as part of the annual medical examination.
In addition to blood and urine tests, stool samples and nasal and throat swabs are sometimes taken from children. So, with frequent inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx in children of different ages, a smear is taken to determine what kind of infection is in the body.
The most common tests for children are to check for genetic diseases, allergies and viral infections.
According to statistics, in Moscow, about 15% of the population suffers from allergies. In Russia and the CIS countries, the number of children susceptible to allergies ranges from 5.2 to 15.5%. We are talking about food allergies, bronchial asthma, skin rashes, neurodermatitis, hay fever, etc.
A number of symptoms indicate an allergy: a prolonged runny nose, sneezing, watery eyes, swollen eyelids. Otherwise, there are no signs of the disease, the child is alert and active (if the allergic reaction does not become severe). Often, parents mistake this condition for signs of a cold and begin appropriate therapy, which does not bring results. In this case, the doctor may prescribe an allergy test. This is indicated by increased production of specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) proteins in the child’s body. Analysis for allergens, both food and plant, allows you to specify what caused the reaction.
The following tests may be prescribed:
7 days before the test you should not take antihistamines. Allergy testing is not recommended on an empty stomach. The analysis is not done during a period of exacerbation of allergies, and it is also contraindicated in children under 3–5 years of age.
A sharp increase in temperature, upset stomach, cough, sore throat, body aches, weakness, dizziness - these and other symptoms are indications for testing for infections.
Viruses can be detected in different ways.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method. The method allows you to identify the DNA of various infections, that is, determine the causative agent of the disease. During the study, a small amount of biological material is placed in a special reactor, which may contain fragments of microbial DNA. For example, when determining a respiratory tract infection, swabs are taken from the nose and throat in children. Special enzymes are added to the material being studied. They bind to the microbe's DNA and synthesize a copy of it.
PCR allows you to detect the presence of a number of infections with high reliability. Very often, children are prescribed a smear for streptococcus. This technique is used, for example, to diagnose whooping cough and diphtheria.
Hereditary diseases can also be found in children born to healthy parents. Moreover, many diseases do not make themselves felt immediately. A timely analysis will make it possible to detect the disease and take timely measures. Let's look at the most common genetic diseases.
Only girls are susceptible to Shereshevsky-Turner disease. With this disease, patients have 45 chromosomes instead of 46. The first signs of pathology are often detected only at 10–12 years of age. The disease is indicated by short stature, low hair growing at the back of the head, lack of sexual development, and mental retardation. In adulthood, the disease threatens infertility.
Another genetic disease diagnosed in boys is Klinefelter's disease. Moreover, if you do not get tested, the disease will only be detected by the age of 16–18. Young men with this diagnosis are tall and have disproportionately long arms. There is also some lag in mental and mental development. In 9 cases out of 10, such patients experience infertility. Research shows that in this case the problem is the extra chromosome 47.
All children under 2–3 months of age should undergo a biochemical urine test to determine the presence or absence of phenylketonuria (pyruvic oligophrenia). The disease is hereditary, and if both parents are carriers of the recessive gene (they themselves may be healthy), the risk of having a sick child is 25%.
For children under 1–1.5 years old, it is advisable to undergo diagnostics to identify another hereditary disease - cystic fibrosis, which affects the respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract. Patients experience symptoms of chronic inflammation of the lungs and bronchi in combination with dyspeptic symptoms (diarrhea alternating with constipation, vomiting and nausea, etc.). The incidence of this disease is 1 case in 2500 children.
Only after a year do children show clinical signs of a fairly common disease - hemophilia. It mainly affects boys, while women are carriers of the recessive gene.
At 4–5 years of age, only boys can show signs of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In this case, just as in hemophilia, the mother is a carrier of the mutation gene. During the course of the disease, first the muscles of the legs, and over the years, all other parts of the body, are replaced by connective tissue that is unable to contract.
Modern medicine makes it possible to diagnose genetic diseases in a timely manner using special laboratory tests. Even during pregnancy, you can undergo tests for immunogenetics, genetic predisposition to diseases of the heart and blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system, cancer and a number of others.
Laboratory tests are faithful assistants to doctors and parents in diagnosing various childhood diseases and monitoring treatment. With the help of tests, viral infections, allergies, and congenital malformations are detected. It is only important to choose the right medical center for the procedure: one that offers the necessary services, ensures accurate results and works with children.
The health of a child is the key to peace in the family. Timely diagnosis will help identify possible health problems and take measures to develop the right course of treatment. So that the baby is not afraid, explain to him that the procedure will not be painful, but will bring a lot of benefits. Nowadays you can find many educational cartoons and videos telling about the composition of blood, diseases and viruses, their treatment - after watching them, children look at the test procedure differently.
We are familiar with the concept of blood from a school biology course. What is a blood test for viruses? If we take a medical term, then such an analysis is called either general or clinical. With its help, blood is broken down into its basic indicators, which determine whether a person is healthy or sick. These indicators mean the level of hemoglobin, ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), how many red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets are present in the blood.
How does the body react to the virus?
Particles of the virus itself, as well as biologically active substances released during the destruction of our cells, can cause increased body temperature, nausea, vomiting, severe weakness, dizziness up to loss of consciousness, disruption of the cardiovascular system, etc. Against the background of disruption of the functioning of various organs and systems, bacterial (staphylococci, streptococci, intestinal bacteria) and fungal (yeast) can join the viral infection, aggravating the inflammatory process with serious consequences, including death.
The life cycle of viruses consists of several stages:
1. The virus attaches to the surface of a sensitive cell. Each virus has its own sensitive cells, for example, for hepatitis - liver cells, for influenza - respiratory tract cells, etc. 2. Penetration of the virus into the cell: either its shell merges with the cell membrane or the cell itself captures and absorbs it. 3. Next in the cell there is a process of “undressing” the virus from all its shells and activation of its nucleic acid. 4. The synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins of the virus begins, i.e. the virus subjugates the host cell systems and forces them to work for its reproduction. 5. Virus assembly is a multi-step process that includes the connection of all components. 6. The last stage is the release of viral particles from the cell by explosive or budding. The full cycle of virus reproduction is completed after 5-6 hours (influenza virus) or after several days (measles virus). A large number of viruses emerge simultaneously from a dying cell, which can remain viable for a long time. As a result, cells affected by the virus mostly die from exhaustion, and new viruses conquer and destroy other cells. But the so-called oncogenic transformation of a cell is also possible: then a cancer tumor appears in the body and begins to grow from mutated cells.
Scraping
Scrapings from the skin and mucous membranes are often taken to diagnose childhood infections. In case of manifestation of the disease, this type of analysis is taken from the foci of infections:
- Chickenpox is detected by taking a test from blisters on the skin;
- Sore throat is diagnosed by scraping the tonsils;
- To confirm lichen, a sample is taken from the skin lesion.
Skin scrapings are often used to diagnose skin diseases such as scabies.
The most common test is scraping for enterobiasis. Based on the results, it will be clear whether the child can attend kindergarten or not.
Such a study is carried out in a clinic at the place of residence, the materials are submitted to the laboratory. To determine the presence of pinworms, patients take scrapings from the folds of the anus. The scraping is taken from the upper layer of the epidermis, which does not cause any discomfort to the child.