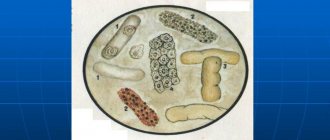
Urates in urine are salts of uric acid. They are small round crystals, which are determined when examining the sediment under a microscope. Most often, their detection in urine does not indicate disease. The concentration of urates can go off scale with excessive consumption of meat or other foods rich in purines. Also, a high concentration of urates can be a sign of a number of diseases. At normal renal filtration rates, uric acid salts are not excreted in the urine.
The main factors for the onset of the disease
As with any other disease, the formation of oxalates has its reasons. The norm for each organism is individual. Let's consider the main factors of the origin of the disease.
- Poor nutrition. An excess of chocolate, asparagus, spinach, apples, tomatoes, ravil, sorrel, beets and other foods containing acids or salts in the daily menu. Lack of vitamin B (pyridoxine, pyridoxal, pyridoxamine) and magnesium in the body. Various types of poisoning, including chemicals. If stones appear, it means that there is a lack of fluid, potassium, and calcium in the body. Or excess salt, meat, sucrose.
- The presence of diabetes mellitus and its non-professional therapy. Also dysbacteriosis, hemorrhages in the kidney tissue, disorders of the process of excreting urine from the body, gastritis, ulcerative colitis.
- The presence or consequences of urolithiasis, chronic inflammation of the kidneys and urinary tract, pyelonephritis. Impaired acid-base balance, in which a general urine test indicates the pH level of acidity
- Hereditary diseases associated with metabolic disorders - chemical reactions in a living organism to maintain its basic functions. Changes in the process of oxalic acid metabolism at the genetic level, hemorrhages in the kidney tissue, doubling of the pyelocaliceal system, congenital urolithiasis.
- Recovery periods after surgery, remission and therapy as a result of removal of benign or malignant tumors.
- Self-medication, which involves excessive consumption of ascorbic acid and vitamin D.
- Constant stress and psychological stress, during which the metabolic process is restructured in a new way in the fundamental organs for processing and eliminating toxins - the kidneys.
- Oxalates often appear in the urine during pregnancy during complex toxicosis, significant loss of fluid during this period, and with infectious diseases of the urinary tract of expectant mothers.
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
- The disease is also provoked by a diet with oxalates in the urine, which is based on a large number of products with a high percentage of oxalic acid.
The reasons for this disorder
Why do urates appear in large quantities in the urine? Increased excretion of these compounds from the body can be affected by changes in metabolism, which develop under the influence of many factors. The cause of uraturia should be sought in the following disorders:
- Mental and emotional stress (depression and stressful conditions cause changes in the rate of metabolic processes).
- Diseases of the urinary system, especially kidney pathologies (glomerulonephritis, hepatitis, pyelonephritis).
- Active physical activity (exhausting work and constant participation in strenuous sports).
- Eating food that contains a lot of purine bases.
- Genetic factor - a predisposition to uraturia can be inherited from parents. In this case, the likelihood of urate occurring in the urine increases several times.
- Severe dehydration (affects the process of water-salt metabolism, changes the functional ability of the kidneys).
- Drinking alcoholic beverages leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the kidney filtering system, as a result of which these organs lose the ability to normally process purines. Because of this, the amount of urea salts in urine increases significantly.
- Prolonged fasting, improper diet.
Urate salts in urine are formed due to the abuse of certain foods. Many purine bases are contained in: smoked meats; mushroom dishes; various canned foods (meat, fish); liver and lungs of animals (liver); concentrated broths made from red meats; coffee, tea, cocoa and products containing it; pork, beef or veal; spinach and tomatoes; legumes.
Important! If a patient’s urine analysis showed the presence of urate in the urine once, and the cause of this phenomenon could not be fully elucidated, then perhaps this is a one-time reaction. This is how the body can respond to the action of some negative factor (stress, eating the above food, drinking alcohol). In such a situation, the disorder is temporary and does not require treatment.
Characteristic symptoms
Excess uric acid salts in urine occur in people of any age.
According to statistics, men are more susceptible to this disease than women. During pregnancy, excess urate is normal. But it is necessary to keep their quantity under control to prevent their excessive accumulation. Violation of the properties of urine in the initial stages is asymptomatic. It is easy to determine excess salt compounds by taking a urine test. The first symptoms of pathology appear when stones form in the kidneys. They are the basis for the formation of urate stones.
The formations tend to gradually increase, they move towards the ureters and enter the bladder. The process of stone formation is accompanied by the development of an infectious inflammatory process. Its manifestations may be as follows:
- significant increase in body temperature;
- increased blood pressure;
- weakness;
- blood in urine;
- attacks of nausea with vomiting.
The acute period is accompanied by pain in the lumbar or abdominal region. A striking symptom of the pathology is painful urination with frequent urge.
If a similar pathology develops in children, then symptoms such as constipation, vomiting after waking up in the morning, and coughing attacks cannot be ruled out. Children diagnosed with elevated urate levels are often hyperactive and are ahead of their peers in physical development.
Excess salts lead to their accumulation in the subcutaneous layer. Because of this, red spots appear on the child's skin. With uraturia, the child has poor sleep; babies often wake up and ask to be held.
Amorphous urates have their own characteristic symptoms - they color the urine brownish-pink. Their excessive accumulation is a sign of diseases such as chronic renal failure, glomerulonephritis or kidney congestion. Urates in urine in large quantities can be hazardous to health. They cause the formation of stones in the urinary tract, bladder, and kidneys.
What are the dangers of excess urate salts?
Urate crystals themselves are not dangerous. They are non-toxic and do not have sharp corners that could injure the epithelium. But these salts are a harbinger of serious diseases.
For example, persistent uraturia in the future will certainly lead to the formation of kidney stones. The urine sediment crystallizes and is retained in the renal pelvis. The pH of urine changes due to metabolic disorders. This creates ideal conditions for stone formation.
Gout, which also causes uraturia, is often complicated by chronic renal failure (CRF). If the terminal phase of chronic renal failure occurs, the person is prescribed lifelong replacement therapy (hemodialysis) or referred for organ transplantation. The first symptoms of gout are pain in the interphalangeal joint of the first toe. The disease requires immediate treatment.
Proper nutrition for pathology
Normalization of nutrition and avoidance of foods that provoke the formation of urates is a mandatory element of the treatment of uraturia. A diet for urate in the urine involves following the main rule - eating foods with a low salt content. The following principles must be adhered to:
- you should not allow yourself to go hungry or stick to a low-calorie diet;
- reduce protein content;
- completely stop eating canned food and offal;
- a ban is imposed on drinking bottled water.
Products excluded:
- fatty meats and fish;
- rich meat broths;
- cocoa;
- mushrooms;
- Black tea;
- beer;
- red wine.
It is necessary to limit consumption as much as possible:
- fish;
- legumes;
- cabbage;
- spinach;
- of bread;
- Luke;
- salt, hot seasonings.
Citrus fruits are allowed, but only on the condition that their consumption does not lead to the formation of oxalates. Their content will be less if you eat dried apricots and apples, fresh pears and grapes. These fruits help remove excess fluid from the body and reduce particles of uric acid salts in the urine.
With uraturia, it is necessary to strictly limit the consumption of meat. All types of meat, except lamb and horse meat, must be kept in water for at least 3 hours before cooking. The first broth from white meat must be drained. Vegetables cooked with it should not be consumed. The daily intake of clean water should be at least 1.5–2 liters per day.
Diet
Once urate is detected in the urine, therapeutic measures should be started immediately. The first and main step is to normalize your daily diet. Treatment of urate in urine involves complete abstinence from the following foods:
- bottled water;
- beer;
- lard and fat;
- chocolate;
- offal;
- canned food
In addition to the listed products, restrictions are also imposed on the consumption of bread, beans, spicy foods and spices, onions, and salt. Cabbage, sorrel, and spinach should be eaten infrequently and carefully.
The therapeutic effect of the diet is enhanced by taking herbal mixtures and tinctures with a diuretic effect. In this case, the amount of liquid consumed daily should not be less than 2 liters.
Principles of therapeutic nutrition
How to remove salts from urine naturally? Specific therapy for this disorder is not carried out if, as a result of following dietary rules, the content of salt crystals in the excreted fluid has returned to normal on its own. Those patients whose urine analysis has an increased content of other components - protein molecules, mucous secretions, red blood cells, cylindrical cells, leukocytes - must undergo a full examination. In such a situation, an excess amount of salts indicates possible inflammation.
An important part of the diet is to increase the volume of fluid the patient takes. You will have to cross out all the products listed below from your menu for a certain time.
The formation of urates in the excreted fluid means that a person should exclude purines from his diet. In such a case, the following foods are recommended to eat:
- cereal products;
- chicken eggs;
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- milk or its derivatives;
- walnuts;
- poultry meat.
To treat oxalaturia, oxalate products are removed from the patient’s menu, and instead they are added:
- seaweed;
- beans;
- pumpkin seeds;
- chicken, beef, pork liver;
- potatoes;
- fruits enriched with vitamins A, E and B6 (cherry, pear, cranberry, lingonberry);
- sprouted bran and wheat.
The following foods and drinks will help eliminate the increase in salts in the urine caused by phosphaturia:
- boiled vegetables;
- broths and soups made from lean red meat and fish;
- berry, fruit drinks and juices;
- boiled brown rice.
For dietary nutrition, it is advisable to use products that have a binding effect and support the correct distribution of energy in the body. You will learn how effective this approach to treatment was from the result of the final urine test. It should be carried out after 14-21 days from the start of therapy. Proper nutrition does not always allow you to completely get rid of excess salts. In this case, the patient is prescribed medications that normalize metabolic processes throughout the body. It is advisable to maintain a rational approach to food intake in the future for preventive purposes.
Increased salt in the urine - if such a disorder is found in an adult, then he should pay more attention to his diet and way of life. You should not be afraid of such a phenomenon until the results of urine analysis are confirmed by other studies. Seek medical help in a timely manner - this will protect you from the unpleasant consequences of many diseases! Be healthy!
Symptoms of uraturia, and what does it mean?
The disease does not show clear signs until urate accumulates in significant quantities. The disease can be detected at an early stage by chance by passing a urine test. There should not be even minimal salt deposits in urine, but an increase to two pluses is considered the norm.
Most often, a person begins to feel some symptoms when inflammatory processes begin to develop in his kidneys, complemented by increased acidity of the urine. These symptoms may be:
- pain in the abdomen or lower back;
- presence of blood in urine;
- pain when urinating;
- nausea and vomiting;
- renal colic;
- increase in body temperature;
- high blood pressure;
- chills;
- weakness.
If a person notices such symptoms, he should consult a doctor.
Reference. Sometimes the symptoms are similar to cystitis, so before starting treatment, you need to confirm the diagnosis by taking tests.
Therapeutic measures
The specialist selects individual treatment. Therapy consists of diet, chemical and herbal medicines. The course of activities takes a long period.
Drugs
Practical medicine uses a number of medications that are dispensed by pharmacists, both with and without a prescription. Let's look at some medications to reduce the concentration of urate salts in the body:
- Plant origin: “Canephron”, “Urolesan”, “Fitolysin”. Promote the outflow of urine, remove urates from the body.
- "Allopurinol." Reduces the production of uric acid and also dissolves salt formations.
- "Blemaren." Used to break down urates and oxalates. A contraindication to the use of the drug is urine phosphates.
Prescribed medications must be taken continuously.
Folk recipes
At the first signs of illness, you can use the herb, diuretic complexes. Natural preparations have no contraindications for use, so they can be used at home. However, they are prohibited for use in severe renal failure.
Prevention of urate formation
Prevention of the development of uraturia should be carried out in patients whose family history is burdened with cases of the development of urolithiasis, as well as in the detection of at least isolated cases of the presence of acidic sediment in urine. To do this, it is important to monitor your diet and minimize the consumption of foods containing purines and acids. The development of various infectious diseases of the urinary system should not be allowed, and if they are present, treated in a timely manner.
A sedentary lifestyle leads to stagnation, which contributes to the deposition of salts. If the job is sedentary, exercise should be done at least 2-3 times a week. Bad habits and exposure to unfavorable working conditions can cause the development of uric acid diathesis. If you suspect the possibility of pathology, you should visit a doctor for early diagnosis and donate urine for research. At home, you can regularly determine the reaction of the liquid using special test strips.
Treatment Options
Since excess urate is a consequence of poor nutrition, normalizing the diet becomes a priority. The accumulation of salts in the kidneys requires medication. It includes taking the following medications:
- Allopurinol - prevents the formation of uric acid, promotes the breakdown of existing urate deposits.
- Blemaren - has the form of effervescent tablets, before use they are dissolved in water. Their main effect is aimed at alkalizing urine, this creates suitable conditions for easy dissolution of uric acid. It is contraindicated if phosphate stones are detected.
- Panangin or Asparkam - this drug contains potassium and magnesium. It helps remove excess salts from the body.
- Canephron, Phytolysin or Urolesan - the action of these drugs is not aimed at dissolving stones, they help eliminate excess salts in the urine.
If excess urate has led to the formation of kidney stones, it is necessary to decide on the choice of method for removing them. For this, both conservative and surgical treatment methods are used.
Therapeutic tactics are developed for each patient individually, taking into account the cause of stone formation. Medicines can remove uric acid crystals if their size does not exceed 5 mm. For the latter, ultrasonic or laser crushing is used.
Surgical treatment for stone formation is used quite widely. General indications for this are:
- acute attacks of renal colic;
- deformation of the kidney due to obstructed urine outflow;
- urination with blood as a constant symptom;
- frequent repetition of attacks of acute pyelonephritis;
- the presence of stones in the ureter or single kidney.
Main directions in treatment
Treatment of the disease should be comprehensive, affecting the cause (etiotropic therapy) and the mechanisms that form urate stones (pathogenetic therapy).
Drug treatment is used when urate stones have already formed:
- Prescribed drugs that neutralize salts and make urine more alkaline (Blemaren).
- To remove urates, take medications containing potassium and magnesium (Panangin, Asparkam).
- As a mild diuretic, it is recommended to take a herbal decoction orally (kidney collection).
- Vitamins A, E, B6.
To remove urate stones, conservative, surgical and instrumental treatment methods are used. The conservative therapy program is selected individually for each patient, taking into account the mechanisms and causes of stone formation. Treatment with drugs is aimed at changing the biochemical composition of blood and urine, and also helps to remove urate crystals up to 5 mm in size. Remote therapy ─ crushing stones with ultrasound or using contact laser lithotripsy.
Surgical treatment is prescribed quite widely. Indications for surgical intervention:
- severe attacks of renal colic, including disability;
- difficulty in the outflow of urine, leading to deformation of the kidney;
- obstructive anuria;
- persistent hematuria (blood in the urine);
- frequent attacks of acute pyelonephritis;
- a stone in the only kidney or in the ureter, and cannot pass on its own.
The prognosis for recovery after abdominal surgery is always favorable.
Causes of increased uric acid salts
Uric acid is a substance that is formed during the metabolism of protein and purines, determines the state of the excretory system and the stability of metabolism. It is in the form of urates. Normally, 12-30 g of it are released per day, and its increased level leads to a large accumulation of salts in the form of crystals that damage organs and systems, causing various pathologies. There are a number of reasons why urate appears in large quantities and is elevated in the urine:
| Cause | Description |
| Nutrition | Uric acid salts appear due to the consumption of foods such as alcohol, canned food, meat products, leafy greens, spicy and smoked foods, and legumes. |
| Kidney disorders | deterioration of blood supply and, as a consequence, the formation of urate stones, occurs due to a number of factors: hydronephrosis, blood clots, kidney prolapse, hot climate. |
| Hereditary factor | a high concentration of uric acid in a child’s urine is possible if his immediate relatives also suffer from this disease. |
Other factors include:
- increased physical activity;
- a large amount of stress and psycho-emotional disorders;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- taking certain medications;
- dehydration;
- infectious diseases.
Salts in urine may fluctuate temporarily due to certain diets.
What kind of salts are these?
It often happens that an absolutely healthy person has an increased level of urate in the urine. What does it mean? Urates are potassium and sodium salts of uric acid. If the kidneys have good filtration function, these compounds should not be present in the sediment. The acidity (pH) of urine plays a big role here. If the discharge is excessively acidic, then urates appear in the urine in large quantities. An alkaline environment is unfavorable for the formation of these salts.
Purine and protein compounds enter our body along with food. They stimulate the formation of uric acid. When you abuse food rich in purines and proteins, crystals are released in the urine - urates, which then precipitate and are determined during analysis.
Research methods
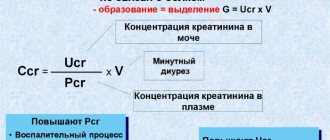
The results of laboratory tests of urine and blood almost always reveal a slight increase in protein, leukocytes, and bacteria (with pyelonephritis).
- The simplest and most accessible method for detecting urate is a clinical urine test. The first sign of the presence of crystals is a rich yellow or red-brown sediment in the urine. pH level > 7.0 (normal pH 5.0─7.0; average 6.25). A urine test shows the presence of calcium, potassium, sodium, and magnesium salts.
- A clinical blood test determines decompensation of kidney function, activation of pyelonephritis, and detects anemia.
- Ultrasound and X-ray ─ diagnose urate sand and stones.
- Excretory urography ─ allows you to see functional and anatomical changes in the kidneys.
- CT (computed tomography) is a method that provides the most accurate information about the size of stones, from small to large. If, according to research results, large quantities of urate are detected, this means that the biochemical properties of urine have changed. Such disorders can be easily corrected with properly organized therapy.
Reasons for the appearance of urates in urine
When they say that the key reasons for the appearance of urates in the urine lie in the excessive consumption of purines in food (that is, animal proteins), they note only the tip of the metabolic iceberg. It is known that dietary purines are only slightly involved in the synthesis of tissue nucleic acids, but, nevertheless, their excessive amounts increase the risk of urate formation.
The lion's share of exogenous purine bases (amino and oxypurines) are converted to 2,6-dioxypurine (hypoxanthine), then to xanthine and finally oxidized to uric acid. At different stages of its formation, pathogenesis may be associated with insufficient enzyme activity.
Thus, inactivation of allosteric enzymes of purine nucleotide metabolism (PRDP synthase, GGPT, etc.) leads to an increase in the level of uric acid in the blood plasma (hyperuricemia) and increased excretion of urate in the urine (uraturia).
The last stage of uric acid formation is ensured by the enzyme xanthine oxidase, synthesized in intestinal and liver cells, the level of which can also cause problems in the form of hereditary xanthinuria.
The reasons for the appearance of urate in the urine may be due to defects in the genes responsible for the secretion of uric acid by the kidneys - SLC2A9, SLC17A1, SLC22A11, SLC22A12, ABCG2, LRRC16A, etc.
In addition, the factor of functional kidney disorders should be taken into account, because urine, with which metabolites and excess salts are removed from the body, is formed precisely in them - as a result of glomerular filtration of blood plasma and reabsorption of water and the main volume of substances needed by the body. Disturbances in these biochemical processes can also cause the appearance of uric acid salts in urine.
High concentrations of poorly soluble uric acid and urate in the urine are not a medical indication, but are associated with various diseases and pathologies. Their ICD 10 code is E79.0 - E79.9 (disorders of purine and pyrimidine metabolism).
One way or another, pyelonephritis and renal tuberculosis are related to these disorders; renal acidosis in diabetes mellitus and alcoholism; fatty infiltration of the kidneys; prolonged fasting or rapid weight loss; Conn's syndrome (primary hyperaldosteronism); loss of fluid due to prolonged vomiting and diarrhea; a drop in potassium levels in the blood; oncopathologies of a hematological nature (leukemia, lymphoma); taking certain medications (for example, ascorbic acid, antibiotics and thiazide diuretics).
The consequences of impaired purine metabolism are manifested by chronic and acute renal failure, and with increased acidity of urine (pH less than 5), urates in the urine precipitate in the tubules of the kidneys with subsequent crystallization, the formation of urate sand and calculi (stones) and the development of urolithiasis - one of the types of urolithiasis diseases. Crystals of uric acid salts (most often calcium) can also settle in articular tissues, causing inflammation of the joints and periarticular structures.
How to treat uraturia
If a high concentration of urates is detected in the urine, complex etiotropic (affects the cause) and pathogenetic (mechanisms of stone formation) therapy is prescribed. If salt deposition is caused by poor nutrition, uraturia is treated with diet. If a pathology caused by other reasons is detected, medications are prescribed that dissolve and prevent the formation of stones.
People with urates in the urine are advised to undergo therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy. Alternative medicine helps with timely detection of stones. They are used as an additional method of treating urate in the kidney structures. For example, drugs from pol-fallow have diuretic properties and are able to remove urates. Celery, parsley, elderberry, currants, and knotweed have a dissolving effect. Recipes for effective remedies:
- Erva herb (30 g) is brewed in 200 ml of boiling water, then infused for an hour. The filtered drink is consumed throughout the day, before meals. Since the plant can destroy tooth enamel, it is better to drink the infusion through a straw. The medicine dissolves urates.
- Dried horsetail herb (20 g) is brewed in 300 ml of boiling water. The composition is left warm for half an hour. Drink 100 ml of filtered drink immediately after waking up.
- Madder roots (15 g) are brewed in 200 ml of boiling water. The container is put in a warm place for an hour. Drink ½ cup of the product twice a day.
If urates cause renal colic, disrupt urine excretion, provoke inflammation, surgery is prescribed.
Diet
Urates have one peculiarity - they are able to dissolve when following a diet and taking medications, and then are excreted in the urine. The main goals of therapeutic nutrition are to increase the acidity of urine, increase the volume of fluid excreted and reduce the production of urea. It is necessary to change the diet gradually, since a sharp shift in pH will lead to the precipitation of phosphate salts, which envelop urate deposits and prevent them from dissolving. Therapeutic nutrition for urate in the kidneys and urine includes:
- Increasing the calorie content of food to 2800 kcal/day.
- Exclusion of bottled water with a high concentration of Ca salts, fatty meat, fish, red wine, beer, rich broths, chocolate, cocoa.
- Limiting salt, legumes, sorrel, spinach, bread, cabbage, onions, spicy foods.
- Eating fruits, nuts, berries, dairy products, eggs, sweet peppers, cereals, cucumbers, eggplants.
- Maintain a drinking regime (2 liters of fluid per day).
- Elimination of overeating.
The diet when detecting urates in the urine also has features regarding the preparation of meat dishes. The consumption of sausage from offal is excluded. When cooking white meat, the first broth is drained, and the onion is placed in the second (it is then removed). When making jellied meat, the vegetables used in the process are thrown away. Before frying or stewing meat, it is soaked in a saline solution for 3 hours.
Drug treatment
Urates in the urine are considered the only type of stones that can be treated with conservative therapy, and its effectiveness is 90%. That is, most people get rid of pathology with the help of medications. Elimination of stones is carried out by treating the underlying disease, which led to the formation of urates in the structures of the kidneys and urine. The following drugs are prescribed:
- Citrate products - Blemaren, Soluran, potassium-sodium-hydrogen citrate, Uralita-U. Dissolve and loosen the stones.
- Medicines that improve blood circulation in the kidneys, removing uric acid and urates - Allopurinol, Cyston, Allohexal.
- Antispasmodics and painkillers - Baralgina, Papaverine, No-shpa.
- Antibiotics - Ceftriaxone, Nitroxoline, Nevigramon. For the prevention and elimination of secondary infection.
- Herbal medicines - Canephron, Urolesan, Fitolysin.
- Vitamins A, E, B6. To strengthen the immune system and restore metabolism.
Table 2 - Regimen for taking medications for urate in the kidneys and urine
| Group | A drug | Multiplicity applications (times/day) | Dosage (g/mg) | Duration course |
| Citrates |
| 2–3 | 3–6 g | 4–5 months |
| Excretory urates |
| 4 | 0.1 g | 30–60 days |
| Painkillers |
| 3 | 2 tabs | 5 days |
| Antibiotics |
| 1 4 | 2 g 1 g | 3 days Week |
| Herbal remedies | Urolesan | 3 | 10 drops | 30 days |
| Canephron | 3 | 2 dragees | 1 month |
Surgery
Radical methods of therapy are used when urates reach a size of 5 mm or more. Such stones can cause colic, disrupt the process of urination, and provoke the development of inflammation. The most common method for removing urate is extracorporeal lithotripsy. The essence of this treatment is to crush the stone without direct contact (laser or electromagnetic method).
For large urates, laparoscopic or endoscopic surgery is used. During the first, the stones are removed using 3 incisions. Instruments and a camera are inserted into the punctures (to display the image on the screen). The procedure is performed using general anesthesia. After removing the stone, a drainage is inserted and the wound is sutured.
Endoscopic surgery is performed using rigid and flexible devices. A nephroscope is used to remove the stone. The device is inserted into the organ cavity through a puncture in the lower back. After removing the stone, a drainage system is installed (for 2 days).
If the formations are large, multiple, as well as in the case of repeated previous surgical interventions or with a single kidney, “sandwich therapy” is used - a combination of abdominal (open) surgery with lithotripsy.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of pathology
The main reason for the increase in uric acid (urate) is considered to be nutritional imbalance: imbalance, monotony, irregularity, excessiveness.
Other reasons contributing to the development of the disease include:
- systematic stress loads on the body;
- hereditary predisposition;
- infectious pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- pyelonephritis, hepatitis, pancreatitis, renal artery thrombosis, kidney prolapse, hydronephrosis and leukemia;
- gout is a metabolic disorder, as a result of which urates are partially excreted by the kidneys, and a large mass of them accumulates in tissues and blood, which leads to acute, recurrent arthritis (inflammation of the joints);
- taking medications: antibiotics, antipyretics, anesthetics (painkillers).
Products that cause increased urate levels in the body:
- Containing salicylic acid: linden tea, raspberries, viburnum.
- Promoting the deposition of protein waste: red meat of young animals (pork, veal), canned food with a long shelf life, sausages, offal (heart, liver, kidneys, stomachs), rich meat and fish broths.
- Smoked products.
- Vegetables: tomatoes, legumes, onions, spinach, cabbage, sorrel.
- Spices, herbs.
Diet for uraturia
Diet is as much a medicine as drug treatment. Nutrition is very specific and should be agreed with your doctor. The following products are capable of actively removing urate through the renal system:
- all types of citrus fruits - grapefruits, lemons and oranges, juices from them;
- any grapes;
- all types of forest apples;
- gooseberries, currants, figs and raisins;
- cucumbers, eggplants and pumpkin;
- any seaweed (most importantly, without salt);
- curdled milk and its analogues.
Meat products in excessive quantities are prohibited for the patient. To get rid of toxins in raw meat, it must be marinated and processed in advance. For example, if you boil a whole piece, you need to throw it into already boiling water.
The kebab is marinated in a salt solution for 4 hours. It is better not to eat minced meatballs because the frying time is not enough to eliminate toxins in the meat. When preparing the broth, the first broth is drained, and in the second you must add an onion, which will absorb all the protein waste from the meat. You can't eat onions, you need to throw them away.
The diet recommended by doctors is No. 6. In this case, you need to drink at least 2 liters of liquid, slightly increasing this amount in the hot season.
Symptoms
Increased crystallization processes cause the formation of stones in the kidneys and bladder. The formation and passage of stones can often cause the development of inflammation and intoxication. At this stage of uraturia, a person experiences the following symptoms:
- Hyperthermia;
- Arterial or renal hypertension;
- Fatigue, weakness;
- Dyspeptic disorders.
Stones and salts in the bladder in young children provoke excessive motor activity and the appearance of redness on the skin. The child sleeps poorly, becomes capricious, and suffers from frequent regurgitation and vomiting in the morning.
Methods for identifying stones
If uric acid diathesis is suspected in adults or children and characteristic symptoms arise, timely diagnosis and treatment help to successfully combat the disease and avoid complications. The attending physician will definitely prescribe a general blood test, urine test, and biochemical examination.
It is better to carry them out in laboratories that have a good reputation and conduct comprehensive research, such as Invitro. It is better not to interpret the meaning of the results yourself; you should learn them from tables on the Internet; a specialist should decipher them. Ultrasound diagnostics will help determine the presence of stones and sand in the kidneys and ureters.
An x-ray with a contrast agent will help identify urates and tumors. It is also used to diagnose the excretory function: several pictures are taken as the drug passes. In this case, it is possible to identify structural defects, acquired and congenital.
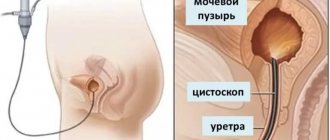
You can visually examine the inner surface of the bladder and canal with a cystoscope. The doctor sees all the processes occurring inside; in case of suspicious formations, it is possible to immediately take a biopsy. For men, this procedure is more complicated and causes discomfort that disappears after a few days.
A special radioactive drug that is injected inside and recorded with a gamma camera will help to study the structure of the tissues and membranes of the excretory organs. On their basis, descriptions and conclusions are made about probable diseases, structural disorders and functional disorders.
Treatment of uraturia
Often, uraturia is a consequence of poor nutrition, so the first thing you need to do is adjust your diet and water-salt levels in the body. Physical therapy, physiotherapy and many other ways to overcome the disease are also additionally prescribed. If drug treatment fails, surgery is used.
Folk remedies and herbal treatment
When detecting urates in a timely manner, a tincture of the herb half-burnt helps a lot. It has a salt-removing and diuretic effect. The composition of the half-fallow is saturated with biologically active plant substances: saponins, flavonoids, polysaccharides, tannins, organic acids and coumarins. Due to its natural source, this herb does not cause any side effects.
Homeopathy
Homeotherapy tends to optimize salt metabolism, helps reduce pain and helps the body eliminate urates. Many people use it to prevent stone formation. Here are a number of medications that are recommended to prevent uraturia:
Taking homeopathic medicines can normalize salt metabolism.
- "Lycopodium";
- "Kalium carbonicum";
- "Causticum";
- “Nux Vomica.”
Medications
The main way to combat urate in the urine is diet. But there are also medications that can help:
- To prevent and dissolve uric acid salts, Blemaren is prescribed. It reduces the excretion of calcium, and, therefore, improves the solubility of oxalates in urine and reduces the rate of crystal formation. Do not use if you have phosphate stones.
- “Asparkam” is suitable for combating urate even for infants with the correct dosage. The main components are potassium and magnesium, which help remove urate salts.
- "Allopurion" disrupts the synthesis of uric acid and reduces its level in the body, promotes the dissolution of urates.
- For the outflow of urine, respectively, and the salts accumulated in it, “Canephron”, “Fitolysin” and “Urolesan” are effective.
Treatment with medications
First of all, the doctor prescribes a diet with limited protein foods. Next, we will consider nutritional rules for urate in the urine. Treatment with medications is aimed at removing and dissolving salts. The following drugs are prescribed:
- Plant-based products: “Canephron”, “Fitolysin”, “Urolesan”. These medications help eliminate uric acid salts.
- The drug "Allopurinol". It reduces the production of uric acid and dissolves urate salts.
- Vitamin and mineral remedy "Asparkam". This medicine breaks down urate deposits and removes them.
- Effervescent tablets "Blemaren". They help remove urate. However, if phosphates are found in the patient along with uric acid salts, then taking this medicine is not recommended.
It is also useful to drink decoctions of elderberry, horsetail, nettle, and lingonberry. Dried collections of these herbs are sold in pharmacy chains.
Urates are easily dissolved. Typically, the use of medications and herbal decoctions leads to the complete removal of salts.
Why do salts accumulate?
The cause of the accumulation of urates is considered to be an unbalanced, monotonous diet, along with its excessiveness and irregularity. Here is an approximate list of products whose consumption affects the concentration of urates:
- red meat;
- all types of canned food;
- offal sausages;
- offal, smoked meats;
- spices, herbs.
The reasons may be related to the following situations:
- genetic predisposition;
- infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- the effect of stress on the body;
- taking medications (antibiotics, painkillers);
- violation of metabolic processes.
The causes of uraturia are associated with dehydration of the body, when poisoning or infectious diseases are accompanied by frequent diarrhea and vomiting.
During pregnancy, small amounts of urate accumulate in the urine due to dehydration of the body that occurs during toxicosis.
When the levels of these substances exceed the norm, it is necessary to exclude infectious diseases of the genitourinary organs. To minimize the development of this situation, it is necessary to maintain water-salt balance and adhere to a diet.
Urate salts accumulate in a child’s urine mainly for the same reason as in adults – poor nutrition. Eating large amounts of meat, fish, cheese, tomatoes, and chocolate leads to the accumulation of salts. Normalizing your diet will help eliminate this problem.
Certain diseases of the child can cause this condition: if before the discovery of this fact the child had a fever, vomiting with diarrhea, then the antibacterial drugs or antipyretics used could affect the results of the analysis. This condition is temporary and does not cause concern to parents.
During pregnancy
Elevated urates are often detected in the analysis of pregnant women. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy, many patients suffer from toxicosis. This leads to vomiting and dehydration, as a result of which the concentration of uric acid salts increases.
Another reason for increased urates may be poor nutrition during pregnancy. Eating spicy and smoked foods, tomatoes, and chocolate contributes to the formation of salts. Such foods should be excluded from the diet. It is also necessary to somewhat limit the consumption of fish and meat.
A common cause of uraturia in pregnant women is insufficient fluid intake. It is important to remember that during gestation the body's need for water increases.
Why you should prepare for testing
The norm for crystal content is complete absence. A one-time fixation of such a condition can be caused neither by a disease, but by an incorrect diet. Most likely, the doctor will not look for other symptoms of the disease, but will prescribe a repeat urine test for salts, which may show their absence. To exclude random causes, you should properly prepare for the study:
- the day before the test, follow a diet excluding fresh fruits and vegetables with bright colors, for example, cherries, carrots, etc.;
- give up alcohol one day before;
- abstaining from taking diuretics;
- For hygienic care use baby soap.
If the presence of salt is confirmed in a urine test, the doctor will prescribe additional diagnostic tests. Only based on the results of these studies, appropriate treatment is prescribed. Some conditions, characterized by the fact that urine contains a lot of salt, are stabilized by adjusting the diet. A diet for salts in the urine, prescribed by a doctor, will help to achieve a decrease in concentration; the norm can be restored without treatment.
Let us recall that normally there should be no salt in the urine of an adult; an increased concentration of salt detected during the study is a reason to consult a doctor. The patient who has taken the test should not independently evaluate the results.
The doctor will help you adjust your diet, and if a disease is detected, you will treat it by prescribing the necessary medications and procedures, which will reduce the high level of salts.
In the future, the reasons leading to this condition should be excluded, since if the concentration of crystals increases regularly, this can lead to the formation of stones.
How to properly prepare for the test and collect urine
On the eve of urine collection, it is undesirable to consume alcohol, spicy and salty foods, as well as foods that can change the color of the sample (carrots, turmeric, beets). Immediately before collecting the material, hygienic washing is carried out. Women are not recommended to donate urine during their periods. For children, the test is collected in special urinals.
It is important to collect urine in sterile pharmacy containers to avoid the ingress of microorganisms and inorganic elements.
To analyze a single portion, a minimum of 10 ml of sample is required.
If a urine test reveals an increased urate content, the diagnosis is repeated 7-10 days after the diet is normalized.
Clinical manifestations
If salts are constantly present in the urine, even in small quantities, this phenomenon indicates the presence of pathological or inflammatory processes in a person. This condition may be accompanied by the following clinical signs:
- the color of urine changes;
- the frequency of urination increases (polyuria);
- the discharge becomes noticeably cloudy and a characteristic sediment appears in it;
- there is irritation, severe itching and a burning sensation in the urethra and external genitalia (the result of damage to the mucous membrane by salty urine);
- disruption of the urination process - namely, its delay up to the complete absence of urine (dysuria);
- lethargy and weakness;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen.
Symptoms of salts in the urine usually do not appear too brightly. In this case, disruption of the functioning of the body in the patient is expressed in the form of increased fatigue and drowsiness. A rapid increase in blood pressure and difficulty in functioning of the cardiovascular system are also possible.
Prevention
To avoid uraturia, you need to eat a balanced diet. You should not eat excessive amounts of protein foods (fatty meat and fish). It is also necessary to minimize alcohol consumption. It is the regular consumption of alcoholic beverages in combination with meat snacks that most often causes an increase in urate.
You need to drink enough liquid throughout the day. With diarrhea and increased sweating, it is important to avoid dehydration and replenish water loss in a timely manner. A person needs to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day. An active lifestyle also plays an important role in the prevention of uraturia. Physical activity prevents the deposition of salts in organs and tissues.
If an increased level of urate is detected in the urine, you should immediately consult a doctor. It may be necessary to prescribe a diet or a special course of treatment. This will help prevent such unpleasant and serious pathologies as urolithiasis and gout.
Classification and symptoms
Precipitated salts form kidney stones, which are divided into types (shown in the photo):
- Oxalates and phosphates are the most common causes of urolithiasis.
- Phosphate-aluminium-magnesium stones. The cause of stone formation is infectious kidney disease.
- Urats. Occurs in approximately 10% of patients. The cause of formation is excess uric acid and some pathologies of the digestive tract.
- Xanthine, cystine. They occur against the background of congenital pathology and genetic changes.
Stones of pure composition are rarely identified; usually, most formations are of a mixed type. If the concentration of mineral salts does not go beyond the normal range, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. Uraturia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of pain in the lumbar region and bladder.
- An increase in blood pressure is observed.
- Sometimes there are blood clots in the urine.
- General malaise of the body.
- Stinging and pain when urinating.
The patient should contact a urologist or nephrologist if these signs occur. The doctor will prescribe a set of diagnostic measures that will help to understand the causes and establish the correct diagnosis. If signs of stones are observed, you need to do an ultrasound (ultrasound examination), as well as an x-ray of the kidney area.
Uraturia in children
In children, this disease is most often observed due to poor nutrition. If a child is often fed fried, fatty and canned foods, this can lead to an increase in the amount of salts in the urine sediment. Sweet carbonated waters, strong tea and chocolate can also cause harm.
Children are often susceptible to gastrointestinal infections and food poisoning. These pathologies are often accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea. In sick children, there is an increase in urate due to dehydration.
An increase in the amount of uric acid salts may be one of the symptoms of helminthic infestation, genitourinary infections, and intestinal dysbiosis. Uraturia should cause particular concern in cases where the child’s parents or immediate relatives have diabetes, obesity, gout and heart disease. In this case, the baby may have a hereditary predisposition to the formation of urate stones.